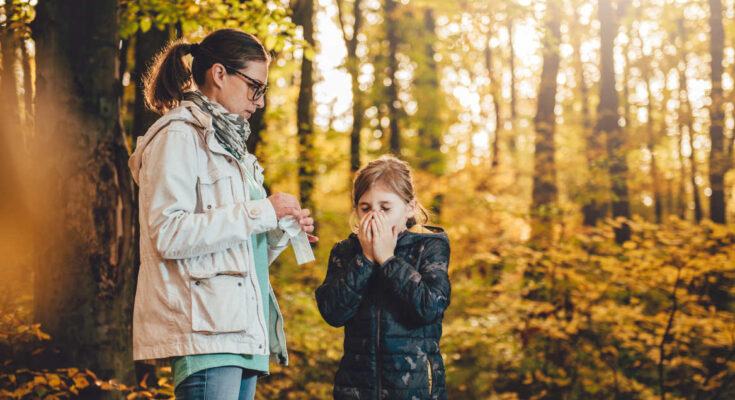
Hay Fever Symptoms: Hay fever, clinically known as allergic rhinitis, is a common condition that affects a significant portion of the population worldwide. It triggers cold-like signs and symptoms such as a runny nose, itchy eyes, congestion, sneezing, and sinus pressure.
However, unlike a cold, hay fever is not caused by a virus. Hay fever is caused by an allergic response to outdoor or indoor allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, or tiny flecks of skin and saliva shed by cats, dogs, and other animals with fur or feathers.
What is Hay Fever?
Hay fever, also known as allergic rhinitis, is a common allergic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when an individual’s immune system overreacts to airborne allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander, resulting in inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages.
Global Prevalence and Impact
Statistics reveal that hay fever affects between 10% to 30% of the global population, making it one of the most common allergic conditions. In the United States alone, it is estimated that about 20% of the population suffers from allergic rhinitis. The condition can affect people of any age, though it often begins in childhood or adolescence.
The impact of hay fever is significant, leading to missed days at school or work and reduced productivity. It is also associated with other health problems such as asthma and sinus infections, further emphasizing the need for effective management and treatment strategies.
Causes of Hay Fever
Understanding what triggers hay fever can help sufferers manage their symptoms more effectively. Here, we delve into the causes of hay fever, examining both environmental and genetic factors, and distinguish between seasonal and perennial forms of this allergy.
Environmental Triggers of Hay Fever
The most common triggers of hay fever are environmental allergens. These include:
- Pollen: This is the most well-known hay fever trigger. Pollen comes from trees, grasses, and weeds. The type of pollen that triggers hay fever varies by season, which is why some people only experience symptoms at certain times of the year.
- Dust Mites: These tiny creatures thrive in warm, humid environments and are commonly found in bedding, upholstered furniture, and carpets.
- Animal Dander: Pets can carry allergens like dander (tiny flakes of skin), saliva, and urine, all of which can trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals.
- Mold: Mold spores can also cause hay fever symptoms. They can be found in damp areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
Genetic Factors
Hay fever often runs in families, suggesting a strong genetic component to this allergic condition. If one or both parents suffer from hay fever or another type of allergic condition, such as asthma or eczema, their children are more likely to develop hay fever.
Seasonal vs. Perennial Hay Fever
The causes of hay fever can be classified into two types, based on how often symptoms occur:
- Seasonal Hay Fever: This type occurs at specific times of the year, primarily when outdoor molds release their spores, and trees, grasses, and weeds release pollen into the air. People with seasonal hay fever are usually allergic to specific types of pollen, and the severity of their symptoms can depend on the pollen count in the air.
- Perennial Hay Fever: Unlike seasonal hay fever, perennial hay fever occurs year-round. It is generally triggered by allergens found indoors, such as dust mites, pet dander, and mold spores. Symptoms may worsen in winter when houses are closed up, which traps allergens inside.
By identifying the specific causes and types of hay fever, individuals can better manage their condition through avoidance strategies, medication, and, in some cases, allergy shots (immunotherapy). Understanding these factors is crucial in reducing the impact of hay fever on daily life and improving overall well-being.
Common Symptoms of Hay Fever
Understanding these symptoms can help you manage them effectively and minimize their impact on your daily life.
Comprehensive List of Hay Fever Symptoms
Hay fever symptoms can vary from mild to severe and often resemble those of a common cold. Here are the most typical symptoms:
- Sneezing: Frequent, intense bouts of sneezing are common and are often the body’s way of trying to expel allergens.
- Runny or Stuffy Nose: A clear, thin nasal discharge (runny nose) or nasal congestion (stuffy nose) can occur, making breathing through the nose difficult.
- Itchy Eyes, Nose, Ears, and Throat: Allergens can cause a bothersome itchiness in areas that come into contact with the air, like eyes and throat.
- Watery, Red Eyes (Allergic Conjunctivitis): Eyes may become red, swollen, and watery, giving the appearance of having cried.
- Postnasal Drip: This involves mucus running down the back of the throat, which can lead to coughing or a sore throat.
- Coughing: A result of postnasal drip and throat irritation, coughing is a frequent symptom of hay fever.
- Fatigue: Many people with hay fever experience general tiredness, which can be exacerbated by poor sleep due to symptoms.
- Headaches: Sinus congestion can lead to pressure headaches, adding to the discomfort caused by hay fever.
How These Symptoms Affect Daily Activities
Hay fever symptoms can significantly disrupt daily activities. For example, frequent sneezing, a runny nose, and itchy eyes can make it difficult to concentrate, affecting performance at work or school. Nasal congestion and postnasal drip might lead to poor sleep quality, resulting in daytime fatigue and reduced alertness. Outdoor activities can become particularly challenging during peak pollen seasons, limiting participation in sports or social events.
Moreover, the discomfort of symptoms like headaches and continuous itchiness can decrease overall productivity and enjoyment of day-to-day life. For those with severe symptoms, hay fever can lead to absenteeism from work or school and can substantially lower life quality.
By recognizing the symptoms early and implementing effective management strategies, individuals can reduce the impact of hay fever on their daily lives and improve their overall well-being.
Diagnosing Hay Fever
Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here’s how medical professionals diagnose hay fever and why it’s important to differentiate it from other allergic reactions.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Hay Fever
The first step in diagnosing hay fever is recognizing its characteristic symptoms, which typically intensify during specific seasons due to pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds. Common symptoms include:
- Runny or stuffy nose: An increase in mucus production leads to these conditions, significantly affecting breathing and comfort.
- Sneezing: Frequent, intense sneezing is a hallmark of hay fever, triggered by the inhalation of allergens.
- Itchy eyes, nose, or throat: These areas become irritated due to allergens, leading to discomfort and an urge to scratch.
- Watery eyes: Caused by the body’s response to allergens, leading to tear production as a defense mechanism.
These symptoms are similar to those of a cold but last longer and are not accompanied by fever.
Diagnostic Tests for Hay Fever
When symptoms are not enough for a definitive diagnosis, doctors may recommend specific tests:
- Skin prick test: This test involves placing a small amount of suspected allergens on the skin, typically the forearm, and then lightly pricking the area to introduce the allergen to the immune system. A positive reaction, typically a raised bump, indicates an allergy.
- Specific IgE blood test: This test measures the levels of IgE antibodies in response to particular allergens in the blood, providing insight into what the patient is allergic to.
Importance of Distinguishing Hay Fever from Other Allergies
Differentiating hay fever from other allergies is vital for several reasons:
- Targeted treatment: Knowing exactly what triggers allergic reactions allows for more specific and effective treatment plans.
- Prevention strategies: Identifying hay fever can lead to better management through avoidance of known triggers, especially seasonal allergens.
- Impact on quality of life: Effective diagnosis and treatment help improve overall quality of life and reduce the risk of developing complications, such as sinusitis or secondary respiratory infections.
However, diagnosing hay fever accurately is essential for effective management and relief. By understanding the symptoms and undergoing appropriate tests, individuals can better differentiate hay fever from other allergies, leading to more targeted treatments and improved health outcomes.
Complications of Untreated Hay Fever
Hay fever, also known as allergic rhinitis, can lead to several complications if not properly managed. Addressing hay fever symptoms promptly not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents the progression of more serious health issues.
1. Sinusitis and Ear Infections
When hay fever is left untreated, the constant inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages can obstruct the sinuses, leading to acute or chronic sinusitis. This condition is characterized by pain, drainage, and a feeling of fullness in the face. Similarly, the eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the throat, can become blocked, resulting in ear infections. These infections can cause pain, hearing difficulties, and, in severe cases, long-term hearing loss.
2. Aggravation of Asthma Symptoms
Individuals with asthma may find that untreated hay fever exacerbates their symptoms. Allergens that trigger hay fever symptoms, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, can also provoke asthma attacks, leading to increased coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Managing hay fever effectively can help control asthma and reduce the frequency and intensity of asthma episodes.
3. Impaired Sleep and Fatigue
Hay fever often disrupts sleep due to symptoms like nasal congestion, sneezing, and coughing that intensify at night. This lack of restorative sleep can lead to significant daytime fatigue, affecting concentration and performance at work or school. Over time, sleep deprivation can also contribute to a weakened immune system, making individuals more susceptible to other infections.
4. Impact on Quality of Life
The symptoms of hay fever can severely impact one’s quality of life. Itchy eyes, a runny nose, and sneezing can make daily activities uncomfortable and less enjoyable. The ongoing discomfort can lead to irritability, mood changes, and decreased participation in social activities. Furthermore, the visibility of symptoms can also affect self-esteem and social interactions.
5. Development of Nasal Polyps
In chronic cases, long-standing inflammation from untreated hay fever may lead to the growth of nasal polyps. These are non-cancerous growths in the lining of the nasal passage or sinuses that can obstruct airflow and lead to a loss of smell. Treatment for nasal polyps might involve steroids or surgery, indicating the severity of leaving hay fever untreated.
Regular consultations with a healthcare provider can ensure that treatment strategies are effective and tailored to individual needs, promoting overall health and well-being.
Management and Treatment Options for Hay Fever
Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding the various treatment methods, including medications and home remedies, along with practical tips for managing hay fever symptoms.
Overview of Treatment Methods
1. Medications:
Medications are a cornerstone in the treatment of hay fever. The most common types include:
- Antihistamines: These drugs help reduce sneezing, itching, and runny nose by blocking histamine, a substance your body makes during an allergic reaction. They are available over-the-counter and by prescription in the form of pills, liquids, nasal sprays, and eye drops.
- Nasal corticosteroids: These are among the most effective medications for treating hay fever. They reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and are available as sprays. Regular use is often necessary for optimal effect.
- Decongestants: These can relieve nasal stuffiness by shrinking swollen membranes in the nose. However, they are only recommended for short-term use to avoid the risk of rebound congestion.
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists: These prescription drugs block the action of certain immune system chemicals involved in allergic reactions. They are sometimes used when nasal corticosteroids and antihistamines are not effective.
2. Home Remedies:
In addition to medications, several home remedies can help alleviate hay fever symptoms:
- Saline nasal rinses: Using a saline solution to irrigate your nasal passages can help relieve congestion, irritation, and allergies.
- Stay indoors on high pollen days: Keep windows and doors closed during high pollen seasons to keep allergens out.
- Use air purifiers: Having an air purifier in your home, particularly in the bedroom, can help remove pollen, dust, and other allergens from the air.
- Herbal treatments: Some people find relief with herbal remedies like butterbur or spirulina, though it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
Tips for Managing Hay Fever Symptoms Effectively
- Monitor pollen forecasts: Stay updated with local pollen forecasts and try to plan your activities when pollen levels are low, especially during early morning or windy days.
- Adjust your home environment: Use allergen-barrier bedding covers, wash bedding in hot water regularly, and vacuum with a HEPA filter to reduce exposure to allergens.
- Wear protective gear: When going outside, wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from pollen. Consider wearing a pollen mask if you need to be outdoors during high pollen times.
- Manage stress: Stress can worsen allergy symptoms, so incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can be beneficial.
- Consult your doctor regularly: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help you manage your hay fever effectively, especially if your symptoms change or your current treatment is no longer effective.
By implementing these medications and home remedies, along with following practical management tips, you can lessen the discomfort caused by hay fever and lead a more comfortable, symptom-free life.
Prevention of Hay Fever
Fortunately, there are several effective strategies to prevent the onset of hay fever symptoms. By making thoughtful changes to your environment and lifestyle, you can minimize exposure to allergens and reduce your symptoms. Here’s a detailed guide on how to achieve this.
Modify Your Environment to Reduce Allergens
- Keep Windows Closed: To prevent pollen from entering your home, keep windows and doors closed during high pollen counts. Use air conditioning in your home and car to help filter out pollen.
- Enhance Indoor Air Quality: Invest in an air purifier with a HEPA filter to capture pollen, dust, and other airborne allergens. Regularly changing the filters in your air conditioning units and air purifiers can also significantly improve indoor air quality.
- Limit Outdoor Activities: Check the local pollen count (available on weather websites and apps) and try to stay indoors when it’s high, typically in the early morning or on windy days.
- Create an Allergen-Free Zone: Designate an allergen-free zone, preferably your bedroom, where no outside clothing is brought in and pets are kept out. This can provide a sanctuary from allergens during peak seasons.
Lifestyle Changes to Combat Hay Fever
- Adjust Your Schedule: Plan outdoor activities for late afternoon or after a heavy rain, when pollen levels are lower. If you exercise outdoors, consider switching your workouts to indoor venues during high pollen seasons.
- Wear Protective Gear: When you do go outside, wearing sunglasses can help shield your eyes from pollen. Additionally, a pollen mask can be worn during peak seasons to prevent inhalation of allergens.
- Maintain Cleanliness: After spending time outdoors, shower and change your clothes to remove pollen. Regularly wash bedding in hot water to kill any lingering pollen and dust mites.
- Opt for Allergy-Friendly Gardening: Choose plants for your garden that are less likely to produce a high amount of pollen, such as hydrangea, clematis, and hostas. Avoid wind-pollinated plants, as they are more likely to trigger hay fever symptoms.
- Consider Dietary Adjustments: Some foods can exacerbate hay fever symptoms due to cross-reactivity with pollen. For instance, if you’re allergic to birch pollen, you might react to apples, carrots, and celery. Keep a food diary to identify any potential triggers and discuss them with an allergist.
By incorporating these environmental modifications and lifestyle changes into your routine, you can effectively reduce your exposure to allergens and alleviate the symptoms of hay fever. Remember, while these strategies can help, it’s also important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
When to See a Doctor for Hay Fever
If you’re struggling with hay fever, knowing when to seek professional medical help can make a significant difference in managing your symptoms effectively. Here are some guidelines on when it’s necessary to see a doctor, what to expect during your visit, and how to prepare for it.
When to Seek Professional Medical Help
While hay fever, or allergic rhinitis, is often manageable with over-the-counter medications and home remedies, there are certain situations where professional medical advice is essential:
- Persistent Symptoms: If your symptoms persist despite using over-the-counter antihistamines and nasal sprays, it’s time to consult a doctor.
- Severe Symptoms: If you experience severe symptoms such as intense nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, or if hay fever is significantly affecting your quality of life, professional assessment is needed.
- Complications: If you develop complications like sinus infections, ear infections, or any unusual symptoms like wheezing, seeing a doctor is crucial.
- Children and Infants: If a child or infant shows symptoms of hay fever, it’s advisable to get a professional evaluation to ensure proper treatment and to rule out other conditions.
What to Expect During the Visit
During your visit, the doctor will typically:
- Review Your Medical History: Be prepared to discuss your personal and family medical history, specifically relating to allergies.
- Physical Examination: The doctor may examine your eyes, ears, nose, throat, and chest to assess the effects of hay fever.
- Allergy Testing: Depending on your symptoms, the doctor might recommend allergy testing to pinpoint the exact allergens causing your discomfort.
How to Prepare for Your Doctor’s Visit
To make the most of your appointment, prepare in advance:
- Symptom Diary: Keep a diary of your symptoms and any potential triggers you’ve noticed. This can help the doctor make a more accurate diagnosis.
- Medication List: List all the medications, supplements, and over-the-counter remedies you have tried. Include information about the effectiveness and any side effects you experienced.
- Questions: Prepare a list of questions you have about your symptoms or treatment options. This ensures you cover all areas of concern during your visit.
Seeking timely medical advice for hay fever can lead to better management of your symptoms and improvement in your overall health and wellbeing. Don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you or your loved ones are affected by severe or persistent hay fever symptoms.
FAQs about Hay Fever Symptoms
1. What are the common symptoms of hay fever?
Hay fever, also known as allergic rhinitis, typically presents a range of symptoms that can include sneezing, a runny or blocked nose, itchy eyes, and a persistent cough. These symptoms result from the body’s immune response to airborne allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander.
2. How can I tell if I have hay fever or a cold?
Differentiating between hay fever and a common cold can be tricky as both share similar symptoms. However, hay fever usually doesn’t involve a fever or body aches and tends to persist longer than the common cold. If symptoms appear seasonally, especially in spring or early summer, it’s likely hay fever.
3. Are hay fever symptoms the same for everyone?
No, hay fever symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Some might experience mild symptoms, while others may face severe disruptions in their daily lives. The intensity can also change with different seasons or environmental conditions.
4. Can hay fever symptoms occur all year?
Yes, while hay fever is often associated with specific seasons (such as spring), some people might experience symptoms year-round. This type of hay fever is known as perennial allergic rhinitis and is usually triggered by indoor allergens like dust mites, pet hair, or mold.
5. What can worsen hay fever symptoms?
Certain factors can exacerbate hay fever symptoms. These include high pollen counts, exposure to smoke or strong perfumes, changes in weather (such as wind that stirs up pollen and dust), and having other respiratory conditions like asthma.
6. How can I manage hay fever symptoms effectively?
Managing hay fever involves a combination of strategies including avoiding known allergens, using over-the-counter antihistamines or nasal sprays, and in some cases, undergoing allergy immunotherapy. Staying indoors on days with high pollen counts and keeping windows closed can also help reduce symptoms.
7. When should I see a doctor for hay fever?
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if hay fever symptoms become unmanageable, persist despite treatment, or if you experience complications such as sinus infections or asthma symptoms. A doctor can offer more specific treatments like prescription medications or refer you for allergy testing.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms and causes of hay fever is crucial for effectively managing this common yet disruptive condition. Recognizing triggers, such as pollen or other allergens, and how they affect your body can empower you to take proactive measures to minimize discomfort.
Whether it’s through medication, lifestyle adjustments, or consulting with healthcare professionals, managing hay fever is within your reach. We encourage you to not only educate yourself about the condition but also take practical steps towards improving your quality of life.
Remember, taking action can significantly alleviate the symptoms of hay fever, helping you enjoy all seasons with less disruption.
References
For those seeking additional information on hay fever symptoms or looking for credible sources to validate the details provided, the following references are highly recommended:
- Mayo Clinic – Provides comprehensive details on symptoms, causes, and treatment options for hay fever. Explore their resource here.
- WebMD – Offers a detailed overview of hay fever, including symptom management and prevention strategies. Check their guide here.
- Healthline – Features an insightful article on natural and medical treatments for hay fever. Read more here.
- CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) – Provides information on allergic reactions including hay fever, with guidelines on how to reduce exposure to allergens. Visit their page here.
These resources are maintained by reputable health organizations, ensuring that the information is accurate and up-to-date. They serve as excellent starting points for anyone looking to understand more about hay fever and its management.