Hearing Loss Symptoms: Hearing loss affects millions worldwide, manifesting through various symptoms and stemming from numerous causes.
It is a health condition that not only impairs auditory function but also significantly impacts daily communication and quality of life.
Recognizing the early signs and understanding the underlying causes is crucial for timely intervention and effective management.
Understanding Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a common condition that affects millions of people globally. It can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, influencing their ability to communicate effectively, maintain relationships, and participate fully in society. This section explores the different types of hearing loss, their prevalence, and their impact on daily living.
Different Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be classified into three primary types, each with unique causes and implications:
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss: This is the most common type and occurs when there is damage to the inner ear or the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. Common causes include aging, exposure to loud noise, and certain medical conditions.
- Conductive Hearing Loss: This type occurs when sound waves cannot properly travel through the outer ear canal to the eardrum and the tiny bones of the middle ear. It can be caused by ear infections, buildup of earwax, and abnormalities in the ear structure.
- Mixed Hearing Loss: This is a combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss, meaning that there may be damage in the outer or middle ear and in the inner ear or auditory nerve.
Understanding the specific type of hearing loss is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Prevalence and Impact on Quality of Life
Hearing loss is not just a health issue; it is a significant societal concern. According to the World Health Organization, over 5% of the world’s population – or 430 million individuals – require rehabilitation to address their ‘disabling’ hearing loss. The prevalence of hearing loss increases with age, affecting approximately one third of people over 65 years old.
The impact of hearing loss on quality of life can be profound. Individuals may experience difficulties in communication, which can lead to social isolation, frustration, and depression. The ability to hear is closely tied to personal safety, educational opportunities, and employment prospects. For children, hearing loss can affect language acquisition and cognitive development, which can have long-lasting effects on academic and professional success.
Symptoms of Hearing Loss
Recognizing the early signs and understanding how symptoms can progress over time is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. Below, we explore the initial indicators, progressive symptoms, and the variability in symptoms according to different types of hearing loss.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Hearing Loss
The onset of hearing loss is often subtle and can be easily overlooked. Here are some common early signs:
- Difficulty Understanding Speech: Struggling to follow conversations, especially in noisy environments, is a typical early symptom.
- Frequently Asking for Repetition: Needing others to repeat themselves regularly during conversations can be an early indicator of hearing difficulties.
- Increased Volume on Devices: Turning up the volume on the TV, radio, or other audio devices more than usual can suggest a decrease in hearing ability.
- Muffled Hearing: Sounds and voices may seem muffled or distorted, making it hard to decipher tones or specific words.
- Trouble Hearing High-Pitched Sounds: Difficulty hearing high-pitched noises like doorbells, alarms, or the voices of children can be an early sign of hearing loss.
Progressive Symptoms That Develop Over Time
As hearing loss advances, symptoms often become more pronounced and disruptive:
- Social Withdrawal: Individuals may start avoiding social interactions due to difficulties in communicating effectively.
- Auditory Fatigue: Experiencing tiredness or stress from straining to hear sounds and voices is common as hearing loss progresses.
- Tinnitus: A ringing, buzzing, or whistling sound in the ears, known as tinnitus, frequently accompanies hearing loss.
- Difficulty Locating Sounds: It may become challenging to determine where sounds are coming from, a symptom known as poor sound localization.
- Increased Misunderstandings: Misinterpreting spoken words and phrases becomes more frequent, potentially leading to miscommunications and frustrations.
Variability by Type of Hearing Loss
The symptoms of hearing loss can vary significantly depending on the type of hearing loss experienced:
- Conductive Hearing Loss: Often caused by obstructions or malfunctions in the outer or middle ear, symptoms include softer sound levels and a reduction in sound clarity.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Resulting from damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, this type often manifests as difficulty understanding speech and may include sensitivity to loud noises or a loss of balance.
- Mixed Hearing Loss: A combination of conductive and sensorineural loss, symptoms can include those of both types, complicating diagnosis and treatment.
If you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional or audiologist is recommended for a comprehensive hearing evaluation.
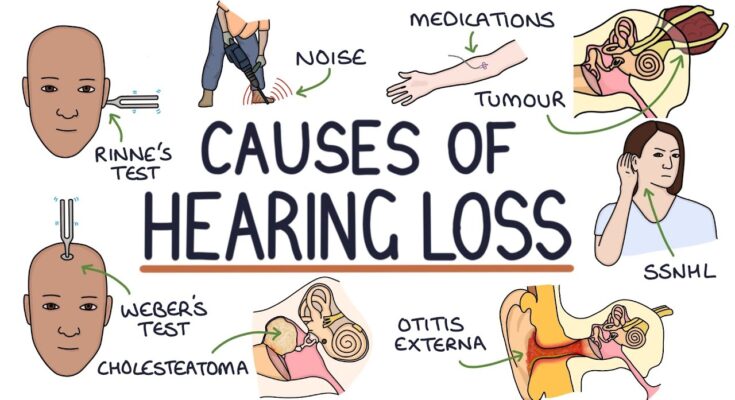
Common Causes of Hearing Loss
Understanding the common causes can help in early detection and management. Here are the primary factors that contribute to hearing impairment:
1. Age-Related Changes in Hearing
As people age, they may experience a natural decline in their hearing ability. This type of hearing loss, known as presbycusis, typically occurs gradually and affects both ears equally. It’s caused by changes in the inner ear and auditory nerve, which transmit sound signals to the brain. Regular hearing check-ups are recommended to monitor changes and manage this condition effectively.
2. Noise-Induced Hearing Damage
Exposure to loud noises is one of the most common causes of hearing loss. This can result from both a one-time exposure to an intense “impulse” sound, like an explosion, or continuous exposure to loud noises, such as those encountered in certain workplaces or during recreational activities. Protective earwear and reducing exposure to loud sounds can help prevent noise-induced hearing damage.
3. Other Medical Conditions
Various medical conditions can also lead to hearing loss. These include:
- Infections: Certain infections like meningitis, measles, and mumps can damage the auditory system.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can affect the ears as well.
- Genetic Factors: Hereditary factors can play a significant role, with some types of hearing loss being passed down through families.
4. Ototoxic Medications
Some medications are known to be harmful to the auditory system. These ototoxic medications can damage the inner ear, leading to hearing loss. Medications that can cause this include certain antibiotics, cancer chemotherapy drugs, and even high doses of aspirin. It is crucial for patients on these medications to have regular hearing assessments to detect any early signs of hearing impairment.
However, understanding these common causes of hearing loss can aid in prevention and early treatment, helping individuals maintain better hearing health throughout their lives.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can affect anyone at any stage of life, making timely and accurate diagnosis crucial for maintaining quality of life. Professional screening and diagnosis methods are essential tools for detecting hearing impairments early and accurately. Here, we delve into the role of audiometric tests, hearing evaluations, and the importance of regular hearing assessments.
Role of Audiometric Tests in Hearing Evaluations
Audiometric tests are the cornerstone of hearing evaluations. Conducted by audiologists, these tests measure an individual’s ability to hear sounds of varying frequencies and volumes. The most common types of audiometric tests include:
- Pure Tone Audiometry: This test involves the individual listening to a series of beeps or tones through headphones, each tone varying in pitch and loudness. The person’s responses help define the specific frequencies and decibels at which hearing loss occurs.
- Speech Audiometry: This assesses the ability to hear and understand speech. The test measures the softest speech sounds (threshold) a person can hear and understand 50% of the time, as well as their ability to correctly repeat back spoken words at a comfortable loudness level.
- Tympanometry: This test evaluates the functioning of the middle ear, particularly the eardrum and the conduction bones. It can help identify issues like fluid in the ear, eardrum perforations, or ossicle bone problems.
These tests are non-invasive, typically conducted in a sound-treated room, and provide valuable data that helps audiologists determine the type and severity of hearing loss.
Importance of Regular Hearing Assessments
Regular hearing assessments are vital for individuals of all ages. They are especially critical for:
- Children: Early detection of hearing issues is essential for speech and language development. Regular screenings, often conducted at school, help identify children who may need further evaluation and intervention.
- Adults: For adults, particularly those exposed to noisy environments or those experiencing age-related hearing changes, periodic hearing evaluations can prevent or manage hearing loss.
- Seniors: Regular assessments can help manage age-related hearing loss, maintaining better communication abilities and overall quality of life.
Regular assessments enable early intervention, which can significantly improve the outcomes of hearing treatments and interventions, such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, or other assistive listening devices.
Managing and Treating Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can significantly impact daily life, but effective management and treatment options are available to improve hearing and quality of life. This article discusses lifestyle changes, technological aids, and surgical options to help individuals navigate the complexities of hearing loss.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventive Measures
Lifestyle adjustments and preventive measures are crucial for both managing existing hearing loss and preventing further damage. Here are key strategies:
- Protect Your Ears: Regular exposure to loud noises can exacerbate hearing loss. Use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in loud environments, such as concerts or construction sites, to protect your hearing.
- Regular Check-Ups: Early detection of hearing loss can significantly improve the effectiveness of treatments. Schedule regular hearing evaluations, especially if you’re frequently exposed to high noise levels.
- Healthy Living: Good cardiovascular health has been linked to better hearing. Exercise regularly, maintain a healthy diet, and monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Avoid Ototoxic Medications: Some medications are harmful to auditory health. Consult with your healthcare provider about the potential hearing risks of any prescribed medications.
Technological Aids
Technological advancements have made significant contributions to hearing loss management. The most common aids include:
- Hearing Aids: These small electronic devices can be tailored to the specifics of an individual’s hearing loss, amplifying sound for clearer understanding. They come in various styles and sizes, offering solutions for virtually all types of hearing impairment.
- Cochlear Implants: For those with severe hearing loss, cochlear implants may be an option. These devices are surgically implanted and work by bypassing damaged parts of the ear to directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
- Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs): ALDs can be used in conjunction with hearing aids or cochlear implants to improve hearing in specific situations, such as in a classroom or meeting.
Surgical Options and Their Considerations
Surgery might be a viable option for treating certain types of hearing loss, especially those related to structural issues of the ear. Common surgical treatments include:
- Tympanoplasty: This procedure repairs a perforated eardrum or the small bones in the ear, which can improve hearing.
- Stapedectomy: Helpful for those with otosclerosis, this surgery replaces a stiffened stapes bone with a prosthetic device to allow sound waves to enter the inner ear more effectively.
- Implantable Hearing Devices: Different from cochlear implants, these devices are designed for those who cannot benefit from traditional hearing aids but do not require cochlear implants.
Each surgical option carries its own risks and benefits, and the decision to proceed should be made in consultation with an audiologist and a surgeon specializing in ear disorders.
By understanding the various strategies and treatments available, individuals experiencing hearing loss can take proactive steps towards improving their hearing health. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, using technological aids, or considering surgical options, there are multiple ways to manage and mitigate the effects of hearing loss.
Prevention Tips for Hearing Loss
Adopting some preventive measures can significantly help in preserving your hearing health. Here, we explore effective strategies to protect your hearing, emphasizing the importance of noise reduction, protective equipment, and regular check-ups.
Strategies to Protect Your Hearing
Protecting your hearing begins with being proactive about the environments you expose yourself to and the protective measures you take:
- Lower the Volume: Frequently listening to loud music through headphones or at concerts can severely impact your hearing. Keep the volume at a moderate level and limit the time spent in noisy environments.
- Use Protective Equipment: In workplaces or during activities where noise levels are high, such as at construction sites or during live events, use protective ear gear like earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones.
- Take Breaks: Give your ears regular breaks during long periods of exposure to high noise levels. This can help your ears recover and reduce the risk of permanent damage.
Importance of Noise Reduction and Protective Equipment
Noise-induced hearing loss is one of the most common occupational hazards and also affects those in noisy recreational environments. Reducing noise exposure is crucial:
- Soundproofing: Implementing noise-reduction measures at home or in the workplace, like using sound-absorbing panels, can significantly decrease noise levels.
- Quality Ear Protection: Investing in high-quality ear protection can drastically reduce the risk of hearing damage. For instance, musicians often use specially designed earplugs that reduce noise levels without distorting sound.
Regular Check-Ups and When to Seek Medical Advice
Regular hearing assessments can catch signs of hearing loss early, leading to better outcomes through timely intervention:
- Routine Hearing Tests: Adults should have their hearing tested periodically, even if they do not notice any problems. This is especially important for those who work in noisy environments or are exposed to loud noises regularly.
- Signs to Watch For: If you experience symptoms like muffled hearing, difficulty understanding conversations, or ringing in your ears (tinnitus), it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly.
However, early detection and protective measures can greatly enhance your quality of life and prevent long-term hearing loss. By understanding the importance of these strategies and implementing them, you can enjoy a lifetime of healthy hearing.
FAQs about Hearing Loss Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of hearing loss?
The most common symptoms of hearing loss include difficulty understanding conversations, especially in noisy environments, frequently asking others to repeat themselves, perceiving sounds as muffled, needing to increase the volume on devices like TVs and phones, and experiencing tinnitus, which manifests as ringing or buzzing in the ears.
Can hearing loss symptoms come on suddenly?
Yes, hearing loss can manifest suddenly, though it is more common for it to develop gradually. Sudden hearing loss, medically termed as “sudden sensorineural hearing loss,” requires immediate medical attention as it can be a symptom of serious underlying conditions.
Are there symptoms that indicate severe hearing loss?
Symptoms of severe hearing loss include an inability to hear most sounds unless they are extremely loud, difficulty understanding speech even with the use of hearing aids, and relying heavily on lip-reading or sign language for communication.
How do I know if my child is experiencing hearing loss?
Signs of hearing loss in children might include lack of attention to sounds, delays in speech and language development, frequent increases in TV or device volume, and clear pronunciation difficulties. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a hearing evaluation.
Does hearing loss cause pain?
Generally, hearing loss itself does not cause pain. However, if hearing loss is associated with ear infections, ear trauma, or other ear disorders, pain can be a symptom. Always seek medical advice if hearing loss is accompanied by discomfort or pain.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored the various symptoms and causes of hearing loss, highlighting the importance of early detection and treatment. From experiencing difficulty understanding conversations to the presence of tinnitus or ear pain, these indicators should not be ignored. Causes of hearing loss can range from exposure to loud noises and aging to infections and genetic factors.
If you or someone you know is showing signs of hearing loss, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Consulting a healthcare professional can lead to early diagnosis and management, potentially preventing further deterioration of hearing ability. Remember, addressing hearing issues promptly can significantly improve the quality of life. So, don’t hesitate—seek help if you notice any symptoms of hearing loss.
References
For further reading on the symptoms of hearing loss and to validate the information provided, consider exploring these reputable sources:
- Mayo Clinic – A comprehensive overview of hearing loss, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Visit their page on hearing loss here.
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) – ASHA provides detailed information on the types of hearing loss and their respective symptoms. Find more details here.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC’s page on hearing loss covers the importance of early diagnosis and includes statistics on the prevalence of the condition. Learn more here.
- National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) – For scientifically backed information on the symptoms of hearing loss and diagnostic strategies, visit the NIDCD site here.
- World Health Organization (WHO) – The WHO provides global statistics and information on the prevention of hearing loss. Access their resources here.
Each of these sources offers valuable insights and has been recognized for their credibility and thorough coverage of health-related topics.