Folliculitis Treatment: In the pursuit of maintaining optimal skin health, understanding and addressing common dermatological conditions is paramount.
Folliculitis, a widespread skin disorder characterized by inflammation of the hair follicles, presents a significant concern for individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diagnosis and treatment of folliculitis, offering invaluable insights for those seeking to alleviate this condition.
Understanding Folliculitis
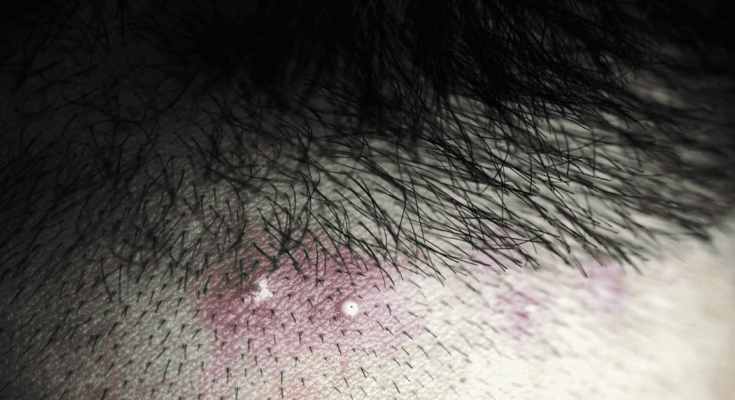
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become inflamed. It’s characterized by the presence of red, swollen bumps that can occur anywhere on the skin where hair grows. These bumps may be itchy or painful and can develop into pus-filled blisters. Understanding the different types of folliculitis, its causes, risk factors, and symptoms can help in managing and preventing this skin condition effectively.
Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis can be classified into two main types based on its severity:
- Superficial Folliculitis: This type affects the upper part of the hair follicle and includes conditions such as:
- Bacterial Folliculitis: Often caused by Staphylococcus aureus, it presents as small, white, pus-filled bumps.
- Pityrosporum Folliculitis: This type is caused by yeast infection and results in chronic, red, itchy pustules on the back and chest.
- Deep Folliculitis: This affects the entire follicle from deep under the skin and can cause more severe symptoms. Types include:
- Sycosis Barbae: This is found in men who shave and is characterized by inflammation of the entire hair follicle.
- Gram-negative Folliculitis: Often occurs when long-term antibiotic treatment for acne alters the natural balance of bacteria in the nose, leading to an outbreak.
Causes and Risk Factors
Folliculitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Infection: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections are common causes.
- Physical Irritation: Shaving, tight clothing, or any activity that irritates the skin can lead to folliculitis.
- Chemical Irritation: Harsh chemicals found in some soaps, creams, or oils can irritate the hair follicles.
- Blocked Follicles: Heavy sweating, or using greasy products, can block hair follicles, making them prone to inflammation.
Risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing folliculitis include:
- Having a pre-existing skin condition, such as acne or dermatitis
- Compromised immune system
- Regular use of hot tubs or swimming pools not properly chlorinated
- Being overweight
Symptoms and Signs
The signs and symptoms of folliculitis include:
- Red or pink bumps around hair follicles
- Pus-filled blisters that break open and crust over
- Itchy, burning skin
- Painful, tender skin
- A large swollen bump or mass (in severe cases)
If you experience symptoms of folliculitis, it’s important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and reduce the risk of complications. With proper care, most forms of folliculitis can be effectively managed, allowing those affected to maintain healthy, comfortable skin.
Diagnosing Folliculitis
Understanding when to seek medical advice and what to expect during the diagnosis process is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here’s a guide to help you navigate these steps.
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing the Symptoms
While mild cases of folliculitis often resolve on their own, certain symptoms warrant professional advice to prevent complications such as infection spreading or scarring. Consider consulting a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent or worsening symptoms despite home care
- Extensive areas of redness, swelling, or pus-filled blisters
- Pain or significant discomfort
- Recurring episodes of folliculitis
- Fever or signs of a more extensive infection
Prompt medical evaluation ensures appropriate treatment and helps rule out more serious conditions.
Diagnosis Process: From Physical Exams to Lab Tests
Healthcare professionals typically diagnose folliculitis through a comprehensive approach:
Physical Examination: The first step is a thorough examination of the affected skin areas. Your doctor will look for the characteristic signs of folliculitis – red, inflamed bumps around hair follicles, often with visible pus or fluid.
Medical History: Discussing your medical history, recent activities, skincare routines, and any prior episodes of skin conditions can provide valuable clues.
Lab Tests: In some cases, to confirm the diagnosis or identify the type of bacteria or fungus causing the infection, your doctor may take a sample from the affected area. This sample could be a swab from a pus-filled blister or a tissue sample (biopsy) in more severe cases. Lab tests help in tailoring the treatment to the specific cause of your folliculitis.
Differential Diagnosis: Ruling Out Other Conditions
Folliculitis can mimic several other skin conditions, making differential diagnosis important. Conditions often considered include:
- Acne: Like folliculitis, acne involves inflamed bumps but usually affects the face, chest, and back, and is related to oil glands rather than hair follicles.
- Heat rash (miliaria): Caused by blocked sweat ducts, heat rash can resemble folliculitis but lacks bacterial or fungal involvement.
- Boils and carbuncles: Deeper infections of hair follicles, these are typically larger, more painful, and filled with pus.
- Keratosis pilaris: A condition that leads to rough, small bumps on the skin, often on the arms or thighs, but these bumps are not infected.
By carefully comparing symptoms, and sometimes through lab tests, healthcare providers can distinguish folliculitis from these and other conditions, ensuring an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Folliculitis Treatment Options
Effective management of folliculitis not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents complications such as scarring or the spread of infection. Below, we explore various treatment strategies for folliculitis, emphasizing the importance of adhering to a comprehensive treatment plan.
Home Care and Lifestyle Changes
Managing mild cases of folliculitis often begins with home remedies and lifestyle adjustments aimed at reducing irritation and preventing further infection:
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm, moist cloth to the affected area several times a day can help soothe irritation and promote drainage of pus.
- Good Hygiene: Regularly washing the affected area with a mild antibacterial soap can prevent the spread of infection.
- Avoid Irritants: Minimize friction from clothing and avoid shaving the affected area until the symptoms improve.
- Over-the-counter Treatments: Products containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can be effective in reducing inflammation and clearing up infections.
Medications
For more severe or persistent cases of folliculitis, your healthcare provider may recommend medications:
- Topical Antibiotics: Creams or ointments that fight bacteria can be applied directly to the skin to treat infections.
- Oral Antibiotics: In cases where the infection is deep or widespread, oral antibiotics may be necessary to eliminate the bacteria.
- Antifungal Medications: If your folliculitis is caused by a fungal infection, antifungal treatments may be prescribed.
Advanced Treatments
When conventional treatments fail to resolve folliculitis, advanced options may be considered:
- Laser Hair Removal: For recurrent or chronic folliculitis, particularly in sensitive areas like the groin or underarm, laser treatment can reduce hair growth and minimize the risk of future infections.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): This involves using light-sensitive medication and a light source to destroy abnormal cells, and can be effective for certain types of folliculitis.
Importance of Following the Treatment Plan
Adhering to your treatment plan is crucial for effectively managing folliculitis. Skipping treatments or not following your healthcare provider’s advice can lead to a recurrence of the infection and potentially more severe complications. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will help monitor your progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure the best possible outcomes.
However, a combination of home care, medications, and possibly advanced treatments can effectively manage folliculitis. Remember, the key to successful treatment lies in early intervention and strict adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen. Always consult a healthcare professional for a diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Managing Folliculitis: Tips and Best Practices
Fortunately, with the right skin care routines, product choices, and lifestyle modifications, managing folliculitis and reducing flare-ups is achievable. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the management of folliculitis with ease.
Skin Care Routines That Help Prevent Folliculitis Flare-ups
A gentle and consistent skin care routine is crucial in preventing folliculitis flare-ups. Here are some tips:
- Cleanse Gently: Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser to gently wash the affected areas twice a day. Avoid scrubbing the skin harshly, as this can aggravate folliculitis.
- Moisturize: Apply a lightweight, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated. This helps maintain the skin’s barrier function and prevents irritants from entering the hair follicles.
- Exfoliate Wisely: While exfoliation can help prevent follicle blockages, overdoing it can irritate the skin. Opt for a gentle exfoliator and limit its use to once or twice a week.
- Dry Well: After bathing or sweating, pat the skin dry with a clean towel instead of rubbing. Moist environments can promote the growth of bacteria and fungi, exacerbating folliculitis.
Recommended Products and What to Avoid
The right products can make a significant difference in managing folliculitis. Here’s what to look for and what to avoid:
- Non-irritating, Non-comedogenic Products: Choose products labeled as non-irritating and non-comedogenic, meaning they won’t clog pores or irritate the skin, thereby reducing the risk of folliculitis flare-ups.
- Avoid Harsh Ingredients: Steer clear of products containing alcohol, fragrances, and other harsh chemicals, as these can irritate the skin and worsen folliculitis.
- Consider Products with Salicylic Acid or Benzoyl Peroxide: These ingredients can help prevent hair follicle blockages and have antibacterial properties, but they should be used with caution and under the guidance of a dermatologist, especially if you have sensitive skin.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle plays a vital role in managing folliculitis. Here are some adjustments that can help:
- Diet: Incorporate a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support overall skin health. While no direct link between diet and folliculitis has been proven, a healthy diet can improve your skin’s condition.
- Clothing: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing, especially during exercise. Tight, non-breathable fabrics can trap sweat and bacteria against the skin, increasing the risk of folliculitis.
- Habits: Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, and clothing, as these can transfer bacteria and fungi that trigger folliculitis. Additionally, if you shave, use a clean, sharp razor and shave in the direction of hair growth to minimize irritation.
By following these tips and best practices, you can reduce flare-ups and maintain healthier, clearer skin. Remember, if your symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a dermatologist is always the best course of action.
Complications and When to Seek Further Medical Advice for Folliculitis
Understanding the potential consequences and recognizing the signs that necessitate further medical consultation is crucial for effective management and prevention of more serious outcomes.
Complications of Untreated or Improperly Treated Folliculitis
- Infection Spread: Without appropriate treatment, the infection can spread to surrounding hair follicles, leading to a more extensive and difficult-to-treat condition.
- Chronic Condition: Folliculitis can become chronic, persisting for months or even years, if the initial infection is not adequately addressed.
- Boils and Carbuncles: Severe infections can result in the development of boils or carbuncles, which are deeper, more painful, and can lead to scarring.
- Scarring and Permanent Hair Loss: Chronic or severe folliculitis can lead to scarring or the destruction of hair follicles, resulting in permanent hair loss in the affected areas.
- Cellulitis: A more severe bacterial skin infection, cellulitis, can develop if the bacteria from folliculitis spread deeper into the skin. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
Signs That Indicate the Need for a Follow-up with a Healthcare Professional
- Worsening Symptoms: If your condition does not improve with initial treatment, or if symptoms worsen, it’s essential to seek further medical advice.
- Recurrent Episodes: Frequent recurrences of folliculitis might indicate an underlying issue that requires professional evaluation and treatment.
- Fever or General Ill Feeling: The presence of fever or a feeling of overall illness can be a sign of a more severe infection.
- Rapid Spreading: If the infection spreads quickly, covering larger areas of your skin, this is a clear signal to consult a healthcare provider.
- Pain and Swelling: Increasing pain, redness, and swelling around the infected follicles are indicators of an escalating condition.
- Drainage of Pus: Any discharge of pus from the affected follicles suggests a need for medical intervention to manage the infection and prevent further complications.
However, should you notice any signs of worsening or complications as mentioned above, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional. Early and effective management is key to preventing the escalation of the condition, ensuring a swift recovery and minimizing the risk of long-term consequences.
FAQ Section: Folliculitis Treatment
What is folliculitis?
Folliculitis is a skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles. It can occur anywhere on the skin and is typically caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. Symptoms include red, swollen bumps, itching, and sometimes pain.
How can you treat folliculitis at home?
Mild cases of folliculitis often respond well to home treatment. Keeping the affected area clean and dry, applying warm compresses, and using over-the-counter antibacterial or antifungal creams can help alleviate symptoms. Avoiding tight clothing and shaving the area can also prevent further irritation.
When should you see a doctor for folliculitis?
You should consult a healthcare provider if your symptoms worsen, spread, or don’t improve with home treatment within a few days. Medical advice is crucial if you experience fever, the area becomes increasingly red, swollen, or painful, or if the bumps drain pus, indicating a more severe infection.
Can folliculitis be prevented?
Yes, you can reduce your risk of developing folliculitis by maintaining good personal hygiene, using a clean razor for shaving, avoiding shared hot tubs and pools that aren’t well-maintained, and wearing breathable, loose-fitting clothing. It’s also helpful to moisturize your skin regularly to keep it healthy.
Are there any specific medications for folliculitis?
The treatment of folliculitis often depends on its cause. For bacterial infections, doctors may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics. Antifungal medications are used for fungal infections. In more severe or recurrent cases, your doctor might recommend other treatments, such as laser hair removal to prevent ingrown hairs that lead to folliculitis.
Can folliculitis recur?
Yes, folliculitis can recur, especially if the underlying causes, such as certain shaving practices or the use of hot tubs, aren’t addressed. Implementing preventive measures and following the treatment plan recommended by your healthcare provider can help minimize recurrences.
Does diet affect folliculitis?
While there’s no direct link between diet and folliculitis, maintaining a balanced diet can support overall skin health. Some individuals may find that certain foods exacerbate their skin condition. It’s beneficial to observe how your skin reacts to different foods and discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional.
Is folliculitis contagious?
Folliculitis caused by an infection can be contagious, especially if it’s due to a bacterial or fungal infection. It’s important to avoid sharing personal items like towels, razors, and clothing to prevent spreading the condition. Non-infectious causes of folliculitis, such as irritation from shaving, are not contagious.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of folliculitis and their respective triggers is the first step towards effective management. Whether it’s a mild case caused by shaving or a more severe form triggered by bacterial infection, the right approach to treatment can alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. Treatments may include over-the-counter remedies, prescription medications, or even lifestyle adjustments to avoid known triggers.
However, self-diagnosis and treatment, while tempting, may not always lead to the desired outcome. This is where the expertise of healthcare providers becomes invaluable. Dermatologists and other medical professionals can offer personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific condition, health history, and lifestyle, ensuring that the approach is both effective and safe.
We strongly encourage anyone dealing with symptoms of folliculitis or other skin concerns to consult a healthcare provider. Seeking professional advice not only helps in achieving clearer, healthier skin but also in understanding how to maintain it. Remember, your skin health is a vital part of your overall well-being, and taking the necessary steps to care for it is always worth the effort.
In summary, while folliculitis can be a distressing condition, understanding its causes, seeking the right treatment, and consulting with healthcare professionals can significantly improve outcomes. Your journey to healthier skin starts with taking that first step towards professional care.
References
In our comprehensive guide on Folliculitis Treatment, we’ve provided detailed insights and recommended practices based on current dermatological knowledge and research. For readers interested in delving deeper into the subject, seeking further validation of the information provided, or exploring additional resources for broader understanding, we recommend consulting the following reputable sources. These references have been selected for their authority in the field, the rigor of their research methodologies, and their commitment to providing up-to-date, accurate health information.
- American Academy of Dermatology Association: Offers a wide range of resources on skin conditions, including folliculitis. Their detailed guides and patient care stories are invaluable for understanding the condition from a clinical and patient perspective. Visit aad.org for comprehensive articles and treatment options.
- Mayo Clinic: Known for its expertise in treating a variety of medical conditions, Mayo Clinic provides an in-depth look at folliculitis, covering causes, symptoms, and treatments. Their resources are scientifically backed and regularly updated. Access their knowledge base at mayoclinic.org.
- National Institutes of Health, MedlinePlus: A reliable source for patient education, MedlinePlus offers accessible information on diseases, including skin conditions like folliculitis. Their articles are a collaboration between numerous health professionals and research organizations. Explore more at medlineplus.gov.
- British Association of Dermatologists: Offers detailed patient information leaflets on various skin conditions, including folliculitis. These leaflets are prepared by dermatologists and provide a U.K. perspective on treatment options. Visit their site at bad.org.uk.
- PubMed Central: An essential resource for those interested in the scientific and medical research aspects of folliculitis. It provides access to thousands of full-text articles from reputable journals, allowing for deep dives into research findings. Explore research articles at ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc.
By consulting these sources, readers can gain a more nuanced understanding of folliculitis, its treatment options, and ongoing research in the field. These references are instrumental in empowering patients and healthcare professionals alike with the knowledge necessary to tackle this skin condition effectively.