Fibromuscular Dysplasia Treatment: Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is a vascular disease that often goes undetected, leading to critical implications for those afflicted.
Understanding the nuances of its diagnosis and the breadth of treatment options available is paramount for patients and healthcare providers alike.
This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the path to recognition and management of FMD, ensuring readers are well-informed and prepared to navigate this complex condition.
What is Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
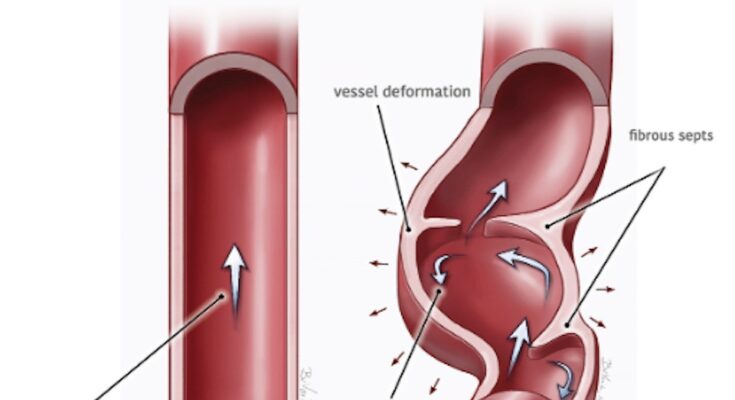
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is a rare vascular condition characterized by abnormal cell development in the walls of one or more arteries, leading to stenosis (narrowing), aneurysms (bulging), or dissections (tears). This disease can affect any artery but is most commonly seen in the renal (kidneys) and carotid (neck) arteries. Symptoms of FMD vary depending on the arteries involved but may include high blood pressure, headaches, or no symptoms at all, making it challenging to diagnose without specific tests.
Types of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
FMD is classified into three main types based on the layer of the artery affected:
- Intimal Fibroplasia: Rare, affecting the innermost layer of the artery, and often leads to severe narrowing.
- Medial Fibroplasia: The most common type, affecting the middle layer, characterized by a “string of beads” appearance on imaging tests due to alternating areas of narrowing and bulging.
- Adventitial Fibroplasia: Affects the outermost layer of the artery and is quite rare.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Fibromuscular Dysplasia is considered a rare condition, though its exact prevalence is unknown due to underdiagnosis. It is estimated to affect around 4% of the population undergoing diagnostic angiography. FMD is more common in women than in men, with a female to male ratio of approximately 9:1. The disease can occur at any age but is most frequently diagnosed in individuals in their 40s and 50s.
Demographically, FMD has been identified across various ethnicities and geographic locations, suggesting a wide impact without specific ethnic or geographical clustering. However, data on ethnicity and race are limited, indicating a need for further research to understand the full demographic impact of FMD.
This comprehensive overview highlights the importance of awareness and early diagnosis of Fibromuscular Dysplasia, given its potential to significantly impact the vascular system and overall health.
Symptoms of Fibromyalgia Dysplasia
Understanding the common symptoms associated with FMD, recognizing how these symptoms can differ among patients, and knowing when to seek medical advice are essential steps for managing this condition. This article aims to provide a clear and concise overview, suitable for anyone looking to understand more about FMD.
Common Symptoms Associated with FMD
Fibromuscular Dysplasia can present a wide array of symptoms, largely depending on which arteries are affected. However, some symptoms are more common than others, including:
- High Blood Pressure: Often one of the first indicators, especially if it is difficult to control or appears suddenly at a young age.
- Headaches or Migraines: Frequent or severe headaches can occur, sometimes due to the reduced blood flow to various parts of the body.
- Tinnitus: A ringing or whooshing sound in the ears, reflecting abnormalities in the carotid artery.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Can result from compromised blood flow to the brain.
- Pulsatile Tinnitus: A specific form of tinnitus where the individual can hear the pulsing of their blood, usually in rhythm with their heartbeat.
- Neck Pain: Particularly in the front part of the neck, which may be due to abnormalities in the carotid artery.
How Symptoms Differ Among Patients and Types of FMD
The experience of FMD symptoms can vary significantly among patients, primarily due to the condition’s ability to affect different arteries in the body. There are two main types of FMD, each associated with its unique set of symptoms:
- Multifocal FMD: Characterized by a “string of beads” appearance on imaging tests due to multiple stenoses separated by areas of dilation. Patients often experience high blood pressure, headaches, and tinnitus.
- Focal FMD: Involves a single area of narrowing in the artery and can lead to localized symptoms depending on the artery’s location, such as diminished pulse in an extremity or localized pain.
The variation in symptoms also reflects the body’s remarkable ability to adapt to reduced blood flow, meaning that some individuals might not exhibit any symptoms until the condition progresses significantly.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Given the potential severity of symptoms and complications associated with FMD, it’s crucial to seek medical advice under the following circumstances:
- Unexplained High Blood Pressure: Especially if it’s difficult to manage or appears suddenly, particularly in younger individuals.
- Sudden Neurological Symptoms: Such as severe headaches, changes in vision, or episodes of dizziness.
- Unusual Sounds in the Ears: Persistent whooshing or ringing sounds, especially if it’s pulsatile tinnitus.
- Any Severe, Unexplained Pain: Particularly if localized to specific areas such as the neck or limbs.
Early detection and management of FMD can significantly improve the quality of life and reduce the risk of complications such as arterial dissections or aneurysms. If you or someone you know exhibits any of the symptoms mentioned above, consulting with a healthcare provider is strongly recommended.
However, while Fibromuscular Dysplasia can present through a variety of symptoms, being aware of the common signs and understanding when to seek professional advice can aid in early diagnosis and management. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized medical advice and treatment options tailored to your specific condition.
Diagnosis of Fibromyalgia Dysplasia
Its diagnosis is crucial for the effective management and treatment of the condition. However, due to its complex nature, diagnosing FMD presents several challenges. This article provides an overview of the diagnostic tests and procedures for FMD, as well as insights into the challenges faced during diagnosis and strategies to overcome them.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures for FMD
Diagnosing FMD requires a careful and detailed evaluation, often involving a combination of the following tests and procedures:
- Physical Examination: Initial assessment by a healthcare provider, focusing on blood pressure discrepancies, abdominal bruits, or physical signs indicating reduced blood flow to certain areas of the body.
- Doppler Ultrasound: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to evaluate the blood flow in arteries. It can detect abnormalities that suggest FMD, such as turbulence or narrowing within the arteries.
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA): This imaging test provides detailed images of the blood vessels and can identify areas of narrowing, beading, or aneurysms indicative of FMD.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): Similar to CTA but uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the arteries without the use of radiation.
- Catheter-Based Angiography: Considered the gold standard for diagnosing FMD, this invasive procedure involves threading a thin tube through the blood vessels to inject a contrast dye, allowing for detailed X-ray images of the arterial walls.
Challenges in Diagnosing FMD and Strategies to Overcome Them
The diagnosis of FMD can be fraught with challenges, primarily due to its nonspecific symptoms and the rarity of the condition. Key challenges and strategies to address them include:
- Lack of Awareness: FMD can often be overlooked by healthcare providers due to its rarity and nonspecific symptoms. Strategy: Increasing awareness and education among healthcare professionals about FMD and its signs and symptoms can lead to more accurate and timely diagnoses.
- Similarity to Other Conditions: FMD’s symptoms can mimic those of other vascular disorders. Strategy: Comprehensive differential diagnosis processes, involving a range of tests and evaluations, can help distinguish FMD from other conditions.
- Access to Advanced Imaging: Not all medical facilities have access to the advanced imaging techniques necessary for diagnosing FMD. Strategy: Referral to specialized centers with the requisite diagnostic tools and expertise in vascular diseases can ensure more accurate diagnosis.
- Interpretation of Imaging Results: The interpretation of results from imaging tests can be complex and requires expertise. Strategy: Collaboration with radiologists and vascular specialists experienced in identifying FMD can improve diagnostic accuracy.
However, overcoming the obstacles requires increased awareness, education, and collaboration among healthcare professionals, ensuring those affected by FMD receive the accurate diagnosis and management they need.
Fibromuscular Dysplasia Treatment Options
With the right treatment approach, individuals living with FMD can lead full and active lives. In this article, we’ll explore the various treatment options available for Fibromuscular Dysplasia, focusing on medication management, interventional procedures, and surgical options when necessary.
Medication Management
Medication is often the first line of defense in managing Fibromuscular Dysplasia. While there’s no cure for FMD, medications can help control symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Blood pressure medications: High blood pressure is a common symptom of FMD. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), and beta-blockers may be used to keep blood pressure within a normal range.
- Antiplatelet agents: To prevent blood clots, doctors may recommend antiplatelet agents like aspirin.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs: Statins may be prescribed to manage cholesterol levels, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
It’s essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to find the most effective medication regimen for their specific situation.
Interventional Procedures
When medication isn’t enough to manage FMD or if the disease progresses, interventional procedures may be considered. These minimally invasive techniques can help alleviate symptoms and improve blood flow. They include:
- Angioplasty: This procedure involves inserting a tiny balloon into a narrowed artery and inflating it to open up the blood vessel.
- Stenting: A stent (a small, metal mesh tube) may be placed in the artery during angioplasty to keep it open.
- Catheter-based treatments: These techniques are used to treat aneurysms or dissections associated with FMD.
Interventional procedures are typically less invasive than traditional surgery and offer shorter recovery times, making them an appealing option for many patients.
Surgical Options When Necessary
In some cases, when FMD has led to significant vascular complications or when less invasive treatments haven’t been effective, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options can vary depending on the affected arteries and may include:
- Bypass surgery: This involves using a graft to bypass the narrowed or blocked section of the artery, restoring normal blood flow.
- Endarterectomy: The surgical removal of the inner lining of the artery that is causing the blockage can be performed in some cases.
- Surgical repair or removal of aneurysms: If FMD has caused aneurysms, surgery might be required to repair or remove them to prevent rupture.
Choosing the right treatment option depends on various factors, including the severity of the disease, the arteries involved, and the patient’s overall health. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers, including vascular specialists, cardiologists, and surgeons, will work together to develop a personalized treatment plan.
From medication management to interventional procedures and surgical options, there are various ways to address the complications associated with FMD. Patients should engage in open and ongoing conversations with their healthcare team to determine the best treatment strategy for their unique needs.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Remedies for Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Living with Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) can be challenging, but making certain lifestyle adjustments and adopting home remedies can significantly ease the symptoms and improve your quality of life. These changes are pivotal in managing the condition effectively alongside medical treatments. This guide delves into the importance of lifestyle modifications, recommended dietary changes, physical activities, and stress management techniques beneficial for individuals with FMD.
Importance of Lifestyle Changes in Managing FMD
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing FMD, as they can help reduce the risk of complications such as high blood pressure and enhance overall well-being. Adapting your lifestyle not only complements medical treatments but also empowers you to take control of your health. Simple changes in diet, exercise, and stress levels can have a profound impact on managing the symptoms and progression of FMD.
Recommended Dietary Changes and Physical Activity
Dietary Changes: A heart-healthy diet is highly recommended for individuals with FMD. This includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Limiting salt intake is crucial to managing blood pressure levels. Additionally, staying hydrated and reducing caffeine and alcohol consumption can also positively affect your condition. It’s beneficial to consult with a dietitian to tailor a diet plan that suits your specific health needs.
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and managing FMD. Activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga can be particularly beneficial. It’s important to start slowly and increase the intensity and duration of exercise gradually. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your condition.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can exacerbate FMD symptoms, making stress management an integral part of managing the condition. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and progressive muscle relaxation can be effective in reducing stress levels. Engaging in hobbies and activities that you enjoy can also serve as a great stress reliever. Moreover, consider seeking support from counseling or support groups to manage emotional stress and connect with others experiencing similar challenges.
However, making lifestyle adjustments and adopting home remedies are key components in managing Fibromuscular Dysplasia effectively. Embracing a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and implementing stress management techniques can significantly improve your symptoms and enhance your quality of life. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your lifestyle to ensure they are safe and suitable for your specific condition.
Monitoring and Long-term Care of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Proper monitoring and long-term care are essential for managing the condition effectively. This article delves into the importance of regular medical check-ups, identifies potential long-term complications, and highlights the significant role of patient support groups and resources in managing FMD.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-Ups
Regular medical check-ups are pivotal for individuals diagnosed with FMD. These check-ups allow healthcare providers to closely monitor the progression of the disease and adjust treatment plans as necessary. Through routine examinations, which may include imaging tests like CT scans, MRI, or ultrasound, doctors can detect changes in the arterial walls and prevent serious complications such as arterial blockages or aneurysms. Additionally, regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial since hypertension can exacerbate the condition. Patients should maintain a proactive relationship with their healthcare team, scheduling appointments at least once a year or more frequently if recommended.
Potential Long-Term Complications and Prevention
Fibromuscular Dysplasia can lead to several long-term complications if not adequately monitored and managed. These complications may include high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease, stroke, and arterial dissections. To minimize the risk of these serious outcomes, patients should adhere to a management plan that includes lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation. Medications may also be prescribed to manage blood pressure and prevent clot formation. Early detection and treatment of complications are critical, highlighting the need for ongoing surveillance and adherence to medical advice.
Role of Patient Support Groups and Resources
The journey with FMD can be challenging, but patient support groups and resources play a crucial role in navigating this path. Support groups offer a platform for sharing experiences, advice, and emotional support among individuals facing similar challenges. These groups can provide valuable information about managing symptoms, treatment options, and coping strategies. Moreover, patient advocacy organizations often have resources such as educational materials, research updates, and directories of specialists experienced in treating FMD. Engaging with these communities can empower patients and their families, fostering a sense of control over their health and well-being.
However, effective management of Fibromuscular Dysplasia requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular medical check-ups, vigilant monitoring for potential complications, and active participation in patient support networks. By adopting these strategies, individuals with FMD can lead fulfilling lives while minimizing the risk of serious health issues. Remember, an informed and proactive stance towards health can make a significant difference in the journey with FMD.
Advances in Fibromuscular Dysplasia Treatment
In recent years, there have been notable advances in the understanding and treatment of FMD, from groundbreaking research findings to the development of innovative therapies. This article explores these advances, emphasizing recent research findings, their implications for treatment, and the promising horizon of emerging therapies and clinical trials.
Recent Research Findings and Their Implications for Treatment
Recent research into Fibromuscular Dysplasia has shed light on its pathophysiology, genetics, and potential therapeutic targets. Studies have identified various genetic markers associated with FMD, suggesting a genetic predisposition that could lead to more personalized treatment approaches. Additionally, advancements in imaging technologies have improved the diagnosis and monitoring of FMD, allowing for earlier and more precise treatment interventions.
The implications of these findings are significant. With better understanding comes the ability to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup and the specific characteristics of their condition. This could lead to more effective management of the disease, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall quality of life for those affected by FMD.
Emerging Therapies and Clinical Trials
As research progresses, emerging therapies for Fibromuscular Dysplasia are being developed and tested. These include new pharmacological treatments aimed at targeting the underlying causes of FMD, as well as interventions designed to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. For example, drugs that relax blood vessels or prevent blood clotting are being explored for their potential to improve blood flow and reduce the risk of arterial dissection or stroke in FMD patients.
Clinical trials are an essential step in bringing these new therapies from the laboratory to the clinic. Several trials are currently underway, testing everything from novel drug therapies to minimally invasive surgical procedures designed to repair affected arteries. These trials not only offer hope for more effective treatments but also contribute to our understanding of FMD by collecting valuable data on its progression and response to treatment.
The landscape of Fibromuscular Dysplasia treatment is evolving rapidly, fueled by advances in research and the development of new therapies. These developments promise a future where FMD can be managed more effectively, with treatments tailored to the needs of each patient. As we continue to learn more about this complex condition, patients and healthcare providers can look forward to improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected by FMD.
FAQs: Fibromuscular Dysplasia Treatment
What is Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD)?
Fibromuscular Dysplasia is a rare vascular condition characterized by abnormal growth within the walls of medium and large arteries. This can lead to a range of complications, including narrowed or blocked arteries, aneurysms, and high blood pressure. It most frequently affects the arteries leading to the kidneys and brain.
How is Fibromuscular Dysplasia treated?
Treatment for FMD depends on the arteries affected and the severity of the symptoms. Options include medication to manage symptoms such as high blood pressure, procedures to restore blood flow in affected arteries, such as angioplasty, and, in rare cases, surgery. A healthcare provider specializing in vascular diseases can offer guidance tailored to individual cases.
Are there any lifestyle changes recommended for someone with FMD?
Yes, individuals diagnosed with FMD are often advised to adopt heart-healthy lifestyle changes. These can include quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, exercising regularly, managing stress, and avoiding the use of birth control pills, which can increase the risk of blood clots.
Can Fibromuscular Dysplasia go away on its own?
FMD is a chronic condition that does not typically resolve on its own. While treatment can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications, ongoing follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential for monitoring the condition over time.
Is surgery a common treatment for FMD?
Surgery is not the first-line treatment for FMD and is generally reserved for cases where other treatments have not been effective or when there is a significant risk of complications, such as arterial aneurysms or severe blockages. Minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty are more commonly used to treat narrowed arteries.
What is the prognosis for someone with Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
With proper management and regular monitoring, many individuals with FMD can live normal, active lives. The prognosis varies depending on the arteries involved and the severity of the condition. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications, making it important to seek medical advice if FMD is suspected.
Can Fibromuscular Dysplasia affect pregnancy?
FMD can have implications for pregnancy, including an increased risk of hypertension and complications. It’s crucial for women with FMD to consult with their healthcare provider when planning a pregnancy to discuss potential risks and the need for specialized care during pregnancy and delivery.
Conclusion:
Navigating the path of FMD treatment is not a solitary endeavor. It necessitates a close partnership between patients and their healthcare providers. This collaboration is pivotal in crafting a treatment plan that is both effective and adaptive to the evolving nature of FMD. Patients are encouraged to actively engage in their care, asking questions, expressing concerns, and participating in decision-making processes. This active involvement fosters a deeper understanding of the condition, enhances treatment compliance, and ultimately contributes to better health outcomes.
Moreover, the dynamic landscape of FMD research continually brings new insights and therapeutic approaches to the forefront. Staying informed about these advancements can empower patients and their healthcare teams to explore novel treatment avenues that may offer improved benefits.
In conclusion, while the journey with Fibromuscular Dysplasia may present challenges, the collaborative spirit between patients and healthcare providers lights the way forward. By working together, navigating treatment options, and embracing the support of the medical community, individuals with FMD can lead fulfilling lives despite the obstacles posed by this condition. Remember, you are not alone on this journey—through shared efforts and persistent advocacy for health, the road ahead can be navigated with hope and resilience.
References
For those seeking more detailed information on Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) treatment or wishing to verify the information provided, the following reputable sources are highly recommended. Each link leads to authoritative resources, offering deeper insights into the diagnosis, treatment options, and ongoing research related to Fibromuscular Dysplasia.
- Mayo Clinic – Fibromuscular Dysplasia Overview
The Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive overview of Fibromuscular Dysplasia, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Their resource is invaluable for patients and healthcare professionals alike seeking detailed and accessible information.
Visit Mayo Clinic’s FMD Page - PubMed Central (PMC) – Research Articles on Fibromuscular Dysplasia
For those interested in the scientific and medical research aspect of FMD, PubMed Central offers access to numerous research articles and clinical studies focused on the condition. It’s a treasure trove for academic and clinical professionals looking to delve into the empirical data.
Search PMC for FMD Studies - The FMD Society of America – Patient and Caregiver Resources
The FMD Society of America is dedicated to supporting patients and their families, providing resources specifically tailored to those living with Fibromuscular Dysplasia. Their site offers patient stories, treatment information, and ways to connect with the community.
Visit The FMD Society of America
By exploring these resources, readers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of Fibromuscular Dysplasia, including the latest treatment options and research findings. Each source is selected for its authority and reliability in the field, ensuring that you receive accurate and up-to-date information.