Eisenmenger Syndrome Treatment: Eisenmenger syndrome represents a complex cardiac condition characterized by specific hemodynamic changes caused by various congenital heart defects.
Understanding its diagnosis, management, and treatment options is crucial for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of Eisenmenger Syndrome, offering valuable insights into its diagnostic procedures and therapeutic strategies.
What is Eisenmenger Syndrome?
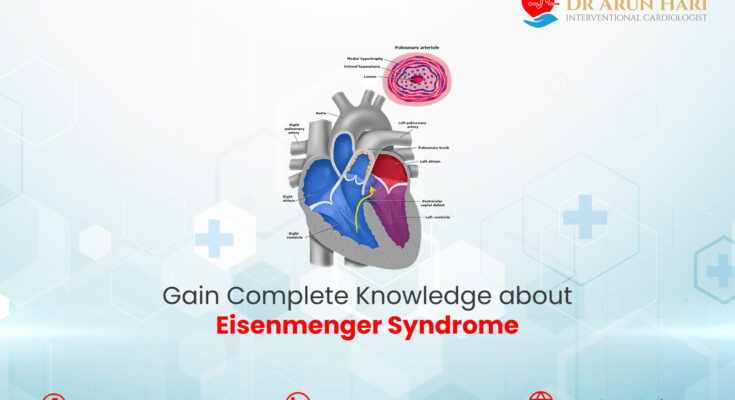
Eisenmenger Syndrome is a complex medical condition that arises as a late complication of untreated congenital heart disease, where a left-to-right cardiac shunt caused by a ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, or patent ductus arteriosus leads to pulmonary hypertension. This condition is characterized by the reversal of the blood flow through the shunt, turning it from left-to-right to right-to-left. As a result, oxygen-poor blood flows into the systemic circulation, leading to cyanosis, or a bluish discoloration of the skin due to insufficient oxygenation.
Understanding the Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of Eisenmenger Syndrome is centered around the development of high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries (pulmonary hypertension) due to increased blood flow from the heart’s left side to the right side. Over time, this increased pressure causes the blood vessels in the lungs to become thick and stiff, reducing their ability to carry blood. Eventually, the resistance in the pulmonary vessels becomes so high that it exceeds the resistance in the systemic circulation, causing the direction of the shunt to reverse. This reversal is a critical development, as it signifies the transition to Eisenmenger Syndrome, making it a severe and irreversible condition. The oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is compromised, leading to symptoms such as difficulty breathing, fatigue, and cyanosis.
Statistics and Prevalence
Eisenmenger Syndrome is considered a rare complication of congenital heart defects, with its prevalence challenging to pinpoint accurately due to variations in diagnostic criteria and reporting practices across different regions. Studies suggest that Eisenmenger Syndrome occurs in a small fraction of patients with congenital heart disease, typically developing in adolescence or early adulthood, although it can manifest at any age depending on the severity and type of the underlying heart defect.
The management of Eisenmenger Syndrome focuses on controlling symptoms and improving the quality of life, as there is currently no cure for the condition. Treatments may include medications to reduce pulmonary pressure, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to avoid situations that could exacerbate symptoms. In some cases, heart or lung transplantation may be considered, although the eligibility for such procedures is evaluated on a case-by-case basis.
However, understanding Eisenmenger Syndrome is essential for early detection and management of congenital heart defects to prevent the progression to this severe complication. Awareness and regular monitoring of individuals with congenital heart anomalies are crucial for mitigating the risks associated with Eisenmenger Syndrome.
Causes and Risk Factors of Eisenmenger Syndrome
Understanding the causes, risk factors, genetic predispositions, triggers, and preventative measures can help in managing and potentially reducing the risk of this syndrome.
Genetic Predispositions and Triggers
- Genetic Predispositions: Eisenmenger Syndrome often originates from congenital heart defects that a person is born with. These defects may include conditions like ventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, and patent ductus arteriosus. Research indicates a genetic component to these congenital defects, suggesting that a family history of congenital heart disease could increase the risk.
- Triggers: The progression to Eisenmenger Syndrome can be triggered by factors that increase blood flow through the lung arteries, causing high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). These triggers include living at high altitudes, engaging in strenuous exercise without medical guidance, and pregnancy.
Risk Factors Leading to Eisenmenger Syndrome
Several risk factors have been identified in the development of Eisenmenger Syndrome, including:
- Congenital Heart Defects: The primary risk factor is the presence of a large, uncorrected heart defect that increases blood flow to the lungs.
- Age: The risk of developing Eisenmenger Syndrome increases with age if congenital heart defects are not corrected.
- Family History: A family history of congenital heart defects may increase the likelihood of developing similar conditions.
Preventative Measures
While Eisenmenger Syndrome itself cannot be prevented once it has developed, certain measures can be taken to prevent its onset in individuals with congenital heart defects:
- Early Detection and Management of Heart Defects: Regular check-ups with a cardiologist and timely interventions for congenital heart defects can prevent the development of pulmonary hypertension and subsequently, Eisenmenger Syndrome.
- Avoiding High-Risk Activities: Those with congenital heart defects should consult their doctor before engaging in activities that increase heart strain, such as high-intensity sports or living at high altitudes.
- Pregnancy Management: Women with congenital heart defects should seek preconception counseling and close monitoring during pregnancy to manage the risk of developing Eisenmenger Syndrome.
With proper management of congenital heart defects and lifestyle adjustments, the progression to Eisenmenger Syndrome can be mitigated. Regular medical check-ups and following the guidance of healthcare professionals are key in managing the risks associated with this condition.
Signs and Symptoms of Eisenmenger Syndrome
Recognizing the early signs and understanding the progression of symptoms are crucial steps in managing this condition effectively. This guide will help you identify key symptoms of Eisenmenger syndrome and understand when it’s critical to seek medical attention.
Early Signs of Eisenmenger Syndrome
The early signs of Eisenmenger syndrome often stem from the underlying heart defect that causes it. Initially, symptoms might be mild or even unnoticed but can become more apparent over time. Key early signs include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity.
- Fatigue that is not relieved by rest.
- Blue tint to the skin, lips, and nails (cyanosis), indicating reduced oxygen levels in the blood.
- Fainting spells or dizziness, particularly after exertion.
- Heart palpitations or racing heartbeat.
These symptoms result from the heart’s inability to pump oxygenated blood efficiently throughout the body due to the congenital heart defect.
Progression of Symptoms
As Eisenmenger syndrome progresses, symptoms tend to become more severe and can significantly impact the individual’s quality of life. Advanced symptoms may include:
- Increased shortness of breath, even at rest.
- Chest pain or discomfort, which might indicate heart strain.
- Swelling in the extremities (edema), due to fluid accumulation.
- Hemoptysis (coughing up blood), a result of increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
- Cyanosis becomes more pronounced, reflecting worsening oxygen saturation in the blood.
These symptoms indicate the progression of the disease and the increasing strain on the heart and lungs.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Early and proactive medical intervention can significantly improve the management of Eisenmenger syndrome. It’s essential to seek medical attention if you or someone you know experiences:
- A sudden increase in the severity of symptoms, such as worsening shortness of breath or fainting.
- New symptoms, like coughing up blood or severe swelling in the limbs.
- Symptoms that interfere with daily activities, making it difficult to perform routine tasks.
- Concerns about the effectiveness of current treatment, or if symptoms persist despite ongoing management efforts.
If you recognize any of the early signs or witness the progression of symptoms as described, consult with a healthcare professional immediately. Early diagnosis and tailored management strategies can help mitigate the effects of Eisenmenger syndrome and improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Diagnostic Approaches to Eisenmenger Syndrome
Understanding the diagnostic methods and distinguishing it from similar conditions are critical steps in the healthcare journey of patients affected by this syndrome. Below, we explore the primary diagnostic approaches, emphasizing the significance of echocardiography and the process of differential diagnosis.
Methods of Diagnosing Eisenmenger Syndrome
The diagnosis of Eisenmenger Syndrome involves a multi-faceted approach, incorporating a variety of tests and evaluations to confirm the presence of the condition and assess its severity:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough medical history review and physical examination are the first steps. Physicians look for signs of cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin due to low oxygen levels), clubbing of fingers, and other physical indicators of chronic hypoxemia and high blood pressure in the lungs.
- Echocardiography: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the heart, allowing doctors to observe its structure and function in real-time. Echocardiography is crucial for identifying structural heart defects associated with Eisenmenger Syndrome and assessing the direction and flow of blood through the heart chambers.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and can detect abnormalities in heart rhythm or structure that may be indicative of Eisenmenger Syndrome.
- Pulmonary Function Tests: These tests measure how well the lungs are working and can help in assessing the impact of the syndrome on lung function.
- Cardiac MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of the heart and blood vessels, offering insights into the anatomy and blood flow that can aid in diagnosing Eisenmenger Syndrome.
- Cardiac Catheterization: Though more invasive, this procedure provides the most definitive diagnosis by measuring the pressure inside the heart and lungs. It can accurately assess the severity of the condition and guide treatment planning.
The Role of Echocardiography in Diagnosing Eisenmenger Syndrome
Echocardiography plays a pivotal role in diagnosing Eisenmenger Syndrome due to its ability to provide comprehensive details about heart function and structure without the need for invasive procedures. It can detect the presence of congenital heart defects, measure pressure gradients across heart valves, and visualize the blood flow pattern that is characteristic of Eisenmenger Syndrome. Echocardiography is often the first test ordered when this condition is suspected and is crucial for ongoing monitoring of the disease progression and response to treatment.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing Eisenmenger Syndrome from Similar Conditions
Differential diagnosis is essential in accurately identifying Eisenmenger Syndrome, as its symptoms and clinical presentations can overlap with other pulmonary and cardiac conditions. Conditions such as primary pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart defects without pulmonary hypertension, and other forms of secondary pulmonary hypertension must be considered and ruled out. Key to this process is the combination of clinical evaluation, echocardiography findings, and, if necessary, cardiac catheterization to measure pulmonary pressures directly. By understanding the specific features and diagnostic criteria of Eisenmenger Syndrome, physicians can accurately differentiate it from similar conditions, ensuring patients receive the most appropriate care and management strategies.
However, diagnosing Eisenmenger Syndrome requires a comprehensive and detailed approach, with echocardiography serving as a cornerstone in the diagnostic process. Through careful differential diagnosis, healthcare providers can distinguish this condition from other similar diseases, facilitating targeted and effective treatment for those affected.
Comprehensive Treatment Strategies for Eisenmenger Syndrome
This article aims to shed light on these treatment avenues, providing patients and caregivers with a deeper understanding of how Eisenmenger Syndrome can be managed to improve quality of life and outcomes.
Medical Management
Medical management is the cornerstone of treating Eisenmenger Syndrome. It primarily focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Key medications used in this regard include:
- Pulmonary vasodilators: These drugs help to reduce blood pressure in the lungs, easing the heart’s workload.
- Anticoagulants: To prevent blood clots, which people with Eisenmenger Syndrome are at an increased risk for.
- Supplemental oxygen: Used to manage hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels), especially during sleep or exertion.
- Iron supplements: Often prescribed to address the iron deficiency anemia commonly seen in patients.
It’s essential for patients to maintain regular consultations with their healthcare provider to adjust medications as necessary and monitor for any side effects.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical options for Eisenmenger Syndrome are considered on a case-by-case basis, given the risks associated with surgery in patients with this condition. However, in specific instances, surgery may offer significant benefits. Options include:
- Heart-lung transplant: This is considered for patients with advanced disease and severe symptoms that do not respond to medical management.
- Repair of the congenital heart defect: In some cases, if feasible, repairing the heart defect that led to Eisenmenger Syndrome can be beneficial.
Decisions regarding surgical interventions depend heavily on individual patient factors, including the severity of the disease, overall health, and the potential for improvement post-surgery.
Lifestyle and Supportive Care
Lifestyle adjustments and supportive care play a vital role in managing Eisenmenger Syndrome effectively. They aim to minimize symptoms, improve quality of life, and reduce the risk of complications. Recommendations include:
- Physical activity: Engaging in light to moderate exercise as recommended by a healthcare provider can help maintain cardiovascular health without overstraining the heart.
- Avoidance of high altitude: Low oxygen levels at high altitudes can exacerbate symptoms; thus, patients are advised to avoid such environments.
- Infection prevention: Staying up-to-date with vaccinations and practicing good hygiene can help prevent respiratory infections, which can be particularly harmful.
- Pregnancy management: Women with Eisenmenger Syndrome should seek specialized care for family planning and pregnancy due to the high risks involved.
By adopting a comprehensive treatment strategy that integrates medical management, potential surgical interventions, and tailored lifestyle and supportive care measures, patients with Eisenmenger Syndrome can manage their condition more effectively. Collaboration with a dedicated healthcare team is crucial to tailor the treatment plan to the individual’s needs, monitor progress, and make adjustments as necessary to optimize outcomes.
Advances in Eisenmenger Syndrome Treatment: Navigating New Horizons
The landscape of Eisenmenger Syndrome treatment is witnessing a transformative era, marked by groundbreaking research findings and the emergence of innovative therapies. This complex condition, characterized by a type of congenital heart defect that leads to pulmonary hypertension, has long challenged medical professionals. However, recent advancements are paving the way for more effective management strategies and a brighter outlook for patients.
Latest Research Findings and Their Implications
Recent studies have unveiled a deeper understanding of the pathophysiology behind Eisenmenger Syndrome, offering new angles for therapeutic intervention. Innovations in genetic profiling and molecular biology have identified potential targets for novel drugs, aiming to address the underlying causes rather than just mitigating symptoms. For instance, research into the role of endothelial dysfunction in Eisenmenger Syndrome has opened the door to treatments that improve blood flow and reduce pulmonary pressures, fundamentally changing the disease’s trajectory.
These findings are not just academic; they have tangible implications for patient care. Enhanced diagnostic techniques, based on genetic markers and advanced imaging, allow for earlier and more accurate identification of at-risk individuals. This early intervention potential could significantly alter the natural course of the disease, improving quality of life and extending survival.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
The therapeutic landscape for Eisenmenger Syndrome is evolving rapidly, with several promising approaches on the horizon. One of the most exciting developments is the use of targeted therapies, drugs designed to specifically address the molecular abnormalities driving the disease. These medications aim to reverse the pathological process at its root, offering hope for a more definitive solution than symptom management alone.
In addition, advancements in non-pharmacological interventions, such as specialized surgical techniques and device implantation, are improving outcomes for those for whom traditional surgery is not an option. The advent of personalized medicine, tailoring treatment plans to the individual’s genetic makeup and disease phenotype, is further enhancing the efficacy of these interventions.
Future Directions in Treatment and Management
Looking forward, the field of Eisenmenger Syndrome treatment is set to expand in several promising directions. Ongoing clinical trials are testing the efficacy of next-generation drugs, with a focus on safety and long-term benefits. Researchers are also exploring the potential of regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy and tissue engineering, to repair heart and lung damage caused by the disease.
Moreover, the integration of digital health technologies, such as remote monitoring and telemedicine, is expected to play a crucial role in managing Eisenmenger Syndrome. These tools can help ensure continuous care and timely interventions, reducing hospitalizations and enhancing patients’ quality of life.
However, the advances in Eisenmenger Syndrome treatment highlight an exciting time in the management of this complex condition. With ongoing research and the development of novel therapies, the future holds promise for improved patient outcomes and the potential for fundamentally altering the disease’s impact on those affected.
Living with Eisenmenger Syndrome
Living with Eisenmenger Syndrome presents unique challenges, but it also offers opportunities for resilience, support, and personal growth. This congenital heart condition, characterized by high blood pressure in the lungs due to abnormal blood flow between the heart chambers, requires careful management and a supportive network to navigate its complexities. Understanding quality of life considerations, coping strategies, and the power of shared experiences can provide valuable insights for patients and their families.
Quality of Life Considerations
For individuals with Eisenmenger Syndrome, quality of life is a multifaceted concept that encompasses physical health, emotional well-being, and the ability to engage in daily activities. It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers to manage symptoms effectively, which can include fatigue, shortness of breath, and cyanosis. Personalized treatment plans that may include medications, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle adjustments are crucial in mitigating symptoms and improving overall health.
Moreover, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in suitable physical activities, and regular medical check-ups are essential strategies for managing this condition. It’s also critical to recognize the emotional and psychological impact of Eisenmenger Syndrome. Accessing mental health support, whether through professional counseling, support groups, or online forums, can provide a vital outlet for expressing concerns and receiving emotional support.
Coping Strategies and Support Systems
Developing effective coping strategies is key to managing the challenges of Eisenmenger Syndrome. Building a strong support system that includes family, friends, and healthcare professionals can offer a foundation of encouragement and assistance. Support groups, specifically for those with congenital heart defects, can also be a valuable resource, offering a sense of community and understanding that is hard to find elsewhere.
Educating oneself about the condition, treatment options, and potential complications can empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare. Advocating for oneself in medical settings and seeking second opinions when necessary are also important aspects of managing Eisenmenger Syndrome.
Patient Stories and Experiences
Sharing patient stories and experiences plays a crucial role in building a community of support and understanding. These narratives offer insight into the daily realities of living with Eisenmenger Syndrome, providing comfort and encouragement to those facing similar challenges. They highlight the importance of resilience, the power of positive thinking, and the strength found in community support.
Personal stories can also illuminate the diverse ways individuals find joy, fulfillment, and meaning in their lives, despite the limitations imposed by their condition. They underscore the message that, although Eisenmenger Syndrome is a significant part of one’s life, it does not define who they are.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Eisenmenger Syndrome
What is Eisenmenger Syndrome?
Eisenmenger Syndrome is a rare, complex heart condition that develops from a congenital heart defect which initially causes left-to-right blood flow through the heart but eventually leads to right-to-left blood flow due to high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). This reversal is known as Eisenmenger’s reaction and results in reduced oxygen levels in the blood, leading to cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin due to lack of oxygen) and other symptoms.
What causes Eisenmenger Syndrome?
The primary cause of Eisenmenger Syndrome is a congenital (present at birth) heart defect that increases blood flow to the lungs, such as a large ventricular septal defect (VSD), atrial septal defect (ASD), or patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). Over time, this increased blood flow causes damage to the lung’s blood vessels, leading to pulmonary hypertension and the reversal of blood flow direction.
What are the symptoms of Eisenmenger Syndrome?
Symptoms of Eisenmenger Syndrome can vary but typically include cyanosis, shortness of breath (dyspnea), fatigue, dizziness, fainting spells, and chest pain. Patients may also experience swelling in the extremities (edema), a reddish tint to the cheeks, and clubbing of the fingers and toes. Symptoms often worsen over time and with physical activity.
How is Eisenmenger Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Eisenmenger Syndrome involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests. These tests might include an echocardiogram (to view heart and blood flow), electrocardiogram (ECG) (to measure heart electrical activity), chest X-rays, MRI of the heart, and cardiac catheterization (to measure pressure in the heart and lungs).
Can Eisenmenger Syndrome be cured?
There is currently no cure for Eisenmenger Syndrome. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Management strategies may include medications to reduce pulmonary hypertension, oxygen therapy, and avoiding situations that can worsen symptoms, such as high altitudes and certain physical activities. In some cases, heart or lung transplant might be considered.
What is the life expectancy for someone with Eisenmenger Syndrome?
Life expectancy for individuals with Eisenmenger Syndrome can vary widely depending on various factors, including the severity of the condition, the age at diagnosis, and how well symptoms are managed. Advances in medical treatment have significantly improved the quality of life and survival rates for people with this condition, but it remains a serious and chronic condition that requires ongoing medical care.
Can Eisenmenger Syndrome be prevented?
Since Eisenmenger Syndrome develops from congenital heart defects, it cannot be prevented in the traditional sense. However, early detection and treatment of congenital heart defects can prevent the development of Eisenmenger Syndrome. Regular prenatal care and early childhood medical screenings can help detect heart defects early, potentially allowing for treatments that can prevent the progression to Eisenmenger Syndrome.
Conclusion:
In summary, the treatment of Eisenmenger Syndrome requires a comprehensive approach that can include medications, oxygen therapy, and in some cases, surgical interventions. The management of this condition is highly individualized, tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of each patient. The goal is always to improve quality of life, manage symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications.
For patients living with Eisenmenger Syndrome and their families, the journey can be challenging, but it’s crucial to remember that you’re not alone. Engaging actively with a dedicated team of healthcare providers is key. This team can guide you through the complexities of treatment options, offer support for the psychological aspects of dealing with a chronic condition, and help navigate the healthcare system.
It’s also important for patients and families to educate themselves about the condition, stay informed about new treatments and research, and connect with support groups where they can share experiences and advice with others facing similar challenges.
Remember, by working closely with your healthcare providers and leaning on the support of your loved ones and community, you can manage the symptoms of Eisenmenger Syndrome more effectively and lead a fulfilling life. Let this journey be one of hope and resilience, knowing that every step taken is a move towards better health and well-being.
Conclusion:
For patients living with Eisenmenger Syndrome and their families, the journey can be challenging, but it’s crucial to remember that you’re not alone. Engaging actively with a dedicated team of healthcare providers is key. This team can guide you through the complexities of treatment options, offer support for the psychological aspects of dealing with a chronic condition, and help navigate the healthcare system.
It’s also important for patients and families to educate themselves about the condition, stay informed about new treatments and research, and connect with support groups where they can share experiences and advice with others facing similar challenges.
Remember, by working closely with your healthcare providers and leaning on the support of your loved ones and community, you can manage the symptoms of Eisenmenger Syndrome more effectively and lead a fulfilling life. Let this journey be one of hope and resilience, knowing that every step taken is a move towards better health and well-being.
References
In this comprehensive guide to Eisenmenger Syndrome Treatment, we have drawn upon a wide range of reputable sources to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided. Below, you will find a list of references that have been instrumental in our research. These sources offer further reading opportunities for those interested in exploring Eisenmenger Syndrome and its treatments in more depth. We encourage readers to consult these references to validate the information and gain a more detailed understanding of this complex condition.
- American Heart Association (AHA) – The AHA provides a detailed overview of congenital heart defects, including Eisenmenger Syndrome, with insights into the latest treatment protocols and research findings. Visit the American Heart Association
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) – As part of the National Institutes of Health, NHLBI offers comprehensive guides on heart, lung, and blood diseases. Their resources on Eisenmenger Syndrome include treatment options, ongoing research, and patient care. Explore NHLBI resources
- PubMed Central (PMC) – An invaluable resource for medical professionals and researchers, PMC houses a vast collection of peer-reviewed articles. Several studies and reviews on Eisenmenger Syndrome treatment strategies can be found here. Search PubMed Central
- European Society of Cardiology (ESC) – The ESC publishes guidelines and clinical practice recommendations, including those relevant to the management of congenital heart diseases like Eisenmenger Syndrome. Discover ESC guidelines
By consulting these references, readers can access a wealth of knowledge that supports the treatment and understanding of Eisenmenger Syndrome. Each source has been chosen for its authority, depth of information, and contribution to the field, ensuring that you receive the most accurate and up-to-date information available.