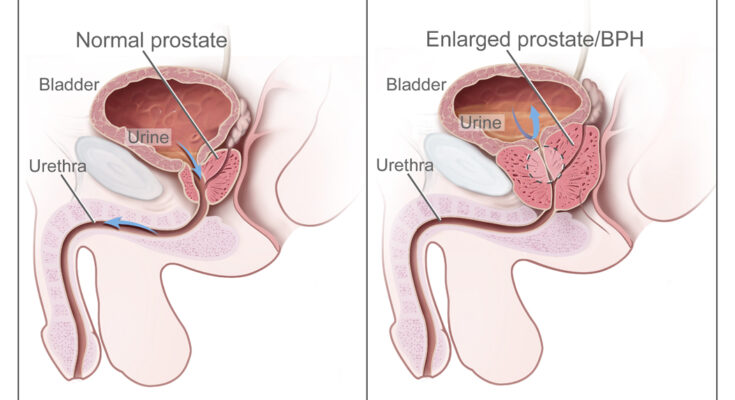
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Symptoms: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, commonly known as BPH, is a condition affecting the prostate gland in men.
As men age, the prostate gland, which surrounds the urethra, can enlarge, leading to a range of urinary symptoms.
It’s crucial to understand that BPH is not prostate cancer and does not increase the risk of cancer. However, it can significantly affect the quality of life.
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as an enlarged prostate, is a non-cancerous increase in the size of the prostate gland. It’s a condition often seen in older men and can lead to various urinary symptoms. The prostate gland, which surrounds the urethra, plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system, primarily responsible for producing fluid that nourishes and transports sperm.
Prevalence of BPH in Different Age Groups
BPH is a widespread condition, affecting men of varying ages. Its prevalence increases with age. Here are some noteworthy statistics:
- Men in their 50s: Approximately 50% show signs of BPH.
- Men over 60: Around 60% are likely to have BPH.
- Men over 70: The prevalence jumps to about 80%.
These statistics indicate that BPH is a common health issue among aging men.
BPH vs. Prostate Cancer: Understanding the Difference
It’s crucial to distinguish BPH from prostate cancer, as they are different conditions. While BPH involves benign growth that does not spread to other parts of the body, prostate cancer involves malignant growth and can be life-threatening. Prostate cancer may also cause symptoms similar to BPH, such as difficulty urinating, but it’s associated with more serious health risks. Regular medical check-ups are essential for early detection and differentiation of these conditions.
Symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
The symptoms of BPH are not just medical concerns; they also have a significant impact on daily life. The most common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: The need to urinate more often, especially at night, can disrupt sleep and daily routines.
- Difficulty Starting Urination: Experiencing a delay or straining to start urinating can be both uncomfortable and frustrating.
- Weak Urine Stream: A noticeable decrease in the strength of the urine stream can indicate BPH.
- Feeling of Incomplete Bladder Emptying: This sensation can lead to frequent trips to the bathroom, affecting one’s comfort and peace of mind.
Understanding how these symptoms can interfere with everyday activities is crucial. They can affect work, social interactions, and overall quality of life, making it important to recognize and address them promptly.
Atypical Symptoms and When to Seek Medical Advice
While the above symptoms are commonly associated with BPH, there are atypical symptoms that should not be overlooked. These include:
- Blood in Urine: Any presence of blood in the urine is a red flag and warrants immediate medical attention.
- Painful Urination: Pain or discomfort during urination is not a typical symptom of BPH and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Urinary Retention: The inability to urinate can be a serious complication of BPH, requiring urgent medical care.
It’s important to seek medical advice if you experience any of these atypical symptoms, as they can indicate more serious health issues. Early detection and treatment of BPH can greatly improve quality of life and prevent complications.
Recognizing the symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and understanding their impact on daily life is essential for managing this common condition. Whether experiencing typical or atypical symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider is key to receiving appropriate care and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Causes and Risk Factors of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Understanding its causes is crucial for those looking to manage or prevent its symptoms. Here’s a detailed look into the factors contributing to BPH:
Hormonal Changes
As men age, hormonal changes occur. The balance between testosterone and other hormones shifts, potentially leading to prostate growth. Studies suggest that especially the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the prostate may influence its enlargement.
Genetics
Your genetic background can play a role. Men with a family history of BPH are more likely to develop the condition, indicating a genetic predisposition.
Lifestyle and Diet
Lifestyle factors, including diet, may impact the risk of developing BPH. High-fat diets, obesity, and lack of physical activity are known contributors. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats might reduce the risk.
Age
Age is the most significant risk factor for BPH. The condition is rare in men under 40 but becomes increasingly common as men age. By the age of 60, over 50% of men exhibit some symptoms of BPH.
Other Factors
Other contributing factors include:
- Ethnicity: BPH is more common in certain ethnic groups.
- Diabetes and heart disease: These conditions, along with the use of beta-blockers, may increase BPH risk.
- Erectile dysfunction: There is a noted correlation between erectile dysfunction and BPH, though the relationship is not fully understood.
Understanding these causes helps in the early identification and management of BPH. If you’re experiencing symptoms or are at risk, consulting a healthcare professional is the best course of action.
Key Risk Factors for Developing BPH
- Age: Age is a significant risk factor. BPH rarely affects men under the age of 40, but its prevalence increases dramatically in men in their 60s and beyond.
- Family History: Genetics play a role. A family history of BPH increases a man’s likelihood of developing the condition, suggesting a hereditary component.
- Lifestyle Choices: Lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, might influence the risk of BPH. Men who are overweight or lead a sedentary lifestyle may have a higher risk of developing BPH.
Busting Myths about BPH Causes
There are many misconceptions about what leads to BPH. It’s important to distinguish fact from fiction:
- Sexual Activity: There’s no conclusive evidence linking sexual activity (either high or low levels) to an increased risk of BPH.
- Medications: While certain medications can influence prostate growth, common over-the-counter drugs are not known to cause BPH.
- Diet: Although a healthy diet can help manage symptoms, no specific foods have been definitively linked to the development of BPH.
However, while age and genetics are non-modifiable risk factors, lifestyle changes can potentially reduce the risk of BPH. It’s also important to dispel myths and rely on factual information for a better understanding of BPH. Regular check-ups and discussions with healthcare professionals are recommended for early detection and effective management of BPH.
Diagnosing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Early diagnosis and management are crucial in improving quality of life and preventing complications.
Common Diagnostic Tests and Procedures for BPH
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): A primary test where a doctor feels the prostate through the rectal wall to check for enlargement.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures the level of PSA in the blood, which can be elevated in men with BPH.
- Urine Test: Analyzes urine to rule out infections or other conditions.
- Uroflowmetry: Assesses the strength and amount of urine flow.
- Postvoid Residual Volume Test: Determines the amount of urine left in the bladder after urinating.
- Prostate Ultrasound: Provides images of the prostate to evaluate its size and shape.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of BPH is vital as it:
- Helps in managing symptoms effectively.
- Reduces the risk of urinary tract infections and other complications.
- Prevents bladder damage and kidney problems.
- Improves the overall quality of life.
Preparing for a Doctor’s Visit
To make the most of your appointment, consider the following:
- List Symptoms: Keep a record of urinary symptoms and how they affect your daily life.
- Note Medical History: Include any other health problems and medications.
- Prepare Questions: Write down questions for your doctor about symptoms, tests, treatments, and lifestyle changes.
- Dietary and Fluid Log: Keep a diary of fluid intake and any foods that seem to worsen symptoms.
- Family History: Share any family history of prostate problems.
By understanding the diagnostic process and actively preparing for medical consultations, individuals can take an essential step towards effective management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Remember, proactive health management is key to maintaining a healthy and active life.
Complications Associated with Untreated Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Understanding the Risks of Ignoring BPH
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as an enlarged prostate, can lead to significant health issues if not properly managed. It’s crucial to understand the potential complications that can arise from untreated BPH, emphasizing the importance of addressing symptoms early.
Urinary Retention: A Primary Concern
One of the most immediate risks of untreated BPH is acute urinary retention. This condition means the bladder is unable to empty completely, leading to discomfort and potential kidney damage. Chronic urinary retention can also develop, increasing the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and bladder stones.
Kidney Damage: A Serious Complication
Extended periods of urinary retention can lead to pressure build-up in the bladder and ureters, eventually affecting the kidneys. This can result in kidney damage or failure, a severe and potentially life-threatening condition.
Bladder Issues: Infections and Stones
The incomplete emptying of the bladder creates an environment conducive to the development of UTIs and bladder stones. These conditions can cause significant pain, discomfort, and further complications if not treated.
Importance of Symptom Management
Early detection and management of BPH symptoms can prevent these complications. Regular check-ups, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions can significantly reduce the risks associated with untreated BPH. It’s imperative to consult with healthcare professionals to develop an effective management plan tailored to individual needs.
Ignoring the symptoms of BPH can lead to severe health complications. Understanding the risks associated with untreated BPH and taking proactive steps to manage symptoms is vital for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Treatment Options for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
The treatment options for BPH range from lifestyle changes to medication and surgery, depending on the severity of symptoms and the patient’s overall health.
- Lifestyle Changes: For mild symptoms, doctors often recommend lifestyle modifications. These include reducing fluid intake before bedtime, limiting caffeine and alcohol, and practicing bladder training exercises.
- Medication: Several medications can help manage BPH symptoms. Alpha blockers like tamsulosin relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, easing urine flow. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride, shrink the prostate over time. Sometimes, a combination of these drugs is prescribed for better results.
- Minimally Invasive Treatments: When medications aren’t effective, minimally invasive procedures might be suggested. These include Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT) and Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA), which use heat to reduce prostate size.
- Surgery: For severe BPH, surgery may be the best option. The most common surgical procedure is Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP). Other surgical options include Prostate Urethral Lift and Prostatectomy, which involve removing or reducing prostate tissue to relieve symptoms.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Research into BPH treatments continues to evolve, offering new hope for those affected. Current developments include:
- Laser Therapy: New laser techniques, such as Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP), provide a less invasive option compared to traditional surgery with potentially fewer side effects.
- Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE): This emerging treatment involves blocking the blood supply to the prostate, causing it to shrink. It’s gaining attention due to its minimally invasive nature and promising results in symptom relief.
- Natural Supplements: Research into herbal treatments and supplements, such as saw palmetto and beta-sitosterol, is ongoing. These natural options might offer symptom relief without the side effects of conventional medications.
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in genetics and personalized medicine are paving the way for more targeted treatments for BPH, focusing on individual patient profiles and genetic predispositions.
However, the range of treatment options for BPH is expanding, with traditional approaches being complemented by new, innovative techniques. It’s essential for patients to discuss with their healthcare providers to choose the best treatment plan tailored to their specific needs and medical history.
Prevention and Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Symptoms
With the right strategies, the symptoms of BPH can be effectively managed or even prevented. Here’s a closer look at how to achieve this.
Tips for Preventing or Managing BPH Symptoms
- Regular Check-Ups: Early detection is key. Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help catch BPH early and manage its symptoms more effectively.
- Hydration Management: While it’s important to stay hydrated, moderating fluid intake, especially before bedtime, can help reduce frequent nighttime urination.
- Bladder Training: Train your bladder by setting fixed times for urination. This can help increase the amount of urine your bladder can hold and decrease the need for frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Avoid Trigger Substances: Caffeine, alcohol, and certain medications can exacerbate BPH symptoms. Limiting these can help manage the condition.
Role of Diet and Exercise in Managing BPH
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve overall health and potentially reduce BPH symptoms.
- Soy and Green Tea: Some studies suggest that soy protein and green tea may help in reducing the risk of BPH.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial as obesity can worsen BPH symptoms.
When to Consider Changes in Treatment Plans
- Symptom Severity: If symptoms worsen or new symptoms appear, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to reassess your treatment plan.
- Medication Side Effects: If current medications are causing significant side effects, a change in medication might be necessary.
- Advancements in Treatments: Stay informed about new treatments or therapies that could offer better management of BPH symptoms.
However, managing BPH involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and staying informed about your health. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a plan that suits your individual needs and to make timely adjustments as required.
Patient Stories and Experiences with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Real-Life Accounts of Managing BPH Symptoms and Treatment Choices
The personal stories and experiences shared by individuals living with BPH provide invaluable insights into the daily challenges, management strategies, and treatment choices for this condition.
Understanding BPH Through Personal Narratives:
- Each story is a unique journey, shedding light on how symptoms like urinary frequency, urgency, and nocturia affect daily life.
- Real-life experiences offer a more personalized understanding of BPH, beyond medical statistics and general information.
Symptom Management Strategies:
- Discover how patients navigate common BPH symptoms.
- Learn about lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and exercise routines, that have proven beneficial.
- Understand the effectiveness of various home remedies and over-the-counter options that patients have tried.
Exploring Treatment Options:
- Personal testimonials provide firsthand insights into the effectiveness and side effects of medications like alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors.
- Stories often include experiences with minimally invasive procedures and surgeries, offering a candid look at post-treatment outcomes and recovery.
- Learn about the decision-making process patients go through when choosing between medication, surgery, and alternative therapies.
Support and Advice:
- These narratives often highlight the importance of support from healthcare professionals, family, and support groups.
- Gain tips and advice from those who have navigated the complexities of BPH treatment and management.
Empowerment Through Sharing:
- Reading and sharing these stories foster a sense of community and understanding among BPH patients.
- They serve as a powerful tool for education and empowerment, helping others feel less alone in their journey.
By presenting these authentic patient stories and experiences, we aim to provide a comprehensive and empathetic understanding of living with and managing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. These narratives are not only informative but also serve as a source of encouragement and hope for those facing similar challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions About Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
1. What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, commonly known as BPH, is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland in men. This condition is common in men over the age of 50 and can lead to uncomfortable urinary symptoms.
2. What causes BPH?
The exact cause of BPH is not fully understood, but it primarily involves changes in hormone levels as men age. Factors like family history, lifestyle, and overall health can also influence the risk and severity of BPH.
3. What are the symptoms of BPH?
Symptoms of BPH vary but often include frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, weak urine stream, and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. In some cases, BPH can lead to more serious issues like urinary tract infections or kidney damage.
4. How is BPH diagnosed?
BPH is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and tests such as a digital rectal exam (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, and urinary flow test. Your doctor may also recommend imaging tests or a cystoscopy.
5. What treatment options are available for BPH?
Treatment for BPH depends on the severity of symptoms and can range from lifestyle changes and medication to minimally invasive therapies and surgery. Common medications include alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors.
6. Can lifestyle changes improve BPH symptoms?
Yes, certain lifestyle changes can help manage BPH symptoms. These include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting caffeine and alcohol, and practicing bladder training techniques.
7. Is BPH related to prostate cancer?
BPH is not prostate cancer, and having BPH does not increase your risk of prostate cancer. However, the symptoms can be similar, so it’s important to get regular check-ups and screenings.
8. When should I see a doctor for BPH symptoms?
If you experience any symptoms of BPH, such as difficulty urinating or changes in urinary habits, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage our readers to seek advice from healthcare professionals if they experience symptoms of BPH. A medical expert can provide a comprehensive evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and a personalized treatment plan. Remember, early consultation can significantly improve the quality of life and manage the symptoms effectively.
Your Health Matters: Don’t hesitate to consult your doctor for a thorough understanding and proper management of BPH. Remember, informed decisions and timely medical intervention are key to maintaining good health.