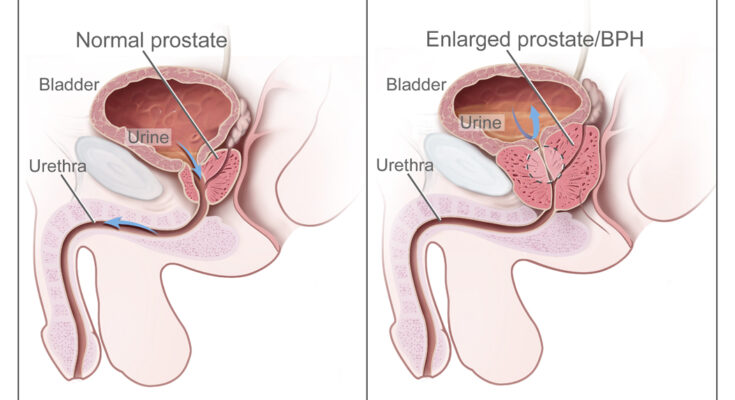
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatment: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, commonly known as BPH, is a condition affecting the prostate gland in men, particularly as they age.
This non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate can lead to uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder.
It’s essential to understand that BPH is a common part of aging for men and not a precursor to prostate cancer.
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as prostate gland enlargement, is a prevalent condition affecting the prostate in men, especially as they age. This condition can lead to uncomfortable urinary symptoms, like blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. BPH can also cause bladder, urinary tract, or kidney problems.
Epidemiology: Prevalence and Risk Factors
BPH is a highly common condition globally, especially in older men. Statistics indicate that:
- Approximately half of men between the ages of 51 and 60 have BPH.
- Up to 90% of men over the age of 80 are affected.
Risk factors for developing BPH include:
- Age: The risk increases significantly as men get older, particularly after age 50.
- Family History: A family history of BPH increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, lack of physical activity, and erectile dysfunction may contribute to the risk.
- Medical Conditions: Diabetes and heart disease have been linked to a higher risk of BPH.
The Role of the Prostate and How BPH Affects It
The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder in men. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows out of the body. The primary function of the prostate is to produce seminal fluid, which is part of semen.
How BPH Affects the Prostate:
- In BPH, the prostate gland enlarges and can squeeze or partly block the urethra.
- This pressure can lead to urinary symptoms such as difficulty starting urination, weak urine stream, frequent urination, or the urgent need to urinate.
- It may also result in incomplete emptying of the bladder, leading to urinary tract infections or bladder stones.
Understanding BPH is crucial for early detection and effective management. If you experience symptoms of BPH, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment options. Remember, a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in preventing or managing BPH.
Symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Recognizing the symptoms of BPH is crucial for early intervention and maintaining a good quality of life.
- Frequent Urination: One of the most noticeable signs of BPH is the need to urinate more often, especially at night.
- Difficulty Starting Urination: Men may experience trouble beginning the urination process.
- Weak Urine Stream: A weakened stream or urine flow is a common symptom.
- Feeling of Incomplete Bladder Emptying: After urinating, there might be a sensation that the bladder isn’t completely empty.
- Urinary Incontinence: This involves involuntary leakage of urine.
How BPH Can Impact Quality of Life
The symptoms of BPH can significantly affect daily life, leading to:
- Sleep Disturbances: Frequent nighttime urination can disrupt sleep patterns.
- Social Embarrassment: Urinary incontinence or frequent trips to the bathroom can cause discomfort in social settings.
- Anxiety and Stress: Concerns about symptoms can lead to increased anxiety.
- Sexual Dysfunction: BPH can sometimes lead to erectile dysfunction or decreased sexual desire.
When to Seek Medical Advice for BPH Symptoms
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if:
- Symptoms Persist or Worsen: Continuous or worsening symptoms need medical attention.
- Painful Urination: This could indicate an infection or other complications.
- Blood in Urine: Visible blood in the urine is a sign to seek immediate medical care.
- Inability to Urinate: This is a medical emergency and requires prompt attention.
Early detection and treatment of BPH can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Regular check-ups and being aware of the changes in your body play a vital role in staying healthy.
Diagnosis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Understanding and diagnosing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is crucial for effective management and treatment. BPH, a common condition affecting the prostate gland in men, particularly as they age, can lead to uncomfortable urinary symptoms. An accurate diagnosis is key to ensuring the right treatment approach.
Initial Assessment: History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing BPH involves a comprehensive history and physical examination. This process includes:
- Medical History: Understanding the patient’s overall health, symptoms, and any previous medical or surgical treatments.
- Family History: Evaluating if there’s a history of BPH or related conditions in the family.
- Symptom Assessment: Discussing urinary symptoms such as frequency, urgency, hesitancy, and nocturia.
- Physical Examination: A focused examination, particularly a digital rectal exam (DRE), to assess the size and texture of the prostate.
Diagnostic Tests
After the initial assessment, several diagnostic tests may be recommended:
- Urinalysis: This test checks for blood, infection, or other abnormalities in the urine.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Elevated levels of PSA can suggest BPH or other prostate issues, including prostate cancer.
- Uroflowmetry: Measures the speed and volume of urine flow.
- Postvoid Residual Volume Test: Assesses if the bladder is emptying completely.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
In some cases, more advanced diagnostic techniques are necessary:
- Ultrasound: Provides imaging of the prostate, which can help in assessing its size and ruling out other conditions.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Offers detailed images of the prostate and surrounding tissues, useful in complex cases.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure where a camera is inserted into the urethra to visually inspect the bladder and prostate.
Early and accurate diagnosis of BPH is essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. If you’re experiencing urinary symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for an appropriate evaluation.
Treatment Options for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The primary goals in treating BPH are to alleviate symptoms, improve urinary flow, and prevent complications. Treatment plans are tailored to individual needs, taking into account the severity of symptoms, overall health, and personal preferences.
Non-Surgical Treatments for BPH
- Medications: A cornerstone in BPH management, medications like alpha-blockers (e.g., Tamsulosin) and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors (e.g., Finasteride) are often prescribed. These drugs help relax bladder neck muscles and shrink the prostate, respectively, improving urinary flow.
- Lifestyle Changes: Simple modifications can have a significant impact. These include reducing fluid intake before bedtime, limiting caffeine and alcohol, and practicing bladder training exercises.
- Minimally Invasive Therapies: Techniques such as transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) or transurethral needle ablation (TUNA) offer alternatives to traditional surgery and are less invasive.
Surgical Treatments for BPH
Surgical intervention may be considered when symptoms are severe or if there is a risk of complications. The types of surgeries include:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): A common and effective surgery where excess prostate tissue is removed.
- Laser Therapy: Utilizes laser energy to remove or shrink prostate tissue.
- Open or Robot-assisted Prostatectomy: Involves the surgical removal of the prostate gland, typically in very large prostates or when other methods are not feasible.
Surgical treatments are generally safe but, like any surgical procedure, come with risks and potential side effects. It’s important to discuss with your healthcare provider what to expect before, during, and after surgery.
Managing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Lifestyle and Home Remedies
While medical treatments are available, lifestyle adjustments and home remedies can play a vital role in managing BPH symptoms. This article explores effective dietary modifications, exercise routines, and other home remedies that can offer relief and improve the quality of life for individuals with BPH.
Dietary Modifications and Their Impact on BPH
A balanced diet is crucial in managing BPH symptoms. Certain foods and nutrients have been found to support prostate health:
- Increase Fruits and Vegetables: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help reduce inflammation and promote urinary health.
- Limit Red Meat and Dairy: Studies suggest that high consumption of red meat and dairy products may worsen BPH symptoms.
- Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish like salmon and mackerel, omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation associated with BPH.
- Soy Products: Soy contains phytoestrogens which may help in reducing BPH progression.
- Stay Hydrated, But Not Too Late in the Day: Drinking plenty of water is essential, but limiting fluid intake in the evening can reduce nocturia (frequent urination at night).
Exercise and Its Role in Managing BPH Symptoms
Regular physical activity is beneficial for overall health and can particularly aid in managing BPH symptoms:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can improve urinary symptoms.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can help in managing urinary incontinence related to BPH.
- Yoga and Stretching: These can reduce stress and may have a positive impact on BPH symptoms.
Other Home Remedies and Practices for Symptom Relief
Alongside diet and exercise, other home remedies can be effective in alleviating BPH symptoms:
- Warm Baths: Soaking in a warm bath can help relieve discomfort associated with BPH.
- Herbal Supplements: Some herbs like saw palmetto, pygeum, and stinging nettle might offer symptom relief, though it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress, which may exacerbate BPH symptoms.
- Regular Urination: Making a habit of urinating regularly can help relieve bladder pressure and discomfort.
However, while BPH is a common condition, implementing lifestyle changes and home remedies can significantly ease symptoms and improve quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or supplement regimen.
Complications of Untreated Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Understanding these complications is crucial for men who are managing this condition.
Acute Urinary Retention
One of the most immediate and distressing complications of untreated BPH is acute urinary retention. This occurs when the enlarged prostate gland obstructs the urethra, preventing urine from flowing out of the bladder. Symptoms can include severe discomfort, an urgent need to urinate but inability to do so, and lower abdominal pain. Immediate medical attention is required to relieve this condition, often involving the temporary use of a catheter to drain the bladder.
Urinary Tract Infections and Other Complications
The incomplete emptying of the bladder, a common issue in BPH, sets the stage for urinary tract infections (UTIs). Recurrent UTIs can be a persistent problem and may lead to more severe complications, such as bladder or kidney infections. In addition to UTIs, chronic bladder outlet obstruction can cause bladder stones, blood in the urine, and reduced bladder capacity, all of which significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Long-Term Impact on Kidney Function
Perhaps the most serious complication of long-standing untreated BPH is its impact on kidney function. The constant pressure from a full bladder can back up into the kidneys, potentially leading to hydronephrosis (swelling of a kidney due to urine buildup) and, over time, chronic kidney disease. Protecting kidney function is a key reason why early diagnosis and management of BPH are so important.
Latest Advances in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatment
Recent Developments in BPH Treatment
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as an enlarged prostate, affects a significant portion of the male population, especially those over the age of 50. The latest advances in BPH treatment reflect a growing understanding of the condition and focus on both efficacy and minimizing side effects.
One notable advancement is the refinement of minimally invasive surgical techniques. Procedures like Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) have evolved, offering fewer complications and shorter recovery times. Similarly, laser therapies, such as Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP), have shown promise due to their precision and reduced risk of bleeding.
Pharmaceutical developments have also been significant. The introduction of new medications that target the prostate more effectively with fewer sexual side effects is a key focus. Combination therapy, using drugs like alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors together, has been found to be more effective than using either alone.
Emerging Therapies and Future Directions in BPH Management
Looking to the future, several exciting therapies are emerging. One area of research is focused on new drug classes that target prostate growth at the molecular level, potentially offering more effective management with minimal side effects.
Another promising direction is the use of personalized medicine. Advances in genetic profiling may allow for tailored treatment plans based on an individual’s specific genetic makeup, enhancing the effectiveness and reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
Additionally, the integration of technology in BPH management is noteworthy. Developments in telemedicine and digital health tools offer the potential for better monitoring and management of BPH symptoms, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
However, the landscape of BPH treatment is rapidly evolving with a focus on more effective, less invasive, and personalized approaches. These advancements offer hope for improved quality of life for millions of men affected by this common condition.
Patient Perspectives and Quality of Life in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Exploring patient experiences with the diagnosis and treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is crucial. This section delves into personal accounts, highlighting the emotional and physical journeys patients undergo. We’ll examine the initial reactions to diagnosis, the complexities of choosing suitable treatments, and the coping mechanisms patients adopt. Emphasizing empathetic understanding, this part aims to provide a comprehensive view of the patient experience in dealing with BPH.
Assessing the Impact of BPH and Its Treatment on Quality of Life
The impact of BPH and its treatments on a patient’s quality of life is a significant concern. This portion of the content focuses on how BPH affects daily activities, mental health, and overall well-being. We’ll explore the side effects of common treatments and how they influence a patient’s life, discussing both the physical and psychological ramifications. This segment aims to offer a thorough understanding of the broader implications of living with and managing BPH.
Support and Resources for Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Access to support and resources is vital for patients dealing with BPH. This section provides valuable information on the various forms of support available, including medical, emotional, and community-based resources. We’ll highlight support groups, online forums, and healthcare services dedicated to BPH, ensuring patients have the knowledge to navigate their condition effectively. This part is designed to empower patients with BPH, providing them with the tools and resources necessary for managing their condition effectively.
Conclusion:
As we conclude, it’s important to emphasize the role of proactive health management in living with BPH. Regular check-ups and staying informed about the latest treatments and lifestyle recommendations can make a significant difference in quality of life.
Remember, BPH, while common, doesn’t have to dictate your life. With the right approach, which includes understanding your condition, working closely with your healthcare provider, and making informed decisions about treatment and lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage BPH.
We encourage you to embrace this journey with optimism and determination. BPH is a manageable condition, and with the right tools and support, you can continue to lead a healthy and fulfilling life. Stay proactive, stay informed, and most importantly, stay positive in your approach to managing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.