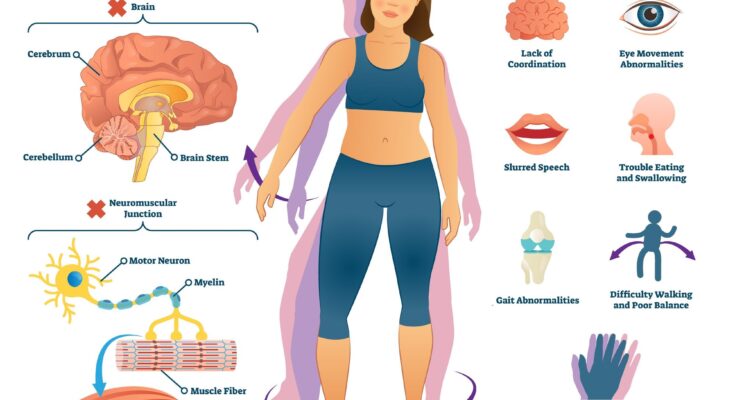
Ataxia Treatment: Ataxia, a neurological disorder characterized by a lack of muscle coordination, affects numerous individuals worldwide. This condition can impact various movements, making daily tasks challenging.
Understanding ataxia’s nuances, from diagnosis to treatment, is crucial for those affected and their caregivers.
Understanding Ataxia
Ataxia, a neurological disorder affecting coordination, is often misunderstood. This condition, characterized by a lack of muscle control, impacts various daily activities. Our objective is to demystify ataxia by exploring its definition, types, and symptoms, providing insights into how it affects daily life.
What is Ataxia?
Ataxia refers to a group of disorders that impair coordination, balance, and speech. It’s caused by damage to the cerebellum, the part of the brain that controls muscle coordination. Though its manifestations vary, ataxia commonly results in unsteady movements and difficulty with fine motor tasks.
Types of Ataxia
Ataxia is categorized into several types, each with distinct characteristics:
- Hereditary Ataxia: This type is genetic, with symptoms often appearing in childhood or early adulthood.
- Acquired Ataxia: Caused by external factors like injury or infection, this type can occur at any age.
- Idiopathic Ataxia: When the cause remains unknown, it’s termed idiopathic.
Understanding these types helps in pinpointing the specific nature of the condition.
Symptoms and Daily Life Impact
Common symptoms of ataxia include:
- Uncoordinated Movements: Difficulty in tasks like writing or buttoning a shirt.
- Gait Disturbance: Challenges in walking straight, leading to frequent stumbling.
- Speech Challenges: Slurred speech, making communication harder.
These symptoms profoundly impact daily life, affecting independence and quality of life. Simple tasks become challenging, necessitating adaptations and sometimes assistance.
However, understanding ataxia is crucial for those affected and their loved ones. Recognizing its types and symptoms aids in better management and adaptation to the challenges it poses in daily life.
Causes of Ataxia
Let’s delves into the common and less common factors leading to ataxia, offering insights for those seeking to understand this condition.
Genetic Factors
- Hereditary Ataxias: These are caused by inherited genetic mutations. Examples include Friedreich’s ataxia and Spinocerebellar ataxia.
- Defective Gene Mutations: Some types of ataxia result from spontaneous mutations in genes responsible for brain function and development.
Acquired Causes
- Alcohol Abuse: Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to brain damage, resulting in ataxia.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies, particularly in Vitamin E and B12, can impair neurological functions.
- Infections: Certain viral or bacterial infections can temporarily or permanently affect the brain and nervous system.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like Multiple Sclerosis (MS) can damage the nervous system, causing ataxia.
- Stroke or Brain Injury: Events leading to brain injury, such as a stroke, can disrupt motor coordination.
- Exposure to Toxins: Heavy metals and certain chemicals can harm the nervous system.
Medical Conditions
- Tumors: Brain tumors, whether benign or malignant, can press against or damage parts of the brain, leading to ataxia.
- Cerebral Palsy: This condition, often arising from early brain damage, can manifest with ataxic symptoms.
- Hypothyroidism: Thyroid function disorders can indirectly contribute to ataxic symptoms.
Rare Causes
- Paraneoplastic Syndromes: These are rare disorders triggered by an immune response to cancer elsewhere in the body.
- Mitochondrial Disorders: Dysfunctions in mitochondria, the energy-producing structures in cells, can affect brain function.
Understanding the causes of ataxia is crucial for diagnosis and management. Each cause requires a unique approach, ranging from genetic counseling and lifestyle changes to medical interventions. By identifying the root cause, individuals can seek targeted treatments and support for better management of ataxia symptoms.
Diagnosing Ataxia: A Comprehensive Guide
Recognizing the significance of an early and accurate diagnosis is crucial in managing Ataxia effectively. Prompt diagnosis not only helps in initiating appropriate treatment plans but also in understanding the progression of the condition, which can be vital for patient care and quality of life.
Steps Involved in Diagnosing Ataxia
- Initial Assessment: The diagnostic process often begins with a thorough medical history and a physical examination. Neurologists will assess symptoms such as unsteady gait, slurred speech, and loss of coordination.
- Neurological Evaluation: This involves a series of tests to evaluate reflexes, muscle strength, balance, coordination, and sensory functions.
- Family History Analysis: Since some forms of Ataxia are hereditary, understanding family medical history can provide valuable insights.
Different Diagnostic Tools and Tests
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI scan is instrumental in examining brain and spinal cord anomalies. It helps in identifying structural changes or abnormalities that may be causing Ataxia.
- Genetic Testing: Particularly crucial for hereditary Ataxias, genetic tests can confirm a suspected diagnosis by identifying specific genetic mutations.
- Blood Tests: These can help rule out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms, such as vitamin deficiencies or thyroid issues.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests assess the electrical activity of muscles and the nerves that control them.
- Additional Tests: Depending on symptoms and initial test results, other assessments like lumbar punctures, toxicology screening, or specialized imaging tests might be required.
Diagnosing Ataxia involves a multifaceted approach, integrating patient history, physical examinations, and a variety of diagnostic tools. The goal is to identify the type and cause of Ataxia accurately, enabling effective management and treatment strategies. Early diagnosis plays a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with Ataxia, highlighting the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms arise.
Treatment Options for Ataxia: A Comprehensive Guide
Ataxia treatment primarily focuses on alleviating symptoms and improving functional abilities. The approach varies depending on the type and cause of ataxia. A personalized treatment plan is often developed to address the unique needs of each individual.
Medications: Managing Symptoms Effectively
Medications play a crucial role in the management of ataxia symptoms. These can include:
- Anticonvulsants: To control muscle spasms and reduce pain.
- Muscle Relaxants: To ease muscle stiffness and improve mobility.
- Medications for Treating Underlying Causes: In cases where ataxia is a symptom of another condition, treating that condition can reduce ataxia symptoms.
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for the right medication and dosage, as each individual’s response to medication can vary.
Physical Therapy: A Cornerstone of Ataxia Treatment
Physical therapy is an integral part of managing ataxia. It involves:
- Tailored Exercises: To improve coordination and balance.
- Strength Training: To enhance muscle strength and prevent atrophy.
- Gait Training: To improve walking ability and reduce the risk of falls.
Physical therapists work closely with patients to develop a regimen that caters to their specific needs and challenges.
Rehabilitation Exercises: Enhancing Mobility and Independence
Rehabilitation exercises are key in helping individuals with ataxia maintain and regain independence. These exercises focus on:
- Balance and Coordination Training: To enhance stability in daily activities.
- Fine Motor Skills Workouts: To improve hand-eye coordination and dexterity.
- Speech Therapy: To address speech difficulties that often accompany ataxia.
While there is no one-size-fits-all solution for ataxia, the combination of medications, physical therapy, and rehabilitation exercises offers a comprehensive approach to managing the condition. Regular consultations with healthcare providers and a commitment to a tailored treatment plan can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with ataxia.
Advanced Treatment Approaches for Ataxia
Let’s delves into the latest developments in ataxia treatment, highlighting emerging treatments, the role of surgery, and future prospects in managing this complex condition.
Emerging Treatments and Research in Ataxia
Recent years have witnessed groundbreaking research leading to novel treatments for ataxia. These advancements primarily focus on targeting the underlying causes of the disorder, rather than merely addressing the symptoms. For instance, gene therapy has shown promise in treating hereditary ataxias by correcting genetic mutations. Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate the efficacy and safety of these innovative approaches.
Another exciting development is the use of neuroprotective drugs. These medications aim to protect nerve cells from damage, thereby slowing the progression of ataxia. Researchers are also exploring the potential of stem cell therapy to regenerate damaged nerve tissues, offering a new ray of hope for patients.
The Role of Surgery in Treating Certain Types of Ataxia
In some cases, surgery plays a crucial role in the management of ataxia. For instance, patients with cerebellar ataxia caused by structural abnormalities in the brain may benefit from neurosurgical interventions. These procedures can alleviate symptoms by correcting the underlying structural issues.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS), a surgical procedure involving the implantation of a device that sends electrical impulses to specific parts of the brain, has also been explored for certain types of ataxia. While still in the experimental stage, early results suggest that DBS may help improve motor functions in some patients.
Future Prospects in Ataxia Treatment
Looking ahead, the future of ataxia treatment appears promising. Advances in genetic research are expected to pave the way for more personalized treatment approaches. For example, therapies tailored to individual genetic profiles could significantly improve outcomes for patients with hereditary ataxias.
Moreover, the integration of technology in treatment, such as advanced neuroimaging techniques and AI-powered diagnostic tools, is set to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of ataxia management. These technologies will not only aid in early diagnosis but also in monitoring the progression of the disease and the response to treatments.
However, the landscape of ataxia treatment is evolving rapidly, with research and technology playing pivotal roles. While challenges remain, the ongoing developments offer hope for improved quality of life and better management of this complex disorder. As we continue to explore these advanced treatment approaches, the future for ataxia patients looks increasingly bright.
Living with Ataxia: Navigating Life with a Neurological Disorder
To manage these challenges effectively, adopting certain lifestyle changes and home care tips is crucial.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Care Tips
- Home Safety Modifications: To reduce the risk of falls and injuries, it’s important to make your living space safer. This includes installing grab bars in bathrooms, ensuring good lighting, and removing tripping hazards.
- Assistive Devices: Utilize tools like walking aids, wheelchairs, or specialized utensils designed for easier handling. These devices can significantly improve independence and safety.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physiotherapy or exercises tailored to your abilities can enhance muscle strength and coordination.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet is vital. Some individuals with ataxia may require special dietary considerations to manage symptoms.
- Speech Therapy: For those experiencing speech difficulties, speech therapy can be beneficial.
Support Systems and Resources
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who are facing similar challenges can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Professional Counseling: Mental health professionals can offer strategies to cope with the emotional aspects of living with ataxia.
- Educational Resources: Understanding your condition is key. Seek out reliable information from healthcare providers or ataxia-related organizations.
Coping Strategies and Mental Health Considerations
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or mindfulness can be effective in managing stress and improving mental well-being.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Focus on what you can achieve and set achievable goals to maintain a sense of accomplishment and purpose.
- Seeking Help When Needed: Don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals or loved ones when you need support.
- Positive Outlook: Maintaining a positive attitude, while acknowledging the challenges, can significantly impact your quality of life.
However, living with ataxia requires adjustments and support, but with the right strategies and resources, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. By focusing on safety, seeking support, and employing coping strategies, one can navigate the challenges of ataxia with resilience and positivity.
Conclusion:
Navigating ataxia’s challenges requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing accurate diagnosis, tailored treatments, and robust support systems. Advancements in research offer hope for more effective therapies, underscoring the importance of ongoing efforts in this field.