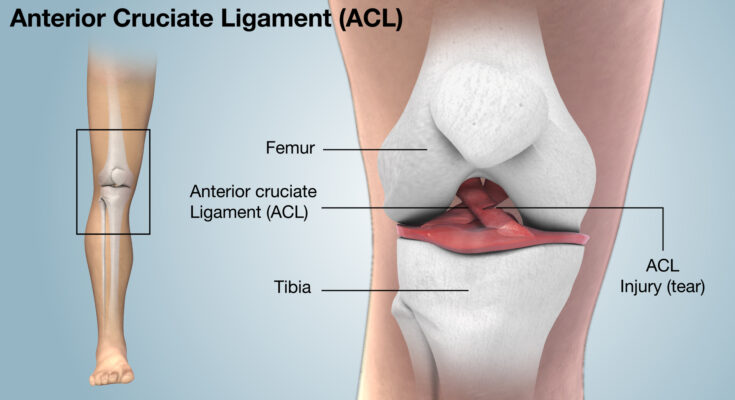
ACL Injury Treatment: The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is a pivotal component of the knee joint, responsible for maintaining stability and facilitating range of movement.
Injuries to the ACL are common among athletes and can be severe, impacting mobility and overall quality of life.
In this article, we delve deep into the diagnosis and treatment of ACL injuries, arming you with the knowledge to navigate this challenging health issue.
What Causes an ACL Injury?
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the key ligaments in the knee, and its injury is unfortunately common, especially among athletes. Understanding the primary causes of an ACL injury can be helpful in its prevention and early diagnosis.
Mechanism of Injury: How ACL Injuries Typically Occur
The ACL is designed to stabilize the knee joint, preventing it from moving too far forward or twisting excessively. An injury to the ACL usually happens when there’s a sudden change in direction or a rapid deceleration. When the knee is subjected to these unexpected movements, the ligament can stretch beyond its limit and tear.
Common Scenarios Leading to ACL Tears
1. Sports Injuries: Athletes participating in sports like soccer, basketball, skiing, and football are at a higher risk. The rapid pivoting, sudden stops, and direct collisions associated with these sports can lead to ACL tears.
2. Accidents: A fall from a height or a misstep, especially when the foot is firmly planted and the knee twists, can cause an ACL injury.
3. Overextension: Overextending the knee joint or landing incorrectly from a jump can exert undue pressure on the ACL, leading to a tear.
By recognizing the causes and mechanisms leading to ACL injuries, individuals can take preventative steps in their daily activities and sports endeavors. Proper training and awareness can significantly reduce the risk of this debilitating injury.
Symptoms of an ACL Injury
An ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) injury can be debilitating and recognizing its symptoms is crucial for timely intervention. Here’s a breakdown of its tell-tale signs:
1. Immediate Signs:
1. Pain: Shortly after the injury, one of the first symptoms you might experience is sharp, intense pain in the knee area.
2. Swelling: The affected knee may swell rapidly, often within a few hours, making it appear larger than the other knee.
3. Inability to Bear Weight: Standing or walking on the injured leg can become exceedingly difficult or painful. You might find it challenging to put weight on that knee without experiencing discomfort.
2. Long-term Symptoms:
1. Knee Instability: Even after the initial pain and swelling subside, you might feel that your knee isn’t as stable as it should be. This sensation can best be described as the knee feeling loose or wobbly, especially during physical activities.
2. Recurrent Giving Way: Over time, if the injury isn’t properly addressed, you might notice that your knee unexpectedly gives out during certain movements or activities.
If you suspect an ACL injury based on these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a medical professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve recovery outcomes. Remember, maintaining the health of your joints ensures a better quality of life.
How is an ACL Injury Diagnosed?
Upon presenting with potential ACL injury symptoms, the following diagnostic measures may be undertaken:
1. Physical Examination:
- Lachman’s Test: This is a pivotal test for diagnosing an ACL injury. The doctor assesses the forward motion of the tibia compared to the femur. Excessive movement often indicates a compromised ACL.
- Anterior Drawer Test: In this test, the patient lies flat with bent knees, and the doctor checks for anterior movement of the tibia against the femur. Similar to the Lachman’s test, excessive movement may suggest an ACL tear.
2. Imaging Tests:
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Recognized as the gold standard in imaging tests for ACL injuries, an MRI provides a clear, detailed view of the knee. It helps in identifying not just ACL tears but also any associated damage to other knee structures.
3. Importance of Early and Accurate Diagnosis:
An early diagnosis can significantly aid in planning an effective treatment strategy, potentially reducing the risk of long-term knee problems. An accurate diagnosis ensures that the treatment is targeted to the specific injury, leading to quicker recovery and minimizing the chances of future complications.
When experiencing knee pain or after a knee injury, always consult with a healthcare professional to get an accurate diagnosis and prevent further damage.
ACL Injury Treatment Options
Depending on the severity and the individual’s requirements, treatment can range from non-surgical methods to surgical interventions. Let’s delve into the available options for ACL injury treatments.
Non-Surgical Treatment
When the ACL injury is less severe, or if the individual’s activity level does not warrant surgery, non-surgical treatments can be highly effective. These are often the first line of action immediately after an injury.
Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE):
- Rest: It’s crucial to allow the knee joint to heal, especially in the initial days after the injury. This means limiting movement and weight-bearing activities.
- Ice: Applying cold packs can reduce swelling and pain. It’s generally recommended to ice the affected area for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours during the first 48 hours post-injury.
- Compression: Elastic compression wraps can help control swelling and provide support to the injured knee.
- Elevation: Keeping the leg elevated above heart level, when possible, further helps in reducing swelling.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Exercises: Regular sessions with a physical therapist can help restore the knee’s range of motion and strengthen the surrounding muscles. Tailored exercises aim at improving stability and preventing further injuries.
Knee Braces and Supports: These devices provide additional support to the knee, limiting unwanted movement and providing a sense of security during the healing process.
Surgical Treatment
For more severe ACL tears, or for those who wish to return to high-impact sports, surgical treatment may be recommended.
Indications for Surgery: Typically, surgery is advised for:
- Complete ACL tears with instability.
- Injuries that involve multiple ligaments.
- Active individuals who want to return to sports or high-demand activities.
Types of ACL Reconstruction Surgery: There are primarily two methods used in ACL reconstruction, based on the source of the graft:
- Autograft: Uses tissue from the patient’s own body, typically from the patellar tendon or the hamstring.
- Allograft: Uses donor tissue, usually from a cadaver. This method might be chosen to reduce surgery time or if there’s a concern about the quality of the patient’s own tendons.
Post-surgical Rehabilitation and Recovery Timeline: Recovery from ACL surgery is a phased process:
- Initial Phase (0-4 weeks): Focuses on reducing swelling, restoring joint motion, and weight-bearing with the aid of crutches.
- Intermediate Phase (4-12 weeks): Strength training and functional exercises are introduced.
- Advanced Phase (3-6 months): Agility and sport-specific training begin.
- Return to Activity (6-9 months): Depending on progress, individuals may start resuming their regular activities, with the full clearance usually given after 9 months.
It’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to ensure the best outcome for any ACL injury. Proper treatment can ensure a swift and efficient return to regular activities and sports.
Recovery and Rehabilitation of ACL Injury
The journey towards recovering from an ACL injury is one that requires patience, dedication, and a commitment to a systematic approach. Understanding the process can be key to achieving the best possible outcomes. Here, we delve into the crucial aspects of recovery, the importance of physical therapy, expected timelines, and measures to ensure you don’t face re-injury.
1. Importance of Adherence to Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a cornerstone in ACL injury recovery. Here’s why sticking to your therapy routine is paramount:
- Structured Recovery: Qualified physical therapists provide exercises specifically tailored to your injury and progress. These exercises strengthen your knee, improve flexibility, and facilitate optimal recovery.
- Reduced Complications: Regular and appropriate physical therapy can prevent complications such as stiffness, loss of range of motion, and muscle atrophy.
- Improved Outcomes: Patients who adhere to their physical therapy regimen often experience faster recovery times and better long-term knee function.
2. Expected Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline for an ACL injury can vary based on the severity of the injury, the method of treatment, and individual factors. However, a general guideline is as follows:
- Immediate Post-Op to 2 Weeks: Focus on reducing swelling and pain. Light movements and partial weight-bearing with crutches may be introduced.
- 2-6 Weeks: Gradual increase in range of motion. Beginning of strength training exercises. Full weight-bearing typically starts.
- 3-4 Months: Most patients can return to daily activities, albeit with care. More intense physiotherapy to regain full knee function.
- 6 Months: Potential return to non-contact sports, depending on progress.
- 9-12 Months: If recovery has been optimal, return to high-impact sports is possible. It’s important to note that the timeline might differ based on individual factors and the advice of healthcare professionals should always be prioritized.
3. Measures to Prevent Re-Injury
Preventing re-injury is crucial for those who’ve experienced an ACL injury. Here are some steps to incorporate:
- Continue Physiotherapy: Even after returning to daily activities or sports, regular exercises can keep your knee strong and flexible.
- Wear Protective Gear: Using a knee brace, especially during sports, can offer additional support.
- Stay Informed: Understand the mechanics of your sport or activity to reduce risk. For instance, learning the right way to pivot or jump can be essential.
- Regular Check-ups: Frequent visits to your orthopedic specialist can help detect potential issues before they become significant problems.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Less strain on the knee reduces the risk of re-injury.
However, ACL injury recovery is a journey that requires a holistic approach. By understanding the process, adhering to physical therapy, and taking preventive measures, you can enhance your recovery and return to an active, fulfilling life. Remember, while the above guidelines offer a general overview, individual experiences may vary, and the advice of healthcare professionals should always be heeded.
Preventing ACL Injuries
Preventing these injuries can help avoid long-term complications, surgeries, and significant downtime. Below are some methods to consider:
Training Modifications:
1. Plyometrics: Incorporate plyometric exercises to improve muscle power and agility. This not only enhances performance but also trains muscles to respond rapidly and effectively during high-intensity activities.
2. Strength Training: Strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings, provides better support and reduces the risk of ACL strain. Follow a well-rounded strength training routine that focuses on both the front and back of the leg.
Proper Footwear and Playing Surfaces:
1. Footwear: Invest in high-quality athletic shoes that offer good support and fit your foot type. Shoes should provide stability and grip, reducing the risk of twisting or turning the knee in an unnatural way.
2. Playing Surfaces: Ensure that the surfaces you’re playing or training on are well-maintained. Avoid uneven terrains or slippery surfaces, which can increase the chances of sustaining an ACL injury.
Role of Knee Braces and Prophylactic Measures:
1. Knee Braces: Using knee braces, especially during high-risk activities, can provide added support and stability to the knee joint. They may help in reducing the risk of ACL injuries, especially for individuals who have had prior injuries.
2. Prophylactic Measures: Regularly warming up before any physical activity and incorporating flexibility exercises into your routine can make a significant difference. These measures increase blood flow, prepare muscles for action, and enhance joint flexibility, all of which can contribute to injury prevention.
Incorporating these strategies can go a long way in keeping your knees healthy and injury-free. Always consult with a professional or trainer to ensure you’re taking the right precautions for your individual needs.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, understanding the importance of early diagnosis and the right treatment for ACL injuries cannot be overstressed. Early intervention not only ensures a quicker recovery but also significantly reduces the risk of potential complications. Remember, your knees play a pivotal role in your mobility, and overlooking an injury can have long-term repercussions on your overall health.
If you suspect you’ve suffered an ACL injury or have any knee-related concerns, it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly. Your health and well-being are invaluable; always prioritize them by consulting a healthcare professional when in doubt. Taking timely action can make all the difference in your recovery journey. Stay safe and take care of those knees!