Bursitis Symptoms: Bursitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, joints, and muscles.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of bursitis is crucial for early detection and effective management.
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is a condition that occurs when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints, become inflamed. These sacs play a crucial role in reducing friction between tissue components during movement. When bursae become inflamed, it results in a condition known as bursitis, characterized by pain, swelling, and limited movement in the affected joint.
Different Types of Bursitis
Bursitis can occur in various parts of the body, with the most common types being:
- Shoulder Bursitis: Involves the shoulder joint and can significantly affect arm movement.
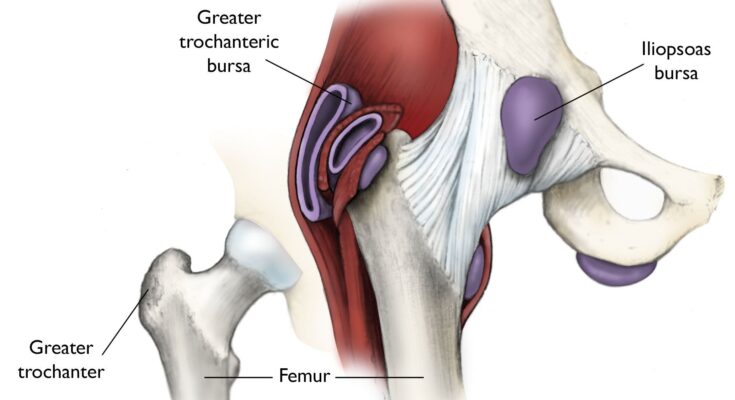
- Hip Bursitis: Typically affects the outer hip, causing pain and discomfort during movement.
- Elbow Bursitis: Often linked to repetitive motion and can affect individuals who lean on their elbows frequently.
- Knee Bursitis: Usually found around the knee joint, particularly in individuals who kneel for extended periods.
- Heel Bursitis: Affects the heel area and can be exacerbated by certain types of footwear or physical activities.
Prevalence and Demographic Most Affected
Bursitis is a common condition, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. It is more prevalent in adults over 40, particularly those who engage in repetitive activities or occupations that put stress on the joints. Additionally, certain sports and physical activities can increase the risk of developing bursitis. Regular movement, proper technique in physical activities, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of bursitis.
This condition highlights the importance of joint health and the need for proper ergonomic practices in both work and leisure activities. By understanding the types of bursitis and recognizing its symptoms, individuals can seek early treatment and prevent further joint damage.
Bursitis Symptoms
Here, we provide a detailed list of common bursitis symptoms, explain how these symptoms manifest differently depending on their location, and emphasize the importance of early recognition.
Common Symptoms of Bursitis
- Pain: The most noticeable symptom, often described as a sharp and intense pain initially, which may become more achy and spread out over time.
- Swelling: Visible swelling or puffiness in the affected area is a common sign.
- Redness and Warmth: The affected area may appear red and feel warm to the touch, indicating inflammation.
- Stiffness or Aching: Movement of the affected joint might be accompanied by stiffness or a constant dull ache.
- Limited Range of Motion: Swelling and pain can restrict the movement of the affected joint.
How Bursitis Symptoms Vary by Location
Bursitis can occur in any bursa in the body but is most common in the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. The manifestation of symptoms varies based on the location:
- Shoulder Bursitis: Difficulty in moving the shoulder, especially lifting the arm overhead.
- Elbow Bursitis: Swelling at the tip of the elbow, with pain worsening when bending or using the arm.
- Hip Bursitis: Pain on the outer thigh or hip, aggravated by prolonged walking or climbing stairs.
- Knee Bursitis: Swelling over the knee, difficulty in kneeling, and pain when moving the knee.
The Importance of Early Recognition
Early identification and treatment of bursitis symptoms can prevent the condition from worsening, potentially leading to joint damage or infection. Ignoring these symptoms may result in chronic pain and significantly restricted mobility. If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or redness around a joint, or if the affected area becomes feverish, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
By understanding these symptoms and their variations, individuals can seek timely medical attention, helping to ensure better outcomes and a faster return to normal activities. Remember, early intervention is key to effectively managing bursitis and maintaining joint health.
Causes of Bursitis: Understanding the Underlying Factors
This comprehensive guide delves into the primary causes of bursitis, shedding light on how these elements contribute to the development of its symptoms.
1. Repetitive Movements or Pressure
One of the most common causes of bursitis is repetitive movement or prolonged and excessive pressure on the joints. Activities such as gardening, painting, playing musical instruments, or sports like tennis and golf often involve repetitive motion, which can lead to irritation and inflammation of the bursae. Professions requiring repetitive movements, like carpentry or tile setting, also increase the risk of developing bursitis.
2. Traumatic Injury
Bursitis can also stem from a traumatic injury. Impacts sustained during sports, falls, or accidents can cause acute inflammation of the bursae. These injuries may lead to immediate bursitis or contribute to its development over time, especially if the injury leads to joint misalignment or chronic inflammation.
3. Age-Related Factors
As we age, our tendons become less elastic and more susceptible to injury. This increased vulnerability can result in a higher likelihood of developing bursitis. Older adults often experience bursitis due to the degeneration of tissues around the joints, making them more prone to inflammation from minor stresses and strains.
4. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Other Systemic Conditions
Systemic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes, can lead to the development of bursitis. These conditions cause systemic inflammation and can specifically target the bursae, resulting in bursitis. For instance, rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder, can cause the body’s immune system to attack the bursae, leading to inflammation and pain.
How These Causes Contribute to Bursitis Symptoms
Each of these causes can contribute to the classic symptoms of bursitis, including pain, swelling, and reduced movement in the affected joint. Repetitive movements or pressure can cause continuous irritation, leading to chronic bursitis. Traumatic injuries can result in immediate inflammation and acute bursitis. Age-related factors and systemic conditions often lead to a gradual onset of symptoms, as the body’s natural defenses weaken or as chronic conditions exacerbate the inflammation of the bursae.
Understanding the specific cause of bursitis is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. For instance, if repetitive motion is the cause, modifying the activity or incorporating rest periods can help. Similarly, managing systemic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can also reduce the risk or severity of bursitis. It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
However, bursitis can be triggered by a variety of factors, including repetitive movements, traumatic injuries, age-related changes, and underlying systemic conditions. Recognizing these causes is the first step in addressing the condition and alleviating its symptoms. With appropriate care and prevention strategies, individuals can effectively manage bursitis and maintain joint health.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Bursitis
Bursitis, a condition characterized by the inflammation of the bursae, can be influenced by a variety of risk factors. Identifying and understanding these factors is crucial in preventing the onset of bursitis. Here are some key risk factors:
1. Repetitive Motion or Pressure
Engaging in repetitive tasks or activities that exert consistent pressure on the bursae, particularly around joints, significantly increases the risk of developing bursitis. This is commonly seen in athletes, musicians, and individuals with certain occupations.
2. Age
As we age, our tendons become less elastic and more susceptible to injury. This factor makes older adults more prone to developing bursitis.
3. Certain Occupations and Hobbies
Occupations that require repetitive motion or pressure on specific joints (like carpentry, gardening, painting, or playing certain musical instruments) can elevate the risk.
4. Previous Injuries or Surgery
Previous injuries or surgeries around a joint can lead to the development of bursitis in the affected area.
5. Health Conditions
Certain systemic diseases and conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or diabetes, can increase the likelihood of bursitis.
Strategies for Prevention
Preventing bursitis largely involves strategies aimed at reducing the strain on your joints and bursae. Here are some effective tips:
1. Modify Activities
Alter your daily activities to avoid repetitive motions or prolonged pressure on the bursae. Taking frequent breaks during activities that cannot be avoided is also beneficial.
2. Exercise Regularly
Engaging in regular exercise helps maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength, which can reduce the risk of bursitis. Focus on exercises that strengthen the muscles around your joints.
3. Use Proper Techniques and Tools
Incorporating ergonomic tools and learning proper techniques for physical activities can greatly reduce joint stress.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight can increase the pressure on your joints, particularly the hips, knees, and ankles, leading to bursitis. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce this risk.
5. Warm-Up Before Exercise
A proper warm-up before exercising can prepare your muscles and joints, reducing the risk of bursitis.
6. Protective Padding
Wearing protective padding during activities that put pressure on your joints (like kneeling or leaning on your elbows) can be a preventive measure.
7. Seek Medical Advice
If you have conditions that increase your risk of bursitis, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and strategies.
By acknowledging these risk factors and implementing preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing bursitis. Remember, a proactive approach to joint health is key in preventing this painful condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Bursitis
Understanding when it’s time to seek medical attention is crucial for managing the condition effectively and preventing further complications. This section provides guidance on recognizing severe symptoms, advice on consulting healthcare professionals, and discusses potential complications if bursitis is left untreated.
Recognizing the Severity of Bursitis Symptoms
While bursitis often presents with joint pain or stiffness, some symptoms might indicate a more serious condition requiring medical intervention. It’s essential to monitor your symptoms closely and look for signs such as:
- Intense or Worsening Pain: If the pain becomes sharp or unbearable, it could suggest a severe inflammation or infection.
- Persistent Swelling: Noticeable swelling that does not reduce with basic home care measures can be a cause for concern.
- Redness and Warmth: Excessive redness or a warm feeling in the affected area might indicate an infection.
- Fever: A fever accompanying joint pain or swelling is a strong indicator that you should seek medical attention immediately.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Seeking advice from a healthcare professional is advisable in the following scenarios:
- Symptoms Persist: If your symptoms don’t improve with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), or if they last longer than two weeks, it’s time to consult a doctor.
- Impaired Movement: Difficulty in moving the joint or completing daily activities warrants a medical evaluation.
- Recurrent Flare-Ups: Frequent episodes of bursitis symptoms might suggest an underlying chronic condition that requires professional management.
Potential Complications of Untreated Bursitis
Neglecting bursitis can lead to various complications, such as:
- Chronic Pain: Unaddressed bursitis can turn into a chronic condition, leading to persistent and prolonged pain.
- Joint Damage: Inflammation over time can result in damage to the joint and surrounding structures.
- Infection Spread: If the bursitis is caused by an infection (septic bursitis), delaying treatment can lead to the spread of infection, potentially becoming life-threatening.
Being proactive about your health is vital. Recognizing when bursitis symptoms are severe, understanding the importance of timely medical consultation, and being aware of potential complications are key steps in managing your joint health effectively. If you experience any concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Bursitis
The process begins with a thorough medical history review and a physical examination. During the examination, doctors look for signs of tenderness or swelling in the bursae areas, which are small fluid-filled sacs cushioning bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. To confirm the diagnosis, medical imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasounds may be employed. These imaging tests help in ruling out other possible causes of joint pain and inflammation, ensuring an accurate diagnosis of bursitis.
A Spectrum of Treatment Options for Bursitis
Once bursitis is diagnosed, a range of treatment options is available. The choice of treatment largely depends on the severity of the condition and the specific needs of the patient.
- Home Remedies and Self-Care: Initial treatment often includes rest, ice, and elevation of the affected area. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or aspirin can also be effective in reducing pain and inflammation. Gentle exercises and stretches can help restore mobility and strengthen the muscles around the joint.
- Physical Therapy: For persistent bursitis, physical therapy is a beneficial option. Physical therapists can provide targeted exercises to improve flexibility and strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, which helps alleviate pressure on the bursae.
- Medications and Injections: In cases where pain is more severe, doctors may prescribe stronger anti-inflammatory medications. Corticosteroid injections directly into the bursa can provide rapid relief from pain and swelling.
- Surgical and Other Medical Interventions: In rare cases where bursitis does not respond to other treatments, surgical options may be considered. This involves removing the affected bursa. Another advanced treatment is aspiration, where fluid is drained from the bursa to reduce swelling and pain.
Targeting Symptoms for Effective Relief
The key to effectively managing bursitis lies in addressing the specific symptoms experienced by the patient. Whether through home remedies, physical therapy, medication, or in severe cases, surgery, the goal is to reduce pain, decrease inflammation, and restore normal movement in the joint. Customizing the treatment plan to the patient’s unique symptoms ensures a more successful outcome in managing bursitis.
However, diagnosing and treating bursitis involves a comprehensive approach, starting from a careful examination to a variety of treatment options tailored to alleviate specific symptoms. By understanding the diagnostic process and the range of available treatments, individuals suffering from bursitis can work with their healthcare providers to find the most effective strategy for relief and recovery.
Living with Bursitis: Managing Symptoms and Seeking Treatment
Living with bursitis can be challenging, but understanding how to manage its symptoms is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and active lifestyle. Bursitis, characterized by inflammation of the bursae (small, fluid-filled sacs cushioning bones, tendons, and muscles), can cause significant discomfort and restrict movement. This guide provides insights into managing bursitis symptoms, lifestyle adjustments, home care tips, and when to seek professional physical therapy or other interventions.
Effective Lifestyle Adjustments
- Stay Active, but Avoid Overexertion: Regular, low-impact exercises like walking or swimming can maintain joint mobility and prevent stiffness. However, avoid activities that exacerbate the pain.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can increase pressure on joints, worsening bursitis symptoms. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help in weight management.
- Proper Posture and Ergonomics: Adopt a posture that reduces strain on affected joints. Ergonomic adjustments at work and home can also alleviate symptoms.
Home Care Strategies
- Rest and Ice: Giving rest to the affected joint and applying ice packs can reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Compression and Elevation: Using an elastic bandage for compression and elevating the affected area can help in reducing inflammation.
- OTC Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can be effective in managing pain and inflammation.
Professional Interventions: When to Consider
- Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: If symptoms persist despite home care, or if there is severe pain and swelling, it’s crucial to seek medical advice.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a customized exercise program to strengthen muscles and improve joint function, thus alleviating bursitis symptoms.
- Medical Treatments: In some cases, doctors may recommend treatments like corticosteroid injections or surgery, particularly when conservative treatments don’t provide relief.
Living with bursitis requires a balance of self-care and professional guidance. By making lifestyle adjustments, following home care tips, and understanding when to seek professional help, individuals can effectively manage bursitis symptoms and maintain their quality of life. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.
FAQ Section: Understanding Bursitis Symptoms and Causes
1. What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs located near joints that reduce friction and cushion pressure points. It commonly affects the shoulder, elbow, hip, and knee.
2. What are the Common Symptoms of Bursitis?
The most typical symptoms of bursitis include joint pain and stiffness, swelling, redness or warmth over the affected area, and increased pain with movement or pressure.
3. What Causes Bursitis?
Bursitis is often caused by repetitive movements or positions that put pressure on the bursae around a joint. Other causes include injury or trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or infection.
4. Can Bursitis be Prevented?
While not all cases are preventable, reducing repetitive motions, using proper posture and body mechanics, and cushioning pressure points can help lower the risk of developing bursitis.
5. How is Bursitis Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider will typically diagnose bursitis based on a physical examination and medical history. In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs, or lab tests may be required.
6. What are the Treatment Options for Bursitis?
Treatment usually involves resting the affected joint, applying ice, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers. In some cases, physical therapy or corticosteroid injections may be recommended. Surgery is rare and only considered in severe cases.
7. Is Bursitis a Chronic Condition?
Bursitis can be either acute or chronic. Chronic bursitis might involve repeated flare-ups with periods of reduced symptoms.
8. When Should I See a Doctor for Bursitis?
If you experience severe joint pain, excessive swelling, redness, bruising, or a fever, you should consult a healthcare professional.
9. Can Lifestyle Changes Help with Bursitis?
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and using ergonomic tools and techniques can help manage and prevent bursitis.
10. Are There Any Risk Factors for Bursitis?
Age is a significant risk factor, as bursitis is more common in adults, especially those over 40. Occupations or hobbies that involve repetitive motion or pressure on joints also increase the risk.
Conclusion
We cannot overstate the importance of prompt treatment. Early intervention not only alleviates pain but also prevents the condition from worsening. If you’re experiencing symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, or stiffness, it’s crucial to take immediate action.
Consulting with healthcare professionals is paramount. They can provide accurate diagnoses, tailor treatment plans to your specific needs, and offer guidance on managing symptoms effectively. Remember, self-diagnosis and treatment can lead to complications; professional advice is your safest bet.
Armed with this knowledge, you are now better equipped to recognize the signs of bursitis and take appropriate steps towards treatment. Don’t let bursitis slow you down. Seek professional consultation, embrace prompt treatment, and pave your way to a healthier, more comfortable life.