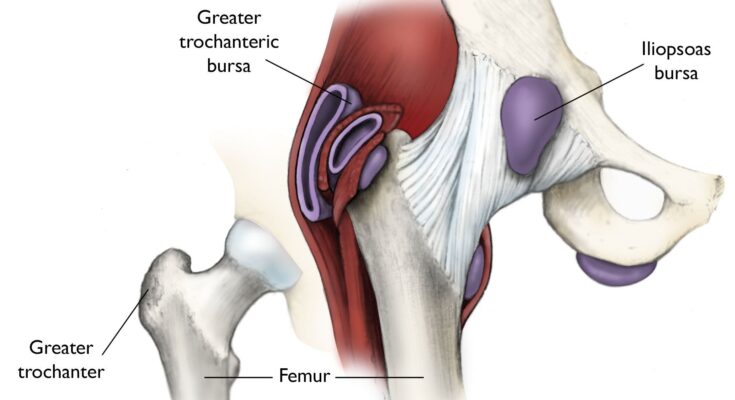
Bursitis Treatment: Bursitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of bursae, which are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints.
This condition can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in affected areas, significantly affecting an individual’s daily activities and quality of life.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for bursitis is essential for managing symptoms and preventing recurrence.
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae (singular: bursa) that act as cushions among your bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints. This condition commonly occurs when bursae become inflamed, resulting in pain, swelling, and limited movement in the affected area. It’s a condition that can affect various parts of the body, including the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, and heel.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of bursitis is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. Here are some of the primary causes:
- Repetitive Motion or Overuse: Engaging in repetitive activities or sports that exert pressure on the bursae around the joints can lead to bursitis.
- Injury or Trauma: A direct hit or fall that injures the bursae can cause inflammation and bursitis.
- Age: The likelihood of developing bursitis increases with age as tendons become less elastic and more susceptible to injury.
- Certain Occupations: Jobs that require repetitive motion or pressure on particular joints increase the risk of bursitis.
- Medical Conditions: Certain systemic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or diabetes can increase the risk.
- Prolonged Pressure: Sitting or kneeling for long periods, especially on hard surfaces, can cause bursitis in the hips or knees.
Common Types of Bursitis
Bursitis can occur in various body parts, each with its specific symptoms and challenges. Here are some common types:
- Shoulder Bursitis (Subacromial Bursitis): This type affects the shoulder joint, often causing pain when lifting the arm.
- Elbow Bursitis (Olecranon Bursitis): It occurs at the tip of the elbow, causing swelling and pain.
- Hip Bursitis (Trochanteric Bursitis): This type affects the outer hip area, often making lying on the affected side painful.
- Knee Bursitis (Prepatellar Bursitis): It’s commonly seen in individuals who kneel frequently, leading to swelling at the front of the knee.
- Heel Bursitis (Retrocalcaneal Bursitis): This affects the bursa located near the Achilles tendon, causing heel pain.
Recognizing the causes, risk factors, and types of bursitis is a step toward effective management and treatment. If you suspect you have bursitis, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, early intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Symptoms and Signs of Bursitis
Bursitis, a condition characterized by the inflammation of the bursae (small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints), presents several identifiable symptoms. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition.
- Joint Pain and Tenderness: The most common symptom of bursitis is a pain that may build up gradually or be sudden and severe, especially during movement or pressure on the affected area.
- Swelling and Redness: The affected joint may appear swollen and may feel warm to the touch. In some cases, the skin over the joint might also look red.
- Stiffness or Achiness: The joint may feel stiff, and you might experience a sense of achiness around the joint area.
- Restricted Movement: Movement of the joint may be limited due to discomfort or swelling, affecting your ability to perform everyday activities.
These symptoms can vary depending on the specific joint affected. Common areas for bursitis include the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, and heel.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Persistent Pain: If the pain lasts for more than a few days or is severe.
- Excessive Swelling, Redness, Bruising, or Rash: These could be signs of infection or other conditions.
- Fever: A fever occurring alongside joint pain and swelling could indicate an infectious condition.
- Difficulty Moving the Joint: If the range of motion in the affected area becomes significantly limited.
Early intervention can prevent the progression of bursitis and reduce the risk of complications. A healthcare provider can diagnose bursitis through a physical examination and, if necessary, imaging tests such as X-ray, MRI, or ultrasound. The treatment typically involves rest, ice, and medications to reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, physical therapy or injections may be recommended.
Understanding these symptoms and when to seek medical advice can help in managing bursitis effectively. Remember, timely medical intervention is key to a speedy recovery and maintaining joint health.
Diagnosing Bursitis: A Comprehensive Guide
Diagnosing Bursitis involves a multi-faceted approach that starts with understanding the patient’s medical history and conducting a thorough physical examination. This article provides a detailed overview of the diagnostic process, emphasizing the importance of imaging tests and the consideration of differential diagnoses.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing bursitis is a detailed medical history and physical examination. During this phase, healthcare providers focus on:
- Symptom Analysis: Understanding the nature, duration, and intensity of the pain and swelling.
- Medical History Review: Assessing past injuries, repetitive activities, or underlying health conditions that might contribute to bursitis.
- Physical Inspection: Examining the affected area for redness, swelling, and tenderness.
- Range of Motion Tests: Evaluating the joint’s functionality and pain response during movement.
This initial assessment is crucial in guiding the direction of further diagnostic tests.
Imaging Tests Used in Diagnosis
To confirm a diagnosis of bursitis, various imaging tests are employed:
- X-rays: While they can’t show bursitis directly, X-rays are useful in ruling out other causes of discomfort such as bone fractures.
- Ultrasound: This is an effective tool for visualizing soft tissue structures, including the bursae, and can show fluid accumulation.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI provides a detailed image of both hard and soft tissues, offering a comprehensive view of the affected area.
These imaging techniques are essential in confirming the presence of bursitis and assessing its severity.
Differential Diagnosis: Conditions that Mimic Bursitis
Bursitis shares symptoms with several other conditions, making differential diagnosis critical. Conditions often mistaken for bursitis include:
- Arthritis: Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can cause joint pain and swelling similar to bursitis.
- Tendinitis: This involves inflammation of the tendons and can mimic the symptoms of bursitis, especially around joints.
- Infections: In some cases, the affected area might be infected, leading to symptoms that resemble bursitis.
- Gout: Characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain and swelling, gout can affect the same joints as bursitis.
Identifying the correct condition is vital for effective treatment. Therefore, healthcare providers often use a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis of bursitis.
Bursitis Treatment Overview
Bursitis, a common condition characterized by the inflammation of the bursae (small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints), requires a well-structured treatment approach. The general strategy for treating bursitis centers around reducing inflammation and pain, while also preserving or improving joint function.
Typically, the initial step in bursitis treatment involves conservative measures. These include:
- Rest: Giving the affected joint a break is crucial. Avoiding activities that exacerbate the condition helps in reducing inflammation and pain.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the inflamed area can help reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort.
- Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs, like ibuprofen or naproxen, are often recommended to manage pain and decrease inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in specific exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist can strengthen the muscles around the joint, improving flexibility and reducing the risk of further injury.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In more severe cases, doctors may suggest corticosteroid injections to provide rapid relief from inflammation.
Emphasizing the Importance of a Tailored Treatment Plan
Each case of bursitis is unique, making it essential to tailor the treatment plan to the individual’s specific needs. Factors like the location of bursitis, the severity of symptoms, the patient’s overall health, and their activity level play a significant role in shaping the treatment approach.
A personalized treatment plan may include:
- Specialized Physical Therapy: Depending on the affected area, certain exercises might be more beneficial. For instance, shoulder bursitis requires different therapeutic exercises compared to hip or knee bursitis.
- Lifestyle and Occupational Changes: Modifications in daily activities or workplace ergonomics can be necessary, especially if repetitive motions or prolonged pressure contributed to the condition.
- Use of Assistive Devices: For some, using tools like braces or splints can provide support and alleviate stress on the affected joint.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture or chiropractic treatments might be suggested as complementary therapies in some treatment plans.
- Surgery: Although rare, surgery might be an option if bursitis does not respond to other treatments. This is usually considered a last resort.
However, treating bursitis effectively demands a combination of general and customized strategies. While common treatments focus on alleviating symptoms, a personalized approach takes into account the unique aspects of each patient’s condition. Consulting with healthcare professionals is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan tailored to individual needs. This comprehensive approach not only addresses the immediate symptoms but also aids in preventing future recurrence of bursitis.
Non-Pharmacological Bursitis Treatments
Dealing with bursitis can be challenging, but there are effective non-pharmacological treatments that can significantly alleviate symptoms and promote healing. This guide will explore the key strategies including rest, activity modification, physical therapy, exercises, and the use of cold and heat therapy.
Rest and Activity Modification
The first and foremost step in treating bursitis non-pharmacologically is to rest the affected area. Rest plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation and preventing further aggravation of the condition. It’s essential to avoid activities that exacerbate the pain or stress the inflamed bursa. For instance, if you have shoulder bursitis, limiting overhead activities can be beneficial.
Modifying your activities is also integral to the healing process. This doesn’t mean complete immobility, but rather adapting your routine to reduce stress on the affected joint. Simple adjustments like using ergonomic tools, altering your workout regimen, or even changing your posture can make a significant difference.
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy is a cornerstone in the management of bursitis. A qualified physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, improve flexibility, and reduce the load on the bursa. These exercises typically focus on gentle stretching and gradual strengthening, avoiding any movements that may worsen the condition.
Specific exercises can also improve joint function and reduce the risk of future flare-ups. For example, rotator cuff strengthening exercises can be beneficial for individuals with shoulder bursitis, while hip abductor strengthening is useful for hip bursitis.
The Role of Cold and Heat Therapy
Cold and heat therapy are simple yet effective tools in managing bursitis pain and inflammation. Cold therapy, such as applying ice packs to the affected area, can be particularly helpful in the acute phase of bursitis to reduce swelling and numb the pain. It’s recommended to apply ice for 15-20 minutes several times a day during the first few days of experiencing symptoms.
On the other hand, heat therapy is beneficial in the chronic stages of bursitis. Applying a warm compress or using a heating pad can help relax muscles, increase circulation, and promote healing in the affected area. Heat therapy is especially effective before performing stretching or strengthening exercises, as it helps prepare the muscles and joints for movement.
Non-pharmacological treatments for bursitis, including rest, activity modification, physical therapy, exercises, and the application of cold and heat therapy, play a vital role in managing symptoms and promoting recovery. By incorporating these strategies into your routine, you can effectively manage bursitis and improve your joint health. Always consult with a healthcare professional to tailor these methods to your specific needs and ensure the best outcomes.
Pharmacological Treatments for Bursitis
Understanding the pharmacological treatments available is crucial for managing this condition effectively. This section will explore over-the-counter pain relief options, prescription medications, and corticosteroid injections, delving into their benefits and risks.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief Options
When it comes to managing bursitis, over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers are often the first line of defense. Medications such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB), naproxen sodium (Aleve), and acetaminophen (Tylenol) can effectively reduce pain and inflammation. Ibuprofen and naproxen are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which not only alleviate pain but also reduce inflammation, making them particularly useful in bursitis treatment. Acetaminophen, while effective for pain relief, does not reduce inflammation. It’s important to follow the recommended dosages and be aware of potential side effects, such as stomach irritation and increased risk of heart issues or kidney damage with prolonged use.
Prescription Medications: When Are They Necessary?
In cases where OTC medications are insufficient, prescription medications may be required. Doctors may prescribe stronger NSAIDs for a limited period to manage more severe pain and inflammation. Additionally, if bursitis is caused by an infection, antibiotics will be necessary. It’s crucial to use these medications under medical supervision due to the potential for more significant side effects and interactions with other drugs.
Corticosteroid Injections: Benefits and Risks
Corticosteroid injections are another treatment option for bursitis, particularly when the pain is severe or not responding to oral medications. These injections can provide quick and effective relief by reducing inflammation directly in the affected bursa. However, they are not without risks. Potential side effects include joint infection, nerve damage, thinning of nearby bone (osteoporosis), and a temporary flare of pain and inflammation in the joint. Additionally, repeated injections over time can weaken tendons and ligaments around the bursa. Therefore, corticosteroid injections are typically recommended only after other treatments have been tried.
However, a range of pharmacological treatments is available for bursitis, each with its own set of benefits and risks. OTC pain relievers offer a first-line option, prescription medications provide a stronger alternative when necessary, and corticosteroid injections can be considered for more severe cases. Consultation with a healthcare professional is vital to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific condition. Remember, managing bursitis effectively often involves a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments, including physical therapy and lifestyle modifications.
Surgical and Advanced Treatment Options for Bursitis
Bursitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae (small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles), can often be managed with conservative treatments. However, in more severe cases, surgical and advanced treatment options may be necessary. This article explores the indications for surgery in bursitis treatment, the various types of surgical procedures available, and the emerging treatments and therapies in this field.
Indications for Surgery in Bursitis Treatment
Surgery for bursitis is generally considered when:
- Non-surgical treatments fail: If standard treatments like medication, physical therapy, and corticosteroid injections do not relieve symptoms, surgery might be recommended.
- Chronic or severe inflammation: Persistent or severe inflammation that affects mobility or quality of life may necessitate surgical intervention.
- Infection: If the bursitis is caused by an infection (septic bursitis), surgery may be required to drain the infected fluid.
- Calcified bursitis: In cases where the bursa becomes calcified, surgical removal may be the only option for relief.
Types of Surgical Procedures
The surgical approach to treating bursitis typically involves one of the following procedures:
- Bursa Removal (Bursectomy): This is the most common surgery for bursitis, where the inflamed bursa is removed.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure used in some cases, arthroscopic surgery involves small incisions and the use of a camera and specialized instruments.
- Open Surgery: In more complex cases, open surgery might be required. This involves a larger incision and direct access to the affected area.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
Medical research is continuously evolving, leading to the development of new treatments and therapies for bursitis:
- Biological Treatments: Research is underway on using biologics, like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell therapy is another area of interest, with the potential to repair and regenerate damaged tissues in the bursa.
- Advanced Physical Therapy Techniques: New physiotherapy techniques, including specialized exercises and modalities, are being developed to enhance recovery and prevent recurrence.
However, while conservative treatments are effective for many individuals with bursitis, surgery and advanced therapies offer hope for those with more severe conditions. As medical science progresses, these treatments are becoming more sophisticated, offering improved outcomes for patients suffering from this painful and debilitating condition.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for your specific case of bursitis.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage and Prevent Bursitis
Bursitis, an inflammation of the bursae that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints, can be effectively managed and even prevented through strategic lifestyle changes. Integrating these modifications into your daily routine can significantly reduce the risk and alleviate the symptoms of bursitis.
1. Regular Exercise: Incorporating a regular exercise routine, especially activities that strengthen the muscles around your joints, can reduce the stress on your bursae. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, or yoga are particularly beneficial as they minimize joint strain.
2. Posture and Ergonomics: Maintaining proper posture and ergonomics, especially at work and during physical activities, can prevent unnecessary stress on your joints. For instance, if you spend long hours at a desk, ensure your chair and desk are ergonomically designed to support your body correctly.
3. Weight Management: Being overweight can increase the stress on the joints, particularly those that bear most of your weight like hips and knees. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of developing bursitis.
4. Joint Protection: Using pads or cushions while kneeling and ensuring proper form during exercises and activities can protect your joints from excessive pressure.
5. Avoid Repetitive Motions: Repetitive movements, especially those involving high pressure or vibration, can irritate the bursae. Limit these activities or take frequent breaks to reduce the risk of bursitis.
Effective Home Remedies and Their Benefits
In addition to lifestyle changes, certain home remedies can provide relief from bursitis pain and inflammation.
1. Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area can reduce inflammation and numb the pain. It is particularly effective when applied for 15-20 minutes several times a day, especially after activities that aggravate your symptoms.
2. Rest: Giving your joints a break from activities that exacerbate bursitis symptoms is crucial. Adequate rest allows the inflamed bursae to heal.
3. Compression and Elevation: Wearing a compression bandage can help reduce swelling, and elevating the affected area above heart level can aid in decreasing inflammation.
4. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. However, it’s essential to use these as directed and consult with a healthcare professional if over-the-counter options are insufficient.
5. Gentle Stretching: Gentle stretching exercises, particularly those recommended by a physical therapist or healthcare provider, can help maintain joint flexibility and reduce stiffness.
However, a combination of lifestyle changes and home remedies can be highly effective in managing and preventing bursitis. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice, especially if symptoms persist or worsen. By prioritizing joint health through these strategies, you can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of bursitis-related complications.
Prevention Strategies for Bursitis
Bursitis, a condition where the bursae (small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints) become inflamed, can cause significant discomfort and limit mobility. However, with the right prevention strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of experiencing bursitis or its recurrence. Here, we explore effective tips and emphasize the critical role of posture and ergonomics in preventing bursitis.
Tips for Preventing Bursitis Recurrence
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength, which are essential in preventing bursitis. Focus on exercises that enhance your core strength and balance.
- Joint Protection: Utilize protective gear, like knee pads or elbow pads, during activities that put pressure on your joints. This is particularly important for athletes or individuals engaged in physical labor.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Always use proper form when lifting objects, no matter how light. Bend at your knees, not your waist, and carry the load close to your body to reduce strain on your joints.
- Stretching and Warm-up: Incorporate stretching into your daily routine, especially before and after exercise. Warming up before strenuous activities helps prevent muscle and tendon strain.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can increase the pressure on your joints, especially the hips, knees, and ankles, leading to bursitis. Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce this risk.
- Avoid Repetitive Motions: If your job or hobbies involve repetitive motions, take regular breaks and try to vary your movements to reduce stress on specific joints.
Importance of Posture and Ergonomics
Good posture and ergonomic practices are vital in preventing bursitis, especially for individuals who spend long hours at a desk or in front of a computer.
- Ergonomic Workspace: Ensure your workspace is set up to support your body correctly. Your chair should support your lower back, and your computer screen should be at eye level to avoid neck strain.
- Posture Awareness: Be conscious of your posture throughout the day. Keep your shoulders relaxed and aligned, your feet flat on the floor, and your body in a neutral, balanced position.
- Movement and Stretching: Periodically change your position and stretch, especially if you’re in a sedentary job. Simple stretches and regular movement can prevent muscle stiffness and joint stress.
- Professional Guidance: If you’re unsure about your posture or how to set up an ergonomic workspace, consider consulting with a physical therapist or an ergonomic expert. They can provide personalized advice tailored to your needs.
By incorporating these prevention strategies into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing bursitis and promote overall joint health. Remember, consistent practice and awareness are key to keeping your joints healthy and pain-free.
FAQs About Bursitis and Its Treatment
1. What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints. This condition commonly affects the shoulder, elbow, and hip, but can also occur in the knee, heel, and the base of the big toe.
2. What Causes Bursitis?
Bursitis often results from repetitive movements or positions that irritate the bursae around a joint. Other causes include injury or trauma to the affected area, certain systemic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, or infections.
3. What are the Symptoms of Bursitis?
Common symptoms of bursitis include joint pain and tenderness, swelling, redness, and limited range of motion in the affected joint.
4. How is Bursitis Diagnosed?
Healthcare providers typically diagnose bursitis based on a physical examination and the patient’s medical history. In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs, and lab tests may be necessary to rule out other conditions.
5. What are the Treatment Options for Bursitis?
Treatment for bursitis often involves rest, ice, and medications to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy can also be beneficial. In severe cases, a doctor might recommend injections or surgery.
6. Can Bursitis be Prevented?
To reduce the risk of bursitis, it’s advised to vary your physical activities, practice proper posture, and use ergonomic tools and equipment. Regular strengthening and stretching exercises can also help.
7. When Should I See a Doctor for Bursitis?
Consult a healthcare provider if you have disabling joint pain, excessive swelling, redness, bruising, or a fever, as these could indicate an infection or other serious condition.
8. Can Bursitis Lead to Complications?
In rare cases, chronic bursitis can lead to a limited range of motion or the development of scar tissue.
9. Is Bursitis the Same as Tendinitis?
While both conditions involve inflammation in the areas around joints, tendinitis affects the tendons, the thick fibrous cords that attach muscle to bone, whereas bursitis affects the bursae.
10. How Long Does Bursitis Last?
The duration of bursitis varies depending on the severity and treatment. Acute bursitis may last for a few days to a few weeks if properly treated, while chronic bursitis can last several months.
Conclusion
While we have provided a thorough overview of bursitis, it’s important to remember that this information serves as a general guide and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Each individual’s situation is unique, and the symptoms of bursitis can sometimes mimic those of other conditions. Therefore, if you suspect you have bursitis or are experiencing joint pain and discomfort, it is imperative to consult with a healthcare professional. They can offer a precise diagnosis and tailor a treatment plan that suits your specific needs.
Healthcare professionals can provide comprehensive care that goes beyond the initial treatment of bursitis. They can also help in identifying and addressing any underlying causes or contributing factors, ensuring a holistic approach to your health and well-being.
In conclusion, while understanding the basics of bursitis is beneficial, it’s equally important to seek professional medical advice to manage your symptoms effectively and maintain optimal joint health. Remember, prioritizing your health is a crucial step towards a pain-free and active life.