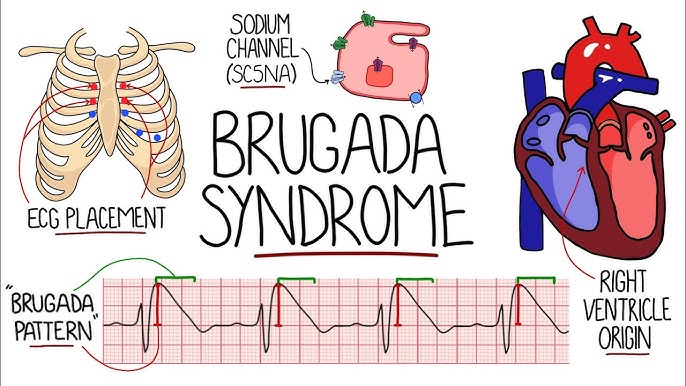
Brugada Syndrome Symptoms: Brugada Syndrome is a rare, yet potentially life-threatening heart rhythm disorder, primarily characterized by abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG) findings and an increased risk of sudden cardiac death.
This condition, often undetected until an individual experiences a severe cardiac event, is critical to understand for both patients and medical professionals alike.
What is Brugada Syndrome?
Brugada Syndrome is a rare, inherited heart condition that can lead to dangerous, irregular heart rhythms and, in some cases, sudden cardiac death. This syndrome is characterized by specific electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormalities and an increased risk of ventricular fibrillation, a type of rapid, irregular heart rhythm that can be life-threatening.
The condition was first identified and described in 1992 by the Brugada brothers, hence its name. They observed distinct patterns in ECG readings that were linked to a higher risk of sudden cardiac arrest in patients without obvious structural heart disease. Since its discovery, Brugada Syndrome has become a significant focus in the field of cardiology, especially in the study of genetic arrhythmia syndromes.
Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Brugada Syndrome is relatively rare, affecting approximately 5 in 10,000 individuals worldwide. However, its incidence can vary significantly among different regions and ethnicities. The syndrome is most commonly diagnosed in men and typically manifests between the ages of 30 and 40.
There is a notable geographic disparity in its prevalence, with a higher incidence reported in Southeast Asia compared to other parts of the world. This variation suggests a potential genetic predisposition linked to specific populations. Additionally, family history plays a crucial role in the syndrome’s occurrence, as it often runs in families, indicating a strong genetic component.
Understanding Brugada Syndrome is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers, as it requires specific management strategies to prevent potentially life-threatening events. Awareness and early detection through ECG screenings, especially in high-risk groups, are key in effectively managing this condition.
Symptoms of Brugada Syndrome
It’s crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to recognize its symptoms, as early detection can significantly impact treatment and prognosis. The primary symptoms of Brugada Syndrome include:
Fainting (Syncope): This is often the first sign and can be triggered by fever or resting.
Irregular Heartbeats: These arrhythmias can be detected through an Electrocardiogram (ECG).
Seizures: Resulting from a lack of blood flow to the brain due to irregular heartbeats.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest: In severe cases, the irregular heart rhythms can lead to sudden cardiac arrest.
Comparison with Symptoms of Other Heart-Related Conditions
It’s important to distinguish the symptoms of Brugada Syndrome from other cardiac conditions:
Compared to Heart Attack: Heart attacks are typically accompanied by chest pain and shortness of breath, which are not common in Brugada Syndrome.
Distinguishing from Arrhythmias: While irregular heartbeats are a symptom of many cardiac issues, the specific pattern on an ECG can help diagnose Brugada Syndrome.
Differentiating from Epilepsy: Seizures in Brugada Syndrome are due to heart rhythm problems, unlike epilepsy which originates in the brain.
Case Studies or Real-Life Examples
While specific case studies of Brugada Syndrome are rare due to its uniqueness, documented instances provide valuable insights:
Case Study 1: A patient experienced fainting episodes during fevers, later diagnosed as Brugada Syndrome through an ECG.
Case Study 2: An individual with a family history of sudden cardiac death underwent genetic testing, revealing Brugada Syndrome.
These real-life examples underscore the importance of awareness and timely diagnosis of this condition.
Causes of Brugada Syndrome
Here, we explore the primary causes and contributing factors of Brugada Syndrome, delving into current research that sheds light on its complex nature.
Genetic Factors
The most significant cause of Brugada Syndrome is genetic. It’s typically inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning a single altered gene from one parent can cause the condition. Research has identified mutations in the SCN5A gene, which plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of heart cells, as a primary contributor. These mutations lead to abnormal heart rhythms, a hallmark of Brugada Syndrome. Understanding one’s family history and genetic testing are key in diagnosing and managing this condition.
Environmental Triggers and Risk Factors
While genetics lay the groundwork for Brugada Syndrome, environmental factors can trigger its onset or exacerbate its symptoms. These include:
Electrolyte Imbalances: Imbalances in bodily minerals like potassium and calcium can affect heart rhythms.
Fever: High body temperature has been known to induce Brugada Syndrome symptoms.
Alcohol and Drug Use: Certain substances can adversely affect the heart’s electrical activity.
Medications: Some medications, particularly those that affect heart rhythm, can trigger symptoms.
Identifying and managing these triggers are crucial in preventing episodes of Brugada Syndrome.
Discussion of Current Research on Causality
Recent studies have expanded our understanding of Brugada Syndrome. Researchers are not only looking at genetic mutations but also how these interact with environmental factors. This includes studying the molecular and cellular mechanisms that lead to the abnormal heart rhythms seen in patients. Additionally, there is ongoing research into how lifestyle choices and medical interventions can mitigate the risks associated with Brugada Syndrome. This holistic approach to research is paving the way for more effective treatments and preventive strategies.
Diagnosing Brugada Syndrome
Brugada Syndrome, a potentially life-threatening heart rhythm disorder, is often elusive in its diagnosis. This section aims to shed light on the various aspects of diagnosing Brugada Syndrome, emphasizing medical tests and procedures, the significance of genetic testing, and the challenges encountered in its diagnosis. Our goal is to provide comprehensive and accessible information for both medical professionals and individuals seeking knowledge about this condition.
Medical Tests and Procedures
The initial step in diagnosing Brugada Syndrome typically involves an electrocardiogram (ECG). The ECG is crucial as it can reveal specific patterns characteristic of Brugada Syndrome. These patterns, often referred to as Type 1 Brugada ECG pattern, are indicative of the syndrome when observed in conjunction with clinical findings.
In some cases, an ajmaline or flecainide test, known as a pharmacological challenge, is conducted. This test involves administering a medication that can unmask the Brugada ECG pattern in individuals who might have the syndrome but do not show the characteristic ECG changes naturally.
Further, an electrophysiology (EP) study may be recommended. This invasive test involves threading catheters through blood vessels to the heart to study its electrical activity and assess the risk of arrhythmic events.
The Role of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing plays a pivotal role in diagnosing Brugada Syndrome. The condition is often linked to mutations in the SCN5A gene, which affects the electrical activity of the heart. Identifying such mutations through genetic testing not only aids in confirming the diagnosis but also has significant implications for family screening, as Brugada Syndrome can be inherited.
It is essential to understand, however, that a negative genetic test does not rule out Brugada Syndrome. Some individuals with the syndrome may not have detectable mutations in the SCN5A gene or might have mutations in other genes that are not yet identified.
Challenges in Diagnosis
Diagnosing Brugada Syndrome presents several challenges. One of the primary challenges is the variability of the ECG patterns; they can fluctuate over time and may even normalize, making it difficult to reach a definitive diagnosis based on a single ECG.
Another challenge is the syndrome’s asymptomatic nature in many individuals. Some people with Brugada Syndrome may never experience any symptoms, yet they are still at risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
Furthermore, distinguishing Brugada Syndrome from other cardiac conditions with similar ECG patterns is crucial yet challenging. This necessitates a comprehensive evaluation by a cardiologist specializing in heart rhythm disorders.
However, diagnosing Brugada Syndrome is a multifaceted process involving various medical tests and genetic analysis. Understanding these diagnostic tools and acknowledging the challenges involved is essential for effective diagnosis and management of this condition.
Potential Complications and Risks
Brugada Syndrome, a rare but serious heart condition, carries certain risks and complications that cannot be overlooked. Understanding these can help in managing the condition more effectively and reducing potential threats to health.
Connection with Sudden Cardiac Arrest
One of the most alarming complications of Brugada Syndrome is its strong connection with sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). This condition can trigger dangerous heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias, which may lead to a sudden and unexpected stoppage of heart function. SCA in the context of Brugada Syndrome can occur without warning, emphasizing the critical need for awareness and monitoring.
Long-term Health Implications
While the immediate concern with Brugada Syndrome is the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, there are also long-term health implications to consider. Individuals with this condition may face a higher risk of persistent heart issues, including arrhythmias that can affect their overall quality of life. It’s essential to understand that Brugada Syndrome is a chronic condition, requiring ongoing medical supervision and lifestyle adjustments.
Importance of Early Detection
The key to effectively managing Brugada Syndrome lies in early detection. Early diagnosis allows for prompt intervention, which can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications like SCA. Regular heart monitoring, genetic testing, and awareness of the syndrome’s symptoms are crucial steps in early detection. By recognizing the signs early and seeking timely medical care, individuals with Brugada Syndrome can lead healthier, more stable lives.
However, Brugada Syndrome, while rare, poses significant risks including sudden cardiac arrest and long-term heart complications. Early detection and regular monitoring are essential for managing these risks and ensuring better health outcomes for those affected.
Treatment and Management of Brugada Syndrome
Understanding the current treatment options, lifestyle adjustments, and future prospects in the field is crucial for those affected by this condition.
Current Treatment Options
The cornerstone of managing Brugada Syndrome lies in addressing its primary risk: sudden cardiac arrest. Here are the key treatments:
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): The most effective treatment for preventing sudden death in Brugada Syndrome is the use of an ICD. This small device, implanted under the skin, continuously monitors heart rhythm and delivers electric shocks to restore normal rhythm when necessary.
Medication: While no specific drugs are approved solely for Brugada Syndrome, certain medications may be prescribed to manage associated symptoms or conditions. It’s important to avoid drugs that might exacerbate the syndrome.
Electrophysiological Testing: This procedure helps identify abnormal heart rhythms and assesses the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. It can guide treatment decisions, including the need for an ICD.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventive Measures
Lifestyle adjustments play a vital role in managing Brugada Syndrome:
Avoidance of Trigger Factors: Certain drugs, high fever, and, in some cases, excessive alcohol or caffeine can trigger arrhythmias. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is crucial.
Regular Medical Check-ups: Ongoing cardiac monitoring and routine check-ups help in early detection of potential complications.
Family Screening: As Brugada Syndrome can be inherited, screening family members is recommended for early detection and management.
Future Prospects in Treatment
The future of Brugada Syndrome treatment is promising, with ongoing research focusing on:
Genetic Therapy: Understanding the genetic basis of the syndrome paves the way for potential genetic interventions.
Advanced Drug Therapies: Research is underway to develop drugs specifically targeting the electrical disturbances seen in Brugada Syndrome.
Improved Diagnostic Tools: Enhancing diagnostic accuracy can lead to better risk stratification and personalized treatment plans.
However, managing Brugada Syndrome effectively involves a combination of current medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and staying informed about emerging therapies. It’s a condition that demands vigilant care and regular medical supervision to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Living with Brugada Syndrome
Let’s delves into the personal experiences of patients, shedding light on their journeys and providing valuable insights for others in similar situations.
Patient Stories and Interviews
Hearing from those who directly experience Brugada Syndrome is invaluable. We gather compelling narratives from patients, allowing them to share their diagnoses, challenges, and triumphs. These stories not only bring a human aspect to the condition but also help in raising awareness and understanding.
Diagnosis and Initial Reactions: Patients recount how they were diagnosed with Brugada Syndrome. They talk about their initial reactions, the confusion and fear that often accompanies such a diagnosis, and how they processed this life-changing information.
Daily Life Adjustments: Living with Brugada Syndrome requires significant adjustments. Patients share how they have adapted their daily lives, discussing everything from dietary changes to activity restrictions, and how they balance health with a desire for normalcy.
Emotional and Psychological Impact: The emotional toll of living with a chronic condition is profound. Through these interviews, patients speak candidly about their mental health struggles, such as anxiety and depression, and how they strive to maintain emotional well-being.
Coping Strategies and Support Systems
Living with Brugada Syndrome is a continual journey, and having effective coping strategies and a strong support system is crucial for managing the condition.
Medical Management: Insights into how patients manage their condition medically, including medication, regular check-ups, and the use of devices like implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs). This section highlights the importance of staying vigilant and proactively managing the condition.
Lifestyle Changes and Adaptations: Learn how patients have modified their lifestyles to accommodate their condition. This includes dietary modifications, exercise routines, and avoiding triggers that might exacerbate the syndrome.
Support Networks: Discover the role of family, friends, and support groups in providing emotional and practical support. Patients discuss how these networks have helped them in their journey and the importance of having people who understand and empathize with their condition.
Mental Health Support: Addressing the psychological aspect, this part focuses on the importance of mental health support, whether through therapy, counseling, or peer support groups. Patients share their experiences with mental health services and how these have helped them cope with the challenges of Brugada Syndrome.
Community and Online Resources: Highlighting the power of community, this section provides information on online forums, social media groups, and other resources where people with Brugada Syndrome can connect, share experiences, and find support.
By presenting these personal stories and coping strategies, we aim to provide a comprehensive and empathetic view of living with Brugada Syndrome, offering guidance, hope, and solidarity to those navigating this challenging path.
Conclusion
Living with Brugada Syndrome, or supporting someone who does, is a journey marked by resilience and hope. It is a path that requires constant vigilance, empathy, and adaptation.
For those living with the condition, it’s about embracing a lifestyle that prioritizes health and well-being, while for supporters, it’s about offering unwavering support and understanding.
The journey with Brugada Syndrome is not just about managing a heart condition; it’s about nurturing a community of care, fostering strength, and inspiring a collective commitment to health and awareness.
In summary, recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of Brugada Syndrome are fundamental. Coupled with the importance of ongoing research and education, they form the backbone of effective management. Living with or supporting someone with this condition is a testament to the human spirit’s resilience and the power of informed, compassionate care.