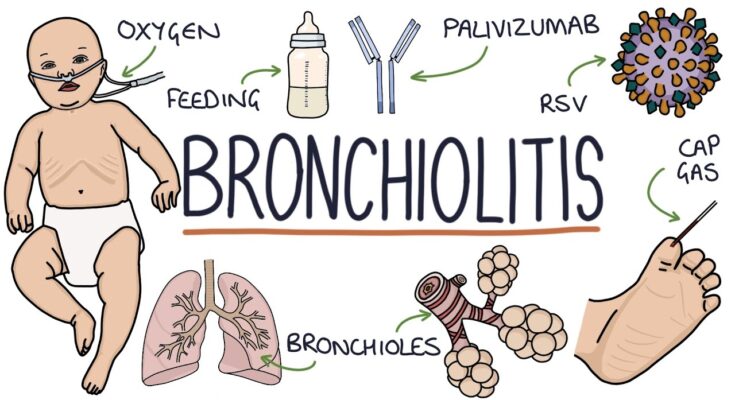
Bronchiolitis Symptoms: Bronchiolitis, a common lung infection among infants and young children, poses significant health challenges during the colder months.
This article delves into the symptoms, causes, and understanding of bronchiolitis, offering comprehensive insights for parents and caregivers.
What is Bronchiolitis?
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory condition, primarily affecting infants and young children. It’s characterized by the inflammation of the bronchioles, the smallest air passages in the lungs. This inflammation is usually caused by a viral infection, most commonly the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). Symptoms of bronchiolitis include coughing, wheezing, and difficulty in breathing, often accompanied by a fever.
Distinction Between Bronchiolitis and Other Respiratory Conditions
Bronchiolitis is often confused with other respiratory conditions like bronchitis and pneumonia. However, it’s distinct in its causes and the demographic it affects. Unlike bronchitis, which can affect people of all ages and often results from bacterial infection, bronchiolitis is viral and predominantly impacts infants and toddlers. Pneumonia, on the other hand, is a more severe condition affecting the alveoli (air sacs) in the lungs and can be caused by both bacteria and viruses.
Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Bronchiolitis is most prevalent in children under two years of age, with the highest risk group being infants under six months. It’s a leading cause of hospitalization in infants and young children during the winter months. While it can occur in children of any background, certain factors such as premature birth, a history of lung or heart conditions, and a weakened immune system can increase the risk. Additionally, exposure to smoke and crowded living conditions can also elevate the risk of developing bronchiolitis.
Common Symptoms of Bronchiolitis
It’s essential to recognize the symptoms of bronchiolitis, as it can often be confused with other respiratory illnesses. Understanding these symptoms can help in timely diagnosis and treatment.
Key Symptoms to Look For
Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when breathing out is a hallmark of bronchiolitis. This distinguishes it from a simple cold.
Coughing: Persistent coughing is common in bronchiolitis. It’s often more severe than a regular cough associated with a cold.
Difficulty Breathing: Watch for signs of labored breathing, such as rapid breaths or flaring nostrils. This can indicate more severe bronchiolitis.
Fever: Although not unique to bronchiolitis, a fever can accompany this condition, especially in its early stages.
Runny Nose and Congestion: These symptoms, similar to a common cold, often precede the development of more severe bronchiolitis symptoms.
Decreased Appetite: Infants and young children with bronchiolitis may show less interest in feeding, which is a concern for hydration and nutrition.
Distinguishing Bronchiolitis from Other Conditions
Duration and Severity: Bronchiolitis symptoms, especially coughing and wheezing, tend to last longer and be more severe than those of a common cold.
Age Group Affected: Bronchiolitis primarily affects infants and toddlers, unlike some other respiratory illnesses which are more common in older children and adults.
Response to Medications: Symptoms of bronchiolitis may not improve with medications typically used for asthma or allergies, helping to differentiate it from these conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s crucial to seek medical attention if your child is experiencing difficulty breathing, is not feeding well, or shows any signs of dehydration. Early medical intervention can prevent complications and ensure proper care.
Understanding these symptoms and how they differ from those of other respiratory conditions can aid in recognizing bronchiolitis in its early stages. This knowledge can be pivotal in seeking timely medical advice and ensuring the best care for your child.
Causes of Bronchiolitis
Recognizing the causes and risk factors of bronchiolitis is crucial in managing and preventing this condition effectively.
Primary Cause: Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
The main culprit behind bronchiolitis is the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). RSV is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It’s also transmitted via direct contact with contaminated surfaces.
Other Viral Causes
While RSV is the predominant cause, other viruses can also lead to bronchiolitis, including:
- Human Metapneumovirus
- Adenoviruses
- Influenza (Flu) Virus
- Parainfluenza Virus
Risk Factors and Susceptible Populations
Certain groups are more susceptible to developing bronchiolitis, often due to their age or underlying health conditions. Key risk factors include:
Age: Primarily affects infants and toddlers, especially those under 2 years old.
Premature Birth: Premature infants have underdeveloped lungs, making them more vulnerable.
Weakened Immune System: Children with a compromised immune system are at higher risk.
Heart and Lung Conditions: Existing heart or lung problems can exacerbate the impact of bronchiolitis.
Exposure to Smoke: Tobacco smoke exposure increases the risk and severity of respiratory infections.
Lack of Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding provides immunity boosters that can help in fighting infections.
Crowded Living Conditions: Places like daycare centers can facilitate the spread of viruses.
Seasonal Factors: Bronchiolitis is more common during the fall and winter months.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is pivotal for early detection and effective management of bronchiolitis. It also underscores the importance of preventive measures like good hygiene practices, avoiding exposure to respiratory infections, and ensuring a smoke-free environment for children.
However, while bronchiolitis is a common condition, awareness of its causes and the populations at risk can significantly aid in its prevention and management, ensuring better health outcomes for young children.
Complications and Risk Factors of Bronchiolitis
Let’s delves into the potential complications that parents and caregivers should be aware of. Complications from bronchiolitis can range from mild to severe and include:
Respiratory Distress: In severe cases, bronchiolitis can cause difficulty in breathing, leading to respiratory distress. This may require medical intervention, such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
Dehydration: Due to difficulties in feeding and increased respiratory rate, infants with bronchiolitis are at a higher risk of dehydration.
Secondary Infections: The infection can lead to secondary complications like pneumonia or ear infections, which can further complicate the child’s health.
Prolonged Illness: In some cases, bronchiolitis can lead to prolonged respiratory issues, including wheezing and cough, which might persist for weeks or even months.
Identifying Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors that can exacerbate bronchiolitis is crucial for early intervention and effective management. These risk factors include:
Age: Infants under 12 months, especially those aged 2-6 months, are at a higher risk.
Premature Birth: Premature infants are more susceptible due to their underdeveloped lungs and immune systems.
Chronic Lung or Heart Conditions: Children with preexisting lung or heart conditions are at greater risk.
Weakened Immune Systems: This includes infants with a history of severe infections or those who are immunocompromised.
Exposure to Smoke: Exposure to tobacco smoke or other pollutants can increase the risk and severity of bronchiolitis.
Preventative Measures
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of bronchiolitis and its complications. Some effective preventative measures include:
Good Hygiene Practices: Regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can help prevent the spread of the virus.
Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding for at least the first six months of life can strengthen the infant’s immune system.
Avoiding Smoke Exposure: Keeping infants away from tobacco smoke and other air pollutants is crucial.
Immunizations: While there is no specific vaccine for bronchiolitis, ensuring the child is up-to-date with all recommended vaccinations can help reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
By understanding the complications and risk factors associated with bronchiolitis, along with implementing preventative measures, parents and caregivers can better protect young children from this common yet potentially serious respiratory condition.
Diagnosis and Identification of Bronchiolitis
This article aims to demystify the diagnostic process, shedding light on the various methods used by healthcare professionals to accurately identify bronchiolitis.
Modes of Diagnosing Bronchiolitis
Diagnosing bronchiolitis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and medical history assessment. The process can be categorized into the following stages:
Clinical Evaluation: Pediatricians start with a thorough clinical evaluation. This involves observing the child’s breathing pattern, checking for signs of respiratory distress like rapid breathing, wheezing, or a persistent cough.
Medical History: A detailed medical history is crucial. Doctors often ask about recent symptoms, such as a runny nose or fever, and inquire if the child has had any recent exposure to respiratory viruses.
Physical Examination: A physical exam is conducted to listen for wheezing or crackling sounds in the lungs, which are indicative of bronchiolitis.
The Role of Symptom Identification
Identifying specific symptoms plays a pivotal role in diagnosing bronchiolitis. Key symptoms include:
Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound while breathing out.
Coughing: Persistent cough that may worsen at night.
Difficulty Breathing: Signs of labored breathing like flaring nostrils or using extra muscles to breathe.
Fever: Although not always present, a fever can accompany bronchiolitis.
Recognizing these symptoms early helps in initiating appropriate treatment and managing the illness effectively.
Possible Tests and Examinations
In some cases, further tests and examinations may be necessary, especially if the symptoms are severe or the diagnosis is unclear. These can include:
Chest X-ray: To rule out pneumonia or other lung conditions.
Viral Testing: Swab tests from the nose or throat to identify the specific virus causing bronchiolitis.
Blood Tests: Occasionally done to check the overall health and to rule out bacterial infection.
Pulse Oximetry: A non-invasive test to measure the oxygen levels in the blood, ensuring the child is getting enough oxygen.
However, the diagnosis and identification of bronchiolitis involve a multifaceted approach. It starts with a careful assessment of symptoms and medical history, followed by physical examinations and, if necessary, additional tests. Early and accurate diagnosis is key to managing bronchiolitis effectively and preventing complications.
Treatment Options for Bronchiolitis
Understanding the available treatment options can significantly aid in managing the symptoms and ensuring a smooth recovery process. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the various treatment methods for bronchiolitis, emphasizing the importance of both home care and professional medical attention. Additionally, we delve into the role of medication and other therapeutic approaches in treating this condition.
Home Care for Bronchiolitis
Managing bronchiolitis often begins at home, particularly for milder cases. Home care primarily focuses on ensuring the child remains comfortable and is receiving adequate hydration and nutrition. Here are some effective home care strategies:
Hydration: Keeping the child well-hydrated is crucial. Offer frequent breastfeeds or bottle feeds to infants, and encourage older children to drink water and clear fluids.
Rest: Adequate rest is essential for recovery. Ensure a quiet and comfortable sleeping environment for the child.
Humidified Air: Using a cool-mist humidifier can help ease breathing by loosening mucus in the airways.
Nasal Saline Drops: These can be used to relieve nasal congestion. Gently clearing the nose with a bulb syringe can also aid in clearing mucus.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of bronchiolitis can be managed at home, it’s critical to recognize when medical attention is needed. Seek immediate medical care if the child shows any of the following symptoms:
- Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing.
- Signs of dehydration, such as reduced urination, dry mouth, or crying without tears.
- Unusual lethargy or irritability.
- Persistent coughing or wheezing.
- Blue tinge to the skin, particularly around the lips and fingernails.
Medication and Therapeutic Approaches
The role of medication in treating bronchiolitis is somewhat limited, as the condition is typically caused by a virus, and antibiotics are not effective against viruses. However, some therapeutic approaches can help manage symptoms:
Inhaled Bronchodilators: Although not routinely recommended, they may be used in some cases to help open up the airways.
Steroids: Not generally recommended for bronchiolitis, but may be considered in specific cases.
Oxygen Therapy: For severe cases, particularly where there is difficulty in breathing, oxygen therapy in a hospital setting may be required.
Physical Therapy: Chest physiotherapy is sometimes used to help clear mucus, although its effectiveness is subject to debate.
Treating bronchiolitis involves a combination of effective home care, vigilance for signs requiring medical attention, and, in some cases, specific medical interventions. Understanding these various aspects can empower caregivers to provide the best possible care for children suffering from this condition. Remember, each child’s situation is unique, and consulting with a healthcare provider for personalized advice is always recommended.
Prevention and Care for Bronchiolitis
Bronchiolitis, a common respiratory infection in infants and young children, can be distressing for both the child and the caregivers. Prevention is key. To reduce the risk of bronchiolitis, follow these practical tips:
Hand Hygiene: Regular hand washing is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of viruses that cause bronchiolitis.
Avoid Crowds: Infants, especially those under three months, should avoid crowded places during peak cold and flu season.
Clean and Disinfect: Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces and objects that children frequently touch, like toys and doorknobs.
Breastfeeding: If possible, breastfeed your baby. Breastfeeding boosts the baby’s immune system, offering added protection against respiratory infections.
Smoke-Free Environment: Keep your child’s environment smoke-free. Exposure to tobacco smoke increases the risk of respiratory infections.
Importance of Hygiene and Avoiding Infection Sources:
Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial in preventing bronchiolitis. Respiratory viruses, such as the RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus), which is the most common cause of bronchiolitis, are highly contagious. They can spread through droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, or via direct contact with contaminated surfaces. Therefore, avoiding close contact with sick individuals and adhering to good hygiene practices is vital in preventing the spread of these viruses.
Advice for Caregivers Looking After Someone with Bronchiolitis:
Caring for a child with bronchiolitis can be challenging, but there are several ways caregivers can help:
Monitor Symptoms: Keep a close eye on the child’s breathing and activity levels. Seek medical attention if you notice any signs of difficulty breathing, dehydration, or lethargy.
Keep the Child Hydrated: Offer regular fluids to prevent dehydration. For infants, this might mean more frequent breastfeeding or bottle-feeding.
Nasal Suction: Using a nasal aspirator can help to clear a baby’s blocked nose, making breathing, feeding, and sleeping easier.
Elevate the Head: When the child is resting or sleeping, slightly elevate their head to help ease breathing.
Humidify the Air: A cool-mist humidifier can add moisture to the air, helping to loosen mucus in the child’s airway.
Remember, while bronchiolitis is usually mild, it can be serious, especially in infants and those with underlying health conditions. Always consult with a healthcare professional for the best care strategies for your child.
FAQs on Bronchiolitis: Symptoms and Causes
What is Bronchiolitis?
Bronchiolitis is an infection of the small airways in the lungs, known as bronchioles. It’s most commonly caused by the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and typically affects infants and young children.
What are the Symptoms of Bronchiolitis?
Symptoms of bronchiolitis include coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, and a runny nose. In severe cases, it may lead to rapid breathing, feeding difficulties, and signs of dehydration.
What Causes Bronchiolitis?
The primary cause of bronchiolitis is the RSV, but it can also be caused by other viruses. It spreads through droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes and can also be transmitted by touching contaminated surfaces.
Can Bronchiolitis be Prevented?
While it’s challenging to completely prevent bronchiolitis, good hygiene practices can reduce the risk. These include regular hand washing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and keeping surfaces clean.
When Should I Seek Medical Attention for Bronchiolitis?
You should seek medical attention if your child experiences difficulty breathing, has a high fever, shows signs of dehydration, or if symptoms worsen.
Is Bronchiolitis Contagious?
Yes, bronchiolitis is contagious, especially in the early stages of the illness. It’s important to keep infected children away from other young children and vulnerable individuals.
Can Adults Get Bronchiolitis?
While bronchiolitis predominantly affects infants and toddlers, adults, especially those with weakened immune systems, can also contract the illness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, your awareness and response to bronchiolitis symptoms play a pivotal role in your child’s health. We urge you not to overlook any respiratory distress or changes in your child’s breathing patterns.
For more information, consider exploring further reading materials or consulting with healthcare professionals. Taking these proactive steps can make a significant difference in managing bronchiolitis and safeguarding your child’s well-being.
Let’s prioritize our children’s health by staying informed and seeking timely medical advice.