Aplastic Anemia Treatment: Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious condition that occurs when your body stops producing enough new blood cells.
This leaves you feeling fatigued and more prone to infections and uncontrolled bleeding. Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is a rare and serious condition affecting the bone marrow. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of aplastic anemia, including its definition, causes, risk factors, and prevalence across various demographics.
What is Aplastic Anemia?
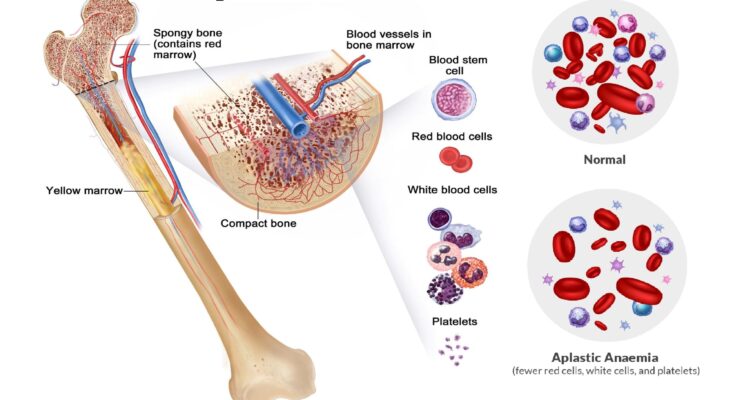
Definition: Aplastic anemia is a medical condition where the body’s bone marrow fails to produce enough new blood cells. This failure leads to a deficiency in all three types of blood cells – red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets – resulting in a range of health problems.
Explanation: In aplastic anemia, the bone marrow’s stem cells are damaged, impairing their ability to generate new blood cells. Red blood cells are crucial for carrying oxygen, white blood cells fight infection, and platelets help with blood clotting. The shortage of these cells can lead to symptoms like fatigue, increased susceptibility to infections, and excessive bleeding.
Causes and Risk Factors of Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia can be caused by various factors, and understanding these can help in both prevention and management:
- Autoimmune Disorders: The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the bone marrow.
- Exposure to Toxic Chemicals: Chemicals such as benzene or certain pesticides and insecticides can damage bone marrow.
- Medications: Some drugs, especially those used in chemotherapy, can harm bone marrow.
- Viral Infections: Certain viruses, like hepatitis, Epstein-Barr, or HIV, can trigger aplastic anemia.
- Genetic Factors: Conditions like Fanconi anemia can increase the risk.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics
Understanding the prevalence and demographic distribution of aplastic anemia is crucial for awareness and research:
- Prevalence: Aplastic anemia is rare, with an estimated incidence of 1-2 cases per million people annually.
- Age Factor: It can affect individuals of any age, but there are peaks in young adults and the elderly.
- Geographic Variations: Some regions, particularly in East Asia, report higher incidence rates.
- Gender and Ethnicity: Research indicates no significant gender bias, but certain genetic forms may be more prevalent in specific ethnic groups.
Signs and Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
Understanding and recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial for timely treatment and management of the condition.
Common Symptoms Experienced by Patients
- Fatigue and Weakness: Due to a lack of red blood cells, individuals often experience extreme tiredness and a general feeling of weakness, making even routine tasks challenging.
- Shortness of Breath: This is a common symptom, especially during physical exertion, as the body struggles to transport oxygen efficiently.
- Pale Skin: A noticeable paleness or a washed-out appearance can be a sign of reduced red blood cell count.
- Frequent Infections: With a compromised immune system due to low white blood cell count, patients are more susceptible to infections.
- Unexplained Bruising or Bleeding: A low platelet count can lead to easy bruising, bleeding gums, or nosebleeds, which are often unexplained and recurrent.
Impact on Daily Life
The symptoms of aplastic anemia can severely impact daily life. Fatigue and weakness can limit a person’s ability to perform work, engage in physical activities, or even carry out simple household tasks. Shortness of breath may restrict participation in activities that require physical exertion. Additionally, the increased risk of infections can necessitate frequent medical visits and a need for more cautious hygiene practices. The tendency to bruise or bleed easily can be distressing and require individuals to be more careful in their daily interactions to avoid injuries.
Importance of Early Recognition
Early recognition of aplastic anemia symptoms is vital. It allows for prompt medical intervention, which can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Early diagnosis can lead to quicker management of symptoms, reducing the risk of complications and improving the quality of life for patients. It also enables healthcare providers to advise on lifestyle modifications and precautionary measures to better cope with the condition.
However, being aware of the signs and symptoms of aplastic anemia, understanding their impact on daily life, and recognizing the importance of early detection are key steps in managing this challenging condition effectively. Regular health check-ups and consulting a healthcare provider if any of these symptoms are observed can lead to early diagnosis and better health outcomes.
Diagnosing Aplastic Anemia: Essential Methods and Challenges
Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike.
1. Overview of Diagnostic Methods
Blood Tests: The initial step in diagnosing aplastic anemia often involves comprehensive blood tests. These tests assess the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, which are typically lower in aplastic anemia patients. Blood tests also help in ruling out other conditions that might mimic aplastic anemia symptoms.
Bone Marrow Biopsy: A definitive diagnosis usually requires a bone marrow biopsy. This procedure involves extracting a small amount of bone marrow tissue, usually from the hip bone, for detailed examination. In aplastic anemia, the bone marrow is often empty (aplastic), lacking the normal amount of blood-forming stem cells.
Additional Tests: Depending on the patient’s symptoms and the results of initial tests, additional assessments like imaging scans or specialized blood tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other disorders.
2. Role of Healthcare Professionals in Diagnosis
Interdisciplinary Approach: Diagnosing aplastic anemia typically involves a team of healthcare professionals. This team may include a primary care physician, a hematologist (a specialist in blood disorders), and sometimes a pathologist (a specialist in disease diagnosis through laboratory methods).
Patient History and Physical Examination: A thorough review of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination are vital. Healthcare professionals look for symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and skin pallor, which are common in aplastic anemia.
Guiding Through the Diagnostic Process: Healthcare providers play a key role in guiding patients through the diagnostic process, explaining the purpose and procedure of various tests, and addressing any concerns or questions.
3. Challenges in Diagnosing Aplastic Anemia
Differentiating from Similar Conditions: One of the main challenges in diagnosing aplastic anemia is distinguishing it from other blood disorders that have similar symptoms, such as myelodysplastic syndromes or leukemia.
Age-Related Factors: The prevalence of aplastic anemia in certain age groups, particularly in children and older adults, can complicate the diagnostic process, as symptoms might be attributed to other age-related health issues.
Asymptomatic Early Stages: In its early stages, aplastic anemia might not present any symptoms, making early detection difficult. Regular monitoring and timely investigation of any unexplained changes in blood counts are crucial.
Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia: A Comprehensive Guide
This article delves into the various treatment methods available, discussing their effectiveness, processes, and suitability for different patients.
Understanding Bone Marrow Transplants
Bone marrow transplants play a pivotal role in treating aplastic anemia. This procedure involves replacing the damaged bone marrow with healthy marrow from a donor. The section on bone marrow transplants will explain:
- Eligibility Criteria: Who is the best candidate for a bone marrow transplant?
- Procedure Details: How is the transplant performed?
- Risks and Benefits: What are the potential risks and success rates of this treatment?
- Post-Transplant Care: How to manage health post-transplant?
The Role of Immunosuppressive Therapy
Immunosuppressive therapy is another cornerstone of aplastic anemia treatment, especially for patients who are not suitable candidates for bone marrow transplants. This segment will cover:
- Mechanism of Action: How does immunosuppressive therapy work in aplastic anemia?
- Treatment Regimen: What drugs are commonly used, and how are they administered?
- Side Effects and Management: What are the potential side effects, and how can they be managed?
- Long-Term Outcomes: What to expect in the long run with this therapy?
Exploring Emerging Treatments and Research
The field of aplastic anemia treatment is evolving, with ongoing research and emerging therapies offering new hope. This section will highlight:
- Novel Therapeutics: What new drugs and treatments are under research?
- Clinical Trials: Insights into recent clinical trials and their findings.
- Future Directions: Where is the research in aplastic anemia heading?
- Patient Participation: How can patients get involved in clinical trials?
This comprehensive guide aims to provide readers with a detailed understanding of the treatment landscape for aplastic anemia, equipping them with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Managing Aplastic Anemia: Essential Tips and Strategies
Here, we’ll explore effective strategies for living with aplastic anemia, focusing on lifestyle modifications, managing treatment side effects, and ensuring long-term health.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Care Tips
- Nutrition: Prioritize a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support blood cell production. Iron-rich foods, leafy greens, and vitamin supplements, as recommended by your doctor, can be beneficial.
- Infection Prevention: Due to a weakened immune system, it’s crucial to avoid infections. Practice good hygiene, stay away from crowded places, and get regular vaccinations.
- Physical Activity: Engage in mild to moderate exercise, as recommended by your healthcare provider. Activities like walking or yoga can boost energy levels and overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate health issues. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and counseling can be helpful.
- Avoiding Harmful Substances: Steer clear of smoking and alcohol, as they can worsen aplastic anemia symptoms and hinder treatment effectiveness.
Managing Side Effects of Treatment
- Medication Side Effects: Stay in close communication with your healthcare team about any side effects from medications like immunosuppressants or antibiotics. They can adjust dosages or provide remedies to ease discomfort.
- Blood Transfusions: For those requiring frequent transfusions, be aware of symptoms like fatigue or shortness of breath and inform your doctor immediately.
- Emotional Impact: Dealing with aplastic anemia can be emotionally taxing. Seek support from support groups, family, and friends.
Long-Term Health Monitoring and Care
- Regular Check-ups: Frequent monitoring of blood counts and overall health is vital. This helps in timely identification and management of any complications.
- Bone Marrow Health: Regular assessments of bone marrow function are crucial. This may involve periodic bone marrow biopsies as advised by your hematologist.
- Secondary Health Concerns: Be vigilant about secondary health issues like osteoporosis or heart problems, which can arise due to prolonged medication use.
- Lifestyle Audit: Regularly review your lifestyle choices with your doctor to ensure they align with your health needs.
By integrating these practices into your daily life, you can effectively manage aplastic anemia, mitigate treatment side effects, and maintain long-term health. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your lifestyle or treatment plan.
The Future of Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Embracing Innovations: Latest Research and Developments
The landscape of aplastic anemia treatment is rapidly evolving, driven by groundbreaking research and innovative medical advancements. This section delves into the latest developments in the field, shedding light on new treatment methodologies, cutting-edge therapies, and significant strides made in understanding this complex condition. By staying abreast of these advancements, patients and healthcare providers can foster a more informed and optimistic outlook towards managing aplastic anemia.
On the Cusp of Change: Potential Future Treatments
Looking ahead, the horizon of aplastic anemia treatment brims with potential. This segment explores the promising treatments currently in the pipeline, including novel pharmaceuticals, advanced gene therapies, and revolutionary stem cell treatments. These emerging therapies, still in various stages of research and clinical trials, hold the potential to redefine the standard of care for aplastic anemia, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for patients.
The Lifeline of Progress: The Importance of Continuous Research and Funding
The journey towards a future free of aplastic anemia hinges on the sustenance of continuous research and robust funding. This final section underscores the critical role that ongoing scientific inquiry and financial support play in driving innovation in treatment. It highlights how sustained research efforts can lead to breakthroughs that transform patient lives, emphasizing the need for investment in this vital area. The piece concludes with a call to action, encouraging support from both the public and private sectors to fuel the next wave of medical discoveries in aplastic anemia treatment.
Conclusion
Aplastic anemia, a rare but serious condition where the bone marrow fails to produce enough new blood cells, necessitates immediate attention and comprehension. This summary emphasizes the pivotal role of early diagnosis and effective treatment in managing aplastic anemia. Timely identification of symptoms can significantly improve treatment outcomes and enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Equally crucial is the need for heightened awareness and increased research funding. Aplastic anemia, though rare, impacts individuals and families deeply, making it essential to support ongoing research. This research not only aids in developing advanced treatment options but also contributes to a better understanding of the disease, potentially leading to preventative strategies.
We call upon the medical community, researchers, policymakers, and the public to join forces in elevating the discourse around aplastic anemia. By increasing awareness and allocating more resources to research, we can hope to unlock new pathways for effective treatments, thereby offering a brighter future for those battling this challenging condition.