Hirschsprung’s Disease Treatment: Hirschsprung’s disease is a rare condition that affects the nerve cells in the colon (large intestine), leading to problems with bowel movements.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the diagnosis and treatment of Hirschsprung’s disease, aimed at offering insights for healthcare professionals, patients, and caregivers.
Understanding Hirschsprung’s Disease
Hirschsprung’s disease is a rare condition affecting the large intestine (colon) and causing problems with passing stool. This disease is present at birth (congenital) and results from missing nerve cells in the muscles of part or all of the baby’s colon. A clearer understanding of Hirschsprung’s disease can aid in early diagnosis and treatment, potentially improving the quality of life for those affected.
Key Statistics: Incidence and Demographics
Hirschsprung’s disease occurs in about 1 in 5,000 live births. It is more commonly diagnosed in males than in females, with a male-to-female ratio of approximately 4:1. The disease tends to be more prevalent among certain ethnic groups; for instance, it is more common in individuals of Asian and African descent than in Caucasians. There is also a genetic component, as the condition can run in families, suggesting a hereditary pattern in some cases.
Common Symptoms and Signs of Hirschsprung’s Disease
The most common symptoms of Hirschsprung’s disease typically appear shortly after birth, often within the first two months. Key symptoms include:
- Failure to pass meconium: Newborns with Hirschsprung’s disease often do not pass their first stool (meconium) within the expected 48 hours after birth.
- Chronic constipation: Infants and older children might experience ongoing issues with severe constipation that do not improve with usual treatment.
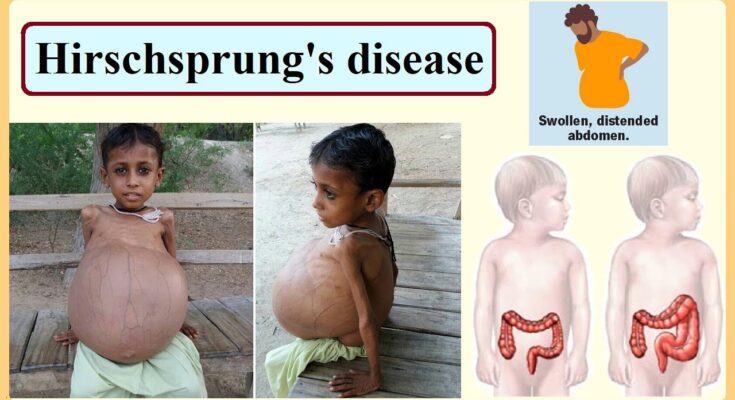
- Swollen belly: A noticeable swelling of the abdomen is common due to bowel obstruction and buildup of stool.
- Gastrointestinal obstruction signs: Symptoms such as vomiting, including a green or brown substance, can indicate a blockage in the intestinal tract.
- Poor feeding and growth: Infants may struggle with feeding difficulties, leading to poor weight gain and growth failure.
- Fatigue and lethargy: The condition can cause an overall state of weakness or tiredness due to malnutrition and the body’s struggle to absorb nutrients properly.
However, awareness and understanding of Hirschsprung’s disease are essential for parents, caregivers, and healthcare providers to ensure prompt and accurate diagnosis and management.
Diagnosing Hirschsprung’s Disease: A Critical Guide
Importance of Early Diagnosis in Hirschsprung’s Disease Management
Early diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s Disease (HD) is crucial for effective management and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. HD, a condition characterized by missing nerve cells in the muscles of part or all of the large intestine, can cause severe constipation and, in severe cases, life-threatening intestinal obstructions. Identifying the disease promptly allows for timely intervention, reducing complications and enhancing outcomes.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Diagnostic Process
The process of diagnosing Hirschsprung’s Disease involves several crucial steps, starting from the initial clinical assessment to specific diagnostic tests. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
1. Initial Clinical Assessment and Symptom Recognition: The first step in diagnosing Hirschsprung’s Disease involves a detailed medical history and physical examination by a healthcare professional. Symptoms to recognize include:
- Chronic constipation starting from infancy
- Swollen belly
- Gaseousness and discomfort
- Failure to pass stool within the first 48 hours of life
- Poor feeding and slow growth in infants Early recognition of these signs is essential for a timely diagnosis.
2. Diagnostic Tests: Several diagnostic tests are pivotal in confirming the presence of Hirschsprung’s Disease. These include:
- Anorectal Manometry: This test measures the muscle tone and reflexes of the anus and rectum. In Hirschsprung’s Disease, the expected reflex that causes muscle relaxation may be absent.
- Rectal Suction Biopsy: Often considered the definitive test for HD, this involves removing a small sample of cells from the rectum to look for the absence of nerve cells.
- Abdominal Imaging: Techniques like X-rays and ultrasound help visualize the condition of the abdomen and detect any abnormalities or obstructions in the bowel.
- Genetic Testing: While not always required, genetic tests can help identify mutations associated with Hirschsprung’s Disease, especially in families with a history of the condition.
However, early diagnosis and timely treatment are key to preventing complications and ensuring better health outcomes for those affected.
Hirschsprung’s Disease Treatment
Treatment generally focuses on alleviating the condition’s blockage of the intestine, and options vary from surgical to non-surgical approaches depending on the severity and extent of the affected intestine.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical intervention is the primary and most effective treatment for Hirschsprung’s disease, aiming to remove the diseased segment of the colon that lacks nerve cells. Here are the common surgical procedures used:
- Pull-through Procedure: This is the most common surgery for Hirschsprung’s disease, where the diseased part of the colon is removed and the healthy part is connected to the anus. This allows normal bowel movements without the need for a colostomy bag. It can be performed using minimally invasive techniques in some cases.
- Ostomy Surgery: In severe cases, or when a child needs to wait for a pull-through procedure, an ostomy may be necessary. This involves creating an opening in the abdomen (stoma) where the intestine is brought to the surface. This can be temporary or permanent, depending on the individual’s condition.
- Transanal Endorectal Pull-through: This is a newer technique where the entire procedure is performed through the anus, with no abdominal incisions. This method has the benefit of a faster recovery and less postoperative pain.
Non-Surgical Treatments
While surgery is the definitive treatment for Hirschsprung’s disease, non-surgical treatments play a crucial role in managing symptoms and preparing for surgery, particularly in newborns and small infants. These include:
- Bowel Management: Before surgery, and sometimes afterward, bowel management including regular enemas and laxatives may be necessary to clear the intestine of stool and prevent infection.
- Nutritional Support: Proper nutritional support is crucial, especially for children who may suffer from malnutrition due to poor intestinal function. Feeding therapies or special diets may be recommended by healthcare providers.
- Antibiotics: If an infection known as enterocolitis occurs, antibiotics are required. This infection is a serious complication of Hirschsprung’s disease and needs immediate treatment.
Optimizing Outcomes
Treatment for Hirschsprung’s disease typically involves a multidisciplinary approach involving pediatric surgeons, gastroenterologists, and nutritionists to ensure the best care and management of the condition. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for improving outcomes and minimizing complications.
However, while surgery is the cornerstone of treatment for Hirschsprung’s disease, non-surgical interventions are equally important for maintaining health before and after surgery and managing any complications effectively.
Living with Hirschsprung’s Disease
Long-term Management
Living with Hirschsprung’s Disease requires ongoing attention to ensure a healthy and comfortable life. Long-term management focuses on maintaining bowel function and preventing complications. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, adherence to prescribed treatments, and monitoring for any changes in symptoms are crucial.
Follow-up Care
Follow-up care is essential for individuals with Hirschsprung’s Disease. This involves regular check-ups with a gastroenterologist to assess bowel function, monitor growth and development, and adjust treatment plans as necessary. Diagnostic tests such as contrast enemas or biopsies might be needed periodically to evaluate the status of the bowel.
Managing Complications
Complications such as enterocolitis, bowel obstruction, and constipation can arise in individuals with Hirschsprung’s Disease. Early recognition and prompt treatment of these issues are vital. Management strategies include maintaining a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, using prescribed medications, and, in some cases, performing bowel management procedures.
Support Groups and Resources
Support groups and resources provide invaluable assistance to individuals and families dealing with Hirschsprung’s Disease. These groups offer a platform to share experiences, gain emotional support, and access information on managing the condition. Resources such as the Hirschsprung Disease Society and online forums can connect families with others who understand their journey.
Quality of Life
Improving the quality of life for those with Hirschsprung’s Disease is a primary goal. This includes addressing both physical and emotional needs. Ensuring proper nutrition, promoting regular physical activity, and fostering a supportive home environment contribute to a better quality of life. Psychological support might also be beneficial to cope with the chronic nature of the disease.
Impact on Daily Activities
Hirschsprung’s Disease can affect daily activities, but with effective management, individuals can lead active and fulfilling lives. Routine activities may need to be adjusted to accommodate bowel management routines. Planning ahead and maintaining flexibility can help manage these challenges, allowing for participation in school, work, and social events.
Coping Strategies for Families
Families of individuals with Hirschsprung’s Disease often face emotional and logistical challenges. Developing coping strategies is essential for maintaining family well-being. This includes educating all family members about the condition, seeking professional counseling when needed, and establishing a network of support. Practicing self-care and maintaining open communication within the family can also help in managing the stresses associated with the disease.
By staying informed and proactive, families can navigate the complexities of Hirschsprung’s Disease, ensuring a supportive environment for their loved ones.
Latest Advances in Hirschsprung’s Disease Treatment
Hirschsprung’s disease, a congenital condition affecting the large intestine, has seen significant advancements in treatment methods in recent years. These innovations are providing new hope for improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
Recent Research and Innovations
Recent research into Hirschsprung’s disease has focused on understanding the genetic and molecular basis of the condition. Scientists are exploring how genetic mutations contribute to the development of the disease, leading to potential targeted therapies. Innovations in diagnostic techniques are also making early and accurate detection more feasible, which is crucial for timely intervention.
Advances in Surgical Techniques
Surgical treatment remains the primary approach for Hirschsprung’s disease, with notable improvements enhancing patient recovery and reducing complications. Minimally invasive surgery, such as laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures, has revolutionized the field. These techniques offer smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. Additionally, advancements in preoperative and postoperative care are contributing to better overall outcomes.
Emerging Non-Surgical Treatments
While surgery is the standard treatment, emerging non-surgical options are gaining traction. Researchers are investigating stem cell therapy and tissue engineering as potential alternatives or adjuncts to surgery. These approaches aim to regenerate or repair affected intestinal tissues, potentially offering less invasive and more sustainable solutions for patients with Hirschsprung’s disease.
Future Directions
The future of Hirschsprung’s disease treatment looks promising with ongoing clinical trials and research. Scientists are continuously exploring novel therapies and refining existing techniques to improve efficacy and safety.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Numerous clinical trials are underway to test new drugs, therapies, and interventions for Hirschsprung’s disease. These trials are crucial for determining the effectiveness and safety of innovative treatments, paving the way for future standard-of-care practices.
Potential Future Treatments
Potential future treatments for Hirschsprung’s disease may include gene therapy, personalized medicine based on genetic profiles, and advanced regenerative techniques. As our understanding of the disease deepens, these cutting-edge approaches could revolutionize treatment paradigms and offer hope for a cure.
However, the latest advances in Hirschsprung’s disease treatment reflect a dynamic and evolving field. Through ongoing research, improved surgical methods, and the exploration of non-surgical options, the future holds promise for better management and potential cures for this challenging condition.
FAQs about Hirschsprung’s Disease Treatment
What is Hirschsprung’s Disease?
Hirschsprung’s Disease is a congenital condition affecting the colon, causing difficulties in passing stool due to missing nerve cells in the intestinal muscles.
How is Hirschsprung’s Disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of a physical exam, imaging tests, and a biopsy to confirm the absence of nerve cells in the affected area of the colon.
What are the treatment options for Hirschsprung’s Disease?
The primary treatment is surgery. Two common surgical procedures are the pull-through procedure and ostomy surgery. These surgeries aim to bypass or remove the affected section of the colon.
What is the pull-through procedure?
In this surgery, the diseased part of the colon is removed, and the healthy part is pulled down and connected to the anus. This procedure allows for normal bowel movements.
What is an ostomy surgery?
An ostomy creates an opening in the abdomen to allow waste to leave the body through a stoma. This can be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of the disease.
What is the recovery process like after surgery?
Recovery involves hospital stay for monitoring, pain management, and gradual reintroduction of diet. Full recovery can take a few weeks to a few months, and follow-up care is essential.
Are there any long-term effects of Hirschsprung’s Disease surgery?
Most children lead normal lives post-surgery, but some may experience complications like enterocolitis, bowel obstruction, or issues with bowel control. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial.
Can Hirschsprung’s Disease be cured?
While surgery can effectively treat the symptoms and improve quality of life, ongoing medical care and monitoring are necessary to manage potential complications.
Is there any way to prevent Hirschsprung’s Disease?
Currently, there is no known prevention for Hirschsprung’s Disease as it is a genetic condition present at birth.
Conclusion
Early detection and treatment of Hirschsprung’s Disease are crucial for improving the quality of life and long-term outcomes for affected individuals. Recognizing the symptoms early allows for timely medical intervention, which can prevent complications and lead to more effective management of the condition.
If you or your child exhibits symptoms of Hirschsprung’s Disease, such as chronic constipation, abdominal swelling, or difficulty passing stool, it is essential to seek medical advice promptly. Early consultation with healthcare professionals can lead to a quicker diagnosis and appropriate treatment, ensuring better health and well-being. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a doctor if you have any concerns, as early action can make a significant difference.
References
For additional information and to validate the content discussed in the article on Hirschsprung’s Disease treatment, the following reputable sources can be consulted. These references have been selected for their authority and depth of coverage on the subject matter:
- Mayo Clinic – Hirschsprung’s Disease Overview: A comprehensive guide detailing symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments of Hirschsprung’s Disease. Available at: Mayo Clinic
- MedlinePlus – Hirschsprung’s Disease: MedlinePlus, a service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine, provides reliable health information about Hirschsprung’s Disease, including an overview of treatment options. Visit: MedlinePlus
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) – Hirschsprung’s Disease: NORD offers a detailed account on the rare condition, including current research and treatment protocols. Read more at: NORD
- PubMed Central: For scientific articles and studies on the latest treatments and research in Hirschsprung’s Disease, PubMed Central is an invaluable resource. Explore at: PubMed Central
These sources are excellent starting points for those seeking deeper knowledge or needing to validate the treatments discussed related to Hirschsprung’s Disease.