Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis Treatment: In the realm of tick-borne diseases, Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis stand out for their significant impact on human health.
These conditions, often overshadowed by their more famous counterpart, Lyme disease, require prompt recognition and treatment to prevent serious complications.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diagnosis and treatment strategies for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, aiming to provide healthcare professionals and patients with the knowledge necessary to tackle these infections effectively.
Understanding Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are tick-borne diseases caused by various species of bacteria belonging to the genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma, respectively. These diseases share similar symptoms, transmission methods, and geographical distribution, making it crucial for individuals, especially those in high-risk areas, to understand their causes, how common they are, and the risk factors associated with transmission.
Causes of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
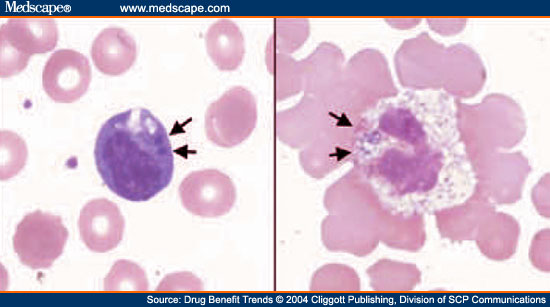
The primary cause of ehrlichiosis is the bacteria Ehrlichia chaffeensis, which mainly affects monocytes, a type of white blood cell. Another type, Ehrlichia ewingii, can also cause illness in humans. Anaplasmosis, on the other hand, is caused by Anaplasma phagocytophilum, targeting neutrophils, another kind of white blood cell. These bacteria are transmitted to humans through the bites of infected ticks, specifically the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum) for ehrlichiosis and the black-legged tick (Ixodes scapularis) for anaplasmosis.
Epidemiology: How Common Are These Diseases?
Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are most commonly reported in the United States, particularly in the southeastern and eastern regions for ehrlichiosis and the northeastern and upper midwestern regions for anaplasmosis. The incidence of these diseases has been increasing, with most cases occurring during the spring and summer months when ticks are most active. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), thousands of cases are reported annually, indicating a significant public health concern.
Risk Factors and Transmission Methods
The risk of acquiring ehrlichiosis or anaplasmosis increases with time spent in grassy or wooded areas where tick exposure is more likely. Key risk factors include:
- Engaging in outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and gardening.
- Living in or visiting areas known for tick activity.
- Having pets that may bring ticks into the home.
Transmission occurs through the bite of an infected tick. It’s important to note that the tick typically needs to be attached for at least 24-48 hours to transmit the bacteria effectively. There is no evidence to suggest that these diseases can be transmitted directly from person to person.
Understanding these factors can greatly reduce the risk of infection. Preventative measures include using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and performing regular tick checks after spending time outdoors. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing these diseases effectively, underscoring the importance of awareness and education on this topic.
By familiarizing oneself with the causes, epidemiology, risk factors, and transmission methods of ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent infection and promote better health outcomes in communities at risk.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Understanding these diseases’ symptoms, recognizing their differences, and acknowledging the importance of early detection are vital for effective treatment and prevention.
Common Symptoms of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Both Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis often present with flu-like symptoms that can appear 1-2 weeks after a tick bite. These symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Severe headaches
- Muscle aches
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
Because these symptoms are common to many illnesses, they can initially be mistaken for more benign conditions. However, timely recognition and treatment are crucial to prevent severe complications.
Differences Between Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis Symptoms
While Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis share many symptoms, there are slight differences that may help distinguish them. Ehrlichiosis may present additional symptoms such as:
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- A rash (more commonly seen in children)
Anaplasmosis, on the other hand, tends to show:
- Milder rash occurrences or none at all
- Slightly higher rates of respiratory symptoms
These differences, though subtle, can aid healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating each condition appropriately.
Importance of Early Detection and the Role of Awareness
Early detection of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis is crucial. Without prompt treatment, these diseases can lead to severe health issues, including respiratory distress, organ failure, and even death. Awareness plays a significant role in early detection. Being informed about the risks of tick bites and the symptoms of these diseases can lead individuals to seek medical advice sooner.
Preventive measures, such as using tick repellents, wearing long sleeves and pants in wooded areas, and performing regular tick checks after outdoor activities, are essential. Additionally, understanding the peak tick activity seasons and the geographical areas most affected can further reduce the risk of infection.
However, recognizing the common symptoms of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, understanding the subtle differences between them, and emphasizing the importance of early detection through awareness can significantly impact the outcomes for those affected. As tick populations continue to grow and spread geographically, public health education and preventive measures become increasingly important.
Diagnosis of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Detecting and treating tick-borne diseases like Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis is crucial for preventing severe health complications. These conditions often present with flu-like symptoms, making accurate diagnosis a challenge. This article explores the diagnostic tests and procedures, the challenges faced during diagnosis, and the significance of medical history and physical examination in identifying Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
1. Blood Tests: The most common and initial diagnostic step involves blood tests to identify markers of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis. These tests look for specific antibodies that the body produces in response to the infection.
2. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Tests: PCR tests are instrumental in detecting the DNA of the Ehrlichia and Anaplasma pathogens. They are highly sensitive and can confirm a diagnosis in the early stages of the infection.
3. Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC can reveal anomalies such as a low white blood cell count, low platelet count, or anemia, which are indicative of these infections.
4. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA): Considered the gold standard for diagnosing these conditions, the IFA test measures the level of antibodies against Ehrlichia and Anaplasma organisms.
5. Liver Function Tests: These tests can help assess the impact of the infection on the liver, as both diseases can lead to elevated liver enzymes.
Challenges in Diagnosing Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Diagnosing Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis poses several challenges:
- Non-specific Symptoms: The symptoms of these infections closely mimic those of other common illnesses, making early diagnosis difficult.
- Lack of Awareness: Limited awareness about these conditions among healthcare providers and the public can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
- Timing of Tests: Antibody tests may not be positive until several weeks after the onset of illness, complicating early diagnosis efforts.
- Variability of Pathogens: There are different strains of Ehrlichia and Anaplasma bacteria, which may not be detected by all tests.
The Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination play a critical role in the diagnosis of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis:
- Tick Exposure: A history of tick exposure, especially in endemic areas, significantly raises the suspicion of tick-borne diseases.
- Symptom Onset: Understanding the timeline of symptom onset can aid in differentiating these conditions from other similar diseases.
- Physical Signs: Physical signs such as rash, although not always present, can provide clues to a tick-borne disease diagnosis.
- Travel History: Information about recent travel to regions where these diseases are prevalent can be crucial for diagnosis.
However, diagnosing Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis requires a multifaceted approach that includes a variety of diagnostic tests and procedures. Despite the challenges in diagnosing these conditions, a detailed medical history and physical examination are invaluable tools that can guide healthcare professionals toward the correct diagnosis. Early detection and treatment are essential for preventing serious health outcomes associated with these tick-borne diseases.
Treatment Options for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Understanding the treatment options available is crucial for managing these infections effectively. Here’s a guide to the treatment options for ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis, with a focus on antibiotics, the first-line treatment choice, and considerations for specific patient groups such as children, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals.
Antibiotics: First-line Treatment Options
Antibiotics are the cornerstone of treatment for both ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. The choice of antibiotic and the duration of treatment depend on the patient’s specific situation, including the severity of the disease, the species of bacteria causing the infection, and the patient’s overall health status. Here are the most commonly used antibiotics for these conditions:
- Doxycycline: This is the antibiotic of choice for treating both ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis in individuals of all ages. It is effective, well-tolerated, and capable of preventing severe disease complications when administered early in the course of the infection.
- Rifampin: In cases where doxycycline is not suitable, such as for certain specific patient groups, rifampin may be used as an alternative. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure this antibiotic is appropriate for the individual’s condition.
Considerations for Specific Patient Groups
Children: Doxycycline is also recommended for children of all ages with ehrlichiosis or anaplasmosis. Concerns about doxycycline affecting teeth and bone development in children under eight years old have been reassessed, with the conclusion that the benefits outweigh the risks for short-term treatment.
Pregnant Women: Managing tick-borne diseases in pregnant women can be challenging due to concerns about the potential effects of medications on the fetus. Doxycycline, traditionally avoided in pregnancy, may still be considered if the benefits are deemed to outweigh the risks. Each case should be evaluated individually, and consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial.
Immunocompromised Individuals: Patients with weakened immune systems, including those with HIV/AIDS, undergoing chemotherapy, or taking immunosuppressive drugs, may require a longer duration of antibiotic treatment. These patients should be closely monitored for complications, as their risk of severe illness is higher.
However, the effective treatment of ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis relies heavily on the prompt use of appropriate antibiotics, with doxycycline being the first-line option. Special considerations should be taken for specific patient groups, including children, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals, to ensure the treatment is both safe and effective. Always consult a healthcare professional for a diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing serious health outcomes associated with these tick-borne diseases.
Managing Symptoms and Complications of Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis
Managing the symptoms and complications of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis effectively is crucial for improving patient outcomes and enhancing their quality of life. These tick-borne diseases can lead to serious health issues if not properly addressed. Here, we explore strategies for symptomatic treatments, supportive care, monitoring and managing complications, and what patients can expect in the long term.
Symptomatic Treatments and Supportive Care
Symptomatic treatments for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis focus on alleviating the symptoms and preventing the progression of the disease. Since these infections can cause fever, headaches, muscle aches, and fatigue, healthcare providers often recommend:
- Antipyretics and Analgesics: Medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help reduce fever and relieve pain.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential, especially if the illness is accompanied by symptoms like vomiting or diarrhea.
- Rest: Adequate rest supports the immune system’s fight against the infection.
It’s important to start antibiotic treatment as soon as possible, typically with doxycycline, to target the underlying infection. This approach not only helps in managing the symptoms but also in curtailing the progression of the disease.
Monitoring for and Managing Complications
Complications from Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis can be severe, including organ failure and, in extreme cases, death. Therefore, close monitoring is essential, especially for people with weakened immune systems, the elderly, or those with coexisting health conditions. Healthcare providers may:
- Regularly assess vital signs and symptoms to detect any worsening of the condition.
- Conduct blood tests to monitor for complications like anemia, thrombocytopenia, or elevated liver enzymes.
- Administer additional treatments as necessary, depending on the specific complications that arise.
Early identification and management of complications are key to preventing long-term health issues.
Long-term Outlook for Patients
Most patients who receive prompt and appropriate treatment for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis can expect a good long-term outlook. Recovery typically occurs within a few weeks, although some individuals may experience lingering symptoms like fatigue for an extended period. It’s important for patients to:
- Follow up with their healthcare provider to ensure the infection is fully resolved and to address any ongoing health issues.
- Take preventive measures against tick bites in the future, as reinfection is possible. This includes using tick repellents, wearing protective clothing, and performing regular tick checks after spending time in areas where ticks are prevalent.
However, effective management of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis involves a combination of symptomatic treatments, supportive care, vigilant monitoring for complications, and a proactive approach to prevention. With timely and appropriate care, most patients can look forward to a complete recovery and minimal long-term effects from these tick-borne diseases.
Prevention and Control of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Preventing these diseases involves a multi-faceted approach focusing on avoiding tick bites, managing environments to control tick populations, and enhancing public awareness and education about the risks and prevention methods. Here’s how you can protect yourself and your community.
Preventive Measures Against Tick Bites
Preventing tick bites is the most effective way to avoid ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. Here are practical steps you can take:
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply EPA-registered insect repellents that contain DEET, picaridin, or IR3535 on exposed skin, following the product instructions carefully.
- Dress Properly: When venturing into wooded or grassy areas, wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants. Tucking your pants into your socks can provide an extra layer of protection.
- Stay on Trails: Avoid walking through dense woods and bushy areas. Sticking to the center of trails minimizes your exposure to ticks.
- Perform Tick Checks: After spending time outdoors, thoroughly check your body, clothing, and pets for ticks. Showering within two hours of coming indoors can help wash off unattached ticks.
Strategies for Tick Control and Environment Management
Reducing tick populations and managing environments can significantly decrease the risk of tick-borne diseases:
- Keep Your Yard Tidy: Clear tall grasses, brush, and leaves where ticks are likely to live. Keep lawns mowed and edges trimmed.
- Use Tick Control Products: Consider using acaricides (tick pesticides) in your yard. Follow the instructions carefully to minimize environmental impact.
- Create Tick-Free Zones: Use wood chips or gravel to separate your lawn from wooded areas and restrict tick migration into recreational areas.
The Importance of Public Awareness and Education
Education plays a crucial role in the prevention and control of tick-borne diseases. Awareness campaigns can inform the public about:
- Symptoms and Risks: Knowing the symptoms of ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment, reducing the severity of the diseases.
- Prevention Techniques: Educating communities on how to avoid tick bites and implement tick control strategies can dramatically reduce the incidence of tick-borne diseases.
- Tick Removal Methods: Proper techniques for removing attached ticks can decrease the chance of infection. It’s important for people to learn and apply these methods correctly.
By combining personal protective measures, environmental management, and public education, we can effectively reduce the risk of ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. Community involvement and individual responsibility are key to combating these tick-borne diseases. Stay informed, stay protected, and contribute to a healthier, tick-free environment.
Current Research and Future Directions of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis are tick-borne diseases that pose significant health threats worldwide. These diseases are caused by bacteria that infect white blood cells, leading to a range of symptoms from mild flu-like signs to severe, life-threatening conditions. Thanks to ongoing research efforts, there have been remarkable advances in understanding, treating, and diagnosing these illnesses. This article explores the recent progress and looks toward the future of battling Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis.
Recent Advances in the Treatment of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
The treatment landscape for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis has evolved significantly in recent years. Traditionally, Doxycycline has been the cornerstone of treatment for both diseases, effectively reducing symptoms and preventing complications when administered early in the infection. Recent studies have focused on identifying alternative antibiotics to address cases with Doxycycline resistance or in populations where its use is contraindicated, such as in pregnant women and young children. Innovative therapeutic strategies, including the use of combination therapies and new antimicrobial agents, show promise in enhancing treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
Ongoing Research on Vaccines and Novel Treatments
Vaccine development represents a critical frontier in the fight against Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis. Current research efforts are aimed at creating effective vaccines to prevent these infections, with several candidate vaccines showing encouraging results in early-stage trials. These vaccines aim to elicit a strong immune response, offering protection against the bacteria responsible for these diseases. Simultaneously, novel treatments, including immunotherapies and targeted drug therapies, are under investigation. These new treatments strive to not only combat the bacteria directly but also to modulate the immune system’s response to infection, potentially reducing the severity of the diseases.
The Future of Diagnostics: Faster, More Accurate Tests
Advancements in diagnostic technologies are crucial for the early detection and treatment of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis. The future of diagnostics lies in the development of faster, more accurate tests that can be easily administered in a variety of settings. Researchers are working on molecular diagnostics, point-of-care tests, and serological assays that promise to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosing these tick-borne diseases. Such advancements would allow for timely initiation of treatment, significantly improving patient outcomes. Moreover, the integration of digital health tools and artificial intelligence in diagnostics could revolutionize how these diseases are detected and managed, paving the way for personalized medicine approaches in the near future.
FAQs on Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
What are Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis are tick-borne diseases caused by different species of bacteria belonging to the families Ehrlichia and Anaplasma, respectively. These diseases are primarily transmitted to humans through the bites of infected ticks, most commonly the lone star tick (for Ehrlichiosis) and the black-legged tick (for Anaplasmosis).
How can I tell if I have Ehrlichiosis or Anaplasmosis?
The symptoms of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis are similar and can include fever, chills, severe headaches, muscle aches, nausea, and sometimes a rash. Because these symptoms are not unique to these diseases, they can be easily confused with other illnesses. If you suspect you’ve been bitten by a tick and are experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Can Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis be treated?
Yes, both Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis are treatable with antibiotics. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent serious health complications. Doxycycline is the most commonly prescribed antibiotic for these diseases.
How can I prevent Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
Prevention of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis involves avoiding tick bites. This can be achieved by using tick repellents, wearing long sleeves and pants when in tick-infested areas, staying on trails when hiking, and performing thorough tick checks after being outdoors. It’s also helpful to keep your yard free of tall grasses and brush where ticks are likely to live.
Are there any long-term effects of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
Most people recover fully from Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis with appropriate treatment. However, if left untreated, these diseases can lead to serious and sometimes life-threatening complications. Long-term effects are rare but can include damage to the nervous system, organs, and in severe cases, death.
Is there a vaccine for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
Currently, there is no vaccine available for Ehrlichiosis or Anaplasmosis. The best way to protect yourself is through prevention and early detection.
Can pets get Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
Yes, pets, particularly dogs, can also be infected with Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis through tick bites. Symptoms in pets can vary but often include fever, lethargy, and loss of appetite. If you suspect your pet has been bitten by a tick and is showing symptoms, contact your veterinarian. Preventative tick control products are available for pets and are an important part of protecting them from these diseases.
Conclusion:
To improve outcomes for patients with Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, continuous education and awareness among healthcare providers and the public are essential. This includes understanding the risk factors, recognizing early symptoms, and knowing the importance of seeking medical care promptly. Additionally, ongoing research and advancements in diagnostic and treatment modalities hold the promise of even better patient outcomes in the future.
In conclusion, the battle against Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis is won through early detection, prompt treatment, and public awareness. As we enhance our strategies in these areas, we move closer to minimizing the impact of these tick-borne diseases on individuals and communities, steering towards a healthier future.
References
For individuals seeking to deepen their understanding of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis treatment, the following reputable sources offer comprehensive insights and validated information. These resources are pivotal for healthcare professionals, patients, and anyone interested in learning more about these tick-borne diseases, their diagnosis, treatment protocols, and preventive measures.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – As a leading national public health institute in the United States, the CDC offers detailed guidance on Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis. Their resources include symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention tips to manage these infections effectively. Visit CDC on Ehrlichiosis and CDC on Anaplasmosis for more information.
- American Lyme Disease Foundation (ALDF) – The ALDF provides resources and research on tick-borne diseases including Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis. Their comprehensive guides cover aspects from tick identification to disease prevention and treatment. Access their insights at American Lyme Disease Foundation.
- Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) – IDSA offers clinical guidelines for the treatment of tick-borne diseases. Their guidelines for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis are based on the latest research and expert consensus, serving as an invaluable resource for healthcare providers. Explore their treatment guidelines at IDSA Guidelines.
- PubMed Central (PMC) – A free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM). It provides access to numerous scientific studies and research papers on Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, offering in-depth knowledge for those interested in the scientific background. Search for related articles at PubMed Central.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its expert healthcare and medical research, Mayo Clinic provides an overview of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, including symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment. Their patient-friendly articles help demystify these diseases for the general public. Find out more at Mayo Clinic on Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis.
By consulting these references, readers can ensure they are getting accurate and up-to-date information regarding the treatment of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis. These resources are essential for understanding the complexity of these diseases and the importance of timely, effective treatment.