Coronavirus Disease 2019 Treatment: The outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has posed unprecedented challenges to global healthcare systems, economies, and societies at large.
As the world grapples with this pandemic, understanding the mechanisms for diagnosis and treatment has become paramount in controlling the spread of the virus and ensuring the well-being of millions.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current methodologies employed in the diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19, leveraging the latest research and clinical practices to offer insights into combating this pandemic effectively.
Understanding COVID-19
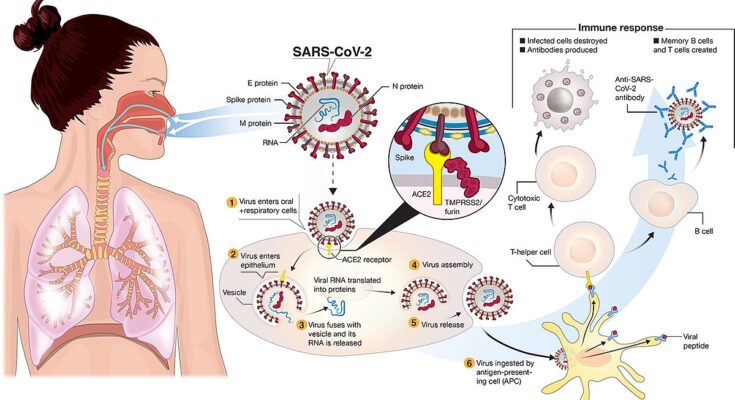
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has marked its place in history as a defining global health crisis of the early 21st century. First identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, the virus quickly spread worldwide, leading to unprecedented challenges in public health, travel, economies, and daily life. This section aims to shed light on the origins and impacts of COVID-19, outline its primary symptoms and modes of transmission, and highlight the importance of continuous research and evolving treatment protocols.
Brief History of COVID-19 and Its Global Impact
COVID-19 originated in late 2019 as a cluster of pneumonia cases with an unknown cause. The disease was soon identified as caused by a novel coronavirus, later named SARS-CoV-2, due to its similarities to the SARS virus of the early 2000s. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in January 2020 and a pandemic in March 2020.
The global impact of COVID-19 has been profound. It has caused millions of deaths worldwide and significantly disrupted societies and economies. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and social distancing became part of everyday life, aiming to slow the virus’s spread. The pandemic has also accelerated innovations in healthcare, such as the rapid development of vaccines, and highlighted the importance of digital technology in maintaining connectivity and supporting remote work and education.
List Symptoms and Transmission of the Virus
COVID-19 symptoms vary widely, ranging from mild to severe, and can appear 2-14 days after exposure to the virus. Common symptoms include:
- Fever or chills
- Cough
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Fatigue
- Muscle or body aches
- Headache
- New loss of taste or smell
- Sore throat
- Congestion or runny nose
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
Transmission occurs mainly through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. It can also spread by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus and then touching the face. The virus’s highly infectious nature underscores the importance of hygiene practices, such as handwashing and wearing masks, to prevent its spread.
The Significance of Ongoing Research and Updates on Treatment Protocols
Ongoing research into COVID-19 is crucial for understanding the virus better, developing effective treatments, and preventing future outbreaks. Scientists and healthcare professionals worldwide are working tirelessly to gather data on the virus’s behavior, treatment responses, and vaccine efficacy against emerging variants.
Updates on treatment protocols reflect the growing body of knowledge. Treatments have evolved from supportive care to include antiviral drugs, steroids, and monoclonal antibodies. Vaccination remains a cornerstone of global efforts to combat the pandemic, with multiple vaccines authorized for emergency use.
The continuous adaptation of treatment protocols, guided by the latest research findings, is essential for saving lives and mitigating the pandemic’s impact. Public health strategies and personal behaviors must also evolve in response to new information about virus transmission and prevention.
However, understanding COVID-19—from its history and global impact to its symptoms, transmission, and the significance of ongoing research—is vital for navigating the pandemic and preparing for future health crises. Keeping informed through reliable sources and adhering to public health guidelines will continue to be essential as the world works together to overcome COVID-19.
Diagnosis of COVID-19
Now, let’s delves into the various diagnostic methods available, factors influencing the accuracy of these tests, and the pivotal role that diagnosis plays in both treatment and containment efforts.
Diagnostic Methods for COVID-19
COVID-19 can be diagnosed using several methods, each with its own application and context of use. The most common diagnostic tests include:
- RT-PCR Tests: Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) tests are considered the gold standard for detecting the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. These tests are highly accurate and are used to confirm active infection.
- Antigen Tests: Rapid antigen tests detect specific proteins from the virus. While they offer faster results, they are generally less accurate than RT-PCR tests and may sometimes require confirmation via RT-PCR.
- Antibody Tests: Also known as serology tests, antibody tests can identify individuals who have been previously infected with the virus by detecting antibodies in their blood. These tests are not used to diagnose an active infection but to understand the spread of the virus and the potential for immunity in a population.
- CT Scans and Chest X-Rays: Imaging tests, such as CT scans and chest X-rays, are used to detect lung involvement in patients with COVID-19. They are typically used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to assess disease severity.
Factors Affecting the Accuracy of COVID-19 Tests
The accuracy of COVID-19 tests can be influenced by several factors:
- Sample Collection: Improper sample collection can lead to false results. The type of sample and the manner in which it is collected play crucial roles in test accuracy.
- Timing of Testing: The timing of the test in relation to exposure and symptom onset affects accuracy. For instance, testing too early or too late can result in false negatives.
- Test Sensitivity and Specificity: The inherent characteristics of the test, including its sensitivity (ability to correctly identify those with the disease) and specificity (ability to correctly identify those without the disease), significantly impact accuracy.
- Viral Load: The amount of virus present in the body can also affect the test’s ability to detect the virus, particularly in the case of antigen tests.
The Role of Diagnosis in Effective Treatment and Containment
Early and accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 plays a vital role in effective treatment and containment strategies. It enables:
- Timely Treatment: Early diagnosis allows for the immediate initiation of treatment, reducing the risk of severe disease progression and improving patient outcomes.
- Contact Tracing and Isolation: Identifying infected individuals promptly helps in implementing isolation measures and contact tracing, crucial steps in preventing further transmission.
- Informed Decision-Making: Accurate diagnostic data aids healthcare authorities in making evidence-based decisions regarding public health policies and resource allocation.
However, the diagnosis of COVID-19 through various testing methods is fundamental in managing and mitigating the impact of the pandemic. Understanding the factors that affect test accuracy and the significance of diagnosis in treatment and containment underscores the complex interplay between medical science and public health strategy. As the situation evolves, so too will diagnostic approaches, highlighting the importance of ongoing research and adaptation in our global response to COVID-19.
Treatment of COVID-19
This guide outlines general treatment guidelines, from supportive care for mild cases to advanced treatments for severe cases, emphasizing the importance of personalized treatment plans.
General Treatment Guidelines for COVID-19
The approach to treating COVID-19 is multifaceted, focusing initially on symptom management and supportive care. As the disease progresses or in cases where patients are at higher risk, more intensive treatments may be necessary. It’s essential to tailor treatment strategies to the patient’s specific needs, considering factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and the severity of symptoms.
Supportive Care and Symptom Management for Mild Cases
For individuals experiencing mild symptoms of COVID-19, supportive care is often sufficient. This includes rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and alleviate pain. Monitoring symptoms is crucial, as COVID-19 can progress rapidly in some cases. Patients should stay in communication with their healthcare providers and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen.
Advanced Treatments for Severe Cases
Severe cases of COVID-19 may require hospitalization and advanced treatments, including:
- Antiviral Drugs: These medications work by inhibiting the virus’s ability to replicate, potentially reducing the severity and duration of the illness.
- Immunotherapies: Designed to boost the immune system’s ability to fight the virus, immunotherapies can be particularly beneficial for patients struggling to mount an effective immune response.
- Steroids and Anti-inflammatory Drugs: For patients experiencing severe inflammation, steroids and other anti-inflammatory medications can be life-saving, reducing the risk of complications from the body’s immune response to the virus.
The Role of Vaccines in Preventing COVID-19
Vaccines play a pivotal role in preventing COVID-19, offering protection against infection and reducing the severity of the disease in breakthrough cases. Widespread vaccination is key to controlling the pandemic, protecting vulnerable populations, and preventing the emergence of new variants.
Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans Based on Patient Condition
Every patient’s experience with COVID-19 is unique, necessitating personalized treatment plans. Healthcare providers consider a range of factors, including the patient’s medical history, the presence of co-existing conditions, and the current state of their immune system, to devise the most effective treatment strategy. This personalized approach ensures that each patient receives the care they need, when they need it, optimizing outcomes and enhancing recovery.
However, the treatment of COVID-19 is complex and requires a comprehensive, personalized approach. From supportive care for mild cases to advanced treatments for severe cases, the focus is on managing symptoms, supporting the body’s fight against the virus, and preventing disease progression. Vaccines remain a critical tool in preventing infection and reducing the impact of the disease on communities worldwide. As the pandemic evolves, so too will strategies for treating and preventing COVID-19, underscoring the importance of ongoing research and adaptation in the face of new challenges.
Emerging Treatments and Research on COVID-19
As the world continues to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists and researchers are tirelessly working to find effective treatments and therapies to combat the virus. This section delves into the latest developments in the fight against COVID-19, highlighting ongoing research, potential future treatments, and the pivotal role of clinical trials.
Overview of Ongoing Research on COVID-19 Treatments
The battle against COVID-19 has mobilized the global scientific community like never before. Researchers across the world are exploring a multitude of treatment options, ranging from antiviral drugs to immune system boosters. One key area of focus is repurposing existing medications, which can significantly accelerate the treatment approval process. Additionally, cutting-edge technologies like mRNA vaccines, which played a crucial role in developing COVID-19 vaccines, are being further researched to enhance treatment strategies.
Potential Future Treatments and Therapies Under Investigation
Future treatments for COVID-19 are looking promising, with several innovative approaches under investigation. These include monoclonal antibodies designed to neutralize the virus, antiviral therapies that inhibit the virus’s ability to replicate, and treatments aimed at modulating the immune system’s response to prevent severe disease. Another exciting area of research is the development of nasal spray vaccines, which could offer a more accessible and non-invasive vaccination method.
Therapeutic research is not just limited to pharmaceuticals. Studies are also exploring the efficacy of dietary supplements, lifestyle changes, and the role of mental health support in improving outcomes for COVID-19 patients. The diversity of research avenues highlights the comprehensive approach being taken to tackle the virus from multiple angles.
The Importance of Clinical Trials in Validating Treatment Efficacy and Safety
Clinical trials are the cornerstone of medical research, providing the necessary validation for new treatments and therapies. Through rigorous testing phases, clinical trials assess the safety and efficacy of potential treatments, ensuring that only the most effective and safe options reach patients. These trials are crucial for determining appropriate dosages, identifying potential side effects, and understanding how treatments interact with various populations.
The global effort to conduct clinical trials for COVID-19 treatments has been unprecedented, with accelerated timelines and international collaboration facilitating the rapid development and approval of new therapies. However, the urgency to find effective treatments does not compromise the thoroughness and integrity of the clinical trial process, as patient safety remains paramount.
However, the ongoing research and development of new COVID-19 treatments and therapies are crucial in the fight against the pandemic. With each new discovery and successful clinical trial, the world moves closer to overcoming COVID-19. The dedication of the scientific community and the critical role of clinical trials in this process cannot be overstated, offering hope for more effective treatments and ultimately, the end of the pandemic.
Preventive Measures and Public Health Guidelines
Adhering to public health guidelines not only protects individuals but also shields communities, contributing to the global fight against the pandemic. Here, we explore essential preventive strategies and the significance of public health directives.
Importance of Preventive Measures in Controlling the Spread of COVID-19
Preventive measures are the cornerstone of controlling COVID-19’s spread. These actions are designed to minimize exposure and transmission of the virus, effectively reducing the number of new cases. By breaking the chain of transmission, we can alleviate the burden on healthcare systems, protect vulnerable populations, and save lives. The collective effort in following these measures plays a pivotal role in managing and eventually overcoming the pandemic.
Hand Hygiene and Respiratory Etiquette
Practicing good hand hygiene is a simple yet powerful tool in preventing the spread of COVID-19. Regularly washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer can kill viruses that may be on your hands. Equally important is adhering to proper respiratory etiquette, which involves covering your mouth and nose with your bent elbow or a tissue when you cough or sneeze. This practice not only protects those around you but also helps maintain public health.
Use of Face Masks and Social Distancing
Face masks and social distancing are critical components of the preventive strategy against COVID-19. Wearing face masks in public settings, especially where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain, can significantly reduce the virus’s spread. Similarly, keeping a distance of at least 6 feet from others helps prevent the transmission of the virus, particularly in crowded or enclosed spaces. Together, these measures form a protective barrier against COVID-19.
Vaccination and its Role in Prevention
Vaccination is a key tool in the fight against COVID-19, offering protection against the virus and reducing the severity of the disease. By getting vaccinated, individuals can contribute to the broader goal of achieving herd immunity, which occurs when a significant portion of the population becomes immune to the virus, thereby limiting its spread. Vaccination not only protects the individual but also reduces the overall burden of the disease on society.
Public Health Guidelines for Individuals and Communities
Public health guidelines provide a roadmap for individuals and communities to navigate the pandemic safely. These guidelines, which include the measures discussed above, are based on the latest scientific evidence and are updated as more is learned about the virus. By staying informed and adhering to these recommendations, everyone can play a part in mitigating the impact of COVID-19 and safeguarding public health.
However, preventive measures and adherence to public health guidelines are crucial in the fight against COVID-19. By embracing these practices, individuals and communities can contribute significantly to controlling the virus’s spread, protecting health, and paving the way for a return to normalcy.
FAQs on COVID-19 Diagnosis and Treatment
What are the common symptoms of COVID-19?
COVID-19 symptoms can range from mild to severe and may appear 2-14 days after exposure to the virus. Common symptoms include fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, muscle or body aches, headache, new loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion or runny nose, nausea or vomiting, and diarrhea. It’s important to monitor your symptoms and consult a healthcare provider if they worsen or if you have concerns.
How can I get tested for COVID-19?
COVID-19 testing is widely available through healthcare providers, pharmacies, and community testing sites. You can opt for a viral test to determine if you have a current infection or an antibody test to see if you had a past infection. Contact your local health department or visit their website for information on testing locations and requirements.
What should I do if I test positive for COVID-19?
If you test positive for COVID-19, follow the guidance of your healthcare provider and the local health department. Generally, you should isolate yourself to prevent spreading the virus to others, monitor your symptoms, stay hydrated, and rest. Seek medical attention if you have trouble breathing, persistent pain or pressure in your chest, new confusion, inability to wake or stay awake, or bluish lips or face.
Are there treatments available for COVID-19?
Treatment for COVID-19 varies depending on the severity of the symptoms. Mild cases may be managed at home with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter fever reducers. More severe cases may require hospitalization and could include treatments such as antiviral medications, corticosteroids, and supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation. Vaccination is also a key tool in preventing COVID-19 and reducing the severity of symptoms if infected.
Is it safe to take over-the-counter medications for COVID-19 symptoms?
Over-the-counter medications can help alleviate some symptoms of COVID-19, such as fever and body aches. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medications, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications that could interact.
How long do I need to isolate if I have COVID-19?
Isolation periods can vary based on current guidelines from health authorities and the severity of your case. Generally, individuals can end isolation after 10 days from the onset of symptoms, provided their symptoms have improved and they’ve been fever-free for at least 24 hours without the use of fever-reducing medications. Always follow the specific guidance provided by your healthcare provider or local health department.
Can COVID-19 be treated at home?
Yes, mild cases of COVID-19 can often be treated at home. Treatment involves resting, staying hydrated, and taking over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and alleviate pain. It’s crucial to isolate from others in your household to prevent the spread of the virus and closely monitor your symptoms. Contact a healthcare provider if your symptoms worsen or if you have concerns about your health.
Conclusion:
We encourage our readers to stay informed through reputable sources. In an age where misinformation can spread faster than the virus itself, turning to trusted, science-based resources for information is more important than ever. Organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and other public health authorities offer up-to-date, accurate information about COVID-19. By staying informed, we can make educated decisions about our health and safety and contribute to the collective effort to overcome this pandemic.
In conclusion, the journey through the COVID-19 pandemic is a testament to human resilience and ingenuity. While we have achieved significant milestones, the path ahead requires our continued vigilance, dedication to science, and commitment to public health measures. Together, by staying informed and adhering to expert guidance, we can navigate through these challenging times and emerge stronger on the other side.