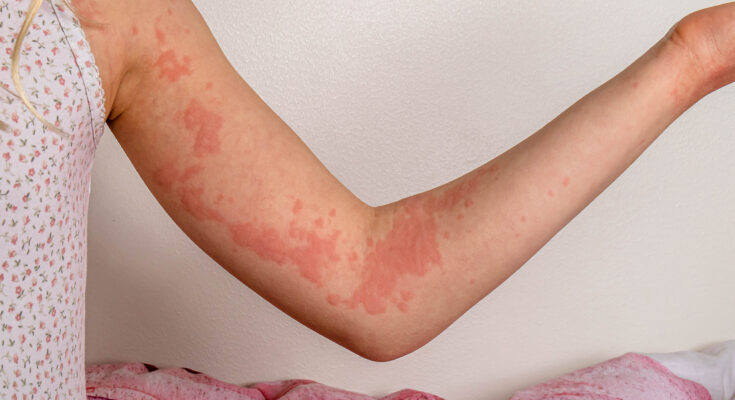
Chronic Hives Treatment: Chronic hives, medically known as chronic urticaria, presents a perplexing and often uncomfortable condition that affects millions globally.
Characterized by the appearance of red, itchy welts on the skin that may last for six weeks or longer, understanding and managing this condition requires a nuanced approach to diagnosis and treatment.
What is Chronic Hives?
Chronic hives, medically known as chronic urticaria, is a condition characterized by the repeated occurrence of red, itchy welts on the skin that can last for six weeks or more. Unlike acute hives that may arise and resolve quickly, chronic hives persist, presenting a significant impact on one’s quality of life. This condition is not just about physical discomfort; it also encompasses emotional and psychological distress due to its unpredictability and visibility.
Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Chronic hives affect a broad spectrum of the population, with studies indicating that approximately 1 to 2% of people will experience chronic urticaria at some point in their lives. It can affect individuals of any age, but it is most commonly observed in adults, particularly women. The condition has a higher prevalence in individuals between the ages of 20 to 40 years. Despite its widespread nature, the exact cause of chronic hives often remains elusive, making management and treatment a challenge for both patients and healthcare providers.
List of Symptoms of Chronic Hives
The symptoms of chronic hives are not only distressing but can also vary significantly from one individual to another. Common symptoms include:
- Red or skin-colored welts (wheals) that can appear anywhere on the body.
- Intense itching that may be more severe at night.
- Swelling (angioedema) around the eyes, lips, and in severe cases, the throat, which can be life-threatening.
- Welts that vary in size, from small spots to large blotches, and may join to form larger areas of flat, raised skin.
- Flare-ups that can occur without an apparent trigger and may persist for several months or years.
Causes and Triggers of Chronic Hives
Identifying the cause of chronic hives is often challenging, as it can be triggered by various factors, and in many cases, no specific cause is found. However, some known causes and triggers include:
- Autoimmune responses: Where the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissue, mistaking it for harmful pathogens.
- Physical triggers: Such as pressure on the skin, temperature extremes, sunlight exposure, and exercise.
- Infections and illnesses: Including viral infections, bacterial infections, and chronic health conditions like thyroid disease or lupus.
- Medications: Some people react to medications like antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or blood pressure medications.
- Stress: Emotional stress is not a direct cause but can exacerbate or trigger flare-ups.
- Food and additives: Certain foods and chemical additives can trigger hives in susceptible individuals.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of chronic hives is crucial for effective management. While the journey to identify triggers and effective treatments can be lengthy, advancements in medical understanding and patient care continue to improve the quality of life for those affected by chronic hives.
Diagnosis of Chronic Hives
Diagnosing chronic hives involves a comprehensive approach to rule out underlying conditions and identify potential triggers. Below is a detailed guide on the modes of diagnosis, a step-by-step approach to diagnosing chronic hives, and the process of differential diagnosis to distinguish it from similar conditions.
Modes of Diagnosis of Chronic Hives
- Medical History Review: The initial step in diagnosing chronic hives involves a thorough review of the patient’s medical history, including the duration of hives, possible triggers (such as food, medication, or stress), and any family history of similar conditions.
- Physical Examination: A detailed physical examination is conducted to observe the characteristics of the hives and to check for any associated signs, such as angioedema (swelling).
- Allergy Testing: While chronic hives are not always related to allergies, allergy tests (such as skin prick tests or blood tests for specific IgE antibodies) can help identify potential allergens in some cases.
- Blood Tests: Comprehensive blood tests can be performed to rule out underlying conditions that might cause or exacerbate hives, including autoimmune disorders, thyroid disease, and infections.
- Autoimmune Screens: Since chronic hives can be associated with autoimmune conditions, tests for autoantibodies, such as the anti-thyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibodies, may be recommended.
- Dermatological Consultation: In some cases, a referral to a dermatologist for further evaluation and specialized tests, such as a biopsy of the hive, may be necessary.
Step-by-Step Approach to Diagnosing Chronic Hives
- Gather Comprehensive Medical History: Begin with a detailed patient interview focusing on the onset, duration, and pattern of hives, as well as any potential triggers or familial predisposition.
- Conduct Physical Examination: Perform a thorough examination of the skin to assess the hives and any associated symptoms.
- Initiate Preliminary Tests: Order basic blood tests and consider allergy testing to exclude common triggers and underlying conditions.
- Evaluate for Autoimmune Conditions: If initial tests are inconclusive, proceed with autoimmune screens to identify any related disorders.
- Consultation and Specialized Testing: Refer to a dermatologist for further evaluation if the diagnosis remains unclear or if specialized tests are deemed necessary.
- Review and Diagnosis: Collect and review all test results, consider the findings in conjunction with the clinical presentation, and arrive at a diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing Chronic Hives from Similar Conditions
Differential diagnosis is crucial in distinguishing chronic hives from other conditions that present with similar symptoms. These conditions include:
- Contact Dermatitis: Characterized by red, itchy rash triggered by direct contact with a substance.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): A condition that makes the skin red and itchy, often seen in people with a history of allergies.
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune condition that causes cells to build up rapidly on the skin surface, forming scales and red patches.
- Heat Rash: A skin condition that often arises in hot, humid conditions, causing small, itchy bumps.
- Insect Bites and Stings: These can sometimes mimic hives but are usually localized to the site of the bite or sting.
To differentiate chronic hives from these conditions, healthcare providers rely on the patient’s history, the appearance and distribution of the rash, and sometimes, specific diagnostic tests. Understanding the nuances of each condition and their presentation is key to accurate diagnosis and effective management.
However, diagnosing chronic hives is a multifaceted process that requires careful evaluation of the patient’s history, physical examination, and a variety of diagnostic tests. By systematically ruling out underlying causes and distinguishing chronic hives from similar conditions, healthcare providers can develop an effective treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Treatment Options for Chronic Hives
Effective treatment strategies aim not only to reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks but also to minimize side effects, ensuring patients can lead more comfortable and fulfilling lives.
First-Line Treatments
First-line treatments for chronic hives focus on non-invasive, readily available options designed to control symptoms with minimal risk:
- Antihistamines: These medications are the cornerstone of chronic hives management. They work by blocking the release of histamine, a chemical your body produces in response to an allergen, which causes itching and swelling. Low-sedation antihistamines are preferred for their fewer side effects, allowing for daily use without significant drowsiness.
- Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists: Often used in conjunction with antihistamines, these drugs can provide additional symptom relief by targeting other inflammatory pathways involved in hives.
- H2 Blockers: Adding these medications to antihistamines can offer further benefits. H2 blockers, typically used to treat acid reflux, can also help manage skin reactions by blocking a different set of histamine receptors.
Second-Line Treatments
When first-line treatments are insufficient, doctors may recommend second-line options:
- Omalizumab (Xolair): This injectable medication is approved for chronic hives unresponsive to antihistamines. It works by targeting and blocking immunoglobulin E (IgE), a key player in the allergic response, thus preventing the occurrence of hives.
- Corticosteroids: For short-term relief of severe symptoms, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed. However, due to their potential for serious side effects, their use is generally limited to brief courses.
- Cyclosporine: An immunosuppressant drug that can be effective in treating chronic hives by reducing the immune system’s activity. Like corticosteroids, cyclosporine is typically considered only after other treatments have failed due to its risk profile.
Emerging Treatments and Research Insights
The landscape of chronic hives treatment is evolving, with ongoing research shedding light on new therapeutic avenues:
- Biologic Therapies: Beyond omalizumab, newer biologic agents targeting different aspects of the immune response are under investigation. These treatments, which include drugs that inhibit interleukins involved in inflammation, hold promise for more targeted and effective management of chronic hives.
- Diet and Lifestyle Modifications: Emerging evidence suggests that certain dietary and lifestyle changes may benefit some patients, though research is still in the early stages. Tailoring diets to eliminate identified triggers and incorporating stress-reduction techniques could complement medical treatments.
- Gene Therapy and Molecular Insights: Advances in understanding the genetic and molecular basis of chronic hives are paving the way for innovative treatments. Gene therapy and personalized medicine approaches are in the research phase but offer hope for more precise interventions in the future.
With ongoing research and the development of new treatments, the outlook for individuals with chronic hives continues to improve. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to find the most effective treatment plan for their specific condition, aiming for the best possible quality of life.
Managing chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, can be a daunting task, but with the right lifestyle adjustments, home care strategies, patient education, and support systems, living with this condition can become more manageable. This guide provides insights into coping strategies and the importance of a supportive community to navigate the challenges of chronic hives.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Care Strategies
Making small changes in your daily routine can significantly impact the management of chronic hives. Here are some key lifestyle adjustments and home care strategies:
- Avoid Known Triggers: Keep a diary to track activities, foods, and products that may trigger hives. Common culprits include certain foods, alcohol, caffeine, stress, and extreme temperatures.
- Dress Comfortably: Wear loose, smooth-textured cotton clothing to avoid irritating the skin.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool, wet cloths to the affected areas can help soothe irritation and reduce itching.
- Gentle Skincare: Use mild, fragrance-free soaps and moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and prevent irritation.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress, which is often a trigger for chronic hives.
Importance of Patient Education and Support Groups
Understanding chronic hives is crucial in managing the condition effectively. Patient education about the nature of chronic hives, potential triggers, and treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their health. Healthcare providers can offer valuable resources and information on managing chronic hives.
Support groups play a vital role in coping with chronic hives. They provide a platform for sharing experiences, tips, and emotional support. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with chronic hives can be incredibly reassuring and reduce feelings of isolation.
Coping Strategies for Living with Chronic Hives
Living with chronic hives requires adopting coping strategies that help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
- Developing a Treatment Plan: Work with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan. This may include medications such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, or other immune-modulating drugs.
- Educational Resources: Utilize resources provided by healthcare professionals, reputable websites, and patient advocacy groups to stay informed about the latest treatments and research.
- Mental Health Support: Consider counseling or therapy to help deal with the emotional impact of chronic hives. Mental health professionals can offer strategies for coping with anxiety, depression, and stress related to living with a chronic condition.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep. This can help improve overall health and potentially reduce the severity of hives.
Managing chronic hives is a multifaceted approach that involves lifestyle changes, education, support, and coping mechanisms. By implementing these strategies, individuals living with chronic hives can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by the condition. Remember, you are not alone, and with the right support and management strategies, you can navigate the complexities of chronic hives.
When to Seek Help for Chronic Hives
Living with chronic hives can be both uncomfortable and frustrating, impacting your daily life and well-being. Recognizing when it’s time to seek medical attention is crucial in managing your condition effectively. Here, we guide you through the signs that indicate a need for professional help, how to navigate the healthcare system to find the right specialist, and what to prepare before your appointment to ensure you get the most benefit.
Recognizing Signs That Require Medical Attention
Chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, are characterized by red, itchy welts on the skin that persist for six weeks or longer. While they may not always indicate a severe health issue, certain signs should prompt you to seek medical help:
- Persistence or Worsening of Symptoms: If your hives do not improve with over-the-counter treatments within a few weeks, or if symptoms worsen, it’s time to consult a doctor.
- Severe Discomfort or Pain: When hives cause severe itching, burning, or pain, affecting your sleep or daily activities, professional guidance can offer relief.
- Accompanying Symptoms: If you experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling in the face, lips, or tongue, or dizziness, seek immediate medical attention, as these could indicate a severe allergic reaction.
- Impact on Quality of Life: When chronic hives significantly impact your quality of life, including emotional distress or social withdrawal, professional help can provide not only medical but also emotional support.
Navigating Healthcare: Choosing the Right Specialist
The path to finding relief from chronic hives often involves consulting with specialists who understand the intricacies of this condition:
- Allergist/Immunologist: These specialists are experts in allergic diseases and immune system disorders. They can perform tests to identify triggers and recommend treatment plans to manage symptoms.
- Dermatologist: A dermatologist specializes in skin conditions and can offer treatments specifically tailored to manage the skin’s reaction in chronic hives.
Choosing the right specialist depends on your symptoms and medical history. Your primary care physician can provide a referral based on your specific needs.
Preparing for Your Appointment: What to Know and What to Ask
Maximizing the benefit of your visit to the specialist involves preparation. Here’s how to get ready for your appointment:
- Medical History and Symptom Journal: Keep a detailed record of your symptoms, triggers, and any treatments you’ve tried, including their effects. This information is invaluable for your specialist.
- List of Medications: Include all medications, supplements, and over-the-counter remedies you are taking or have taken for your hives.
- Questions to Ask: Prepare a list of questions for your specialist. Consider asking about potential triggers, diagnostic tests, treatment options, lifestyle adjustments, and prognosis.
Seeking medical help for chronic hives is a step toward regaining control of your life and comfort. Recognizing the signs that warrant professional advice, choosing the appropriate specialist, and preparing for your appointment can significantly improve your management of chronic hives, leading to better health outcomes and quality of life.
FAQs on Chronic Hives Treatment
What are chronic hives?
Chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, are red, itchy welts that appear on the skin. Unlike acute hives, which may last a few days to a few weeks, chronic hives persist for six weeks or more, often without an identifiable cause. These welts can vary in size and may join together to form larger areas of swelling.
What causes chronic hives?
The exact cause of chronic hives is often difficult to pinpoint. In some cases, they may be an autoimmune response, where the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues. Other potential triggers include infections, stress, exposure to certain chemicals, temperature changes, and pressure on the skin. However, in many cases, no specific cause is identified.
How are chronic hives treated?
Treatment for chronic hives focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing outbreaks. Common treatments include:
- Antihistamines: These are the first-line treatment and can be taken daily to reduce itching and swelling.
- Corticosteroids: For more severe cases, short-term use of corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation.
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists: These may be used alongside antihistamines to enhance symptom control.
- Immunosuppressants: In cases resistant to other treatments, medications that modulate the immune system may be considered.
- Biologic drugs: Omalizumab (Xolair) is a biologic therapy specifically approved for chronic hives that haven’t responded to antihistamines.
Can diet affect chronic hives?
While there’s no one-size-fits-all diet for managing chronic hives, some people find that certain foods can trigger their symptoms. Keeping a food diary can help identify potential food triggers. It’s also advisable to maintain a balanced diet and stay hydrated to support overall health.
Are there any natural remedies for chronic hives?
Some natural remedies may provide relief, although it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying them. These include:
- Cool compresses: Applying a cool, wet cloth to the affected area can help soothe itching and reduce inflammation.
- Oatmeal baths: Taking an oatmeal bath can provide relief from itching and help soothe the skin.
- Aloe vera: Applying aloe vera gel to the skin can help reduce redness and inflammation.
When should I see a doctor for chronic hives?
It’s important to see a doctor if you experience chronic hives, especially if they persist for more than six weeks, are severe, or are accompanied by other symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling around the eyes or mouth, or dizziness. A healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan for you.
Conclusion
We encourage patients not to lose hope and to remain proactive in their care. Chronic hives, while persistent and sometimes baffling, can often be managed effectively with the right approach and support. Remember, you are not alone in this fight. With the right knowledge and resources, alongside a supportive healthcare team, managing chronic hives becomes a more navigable journey.
In closing, understanding, diagnosing, and effectively treating chronic hives is a critical step towards reclaiming your health and well-being. Let this article serve as a resource and a reminder of the power of comprehensive care and the importance of open communication with your healthcare provider. Together, you can find a path forward, toward relief and better health.