Prostatitis Symptoms: Prostatitis is a common yet frequently misunderstood condition that affects the prostate gland, a vital part of the male reproductive system.
This condition manifests in various forms, each presenting a unique set of symptoms and challenges.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of prostatitis is essential for effective diagnosis and management.
What is Prostatitis?
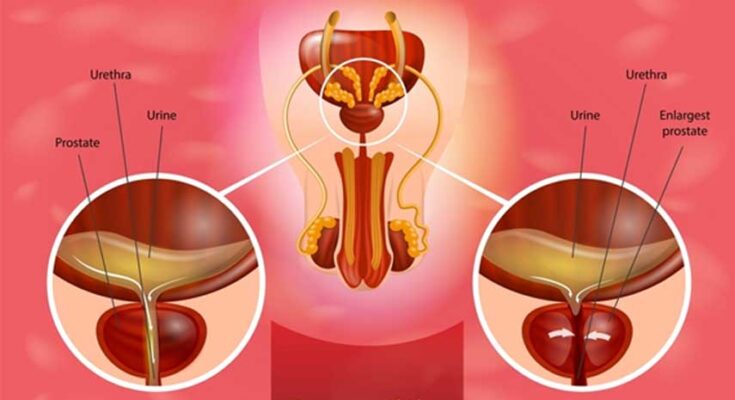
Prostatitis is a common condition that involves inflammation of the prostate gland, a small walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder in men. This gland is crucial for the production of seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. Prostatitis can affect men of all ages and is characterized by a variety of symptoms that may include pain, difficulty urinating, sexual dysfunction, and general discomfort in the pelvic area. The severity and persistence of symptoms can vary, making it essential for affected individuals to seek medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Prostatitis
Prostatitis is categorized into four main types, each with distinct characteristics and causes:
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: This is the least common but most severe form. It is caused by a bacterial infection and can lead to severe urinary symptoms and other systemic symptoms like fever and chills. Immediate medical treatment is crucial to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: Similar to the acute version but less severe, this type involves a persistent bacterial infection that can come and go over time. Symptoms might be less pronounced and can fluctuate in intensity, often requiring prolonged treatment with antibiotics.
- Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP/CPPS): This is the most common type of prostatitis, though its exact cause is often unclear. Symptoms include pelvic or genital pain without evidence of urinary tract infection, and they may persist for more than three months. Managing this form of prostatitis can be challenging and often requires a combination of treatments.
- Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis: This type is often diagnosed incidentally during examinations for other conditions. It is characterized by inflammation of the prostate found on biopsy or lab tests without any noticeable symptoms. Typically, no treatment is needed unless it affects fertility or other conditions are present.
If you suspect you might be suffering from any form of prostatitis, consulting with a healthcare provider is strongly advised.
Symptoms of Prostatitis
Understanding the symptoms associated with each type can aid in early detection and effective management. Here, we explore the common symptoms of both acute and chronic prostatitis, highlighting how these symptoms can vary between the two.
Common Symptoms of Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Acute bacterial prostatitis is typically characterized by sudden and severe symptoms, including:
- Painful urination: Experiencing pain or burning sensations during urination is a prominent symptom.
- Urinary urgency: Frequent and sudden urges to urinate, often with little urine passed.
- Pelvic pain: Sharp or severe pain in the pelvic area, including the lower back and genital area.
- Flu-like symptoms: Many patients report fever, chills, and body aches, similar to flu symptoms.
- Painful ejaculation: Experiencing pain during or after ejaculation is another common complaint.
Common Symptoms of Chronic Prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis, which may not stem from a bacterial infection, often presents with milder, but persistent, symptoms:
- Dull pelvic pain: Ongoing discomfort or pain in the pelvic region that can last for months.
- Urinary symptoms: Persistent discomfort during urination, including a burning sensation or difficulty starting and stopping urine flow.
- Sexual dysfunction: This may include erectile dysfunction or painful ejaculation.
- Psychological impact: Chronic discomfort can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression, further complicating symptoms.
Variations in Symptoms Between Acute and Chronic Prostatitis
The symptoms of prostatitis vary significantly between its acute and chronic forms:
- Intensity of symptoms: Acute prostatitis symptoms are more intense and sudden compared to the often mild and developing symptoms of chronic prostatitis.
- Nature of pain: Acute prostatitis usually involves sharp, severe pain, whereas chronic prostatitis features dull, persistent pain.
- Systemic symptoms: Flu-like systemic symptoms such as fever and chills are typically associated with acute prostatitis but are rare in chronic prostatitis.
- Duration and persistence: Symptoms of acute prostatitis are short-lived with proper treatment, while symptoms of chronic prostatitis can persist or recur over a longer period.
However, understanding these symptoms and their variations can help individuals seek timely medical intervention, enhancing the effectiveness of treatment and improving quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors of Prostatitis
This condition can affect men of all ages and has various causes and risk factors that can increase susceptibility. Understanding these can help in prevention and management strategies.
Causes of Prostatitis
The causes of prostatitis vary depending on the type of prostatitis diagnosed. Here are the primary causes:
- Bacterial Infection: Acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by bacterial infections, often the same bacteria responsible for causing urinary tract infections. Chronic bacterial prostatitis, although less common, involves persistent bacterial infection.
- Nonbacterial Prostatitis: This form, also known as Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS), is not due to bacterial infection and the exact cause is often unknown.
- Prostatic Stones: Tiny stones found within the prostate gland can harbor bacteria and contribute to chronic inflammation.
- Urinary Catheter Use: The use of catheters can sometimes lead to bacterial infections, which can spread to the prostate.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Certain STIs can lead to prostatitis, highlighting the importance of safe sexual practices.
Risk Factors of Prostatitis
Several factors can increase the risk of developing prostatitis:
- Recent Urinary Tract Infection: A recent UTI can increase the risk of developing bacterial prostatitis.
- Bladder Outlet Obstruction: Conditions that restrict urine flow, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can predispose men to prostatitis.
- Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake can lead to concentrated urine, which may irritate the prostate.
- Pelvic Trauma: Any trauma or injury to the pelvic area can increase the risk of prostatitis.
- Age: Men of any age can develop prostatitis, but it is more common in men younger than 50.
- Immune System Disorders: Men with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of infections that can lead to prostatitis.
Discussion of Contributing Factors
In addition to direct causes and risk factors, other elements can contribute to the development and exacerbation of prostatitis:
- Bacterial Infections: Bacteria entering the urinary tract can ascend to the prostate, leading to infection and inflammation. Acute infections can become chronic if not adequately treated.
- Immune System Issues: An immune system that is either too active or underactive can fail to properly respond to infections or may cause unnecessary inflammation in the prostate.
- Nerve Damage in the Pelvic Area: Damage to nerves in the pelvic region can affect prostate health by disrupting the normal functioning of the urinary and reproductive systems, potentially leading to or exacerbating prostatitis.
Awareness and preventative measures, such as maintaining good urinary health, practicing safe sex, and managing health conditions that can lead to prostatitis, are crucial in reducing the prevalence of this condition.
Diagnosis of Prostatitis
Prostatitis, the inflammation of the prostate gland, is a condition that affects many men and requires a thorough diagnostic process to ensure accurate identification and treatment. Understanding the various tests and examinations used in diagnosing prostatitis is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Diagnostic Process for Prostatitis
The diagnosis of prostatitis involves several steps, each designed to gather comprehensive information about the patient’s symptoms and medical history:
- Medical History Review: The doctor will begin by asking about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and any prior urinary or sexual issues. This initial conversation is vital for understanding the context and severity of the condition.
- Symptom Evaluation: Patients typically report symptoms such as pain, difficulties in urination, sexual dysfunction, and sometimes flu-like symptoms. The physician will assess these symptoms to distinguish between the different types of prostatitis.
- Physical Examination: A key component of the diagnostic process is the digital rectal examination (DRE). During this exam, the doctor manually examines the prostate gland through the rectum to check for pain, swelling, or abnormalities.
- Urine Tests: Urine samples are tested for signs of infection or inflammation, which are indicative of prostatitis.
- Microscopic Examination: The urine sample may also undergo microscopic examination to detect white blood cells or bacteria, which suggest an infection.
- Prostate Secretion Test: Post-DRE, secretions from the prostate are sometimes analyzed to identify the presence of bacteria or other infectious agents.
Common Tests and Examinations Used to Identify Prostatitis
Several tests and examinations are commonly used to confirm the diagnosis of prostatitis:
- Urine Culture: This test helps identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection, allowing for targeted antibiotic therapy.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for signs of infection and other related conditions.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the prostate can help visualize the prostate gland and detect abnormalities. It is particularly useful in assessing the size and shape of the prostate.
- CT Scan or MRI: In more complex cases, a CT scan or MRI might be necessary to get a detailed view of the prostate and surrounding tissues.
- Urodynamic Tests: These tests measure the urine flow and bladder pressure, helping to identify issues with bladder function.
- Cystoscopy: In certain situations, a cystoscope is inserted through the urethra to directly view the urinary tract and assess the health of the bladder and prostate.
However, understanding these diagnostic steps and tests is essential for those experiencing symptoms of prostatitis, ensuring they receive a prompt and accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Prostatitis
Here, we explore various treatment strategies that include medications, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
Types of Prostatitis and Corresponding Treatments
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis:
- Medications: Immediate treatment with antibiotics is essential. Common choices include fluoroquinolones or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Pain relief medications and alpha-blockers may also be prescribed to relieve discomfort and urinary symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Increasing fluid intake can help flush out the urinary tract. Rest is generally recommended during the acute phase.
- Surgical Interventions: Rarely required, but drainage may be necessary if there’s abscess formation.
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis:
- Medications: Long-term antibiotic treatment, typically lasting from 4 to 12 weeks, is standard. The exact duration depends on the severity and recurrence of symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Stress management techniques and pelvic floor physical therapy can be beneficial in managing chronic symptoms.
- Surgical Interventions: Surgical removal of the infected prostate segments may be considered in severe cases unresponsive to other treatments.
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP/CPPS):
- Medications: A combination of alpha-blockers, pain relievers, and muscle relaxants are commonly used to manage pain and urinary issues.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, particularly aerobic exercise, can reduce symptoms. Dietary changes, avoiding spicy foods, and reducing caffeine and alcohol intake can also help.
- Surgical Interventions: Surgery is not typically recommended for CP/CPPS unless there is a specific diagnosable reason.
Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis:
- Medications: Generally, no treatment is needed unless there are elevations in PSA levels or complications.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular check-ups and monitoring are advised to ensure no progression of symptoms.
- Surgical Interventions: Not applicable as this type typically does not cause symptoms or require treatment.
However, consulting with a healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan based on individual symptoms and health conditions is essential. Effective management of prostatitis not only improves urinary function and comfort but also enhances overall well-being.
Prevention Tips for Prostatitis
While certain factors like bacterial infections are not always preventable, adopting a range of lifestyle and dietary modifications can help reduce the risk of developing prostatitis. Here are some practical recommendations to help maintain prostate health and prevent the onset of prostatitis.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Stay Active: Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces pressure on the prostate. Activities like jogging, swimming, or cycling can improve your overall health and potentially lower the risk of prostate issues.
- Hydrate Well: Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water, helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract, reducing the risk of infections that could lead to prostatitis.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Maintaining good personal hygiene, especially in the genital area, can help prevent bacterial infections that might lead to prostatitis.
- Manage Stress: High stress levels can impact your immune system and increase the risk of infections. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting: Long periods of sitting can increase pressure on the prostate and the pelvic area. Take regular breaks to stand up and walk around if your job requires sitting for extended periods.
Dietary Tips
- Increase Fruit and Vegetable Intake: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help reduce inflammation and support prostate health. Tomatoes, watermelon, and pink grapefruit, which are high in lycopene, are particularly beneficial.
- Reduce Red Meat and Dairy: Eating less red meat and dairy products can help reduce inflammation and may lower the risk of prostatitis.
- Include Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, mackerel, and flaxseeds, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can support overall prostate health.
- Limit Spicy and Acidic Foods: These can irritate the bladder and worsen symptoms of prostatitis, so it’s best to consume them in moderation.
- Stay Hydrated, but Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both caffeine and alcohol can irritate the urinary tract and bladder. While it’s important to stay hydrated, opt for water or herbal teas over caffeinated drinks and alcohol.
Preventative Healthcare Measures
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help catch symptoms of prostatitis early before they develop into more severe problems.
- Urinate When Needed: Avoid holding urine for long periods, as this can increase the risk of bacterial infections leading to prostatitis.
- Safe Sexual Practices: Practicing safe sex and maintaining good sexual health can prevent sexually transmitted infections, which are potential causes of prostatitis.
- Consider Pelvic Floor Exercises: These exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the prostate and urinary tract, potentially reducing the risk of prostatitis.
By incorporating these lifestyle modifications, dietary tips, and preventative healthcare measures into your routine, you can help safeguard your prostate health and reduce the risk of developing prostatitis.
When to See a Doctor
Knowing when to seek medical advice is crucial for maintaining your health and preventing complications from untreated conditions. Here are guidelines on recognizing severe or persistent symptoms and the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Recognizing Severe or Persistent Symptoms
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional promptly:
- Persistent Pain: Any pain that lasts longer than a few days or is severe enough to disrupt your daily activities should be evaluated by a doctor.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying can be a sign of an underlying health condition.
- High Fever: A fever above 102°F (38.9°C) or one that lasts more than three days indicates a need for medical evaluation.
- Difficulty Breathing: Shortness of breath or labored breathing that occurs suddenly or progressively worsens should not be ignored.
- Changes in Mental Status: Sudden confusion, alterations in consciousness, or severe disturbances in mental faculties warrant immediate medical attention.
- Unusual Bleeding or Bruising: These symptoms can indicate serious conditions such as bleeding disorders or other underlying issues.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and timely treatment are pivotal for many health conditions, often improving outcomes and enhancing quality of life:
- Better Prognosis: Early stages of diseases are generally more manageable and have a wider range of treatment options available.
- Prevent Complications: Timely medical care can prevent conditions from worsening or leading to irreversible damage.
- Cost-Effective: Early intervention can reduce the need for more extensive and expensive treatments later.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing exactly what you are dealing with can reduce anxiety and help in planning for the future.
If you’re unsure whether your symptoms warrant a doctor’s visit, it’s always better to err on the side of caution. Seeking medical advice early can be the key to effective treatment and recovery.
FAQs about Prostatitis Symptoms
What is prostatitis?
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland, which is part of the male reproductive system. It can affect men of all ages and is categorized into several types, each with distinct symptoms and causes.
What are the common symptoms of prostatitis?
Common symptoms of prostatitis include pain in the groin, pelvic area, or genitals, and difficulties with urination such as urgency, discomfort, or frequent need to urinate, especially at night. Other symptoms might include painful ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, or flu-like symptoms in cases of bacterial prostatitis.
Does prostatitis cause severe pain?
Yes, prostatitis can cause severe pain, particularly in the pelvic area or lower back. Acute bacterial prostatitis can also cause intense pain, swelling in the prostate gland, and flu-like symptoms, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Can prostatitis affect sexual function?
Yes, prostatitis can impact sexual function, leading to painful ejaculation or erectile dysfunction. These symptoms can affect a man’s sexual health and overall quality of life, making it important to seek treatment.
Is prostatitis a common condition?
Yes, prostatitis is a fairly common condition that affects men of all ages but is most prevalent in men younger than 50. It’s estimated that up to 50% of men experience symptoms of prostatitis at some point in their lives.
How is prostatitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of prostatitis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination including a digital rectal exam, and possibly urine tests, blood tests, or a prostate secretion test to identify bacteria or other signs of inflammation.
What treatments are available for prostatitis?
Treatment for prostatitis depends on the type. Bacterial prostatitis is treated with antibiotics, while chronic forms may require a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes physical therapy. Pain management and addressing urinary symptoms are common aspects of treatment.
Can lifestyle changes help manage prostatitis symptoms?
Yes, certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms of prostatitis. These include staying hydrated, reducing spicy food intake, managing stress, and performing pelvic floor exercises to help ease pain and urinary symptoms.
Is prostatitis contagious?
No, prostatitis itself is not contagious. However, if it is caused by a sexually transmitted infection, the underlying infection could be contagious.
When should someone see a doctor for prostatitis symptoms?
It is advisable to see a doctor if you experience any of the common symptoms of prostatitis, especially if they persist or cause significant discomfort. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
In summary, recognizing the symptoms of prostatitis and understanding its causes are crucial steps in managing this common but often overlooked condition. Symptoms such as pelvic pain, difficulties in urination, and sexual dysfunction are not only discomforting but can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Awareness and education about prostatitis can lead to earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any symptoms associated with prostatitis, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. Seeking timely medical advice can lead to better health outcomes and prevent complications. Remember, prioritizing your health is key to maintaining a fulfilling and active life.
References
For those seeking more detailed information about the symptoms of prostatitis and their management, the following reputable sources offer valuable insights:
- Mayo Clinic: Provides a comprehensive overview of prostatitis, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Read more about prostatitis on the Mayo Clinic website.
- WebMD: Features an extensive article on the different types of prostatitis, their symptoms, and the latest treatment methodologies. Explore prostatitis symptoms at WebMD.
- National Health Service (NHS): Offers in-depth information on the symptoms of prostatitis and practical advice on managing the condition. Visit NHS for more information on prostatitis.
- Harvard Health Publishing: Provides an expert analysis of chronic prostatitis, focusing on symptoms, diagnosis, and long-term management strategies. Learn about chronic prostatitis at Harvard Health.
- MedlinePlus: A resource by the U.S. National Library of Medicine, offering detailed medical information and research updates on prostatitis. Read about prostatitis at MedlinePlus.
These sources are recognized for their authority and accuracy in medical information, making them excellent resources for anyone looking to understand more about prostatitis and its implications.