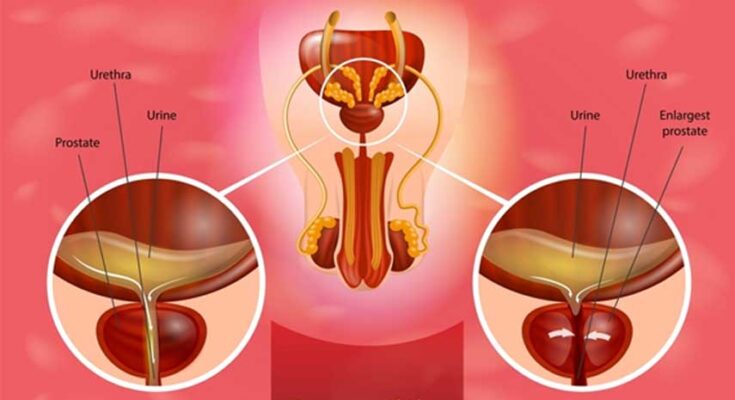
Prostatitis Treatment: Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland, a critical component of the male reproductive system.
This condition can affect men of all ages and often brings with it a variety of uncomfortable symptoms.
Understanding the nature of prostatitis, its various forms, and effective treatments is essential for effective management and recovery.
Understanding Prostatitis
Prostatitis is an inflammatory condition of the prostate gland that affects men of various ages. It is essential to recognize the symptoms and understand the underlying causes to seek appropriate treatment and manage the condition effectively.
Types of Prostatitis
Prostatitis is categorized into four main types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches:
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: This type is the least common but most severe, characterized by sudden and severe symptoms. It is caused by a bacterial infection and requires immediate medical treatment.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: A recurrent bacterial infection of the prostate, this form presents milder symptoms than the acute version but can be troublesome due to its persistent nature.
- Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP/CPPS): This is the most common type of prostatitis, which isn’t caused by a bacterial infection and can be more challenging to treat. Symptoms may vary and persist over a long time.
- Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis: Men with this type of prostatitis do not exhibit symptoms despite the presence of inflammation.
Common Symptoms of Prostatitis
Symptoms of prostatitis can vary depending on the type but commonly include:
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating.
- Frequent urges to urinate, especially at night.
- Difficulty starting urination or an interrupted flow of urine.
- Pain in the abdomen, groin, or lower back.
- Painful ejaculation.
- Presence of blood in urine or semen.
Potential Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of prostatitis differ based on the type of prostatitis, with some common risk factors including:
- Bacterial Infection: For acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis, bacteria that enter the prostate from the urinary tract or through direct contact are the primary culprits.
- Pelvic Trauma: Any trauma to the pelvic area, such as injuries from sports or accidents, can increase the risk of developing prostatitis.
- Urinary Catheter Use: The use of catheters can sometimes lead to bacterial infections that may spread to the prostate.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake may increase the risk of urinary infections, leading to prostatitis.
- Sexual Activity: Frequent or intense sexual activity can sometimes lead to nerve and muscle strain, contributing to the onset of CP/CPPS.
- Immune System Disorders: An immune system that is either too active or not active enough can lead to inflammation without infection.
However, early consultation with a healthcare provider can lead to better outcomes and alleviate the discomfort associated with prostatitis.
Diagnosing Prostatitis
Accurately diagnosing prostatitis is crucial for effective treatment. Here, we outline the diagnostic steps used to identify this condition, including initial assessments, physical examinations, laboratory tests, and advanced diagnostic techniques.
Initial Assessment
- Patient History: Collecting detailed patient history is the first step. This includes symptoms, pain duration and severity, urinary patterns, sexual history, and any previous urological issues.
- Symptom Questionnaire: Doctors often use standardized questionnaires like the National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) to quantify symptoms and impact on quality of life.
- Urinary Diary: Patients may be asked to keep a record of their urinary habits, noting frequency, urgency, and pain.
Physical Examinations
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): This primary physical test involves the doctor feeling the prostate gland through the rectal wall to check for size, tenderness, and abnormalities.
- Urine Flow Test: Measures the strength and amount of urine flow to evaluate bladder and urethra functionality.
- Post-Void Residual Volume Test: Determines the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination, assessing potential blockages or urinary retention.
Laboratory Tests
- Urine Tests: Analysis of urine can detect signs of infection and inflammation. This may include a urinalysis or urine culture.
- Blood Tests: Check for signs of infection and other prostate-related issues, such as a PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) test to rule out prostate cancer.
- Semen Analysis: In chronic cases, analyzing semen can help identify the presence of bacteria or other inflammatory cells.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS): A probe is used to create an image of the prostate via the rectum, helping to identify abnormalities or assess prostate size.
- Cystoscopy: A thin scope is inserted through the urethra to view the urethra and bladder, checking for structural problems.
- MRI of the Pelvis: Provides a detailed image of the pelvic area, including the prostate, which is useful for diagnosing complications of prostatitis or ruling out other conditions.
By utilizing these diagnostic steps, healthcare providers can effectively identify prostatitis and tailor a treatment approach that best fits the patient’s condition. Early and accurate diagnosis is key to managing symptoms and improving outcomes.
Prostatitis Treatment Options
Understanding the range of treatment options available can help manage this condition effectively. Here we explore the various strategies to alleviate symptoms, manage pain, and improve overall prostate health.
Treatment Goals
The primary objectives in treating prostatitis include:
- Alleviating Symptoms: Reducing discomfort, urinary problems, and sexual dysfunction.
- Eliminating Infection: For bacterial types, eradicating the underlying infection with appropriate medications.
- Preventing Complications: Avoiding the progression to chronic prostatitis or other related health issues.
- Improving Quality of Life: Enhancing daily functioning and overall well-being.
Methods of Prostatitis Treatment
Prostatitis treatment varies based on whether the condition is acute or chronic, and whether it is bacterial or non-bacterial:
- Antibiotics: Used primarily for bacterial prostatitis, the type and duration of antibiotics depend on the severity of the infection.
- Alpha-blockers: These medications help relax the muscle fibers in the prostate and bladder neck, easing urinary symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory Agents: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Thermal Therapy: Heat therapy through sitz baths can be effective in reducing pelvic discomfort.
- Prostate Massage: In some cases, massaging the prostate can help relieve pressure and buildup in the gland.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain is a critical component of the treatment for prostatitis. Effective strategies include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Heat Therapy: Applying heat pads or taking warm baths can help soothe muscle pain and pelvic discomfort.
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can help minimize symptoms.
- Stress Reduction: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and other relaxation methods can alleviate stress, which might exacerbate pain.
Role of Physical Therapy in Managing Chronic Prostatitis
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of chronic prostatitis, particularly in cases of chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS). Here’s how it helps:
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Training: Physical therapists can teach exercises to strengthen pelvic muscles, improving urinary control and reducing pain.
- Biofeedback: This method helps patients gain awareness and control over pelvic muscles, aiding in effective management of symptoms.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques including stretching and myofascial release can decrease tension in the pelvic floor, thus alleviating pain.
Always consult with a healthcare provider for a diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
Complications and Management of Prostatitis
Understanding these potential risks is crucial for timely and effective management. Moreover, managing chronic prostatitis and recurrent symptoms effectively can help mitigate these risks and lead to better health outcomes.
Possible Complications of Untreated Prostatitis
- Bacterial Spread: In cases of bacterial prostatitis, the infection can spread to the bloodstream or nearby organs, leading to more severe health issues such as sepsis or epididymitis.
- Bladder Issues: Persistent inflammation can lead to problems with bladder control, including urinary retention or severe urinary tract infections.
- Prostate Abscesses: Untreated prostatitis can result in the formation of abscesses in the prostate, which are collections of pus that require surgical intervention.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Chronic prostatitis can impact sexual function, leading to painful ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, or reduced libido.
- Psychological Impact: The ongoing pain and discomfort associated with untreated prostatitis can lead to psychological issues, including depression and anxiety.
- Fertility Problems: Chronic inflammation can affect the prostate gland and adjacent areas critical for reproductive function, potentially impacting fertility.
Managing Chronic Prostatitis and Recurrent Symptoms
- Regular Medical Evaluations: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring symptoms and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
- Antibiotic Therapy: For bacterial prostatitis, long-term antibiotic therapy may be required to eradicate the infection completely.
- Pain Management: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to reduce pain and swelling. In more severe cases, stronger pain relief medications might be prescribed.
- Thermal Therapy: Techniques like microwave therapy or heat therapy can help reduce symptoms by promoting blood flow and relaxing muscles in the pelvic area.
- Physical Therapy: Pelvic floor physical therapy can help relieve the symptoms of chronic prostatitis by addressing muscle tightness and dysfunction.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce the psychological impact of living with chronic prostatitis.
- Dietary Changes: Adjusting one’s diet to include more anti-inflammatory foods and less irritative substances like caffeine and spicy foods can help manage symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular exercise helps improve overall body health and can reduce the symptoms of prostatitis by improving immune function and reducing stress.
By addressing both the potential complications and the management strategies for chronic prostatitis, patients can better navigate their condition and improve their quality of life. Prompt and effective treatment is key to managing this often challenging condition.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Remedies for Prostatitis
Managing this condition can be significantly improved through various home remedies and lifestyle adjustments. Below, we explore effective changes you can make at home to alleviate the symptoms of prostatitis.
1. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of fluids is crucial for those suffering from prostatitis. Hydration helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract, reducing the risk of infections and aiding in the relief of urinary symptoms. Aim for 6-8 glasses of water daily, but remember to limit caffeine and alcohol, which can irritate the bladder.
2. Adopt a Prostatitis-Friendly Diet
Diet plays a vital role in managing prostatitis symptoms. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet to reduce inflammation. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as tomatoes, berries, and green leafy vegetables, are particularly beneficial. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and sardines, can also help reduce inflammation. Avoid spicy foods, citrus juices, and hot peppers, which can exacerbate symptoms.
3. Avoid Irritants
Certain substances can aggravate prostatitis symptoms. Reduce or eliminate the consumption of caffeinated beverages, acidic foods, and alcohol. Smoking is another irritant that can worsen symptoms, so quitting smoking is a recommended lifestyle change for those experiencing prostatitis.
4. Exercise Regularly
Engaging in regular exercise can significantly benefit those with prostatitis. Physical activity helps boost the immune system and reduce inflammation. Activities such as walking, jogging, or light aerobic exercises can improve blood flow and help relieve symptoms. It’s important, however, to avoid activities that put pressure on the prostate area, such as biking.
5. Practice Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress can exacerbate symptoms of prostatitis. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial in managing stress levels. These practices not only help reduce stress but also enhance overall well-being, which can improve the management of prostatitis symptoms.
By implementing these lifestyle adjustments and home remedies, individuals with prostatitis can experience significant relief from their symptoms. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment regimen, especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
When to See a Doctor for Prostatitis
If you’re experiencing symptoms that might indicate prostatitis, it’s important to recognize when to seek medical advice. Prostatitis, which refers to inflammation of the prostate gland, can cause uncomfortable and sometimes severe symptoms. Timely consultation with a healthcare provider can lead to quicker diagnosis and management, improving your overall health and comfort.
Signs That Indicate a Need for Immediate Medical Attention
Certain symptoms of prostatitis are more alarming and warrant immediate medical attention. If you experience any of the following, contact your doctor or visit the emergency room:
- Persistent High Fever: A high fever along with chills might indicate a bacterial infection that could require urgent treatment.
- Severe Pain: Intense pain in the pelvic area, lower back, or genital area that doesn’t improve with over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Urinary Retention: Difficulty urinating or an inability to urinate can be a sign of a serious complication and requires immediate attention.
- Blood in Urine: Visible blood in the urine is a concerning symptom that should be evaluated by a healthcare professional without delay.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms, when associated with other signs of prostatitis, could indicate a severe infection.
What to Expect from a Consultation and How to Prepare for It
Knowing what to expect during a consultation for prostatitis can help you prepare effectively and ensure a more productive visit.
- Medical History Review: Be ready to discuss your medical history, including any previous urinary or prostate issues, surgeries, and current medications.
- Symptom Description: Prepare to describe your symptoms in detail, including their onset, duration, and any factors that worsen or alleviate them.
- Physical Examination: Expect a physical exam that may include a digital rectal examination (DRE) to assess the size and condition of your prostate.
- Possible Tests: Your doctor might order urine tests, blood tests, or imaging studies to help diagnose your condition accurately.
- Discussion of Treatment Options: Based on the diagnosis, treatment options will be discussed. These may include medications, lifestyle adjustments, or more specialized treatments.
How to Prepare for Your Consultation
- List Your Symptoms: Write down all your symptoms and other health concerns to ensure you don’t forget to mention them during your visit.
- Document Your Medical History: Have a list of all medications, supplements, and previous surgeries ready.
- Write Down Questions: Prepare a list of questions you have about your symptoms, treatment options, and potential outcomes.
- Bring a Companion: If possible, bring someone with you to help remember the information provided during your consultation.
Seeking prompt medical attention when experiencing signs of prostatitis can significantly impact your health outcomes. Being well-prepared for your consultation can help your healthcare provider offer the best care possible.
FAQs about Prostatitis Treatment
What is prostatitis?
Prostatitis refers to the inflammation of the prostate gland, a small organ in men located below the bladder. It can cause various urinary and pelvic symptoms, affecting men of all ages but is most common in adults under 50.
What are the symptoms of prostatitis?
Symptoms of prostatitis can vary but often include frequent and urgent needs to urinate, pain or burning during urination, pelvic or lower back pain, and sometimes flu-like symptoms.
How is prostatitis diagnosed?
Prostatitis is diagnosed based on medical history, a physical examination including a digital rectal exam, and various tests such as urine tests, blood tests, and possibly imaging studies like ultrasound.
What are the treatment options for prostatitis?
Treatment depends on the cause, but may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, alpha-blockers and pain relievers to ease symptoms, and lifestyle changes such as increased hydration and dietary adjustments.
Is prostatitis contagious?
Bacterial prostatitis can be caused by transmittable bacterial infections; however, the condition itself is not considered contagious. Nonbacterial prostatitis is not infectious and cannot be transmitted between partners.
Can prostatitis be cured?
Bacterial prostatitis often responds well to antibiotics and can be cured with proper treatment. Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, also known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome, is more challenging to treat, and management focuses on relieving symptoms.
How can I prevent prostatitis?
Preventive measures include maintaining good urinary tract health, staying hydrated, practicing safe sex, and regular medical check-ups to manage risk factors effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, prostatitis is a condition that affects the prostate gland, which can manifest in various forms, including acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. Effective diagnosis involves a thorough examination, including medical history, physical examinations, and potentially, urine tests, blood tests, and imaging studies. Treatment strategies vary depending on the type of prostatitis but may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, alpha-blockers, and in some cases, more holistic approaches such as physiotherapy or acupuncture.
It is crucial for individuals diagnosed with prostatitis to adhere closely to the prescribed treatment plans and maintain regular follow-ups with their healthcare provider. Professional guidance ensures the management of symptoms and prevents complications. Patients are encouraged to communicate openly with their healthcare team about their symptoms and treatment progress. Remember, early intervention and consistent management are key to effectively handling prostatitis.
References
For those seeking more detailed information on prostatitis treatment and the latest research findings, the following sources are highly recommended. These resources offer in-depth discussions on various treatment methodologies, the effectiveness of current medical interventions, and ongoing research in the field. They are excellent for validating the information provided and for further exploration into the subject.
- Mayo Clinic – The Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive overview of prostatitis, including symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. Explore their detailed guide at Prostatitis Treatment at Mayo Clinic.
- National Health Service (NHS) – The NHS offers valuable insights into the management and treatment of prostatitis, covering everything from lifestyle adjustments to medical treatments. Read more on their official page: NHS Overview of Prostatitis.
- PubMed Central – For those interested in the scientific and medical research aspects, PubMed Central provides access to numerous research articles and clinical studies on prostatitis. Access their resources at PubMed Central Prostatitis Articles.
- WebMD – WebMD is a trusted source for patient-friendly information on the symptoms, causes, and treatments of prostatitis. Their resource can be accessed here: WebMD on Prostatitis.
These sources are respected for their credibility and depth of information. They provide both patients and healthcare providers with valuable knowledge on the current best practices for treating prostatitis.