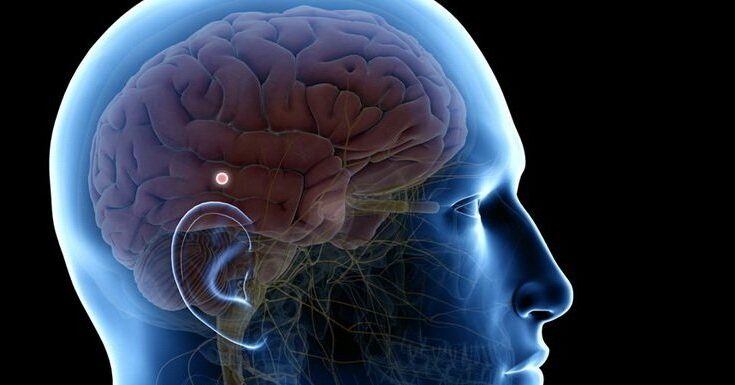
Pineoblastoma Symptoms: Pineoblastoma is a rare, aggressive type of brain tumor that originates in the cells of the pineal gland.
This gland, which is responsible for producing the hormone melatonin, plays a pivotal role in regulating sleep-wake cycles.
Pineoblastoma is classified as a primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) and is most commonly diagnosed in children, although it can occasionally affect adults.
What is Pineoblastoma?
Pineoblastoma is a rare and aggressive type of brain tumor classified as a primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET). This malignancy primarily arises in the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain that produces the hormone melatonin, which regulates sleep patterns. Due to its origin, pineoblastomas are part of a larger group of cancers known as pineal region tumors.
Classification as a Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET)
As a PNET, pineoblastoma belongs to a group of tumors that originate from primitive (or embryonal) cells in the nervous system that have the potential to develop into various forms of tissue. PNETs are known for their aggressive behavior and tendency to spread, making them particularly challenging to treat. Pineoblastoma, as a type of PNET, shares these characteristics and is treated with a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, depending on the extent of the disease.
Areas of the Brain Affected by Pineoblastoma
The primary area affected by pineoblastoma is the pineal gland, located deep within the brain at the center of the skull. This location makes surgical intervention challenging. The tumor can also affect surrounding structures within the brain, including the third ventricle, which can lead to complications such as hydrocephalus (an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain). This condition can cause symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and changes in vision.
However, understanding pineoblastoma is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Given its aggressive nature, timely and aggressive treatment strategies are essential to improve outcomes for those affected by this challenging brain tumor.
Symptoms of Pineoblastoma
Understanding the symptoms associated with pineoblastoma can aid in early detection and treatment. Here’s a detailed look at the common symptoms and why they occur:
Common Symptoms of Pineoblastoma
- Headaches: Often severe, these headaches are caused by increased pressure in the brain as the tumor grows.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms are typically a direct result of the pressure the tumor exerts on surrounding brain structures, disrupting normal brain function.
- Vision Problems: Patients may experience double vision, blurred vision, or loss of peripheral vision. This occurs because the pineal gland is located near the visual pathways.
- Fatigue and Lethargy: As the tumor impacts the brain, it can interfere with various bodily functions, leading to overwhelming tiredness.
- Balance and Coordination Difficulties: These symptoms arise when the tumor affects the neurological pathways that control physical movements.
- Sleep Disturbances: The pineal gland plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle, and a tumor in this area can disrupt normal sleep patterns.
- Changes in Behavior or Personality: As with many brain tumors, changes in one’s behavior or personality might occur, depending on the tumor’s location and the areas of the brain it affects.
Why These Symptoms Occur
The symptoms of pineoblastoma primarily occur due to the tumor’s location and its effect on the surrounding neural structures. The pineal gland, where pineoblastoma develops, is nestled between the cerebral hemispheres at the brain’s center, near critical structures such as the brainstem and the thalamus. This proximity to crucial neural pathways means that even a small tumor can have significant effects, such as disrupting the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to increased intracranial pressure. This pressure contributes to headaches, nausea, and other neurological symptoms.
Moreover, the pineal gland’s role in regulating hormones and sleep-wake cycles explains why disturbances in sleep and systemic hormonal imbalances occur. The visual disturbances result from the compression of the adjacent visual pathways by the growing tumor.
Early recognition of these symptoms and prompt medical consultation can lead to timely diagnosis and improved management of pineoblastoma, enhancing the quality of life and survival rates for affected individuals.
Causes and Risk Factors of Pineoblastoma
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with pineoblastoma is crucial for early detection and effective management. Here, we explore the potential causes and risk factors linked to this serious condition.
Causes of Pineoblastoma
The exact causes of pineoblastoma remain unclear. However, research suggests that these tumors could arise from genetic mutations in the cells of the pineal gland. These mutations are not typically inherited but occur spontaneously. The rapid division and growth of these mutated cells result in the formation of a pineoblastoma. Current studies are ongoing to identify specific genetic alterations that contribute to the development of this tumor.
Risk Factors of Pineoblastoma
While the specific causes of pineoblastoma are not well-defined, several risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing this tumor:
- Age: Pineoblastoma most commonly affects children and young adults, although it can occur at any age.
- Genetic Syndromes: Certain genetic disorders, such as hereditary retinoblastoma, are associated with an increased risk of developing pineoblastoma. This link is due to mutations in the RB1 gene, which is also implicated in other types of cancers.
- Family History: Although very rare, individuals with a family history of pineoblastoma may have a higher risk, suggesting a possible genetic component that may predispose them to the disease.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to ionizing radiation, particularly during childhood, has been associated with a higher risk of developing various types of brain tumors, including pineoblastoma.
However, early diagnosis and intervention can significantly influence the management and prognosis of those affected by this challenging condition.
Diagnosing Pineoblastoma
Pineoblastoma, a rare and aggressive type of brain tumor found in the pineal gland, requires meticulous diagnostic methods to ensure accurate detection and treatment planning. Early diagnosis is crucial to managing this condition effectively.
Methods of Diagnosing Pineoblastoma
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans are pivotal in the initial detection of pineoblastoma. They provide detailed images of the brain, highlighting any abnormal growths in the pineal gland.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: While not as detailed as MRIs, CT scans can help detect calcifications within tumors, which are sometimes seen in pineoblastoma.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is performed to confirm the diagnosis by examining a small sample of tumor tissue under a microscope. This method determines the exact nature of the cells and the aggressiveness of the tumor.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): This procedure tests cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for tumor markers or cancerous cells that might have spread from the pineal gland.
- Blood Tests: Although not diagnostic for pineoblastoma directly, blood tests can help assess the overall health of the patient and detect markers indicating cancer.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: This imaging test helps to see if the tumor has spread to other parts of the brain or body, which is crucial for staging the disease.
Role of Specialists in the Diagnosis of Pineoblastoma
- Neurologists: They play a key role in assessing neurological symptoms and are often the first to suspect a brain tumor based on clinical evaluations.
- Neurosurgeons: These specialists are involved in the surgical biopsy procedures and in the removal of the tumor, when possible.
- Neuroradiologists: Experts in reading brain images, neuroradiologists help confirm the presence and extent of the tumor using MRI, CT scans, and other imaging techniques.
- Pathologists: Once a biopsy is performed, pathologists analyze the tissue to confirm the type of tumor, which is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
- Oncologists: Medical oncologists evaluate and manage chemotherapy treatments if needed, while radiation oncologists focus on providing targeted radiation therapy.
However, the collaboration among these specialists is essential to devise an effective treatment strategy and provide the best care possible for patients diagnosed with pineoblastoma.
Treatment Options for Pineoblastoma
Due to its severity and complexity, understanding the available treatment options is crucial for patients and their families. This section outlines the goals and current strategies for treating pineoblastoma.
Treatment Goals
The primary objectives in treating pineoblastoma are to:
- Remove the Tumor: Surgical resection aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible, considering the tumor’s location and the risks associated with surgery.
- Minimize Symptoms: Alleviating symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients are key considerations, especially since complete tumor removal may not be possible.
- Prevent Recurrence: Following initial treatment, the focus shifts to preventing the tumor from returning, which is a common challenge in cancer treatment.
- Prolong Survival: Due to the aggressive nature of pineoblastoma, extending the patient’s life while maintaining quality of life is a significant goal.
- Manage Side Effects: Treatment strategies aim to minimize the side effects associated with intensive therapies like chemotherapy and radiation.
Current Treatment Strategies
The treatment of pineoblastoma typically involves a combination of therapies, tailored to the individual’s needs based on the size, location, and genetic makeup of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health. Here are the most common treatment strategies:
- Surgery: The first line of treatment is often surgical removal of the tumor. The goal of surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without causing damage to the surrounding brain structures.
- Radiation Therapy: Postoperative radiation therapy is commonly used to destroy any remaining tumor cells, especially in areas where surgical removal is risky. For pineoblastoma, craniospinal radiation is often recommended to address the risk of tumor spread along the central nervous system.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be used before surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to eliminate any residual tumor cells. In young children, chemotherapy can sometimes be used to delay or reduce the need for radiation therapy to minimize long-term side effects.
- Targeted Therapy: Recent advances have led to the development of targeted therapies that focus on specific genetic components of the tumor. These treatments can potentially reduce the side effects associated with more conventional therapies.
- Clinical Trials: Participating in clinical trials can provide access to new and potentially more effective treatments that are not yet widely available. This is particularly important for treating rare cancers like pineoblastoma, where standard treatments may be limited.
- Supportive Care: Managing symptoms and side effects is a crucial part of treatment, involving a multidisciplinary team to provide comprehensive care and improve patient quality of life.
However, ongoing research and clinical trials continue to explore new possibilities for treating this challenging condition, offering hope for improved treatment approaches in the future.
Prognosis and Outcomes of Pineoblastoma
Understanding the factors that influence prognosis and the statistical outcomes associated with this disease is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the prognosis of pineoblastoma:
- Age at Diagnosis: Younger patients, particularly children, tend to have better outcomes compared to adults. This is due to the differences in tumor biology and the resilience of younger patients to aggressive treatments.
- Extent of Resection: The ability to surgically remove the tumor completely is a significant prognostic factor. Complete resection is often challenging due to the tumor’s location and its proximity to critical brain structures.
- Molecular Genetics: Recent advances in molecular biology have identified specific genetic markers that can influence the aggressiveness of pineoblastomas. For instance, certain mutations might be associated with poorer outcomes.
- Treatment Regimen: The choice of treatment, which typically includes surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, affects prognosis. Patients who respond well to initial treatments often have better long-term outcomes.
- Presence of Metastasis: The spread of cancer to other parts of the central nervous system or the body significantly worsens the prognosis.
Statistical Outcomes
Given its rarity, comprehensive statistics on pineoblastoma are limited; however, some studies provide insight into the survival rates:
- Overall Survival: The overall 5-year survival rate for pineoblastoma patients can vary, with estimates generally ranging between 30% to 60%. This range reflects the variability in age of patients, the extent of disease at diagnosis, and differences in treatment approaches.
- Impact of Age: Studies have indicated that children under the age of 10 years have a slightly better 5-year survival rate compared to adolescents and adults.
- Advancements in Treatment: Over the past decades, improvements in neurosurgical techniques and more effective chemotherapy and radiation protocols have gradually improved survival rates.
However, the prognosis for pineoblastoma largely depends on a combination of factors including age, genetic characteristics of the tumor, the extent of its removal, and the effectiveness of the subsequent treatment plan.
Managing Symptoms of Pineoblastoma
Here are some effective strategies to manage common symptoms, the role of supportive care and rehabilitation, and the importance of mental health support.
Strategies for Managing Common Symptoms
- Medication Management: Utilize medications to control pain, seizures, and other neurologic symptoms. Regular consultations with a healthcare provider can help adjust dosages and explore new treatment options.
- Nutritional Support: Work with a dietitian to ensure the patient receives adequate nutrition, which can be challenging if the patient experiences nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite.
- Physical Therapy: Engage in physical therapy to manage and improve motor skills and balance issues, which can be affected by the tumor.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent medical checkups are essential to monitor the effects of the tumor and the side effects of treatments, adjusting as necessary to alleviate discomfort.
Role of Supportive Care and Rehabilitation
- Rehabilitative Services: Access to occupational therapy, speech therapy, and physical therapy can help maintain and improve quality of life by addressing the physical and cognitive challenges posed by the tumor.
- Palliative Care: Incorporating palliative care early can help manage symptoms and improve comfort for those with severe manifestations of the disease.
- Holistic Approaches: Consider holistic approaches such as massage, acupuncture, or music therapy to complement medical treatments and address the broader needs of the patient.
Importance of Mental Health Support for Patients and Families
- Psychological Counseling: Provide access to mental health professionals for both patients and their family members to help cope with the emotional and psychological stress of the disease.
- Support Groups: Participate in support groups where patients and families can connect with others experiencing similar challenges, which can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Educational Resources: Offer educational materials and sessions to help patients and families understand the disease, treatment options, and how to manage day-to-day challenges.
By focusing on these strategies, supportive care, and mental health support, patients with pineoblastoma and their families can navigate the complexities of the disease with better equipped tools and a stronger support network.
FAQs about Pineoblastoma Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of pineoblastoma?
Pineoblastoma typically presents symptoms related to increased pressure within the brain. These symptoms may include headaches, especially in the morning, nausea, vomiting, and double vision. Some individuals might also experience problems with balance, coordination, or walking.
Can pineoblastoma cause changes in behavior?
Yes, changes in behavior and personality can occur with pineoblastoma. This is due to the tumor’s potential impact on the brain’s functioning. Patients might exhibit increased irritability, mood swings, or even subtle cognitive changes such as difficulty concentrating or memory issues.
Does pineoblastoma affect vision?
Pineoblastoma can affect vision, leading to symptoms like blurred or double vision. This happens when the tumor exerts pressure on parts of the brain responsible for visual processing. In some cases, patients might also experience abnormal eye movements or drooping eyelids.
Are there any early warning signs of pineoblastoma?
Early signs of pineoblastoma often mimic common neurological disorders, making them difficult to recognize immediately. These early signs can include persistent headaches, nausea, and fatigue. Due to the tumor’s aggressive nature, symptoms can progress quickly and may worsen over a short period.
How quickly do symptoms of pineoblastoma develop?
The symptoms of pineoblastoma can develop rapidly, reflecting the aggressive growth rate of the tumor. Patients might notice a sudden onset of symptoms or a rapid deterioration in their neurological function, prompting an urgent medical evaluation.
What should I do if I notice symptoms of pineoblastoma in myself or a loved one?
If you or someone you know exhibits symptoms that could be indicative of pineoblastoma, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly impact the outcome and management of this condition. Consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate diagnostic tests.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of Pineoblastoma early is essential for timely intervention and treatment. As we have discussed, the onset of symptoms such as headaches, sleep disturbances, and changes in vision can be indicators of this serious condition.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional without delay. Early medical advice can lead to more effective management and potentially better outcomes.
Remember, your health is paramount, and prompt action could make a significant difference.
References
For those seeking more detailed information about Pineoblastoma symptoms and related medical insights, the following sources are invaluable. Each provides a comprehensive look at Pineoblastoma, enhancing understanding and offering further validation of the information provided in our discussion:
- National Cancer Institute – This site offers a wealth of detailed medical data on various types of brain tumors, including Pineoblastoma. It’s an essential resource for understanding the medical and scientific background of the disease. Visit the National Cancer Institute.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its easy-to-understand patient education materials, the Mayo Clinic provides symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Pineoblastoma. Their resources are highly reputable and useful for patients and caregivers alike. Explore Mayo Clinic’s resources.
- American Cancer Society – A comprehensive guide to Pineoblastoma can be found here, including symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment pathways. The American Cancer Society is a trusted source for cancer information and patient support resources. Learn more at the American Cancer Society.
- PubMed Central – For those interested in the latest research articles and clinical studies on Pineoblastoma, PubMed Central offers a vast collection of peer-reviewed articles. This is a critical resource for those looking to delve deeper into the scientific studies surrounding this condition. Access studies on PubMed Central.
These resources are recommended for their credibility and the depth of information they provide, making them excellent references for anyone looking to further their understanding of Pineoblastoma symptoms and treatments.