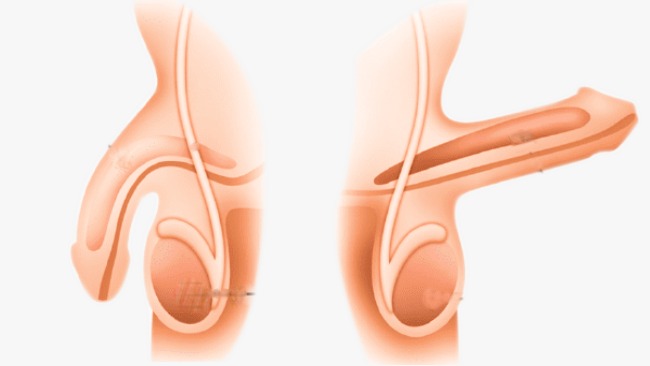
Peyronie Disease Treatment: Peyronie’s Disease is a medical condition characterized by the development of fibrous scar tissue inside the penis, which causes curved, painful erections.
Men suffering from this condition may experience significant bend or pain during erections, which can affect sexual intercourse and lead to psychological distress.
Understanding the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding Peyronie’s Disease
Peyronie’s Disease is a medical condition characterized by the development of fibrous scar tissue inside the penis, leading to curved, painful erections. Men with this condition often experience significant physical and psychological discomfort. Here, we will explore the prevalence and demographics of Peyronie’s Disease, as well as its pathophysiology, to offer a comprehensive understanding of how it develops.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Peyronie’s Disease primarily affects men aged 40 to 70, but it can occur in younger and older men as well. Studies estimate that Peyronie’s Disease may affect between 3% to 9% of the male population. However, the condition is likely underreported due to the embarrassment or discomfort men may feel about discussing symptoms.
The prevalence of Peyronie’s Disease varies by age and other factors:
- Age: The likelihood of developing Peyronie’s Disease increases with age.
- Ethnicity: There is no conclusive evidence linking Peyronie’s Disease to specific ethnic groups, suggesting it can affect men of any ethnicity equally.
- Associated Conditions: Men with certain medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease may have a higher risk of developing Peyronie’s Disease.
Pathophysiology: How Peyronie’s Disease Develops
Peyronie’s Disease begins with trauma or injury to the penis. This injury may not necessarily be severe or even noticeable. It could occur during sexual activity, sports, or as a result of an accident. Following the trauma, an abnormal healing process begins where scar tissue forms in an irregular manner.
The development of Peyronie’s Disease involves several key steps:
- Injury to the Tunica Albuginea: The tunica albuginea, the thick sheath of tissue surrounding the penile chambers that fill with blood during an erection, is damaged. The damage leads to the formation of scar tissue, known as plaque.
- Fibrous Plaque Formation: Over time, this plaque can harden and reduce the elasticity of the penis in the affected area.
- Abnormal Curvature: During an erection, the less flexible scarred part of the penis does not stretch as much as the rest of the penis, causing a bend or curve, which can be painful.
- Pain and Functional Problems: The curvature can make sexual intercourse painful or difficult, and in severe cases, it can lead to erectile dysfunction.
By recognizing the symptoms early and consulting healthcare providers, individuals can manage the condition more effectively and minimize its impact on quality of life.
Symptoms of Peyronie’s Disease
Understanding the symptoms of Peyronie’s disease is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. This guide outlines the early signs, progression of symptoms, and their impact on quality of life and sexual health.
Early Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
The initial symptoms of Peyronie’s disease may be subtle and develop gradually. Here are the early signs to be aware of:
- Painful Erections: One of the first and most common symptoms is pain during erections, which can occur even before any physical deformity is noticeable.
- Penile Curvature: As scar tissue forms, a noticeable bend in the penis may develop. This curvature can occur gradually and may vary in severity.
- Lumps in the Penis: Small, localized hard spots or lumps may be felt under the skin of the penis, indicating the formation of scar tissue.
- Soft Spots or Divots: Some men may notice softer areas or indentations along the shaft, which can affect the shape of the penis during an erection.
- Shortening of the Penis: Peyronie’s disease can cause a noticeable shortening of the penis over time.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty in achieving or maintaining an erection may also be an early sign, often due to pain or the psychological impact of the disease’s physical manifestations.
How Symptoms Can Evolve Over Time
The symptoms of Peyronie’s disease can evolve and change as the condition progresses. Here’s how symptoms may develop over time:
- Increase in Curvature: Without treatment, the curvature of the penis may become more pronounced.
- Pain Changes: While pain during erections is common in early stages, it may actually decrease over time, even as the physical deformity worsens.
- Stability of Symptoms: After a period of progression, symptoms often stabilize within 12-18 months, at which point the condition may not continue to worsen.
Impact on Quality of Life and Sexual Health
The effects of Peyronie’s disease extend beyond physical symptoms, impacting emotional and psychological well-being:
- Emotional Distress and Anxiety: The appearance of the penis and the difficulties associated with sexual activity can lead to significant stress and anxiety.
- Challenges in Sexual Relationships: The physical limitations caused by pain and curvature can complicate sexual intercourse, potentially leading to strained relationships.
- Decreased Sexual Confidence: Men may experience a reduction in self-esteem and sexual confidence, which can exacerbate feelings of isolation or depression.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation and to discuss potential treatment options. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Diagnosing Peyronie’s Disease
Diagnosing this condition accurately is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here’s an overview of the diagnostic procedures and tools used to confirm Peyronie’s Disease.
Common Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
- Physical Examination: A primary method for diagnosing Peyronie’s Disease, where a healthcare provider feels (palpates) the penis for the presence of scar tissue or plaques. This exam can be conducted both when the penis is erect and flaccid, providing insights into the extent of curvature and the location of fibrous tissue.
- Photographs: Patients may be asked to provide photographs of their erect penis from different angles. These photos help the doctor assess the degree of curvature and the physical changes over time.
- Ultrasound: This imaging test is vital for visualizing the presence of plaques within the penile tissue, especially those that aren’t easily felt. Ultrasound can also assess blood flow to the penis, which is crucial for determining erectile function and the severity of the condition.
- X-ray or Penile Radiographs: Although less common, these can be used to detect calcification in penile plaques, which occurs in more advanced stages of Peyronie’s Disease.
The Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
The medical history and physical examination play a pivotal role in diagnosing Peyronie’s Disease. During the consultation, the doctor will inquire about:
- Symptoms onset: When and how symptoms like pain, curvature, and erectile dysfunction began.
- Sexual Function: Any changes or difficulties in sexual function or performance.
- Previous Injuries: Incidents of genital trauma or previous surgeries, which might have contributed to the development of fibrous tissue.
- Family and Personal Medical History: Any family history of connective tissue disorders or personal medical conditions that might influence Peyronie’s Disease.
These insights from the patient’s history complement the findings from the physical examination, guiding the clinician towards an accurate diagnosis.
Advanced Imaging and Other Diagnostic Tools
In addition to the basic diagnostic methods, more advanced tools may be employed, particularly in complex cases:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Offers a detailed image of the penile structure, which is helpful in planning surgical interventions if needed.
- Biothesiometry: This test can help detect changes in the sensitivity of the penis, which might affect sexual function.
- Dynamic Infusion Cavernosometry and Cavernosography (DICC): These are specialized tests used to evaluate the vascular response of the penile tissue. They are particularly useful in cases where vascular disease may also be present or when the diagnosis is unclear.
- Penile Doppler Ultrasound: An advanced form of ultrasound that provides comprehensive details about blood flow and vascular condition within the penis, aiding in the assessment of erectile function.
By using a combination of these diagnostic tools, healthcare providers can effectively diagnose Peyronie’s Disease, assess its severity, and tailor a treatment plan that best suits the patient’s condition.
Treatment Options for Peyronie’s Disease
Here’s an overview of the treatment goals and options for Peyronie’s disease, ranging from non-surgical to surgical interventions.
Treatment Goals
The primary objectives in treating Peyronie’s disease include:
- Alleviating Pain: Reducing or eliminating pain during erections, which is often the most immediate concern for affected individuals.
- Correcting Curvature: Minimizing the degree of penile curvature to improve sexual function and decrease discomfort.
- Restoring Function: Aiming to restore normal sexual function and overall penile health.
- Preventing Progression: Stabilizing the condition to prevent further progression of curvature or pain.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical options are typically considered for men with less severe curvature, less pain, and in cases where the disease is in its active phase. These include:
- Medications: Oral drugs like pentoxifylline or potassium para-aminobenzoate may be prescribed to manage symptoms or slow disease progression.
- Injections: Collagenase clostridium histolyticum (brand name Xiaflex) is FDA-approved for directly injecting into the scar tissue to break down the buildup of collagen.
- Shockwave Therapy: This method uses sound waves to potentially break up scar tissue and reduce pain in the penis.
- Traction Devices: Penile traction devices can be used to gently stretch the penis, potentially reducing curvature over time.
- Topical Treatments: Applying medications directly to the penis skin that aim to soften the hard scar tissue.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be recommended for men who do not respond to non-surgical treatments or who have severe or stabilized curvature after the acute phase has passed. Surgical options include:
- Nesbit Procedure: Removal or alteration of tissue opposite to the scar tissue to straighten the penis.
- Incision or Excision and Grafting: Removing the scar tissue and replacing it with a graft to allow more natural straightening.
- Penile Prosthesis Implantation: In cases with severe curvature and erectile dysfunction, implanting a device to help achieve an erection and reduce curvature.
However, each treatment option has its potential benefits and risks, and the choice of treatment should be guided by individual patient needs, severity of symptoms, and personal preferences, often after a detailed discussion with a healthcare provider specializing in men’s health or urology.
Innovations in Peyronie’s Disease Treatment
This article explores the latest innovations in Peyronie’s Disease treatment, including new medications, therapies, and what the future might hold for PD management.
Recent Advancements in Treatment Options
The treatment landscape for Peyronie’s Disease has seen substantial progress in recent years. Here are some of the notable advancements:
- Collagenase Clostridium Histolyticum (CCH) Injections: Approved by the FDA, these injections are currently the only non-surgical treatment specifically approved for PD. They work by breaking down the buildup of collagen that causes penile curvature.
- Shockwave Therapy: While traditionally used for kidney stones, shockwave therapy has been adapted for PD treatment. It involves sending acoustic waves to the penis, which can help break down penile plaques and reduce curvature.
- Penile Traction Therapy (PTT): This mechanical treatment uses a device to stretch the penis gently, which can help reduce curvature and lengthen the penis that might have been shortened by PD.
- Improved Surgical Techniques: For severe cases, surgery remains an option. Recent innovations in surgical techniques have improved outcomes, with less invasive options and better recovery times.
Research on New Medications and Therapies
Research into new medications and therapies for Peyronie’s Disease is ongoing, reflecting a growing understanding of the condition’s biological underpinnings. Highlights include:
- Topical Gels and Creams: Researchers are investigating topical treatments that could be applied directly to the penis, targeting fibrosis without systemic side effects.
- Gene Therapy: At the experimental stage, gene therapy aims to introduce genetic material into cells to compensate for abnormal genes or to make a beneficial protein, potentially addressing the root causes of PD.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Early studies suggest that stem cells could be used to repair or replace damaged tissue in the penis, offering a novel approach to treatment that could restore normal function and reduce curvature.
The Future of PD Treatment
The future of Peyronie’s Disease treatment looks promising, with several innovative approaches on the horizon:
- Personalized Medicine: As genetic research advances, treatments could become more personalized based on an individual’s genetic makeup, potentially increasing efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Integrated Treatment Approaches: Combining physical therapy, medications, and non-invasive treatments might offer a holistic approach to managing PD, focusing on both symptoms and underlying causes.
- Advanced Bioengineering: The development of new materials and biomedical devices could lead to more effective non-surgical options for correcting penile curvature and treating PD at its source.
As research progresses, these treatments not only promise to reduce the physical symptoms of PD but also aim to address the psychological impact, improving the quality of life for many patients.
Managing Life with Peyronie’s Disease
Living with Peyronie’s disease can be challenging, but effective management can help individuals maintain a fulfilling life. This section explores lifestyle modifications, home remedies, coping strategies, and the importance of support from partners and healthcare professionals.
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
Adopting certain lifestyle changes and exploring home remedies can play a crucial role in managing symptoms of Peyronie’s disease:
- Exercise Regularly: Gentle exercises, especially those that promote pelvic floor strength, can improve blood flow and may help reduce discomfort.
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce inflammation and support tissue health.
- Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Smoking can impair blood flow, worsening symptoms, while excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact sexual health.
- Use of Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the area can reduce pain and discomfort.
- Over-the-counter Pain Relievers: Medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to manage pain, although it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any medication.
Coping Strategies for Emotional and Psychological Impacts
Peyronie’s disease can also affect emotional and psychological well-being. Here are some coping strategies:
- Counseling: Professional therapists or counselors who specialize in chronic illness or sexual health can provide valuable support.
- Communication: Open dialogue with sexual partners about one’s feelings and the impact of Peyronie’s disease can alleviate stress and build understanding.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help manage stress and anxiety.
- Joining Support Groups: Connecting with others who are facing similar challenges can provide emotional support and helpful insights.
Importance of Support from Partners and Healthcare Professionals
The support from partners and healthcare professionals is indispensable in managing Peyronie’s disease:
- Partners: Supportive partners can significantly influence emotional health and coping. They can assist in treatment processes and provide emotional comfort.
- Healthcare Professionals: Regular consultations with healthcare providers are crucial. These specialists can offer medical treatments, suggest physical therapies, and provide guidance on managing the condition effectively.
Managing Peyronie’s disease involves a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle adjustments, emotional support, and medical care. With the right strategies and support, individuals can lead a more comfortable and satisfying life.
FAQs about Peyronie’s Disease Treatment
What is Peyronie’s disease?
Peyronie’s disease is a medical condition characterized by the development of fibrous scar tissue inside the penis, which can cause curved, painful erections. This curvature can make sexual intercourse difficult or even impossible in severe cases.
How is Peyronie’s disease treated?
Treatment options for Peyronie’s disease vary depending on the severity of the condition and how much it affects the individual. Common treatments include:
- Medications: Oral or injected drugs can help reduce inflammation and dissolve scar tissue.
- Physical Therapy: Stretching exercises and massage techniques can help alleviate pain and reduce curvature.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature of the penis.
When should someone seek treatment for Peyronie’s disease?
It is advisable to seek medical advice if you notice any significant bend in the penis that causes pain or interferes with sexual activity. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms more effectively.
Are there any side effects to Peyronie’s disease treatments?
Yes, treatments for Peyronie’s disease can have side effects. For example, medications might cause nausea, dizziness, or other side effects, while surgery can lead to complications such as changes in penis size or erectile dysfunction. Discussing these potential side effects with a healthcare provider is crucial.
Can Peyronie’s disease resolve on its own?
In some cases, Peyronie’s disease may improve without treatment, especially if the symptoms are mild. However, in many cases, treatment is necessary to prevent worsening of the symptoms and to improve quality of life.
Is Peyronie’s disease common?
Peyronie’s disease affects about 3 to 9% of men, although the actual number may be higher as some men may not seek help due to embarrassment or mild symptoms.
Conclusion
If you suspect you might have Peyronie’s Disease, it’s crucial not to self-diagnose or delay seeking professional help. Medical experts can provide a thorough diagnosis and recommend treatment options tailored to your specific condition, which may include medications, surgery, or non-surgical therapies. Addressing this condition promptly can significantly enhance your quality of life and sexual health.
We encourage anyone experiencing symptoms of Peyronie’s Disease to consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment. Remember, early intervention is key in managing health conditions effectively.
References
For those seeking more detailed information and to verify the insights shared about Peyronie’s Disease treatment, the following reputable sources are highly recommended:
- Mayo Clinic – This trusted medical resource offers a comprehensive overview of Peyronie’s Disease, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Learn more at Mayo Clinic’s Peyronie’s Disease Section.
- National Institute of Health (NIH) – NIH provides scientific and research-oriented details on Peyronie’s Disease, helping patients and healthcare providers understand the underlying biological mechanisms and potential treatments. Access their resources at NIH’s Peyronie’s Disease Page.
- American Urological Association (AUA) – The AUA offers guidelines and treatment pathways for urologists treating Peyronie’s Disease, including the latest research and clinical practice guidelines. Visit their site at AUA’s Guidelines on Peyronie’s Disease.
These sources are valuable for both patients and healthcare providers looking for reliable information on the management and treatment of Peyronie’s Disease.