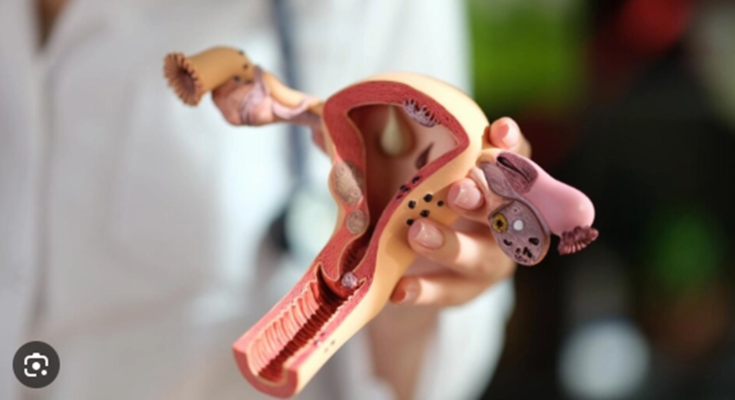
Ovarian Cysts Treatment: Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or within an ovary. While often asymptomatic, they can occasionally cause pain and other disturbances, necessitating medical attention.
Understanding the nuances of diagnosis and treatment options is crucial for effective management and optimal health outcomes.
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets within or on the surface of an ovary. Women have two ovaries — each about the size of an almond — located on each side of the uterus. Eggs (ova), which develop and mature in the ovaries, are released in monthly cycles during the childbearing years.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are various types of ovarian cysts, each with distinct characteristics:
1. Functional Cysts: These are the most common types and are related to the menstrual cycle. Functional cysts are typically harmless, do not cause pain, and often dissolve on their own within two to three menstrual cycles. They include:
- Follicular Cysts: Form when the follicle does not rupture or release its egg, but continues to grow.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: Occur when the follicle releases the egg and then reseals and fills with fluid.
2. Dermoid Cysts: Also known as teratomas, these cysts can contain hair, skin, and even teeth. They are rarely cancerous but can be painful if they grow large.
3. Cystadenomas: These cysts develop from ovarian tissue and can be filled with a watery or mucous material. They can grow quite large and potentially cause pain and discomfort.
4. Endometriomas: These cysts form in women suffering from endometriosis. They are often filled with dark, reddish-brown blood and can be quite painful.
Common Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
While many ovarian cysts present no symptoms and are often discovered during a routine pelvic exam, some can cause noticeable symptoms, particularly as they grow. These symptoms can include:
- Bloating or swelling in the abdomen
- Painful bowel movements
- Pelvic pain before or during the menstrual cycle
- Pain during intercourse
- Pain in the lower back or thighs
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting, especially if the cyst is causing the ovary to twist
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cysts
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing ovarian cysts:
- Hormonal problems: These include taking fertility drugs, which can induce the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
- Pregnancy: During early pregnancy, the cyst that forms the egg can sometimes persist and grow larger.
- Endometriosis: Women with this condition are at higher risk of developing endometriomas.
- Severe pelvic infections: These can spread to the ovaries and fallopian tubes and lead to the formation of cysts.
- Previous ovarian cysts: Having had one increases the risk of developing more.
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts
Early diagnosis can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Here’s a detailed look at the initial assessments and symptoms that are key to recognizing ovarian cysts.
Initial Assessments
When a patient presents with potential symptoms of an ovarian cyst, healthcare providers typically start with a detailed medical history. This includes questions about:
- Menstrual cycle regularity
- Symptoms experienced (type, duration, and severity)
- Family history of ovarian cysts or ovarian cancer
- Any previous occurrences of cysts
A physical exam is also crucial. During this, the doctor may palpate the abdomen to detect any swelling or abnormalities.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures for Ovarian Cysts
Once initial assessments indicate the possibility of ovarian cysts, further diagnostic tests and procedures are conducted to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. Here are the most common diagnostic tools used:
Diagnostic Tests
- Pelvic Ultrasound: This is the primary diagnostic tool for ovarian cysts. It uses sound waves to create images of the ovaries, allowing doctors to see the cyst’s size, composition, and location.
- Blood Tests: Certain blood tests can help detect cancerous cysts. For instance, a CA-125 test may be ordered if there’s a suspicion of ovarian cancer, especially in postmenopausal women.
Procedures
- Laparoscopy: For a more detailed examination, a laparoscopy may be performed. This minimally invasive surgery involves a small incision and a camera to look directly at the ovaries.
- CT Scan or MRI: These imaging tests provide detailed images of the internal organs and can be used if ultrasound results are inconclusive or if there’s a need to rule out other conditions.
Through these diagnostic tests and procedures, healthcare providers can determine the nature of the cyst, and devise an appropriate treatment plan if necessary. Early detection and regular check-ups are essential for managing ovarian cysts effectively and preventing potential complications.
Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets within or on the surface of an ovary. While most ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some may require medical intervention. Here, we explore the various treatment options available, focusing on medications and surgical procedures.
Medications for Ovarian Cysts
The use of medications in the treatment of ovarian cysts primarily aims to manage symptoms and prevent the formation of new cysts, rather than eliminating existing ones. Here are some commonly prescribed medications:
- Birth Control Pills: Oral contraceptives are often recommended to reduce the likelihood of new cysts developing during future menstrual cycles. These pills do not shrink the current cysts but prevent new ones.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be used to help manage pain associated with ovarian cysts. For severe pain, your doctor may prescribe stronger painkillers.
- Hormonal Therapies: In some cases, other hormonal therapies, such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, may be used to halt ovulation and lower estrogen levels, which may help reduce the size and formation of ovarian cysts.
Surgical Options for Ovarian Cysts
Surgery might be considered if ovarian cysts are large, don’t appear to be functional (related to the menstrual cycle), cause symptoms, or persist over multiple menstrual cycles. The main surgical options include:
- Laparoscopy: For smaller cysts or those that appear benign (non-cancerous), a laparoscopy can be done. This is a minimally invasive surgery where small incisions are made, and a laparoscope (a small, lighted instrument) is inserted to remove the cysts.
- Laparotomy: Larger cysts or those that may be potentially cancerous require a more invasive procedure called a laparotomy. This involves a larger abdominal incision to remove the cysts and possibly the ovary.
- Oophorectomy: In cases where cysts are recurrent or if there’s a high risk of ovarian cancer, an oophorectomy, which is the removal of one or both ovaries, may be necessary.
- Cystectomy: During a cystectomy, the cyst is removed while preserving the ovary itself. This option is often suitable for younger women who wish to maintain their fertility.
However, early detection and treatment can improve outcomes significantly, especially in cases where the cysts may affect fertility or have the potential to become cancerous.
Complications Associated with Ovarian Cysts
Understanding these potential issues is crucial for women’s health. This article discusses the immediate complications requiring urgent attention and the long-term implications of untreated ovarian cysts.
Complications Needing Immediate Attention
Certain symptoms and complications associated with ovarian cysts necessitate prompt medical intervention to prevent severe health outcomes. These include:
- Ovarian Torsion: This occurs when a cyst becomes large enough to cause the ovary to move from its usual position, potentially twisting the structures around it. This can cut off blood supply to the ovary, leading to severe pain and possibly permanent ovarian damage if not treated quickly.
- Rupture: A cyst can burst, leading to sudden and severe pain. A ruptured ovarian cyst can also cause internal bleeding and infection, conditions that require immediate medical attention.
- Hemorrhage: Some cysts can bleed internally, which may not only cause pain but also lead to significant blood loss, necessitating urgent medical care.
- Infection: Though rare, an infected ovarian cyst can become a severe problem if the infection spreads to nearby pelvic organs, a condition known as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Long-term Implications if Untreated
Ignoring ovarian cysts can lead to several long-term health issues, particularly if they are symptomatic or of a specific type like endometriomas or cystadenomas. Here are the potential long-term implications of untreated ovarian cysts:
- Infertility: Certain types of cysts, such as endometriomas, are associated with endometriosis and can affect fertility. They may cause scarring and adhesions that impact the ovaries and other reproductive organs.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain: Ongoing discomfort or pain in the pelvis can arise from persistent cysts or from complications associated with previous cysts, such as adhesions or chronic inflammation.
- Repeated Cyst Formation: Without treatment or monitoring, individuals may experience recurrent cysts, which can continuously affect health and quality of life.
- Cancer: Though rare, some cysts, particularly complex cysts with solid components, have the potential to develop into ovarian cancer. Regular monitoring and appropriate management of ovarian cysts can help mitigate this risk.
However, understanding these complications underscores the importance of regular gynecological check-ups for women, particularly those who experience symptoms indicative of ovarian cysts.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Ovarian Cysts
Adopting certain lifestyle and home remedies can help manage symptoms or potentially reduce the risk of developing cysts. Here’s how you can address ovarian cysts through diet and lifestyle changes, and understand the importance of regular pelvic examinations.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes to Manage or Prevent Ovarian Cysts
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy weight and balance hormones. Include foods high in fiber to help reduce estrogen levels which can influence cyst formation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps detoxify the body and maintain overall health, which is crucial in managing ovarian cysts.
- Limit Intake of Harmful Substances: Reduce consumption of alcohol and caffeine, and avoid smoking, as these can affect hormonal balance and overall reproductive health.
- Incorporate Healthy Fats: Include a moderate amount of healthy fats in your diet, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon and mackerel, which can help reduce inflammation and hormone disruptions.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces hormonal imbalances, and can alleviate some of the discomfort associated with ovarian cysts.
- Manage Stress: High stress levels can affect hormonal balance. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress effectively.
Importance of Regular Pelvic Examinations
Regular pelvic examinations are crucial for women’s health. These exams allow healthcare providers to detect any abnormalities in the reproductive organs, including the presence of ovarian cysts. Here are key reasons why regular pelvic exams are important:
- Early Detection: Regular exams can help detect ovarian cysts early, often before they cause any symptoms. Early detection can lead to simpler and more effective management strategies.
- Monitoring Changes: For women with known cysts, regular pelvic exams help monitor the cysts’ growth or resolution and check for any signs of complications, such as rupture or torsion.
- Preventive Health: Pelvic examinations provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to discuss other aspects of reproductive health, including menstrual irregularities and family planning.
By adopting healthy lifestyle changes and ensuring regular pelvic examinations, women can manage their risk and the impact of ovarian cysts more effectively. This proactive approach promotes better health outcomes and peace of mind.
Future Directions in the Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or within the ovary. While many cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some can cause symptoms and require treatment. As medical science advances, new treatments and research trends are emerging that promise more effective and less invasive options for managing ovarian cysts.
Advances in Medical Treatments
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Enhancements in laparoscopic techniques continue to minimize the invasiveness of surgeries required to remove problematic ovarian cysts. Surgeons use smaller incisions, which lead to quicker recovery times and reduced risk of complications.
- Hormonal Therapies: The development of new hormonal medications that regulate the menstrual cycle can help prevent the formation of ovarian cysts, especially those related to ovulatory disorders.
- Precision Medicine: Tailored treatment approaches based on genetic profiling can predict the behavior of cysts and guide personalized therapy decisions, increasing the effectiveness of treatments.
- Image-guided Therapies: Advances in imaging technology have led to treatments that can be directed precisely at the cysts, reducing the need for invasive procedures. For example, ultrasound-guided aspiration allows for cysts to be drained without major surgery.
Research Trends and Emerging Therapies
- Stem Cell Research: Investigating the role of stem cells in ovarian health and regeneration offers potential for developing novel treatments that could prevent cyst formation or promote healing of ovarian tissue after cyst removal.
- Anti-inflammatory Approaches: Understanding the inflammatory processes that may contribute to cyst formation has opened the door to treatments that target these pathways, potentially offering new ways to manage cyst-related symptoms.
- Biological Therapies: Research into biological agents that specifically target ovarian cyst cells without affecting healthy ovarian tissue is ongoing. These therapies aim to reduce the size of the cysts or eliminate them entirely with minimal side effects.
- Nanotechnology: The use of nanoparticles to deliver drugs directly to the cysts is a promising area of research. This method ensures that the medication is concentrated at the site of the cyst, maximizing effectiveness and minimizing systemic side effects.
The future of ovarian cyst treatment looks promising with these advances and ongoing research. As these technologies and therapies develop, patients can look forward to more effective, less invasive treatment options, improving both outcomes and quality of life.
FAQs about Ovarian Cysts Treatment
What are ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside an ovary. They are common and usually form during the ovulation process. While most ovarian cysts are benign (non-cancerous) and may dissolve on their own, some can cause symptoms and require treatment.
How are ovarian cysts diagnosed?
Ovarian cysts are often diagnosed during a routine pelvic examination. If a cyst is suspected, your doctor may recommend further testing, such as an ultrasound, to confirm the presence of a cyst and to determine its size, shape, and composition.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cysts?
Many ovarian cysts do not cause any symptoms and are often discovered incidentally during routine exams. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include pelvic pain, bloating, swelling, or pain during intercourse. Severe symptoms like sharp or severe pelvic pain, fever, or faintness may indicate a medical emergency such as a ruptured cyst.
What are the treatment options for ovarian cysts?
The treatment for ovarian cysts can vary depending on the size of the cyst and the symptoms presented. Common treatment options include:
- Observation: Small, symptom-free cysts may just be monitored over time with regular pelvic ultrasounds.
- Medication: Hormonal contraceptives may be prescribed to prevent the development of new cysts in those who frequently have them.
- Surgery: Large, painful, or suspicious cysts may require surgical removal. The type of surgery depends on the cyst’s characteristics.
Can ovarian cysts lead to cancer?
Most ovarian cysts are benign and do not lead to cancer. However, some cysts, known as cystadenomas, can become cancerous over time. It is important to have regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider if you have been diagnosed with ovarian cysts, especially if they persist or change in size.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage or prevent ovarian cysts?
While specific lifestyle changes to prevent ovarian cysts aren’t universally recommended, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and eating a balanced diet can help maintain your overall reproductive health. Additionally, regular check-ups can help detect changes early.
Conclusion
In summary, the treatment of ovarian cysts involves a variety of methods tailored to the individual’s condition and the specifics of the cysts themselves. These treatments range from watchful waiting for functional cysts that are likely to resolve on their own, to medications that help regulate hormone levels, and in more severe cases, surgical interventions that ensure the cysts do not cause further health complications.
It is crucial for women to prioritize their health and undergo regular check-ups. Early detection through routine health screenings can lead to more effective management of ovarian cysts and help prevent potential complications. Therefore, every woman should be encouraged to maintain regular visits to her healthcare provider, ensuring ongoing monitoring and the best possible outcomes for her reproductive health.
References
For further reading and to validate the information provided on the treatment of ovarian cysts, consider exploring the following reputable sources:
- Mayo Clinic: Offers a comprehensive overview of ovarian cysts, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Detailed information can be found on their official website. Mayo Clinic on Ovarian Cysts.
- WebMD: Provides insights into the diagnosis and treatment processes for ovarian cysts, alongside expert opinions and patient care guides. For more details, visit WebMD Ovarian Cysts Resource.
- Healthline: Features user-friendly articles that explain the different types of ovarian cysts, risk factors, and modern treatment methods. Learn more by accessing Healthline’s Guide to Ovarian Cysts.
- MedlinePlus: A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine, this site offers trustworthy information on medical conditions, including ovarian cysts, supported by research and clinical guidelines. Check out MedlinePlus for Ovarian Cysts.
These sources are renowned for their medical accuracy and reliability, making them excellent references for anyone seeking more in-depth information on the treatment of ovarian cysts.