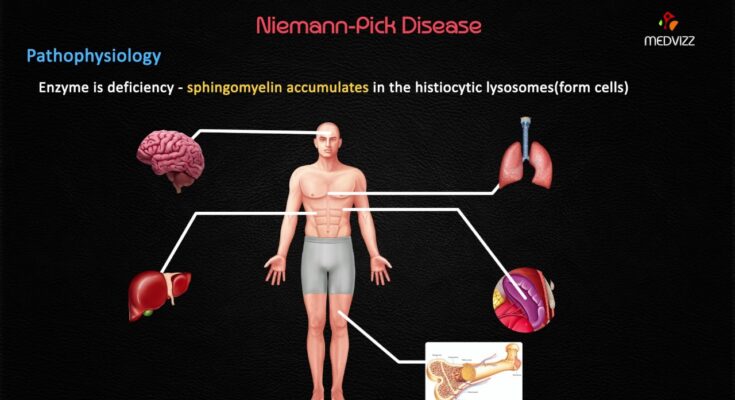
Niemann-Pick Disease Treatment: Niemann-Pick disease is a rare and inherited metabolic disorder where the body is unable to properly metabolize cholesterol and other lipids within the cell.
This dysfunction leads to the accumulation of these substances, causing damage to various organs, particularly the brain, liver, and spleen.
However, this article delves deeply into the diagnosis and treatment options available for Niemann-Pick disease, providing critical insights for healthcare professionals, patients, and their families.
What is Niemann-Pick Disease?
Niemann-Pick disease (NPD) is a group of inherited metabolic disorders known as lysosomal storage diseases. The condition primarily affects the body’s ability to metabolize lipids (fats), which accumulate in various organs and tissues, leading to dysfunction and a range of health issues. NPD can significantly impact the neurological system, liver, spleen, and lungs. The severity and specific symptoms of the disease can vary widely among affected individuals.
Types of Niemann-Pick Disease
Niemann-Pick disease is classified into several types, each differing in symptoms, genetic causes, and progression:
- Type A: A severe neurological form that typically manifests in early infancy.
- Type B: Mainly affects the spleen and liver with little or no neurological involvement, and presents later in childhood.
- Type C1 and C2: Known for causing neurological symptoms and may occur at any age, typically diagnosed in childhood.
- Type E: A rare form that begins in adulthood and involves neurodegenerative complications.
Genetic Causes and Epidemiology
Niemann-Pick disease types A and B are caused by mutations in the SMPD1 gene, which leads to deficient activity of the enzyme acid sphingomyelinase, crucial for the proper breakdown of lipids. Types C1 and C2 result from mutations in either the NPC1 or NPC2 genes, affecting cellular lipid transport.
The prevalence of Niemann-Pick disease varies, with types A and B being more common in individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish descent, featuring a carrier frequency of about 1 in 90 in this population. Type C affects approximately 1 in 150,000 individuals worldwide, making it the more common form globally.
Symptoms and Progression of Niemann-Pick Disease
The symptoms of Niemann-Pick disease depend largely on the type:
- Type A: Rapidly progressive neurodegeneration, failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen), and severe motor and cognitive decline. Life expectancy is typically only a few years.
- Type B: Symptoms include hepatosplenomegaly, pulmonary issues, and a survival rate into adulthood, with variable degrees of liver dysfunction and possible neurological complications.
- Type C: Characterized by progressive neurological symptoms, such as ataxia (loss of muscle control), dementia, seizures, and psychiatric disorders. The onset can range from infancy to adulthood, with the progression and life expectancy varying widely.
- Type E: Symptoms usually appear in mid-to-late adulthood and may include psychiatric symptoms and progressive neurodegeneration.
However, current treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life, as there is no cure for the disease at this time.
Diagnosing Niemann-Pick Disease
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing the disease effectively. Here’s a detailed look at the diagnostic tests and procedures, the role of genetic testing, and the challenges faced in diagnosing the different types of NPD.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
- Physical Examination: Initial assessment involves a thorough physical examination to check for common signs like enlarged liver or spleen, and neurological abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: These tests can help detect abnormalities in liver function, cholesterol levels, and other substances that may indicate NPD.
- Imaging Studies: Techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans are employed to visualize internal organ status, especially the size and health of the spleen and liver.
- Biopsy: A tissue biopsy, usually of the liver or bone marrow, can be performed to observe the cellular structure and detect the presence of lipid storage cells typical of NPD.
- Filipin Staining: A specific diagnostic test that uses a fluorescent dye to detect the storage of cholesterol in cells from skin or conjunctival biopsies.
Role of Genetic Testing in Identifying NPD
Genetic testing plays a pivotal role in diagnosing Niemann-Pick Disease. It involves:
- Mutation Analysis: Identifying mutations in specific genes such as SMPD1 (for Type A and B) and NPC1 or NPC2 (for Type C) that are responsible for NPD.
- Carrier Testing: Helpful for at-risk couples who may be carriers of the genes associated with NPD, allowing for informed family planning decisions.
- Prenatal Testing: For families with a history of NPD, prenatal genetic tests can determine if the fetus has inherited the disorder, facilitating early intervention strategies.
Challenges in Diagnosing Different Types of NPD
Diagnosing NPD comes with its own set of challenges, which vary depending on the type of the disease:
- Symptom Overlap: The symptoms of NPD often resemble those of other lysosomal storage disorders, leading to potential misdiagnosis.
- Variability of Presentation: Symptoms can vary widely even within the same type, especially in Type C, which affects neurological development and can appear anytime from infancy to adulthood.
- Access to Testing: Genetic testing and specialized diagnostic procedures are not widely available in all regions, which can delay diagnosis.
- Interpretation of Genetic Results: The presence of mutations in the SMPD1, NPC1, or NPC2 genes can be challenging to interpret, requiring specialized genetic counseling to understand the implications.
By addressing these challenges and employing a comprehensive diagnostic approach, healthcare providers can improve the accuracy of diagnosing Niemann-Pick Disease, leading to better management and care outcomes for affected individuals.
Current Treatments for Niemann-Pick Disease
Effective management of this disease is crucial for enhancing the quality of life of affected individuals. This article explores the current treatments available for Niemann-Pick disease, focusing on the specific therapies for Types A, B, and C and the roles of enzyme replacement therapy and substrate reduction therapy.
List of Available Treatments and Their Targets
The treatments for Niemann-Pick disease are primarily targeted at managing symptoms, preventing complications, and, in some cases, slowing the progression of the disease. Available treatments include:
- Supportive Care: This includes nutritional support, physical therapy, and respiratory care, which are essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Medication: Certain medications can help manage or alleviate symptoms such as seizures, sleep disturbances, and liver problems.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT): Specifically used for Niemann-Pick disease Type B, ERT involves the administration of synthetic enzymes to replace the deficient or malfunctioning enzymes.
- Substrate Reduction Therapy (SRT): This treatment reduces the substrate (the material that accumulates due to the enzyme deficiency), thereby lessening the burden on cells.
- Gene Therapy: Although still in experimental stages, gene therapy holds promise for addressing the genetic root causes of the disease.
Specific Treatments for Type A, B, and C Niemann-Pick Disease
- Type A and B: Type A Niemann-Pick disease is generally more severe, with no current curative treatments and care primarily focusing on symptom management. Type B patients might benefit from enzyme replacement therapies such as recombinant acid sphingomyelinase, which has shown potential in clinical trials.
- Type C: Treatment for Niemann-Pick disease Type C includes the use of miglustat and, more recently, cyclodextrin. Miglustat helps in slowing the progression of neurological symptoms, while cyclodextrin has been studied for its potential to reduce cholesterol accumulation in brain cells.
Role of Enzyme Replacement Therapy and Substrate Reduction Therapy
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT): ERT is pivotal in treating Type B Niemann-Pick disease. By replacing the deficient sphingomyelinase enzyme, this therapy helps reduce lipid accumulation in cells, improving organ function and quality of life. The effectiveness of ERT varies among individuals and requires regular administration.
- Substrate Reduction Therapy (SRT): SRT serves as a complementary approach, particularly in Type C Niemann-Pick disease. It works by reducing the production of lipids that accumulate due to the enzyme deficiency. This therapy can help manage symptoms and delay disease progression.
However, while there is no cure for Niemann-Pick disease, various treatments are available that target specific symptoms and disease mechanisms. Research into more effective treatments, including gene therapy, continues to offer hope for future advancements.
Emerging Research and Future Therapies for Niemann-Pick Disease
Recent Advancements in Niemann-Pick Disease Treatment
In recent years, the scientific community has made significant strides in treating Niemann-Pick Disease (NPD). One of the most promising advancements includes the development of enzyme replacement therapies, which have shown potential in reducing disease burden and improving quality of life for affected individuals. Additionally, substrate reduction therapy has emerged as a viable option, aiming to decrease the accumulation of harmful substances in cells, thus mitigating disease symptoms and progression.
Clinical Trials and Experimental Treatments
A number of clinical trials are currently underway to explore new treatment avenues for NPD. These trials focus on various aspects of the disease, ranging from novel pharmaceuticals to advanced biotechnological interventions. Experimental treatments being tested include small molecule drugs that target the genetic mutations causing the disease, as well as chaperone therapies designed to enhance the function of residual enzymes in affected individuals.
The Potential of Gene Therapy in Treating Niemann-Pick Disease
Gene therapy holds exceptional promise for the future treatment of NPD. This approach involves correcting the underlying genetic defects that cause the disease by introducing functional genes into patients’ cells. Recent studies have shown that gene therapy can effectively address the root causes of NPD, offering a potential cure by repairing or replacing the faulty genes. Ongoing research continues to optimize delivery mechanisms and ensure long-term safety and efficacy, setting the stage for potential breakthroughs in the treatment landscape of Niemann-Pick Disease.
Managing Life with Niemann-Pick Disease
Living with Niemann-Pick Disease (NPD) presents unique challenges, requiring comprehensive support and strategic lifestyle adjustments. This guide highlights supportive care, the importance of multidisciplinary teams, and resources to help patients and their families navigate life with NPD.
Supportive Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Nutritional Management: Tailoring a diet to meet specific nutritional needs is crucial. Consulting a dietitian can help in creating a balanced meal plan that supports overall health.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy helps maintain mobility and reduce the risk of complications due to immobility.
- Respiratory Care: Regular check-ups with a pulmonologist are essential, as respiratory issues are common. Learning and using breathing exercises can also be beneficial.
- Medication Management: Adhering to prescribed medications can help manage symptoms effectively. Regular consultations with healthcare providers ensure optimal treatment plans.
- Home Modifications: Adjusting the living environment to enhance safety and accessibility can significantly improve quality of life.
Importance of Multidisciplinary Care Teams
- Comprehensive Care: A team of healthcare professionals including neurologists, geneticists, cardiologists, and mental health experts ensures all aspects of NPD are addressed.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Multidisciplinary teams develop tailored treatment plans that cater to the individual needs of each patient, enhancing the effectiveness of interventions.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Regular interaction with psychologists or counselors helps address the emotional and psychological challenges of living with a chronic condition.
Resources and Support Groups for Patients and Families
- National Niemann-Pick Disease Foundation (NNPDF): Provides comprehensive information, support services, and connection to others affected by NPD.
- Global Genes: Offers resources and support for patients with rare diseases, including NPD.
- Online Communities: Platforms like RareConnect connect patients and families globally, providing a space to share experiences and support.
- Local Health Services: Contacting local health departments can provide information on available local support services and healthcare providers specialized in NPD.
By leveraging these resources, engaging with care teams, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, patients and families can manage Niemann-Pick Disease more effectively, leading to improved quality of life and well-being.
FAQs about Niemann-Pick Disease Treatment
What is Niemann-Pick disease?
Niemann-Pick disease is a rare, genetic disorder that affects the body’s ability to metabolize fat (lipids) within cells. These cells malfunction and, over time, cause damage to tissues and organs throughout the body.
What are the treatment options for Niemann-Pick disease?
Treatment options vary depending on the type of Niemann-Pick disease. There is no cure for any of the types, but treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include medication to help reduce or manage symptoms, physical therapy, and in some cases, stem cell transplantation.
Is gene therapy available for Niemann-Pick disease?
Gene therapy for Niemann-Pick disease is currently under research and not widely available as a standard treatment. Clinical trials are ongoing to explore gene therapy as a potential effective treatment for some types of Niemann-Pick disease.
How can diet and lifestyle changes affect Niemann-Pick disease?
While diet and lifestyle changes will not cure Niemann-Pick disease, they can help manage symptoms. Health professionals often recommend a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of substances that can stress the liver and spleen.
Can Niemann-Pick disease be prevented?
As a genetic disorder, Niemann-Pick disease cannot be prevented if the person inherits the faulty genes. Genetic counseling is recommended for individuals or couples with a family history of the disease who are considering having children.
Conclusion
In this discussion, we’ve explored the critical aspects of diagnosing and treating Niemann-Pick Disease, a complex genetic disorder that demands a nuanced understanding and approach. Early diagnosis is pivotal, enabling targeted therapies that can significantly enhance quality of life. Treatment options, while still evolving, range from enzyme replacement therapies to supportive care aimed at managing symptoms and improving patient outcomes.
The importance of ongoing research cannot be overstated. It fuels the hope for groundbreaking treatments and potentially a cure in the future. Each study and trial brings us closer to deeper insights and more effective interventions.
For patients and their families, the journey with Niemann-Pick Disease is challenging. However, seeking care from specialists who understand the intricacies of this condition is crucial. Specialized care centers not only provide access to the latest treatments but also offer a support network that is invaluable.
Encouragement for those affected by Niemann-Pick Disease is essential. Patients and families are urged to connect with healthcare providers, support groups, and organizations dedicated to this condition. Together, there is strength in the shared experience and hope in the advancements on the horizon.
References
For further reading and validation of the information provided on Niemann-Pick Disease Treatment, the following sources are highly reputable:
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – This comprehensive resource offers detailed information on the genetic aspects and ongoing research related to Niemann-Pick Disease. Access the website here: NIH Niemann-Pick Disease.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its patient-centered approach, the Mayo Clinic provides useful insights into the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments available for Niemann-Pick Disease. Visit their official page: Mayo Clinic – Niemann-Pick Disease.
- NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders) – NORD provides a wealth of information, including patient advocacy resources and treatment options for those affected by Niemann-Pick Disease. Find more information at: NORD – Niemann-Pick Disease.
- Genetics Home Reference – Managed by the U.S. Library of Medicine, this resource offers genetic information and an educational overview of Niemann-Pick Disease. Explore more through their link: Genetics Home Reference.
These sources are instrumental in providing credible and detailed information that supports a deeper understanding and management of Niemann-Pick Disease.