Multiple Myeloma Symptoms: Multiple Myeloma is a complex and severe form of cancer that primarily affects the plasma cells in the bone marrow.
This type of cancer is distinguished by the abnormal proliferation of plasma cells, which can lead to a myriad of both physical and systemic complications.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of Multiple Myeloma is crucial for early detection and effective management of the disease.
Understanding Multiple Myeloma
Multiple Myeloma is a distinct type of cancer that primarily affects the plasma cells, a vital part of the immune system that produces antibodies. This malignancy differs in several key ways from other cancers, highlighting its unique characteristics and challenges. Understanding these differences is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
How Multiple Myeloma Differs from Other Types of Cancer
- Origin of Cancer Cells: Unlike many cancers that originate in solid organs or tissues, multiple myeloma begins in the bone marrow. It specifically targets the plasma cells, which are crucial for producing antibodies that help fight infections.
- Pattern of Spread: Multiple myeloma typically does not form a lump or mass, which is common in other types of cancer. Instead, it causes widespread effects throughout various bones in the body, leading to pain, fractures, and other bone problems.
- Symptoms: The symptoms of multiple myeloma can be vague and similar to those of other less serious conditions. Common symptoms include fatigue, bone pain, and recurrent infections, which can delay diagnosis.
- Effect on the Body: This type of cancer significantly affects the body’s ability to fight infections and can lead to severe anemia and kidney problems, unlike many other cancers which might not directly impact these systems.
- Diagnostic Tools: Diagnosis of multiple myeloma relies heavily on blood tests and bone marrow biopsies, as opposed to scans and imaging tests used commonly in other cancers to locate tumors and assess their size.
The Prevalence and Impact of Multiple Myeloma Globally
Multiple myeloma, while not the most common cancer, has a profound impact on populations worldwide:
- Global Prevalence: It is estimated that nearly 160,000 people are diagnosed with multiple myeloma each year globally. The disease is more prevalent in older adults, particularly those over the age of 60.
- Impact on Life Expectancy: Despite advancements in treatment, multiple myeloma remains incurable and significantly shortens life expectancy. The average survival rate post-diagnosis is approximately five years, though this can vary widely depending on a variety of factors.
- Economic Burden: The treatment of multiple myeloma is often long-term and costly, involving combinations of chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and sometimes stem cell transplants. This places a significant financial strain on healthcare systems and patients alike.
- Quality of Life: Due to its chronic nature and the severe symptoms it can cause, multiple myeloma heavily impacts the quality of life of patients, affecting their physical, emotional, and social well-being.
By understanding the unique aspects of multiple myeloma, researchers continue to develop targeted treatments that address the specific needs of those affected by this challenging disease.
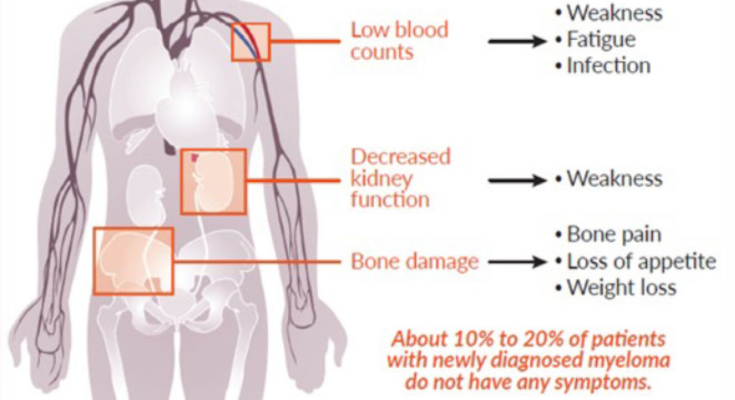
Symptoms of Multiple Myeloma
Multiple Myeloma, a type of cancer that forms in plasma cells, can manifest through a range of symptoms varying in severity and occurrence among individuals. Understanding these signs can aid in early detection and management of the disease.
Early Signs and Common Symptoms of Multiple Myeloma
The early signs and common symptoms of multiple myeloma often relate to the effects of abnormal plasma cells accumulating in the bone marrow. These include:
- Bone Pain: Primarily in the spine, chest, or pelvis, the pain can be intense and is often described as dull or aching.
- Fatigue: A pervasive sense of exhaustion that does not improve with rest.
- Frequent Infections: Due to impaired immune function, individuals may experience repeated infections.
- Anemia: Characterized by a decrease in red blood cells, leading to weakness and pallor.
- High Calcium Levels: Excessive calcium released into the bloodstream can cause thirst, frequent urination, constipation, and impaired kidney function.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss without trying can be a significant indicator.
- Nausea or Loss of Appetite: Often related to elevated calcium levels.
Less Common Symptoms That Can Indicate Multiple Myeloma
While less frequent, there are other symptoms that, when present, can still suggest the presence of multiple myeloma:
- Neurological Issues: Such as numbness, weakness, or tingling, particularly in the legs.
- Increased Viscosity of the Blood: Leading to problems like blurred vision, headaches, and dizziness.
- Hyperviscosity Syndrome: This includes confusion, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
- Kidney Problems: Manifested as changes in urine output and color, which can indicate kidney impairment or failure.
Variation in Symptoms Between Individuals
The symptoms of multiple myeloma can vary widely between individuals, influenced by factors such as the stage of the disease, the rate of progression, and individual health status. Some may experience severe symptoms early on, while others might have subtle symptoms that gradually worsen. Additionally, some individuals might remain asymptomatic for years, diagnosed only through routine health screenings.
Causes and Risk Factors of Multiple Myeloma
While the exact causes of multiple myeloma are not fully understood, several risk factors have been identified that may increase the susceptibility to developing this disease. Understanding these factors can help in early detection and prevention strategies.
Causes of Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma does not have a clearly defined cause but it starts with one abnormal plasma cell in the bone marrow—the soft, blood-producing tissue that fills in the center of most bones. This cell multiplies rapidly due to mutations in its DNA. Over time, these cancerous cells crowd out healthy cells and produce harmful proteins that cause kidney damage and other serious health problems.
Risk Factors That Increase Susceptibility to Multiple Myeloma
- Age: The risk of developing multiple myeloma increases with age, with most people diagnosed in their mid-60s or older.
- Gender: Men are slightly more likely to develop multiple myeloma than women.
- Race: African Americans are about twice as likely to develop multiple myeloma as white Americans. The reasons for this disparity are not fully understood.
- Family History: Having a sibling or parent with multiple myeloma increases your risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of multiple myeloma.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene and other petrochemicals, has been linked to a higher risk of developing multiple myeloma.
- Radiation Exposure: People exposed to ionizing radiation, such as atomic bomb survivors or those exposed through their occupation, may have an increased risk of multiple myeloma.
- Personal History of a Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS): MGUS is a benign condition that can precede multiple myeloma. Although it doesn’t cause symptoms, people with MGUS have an increased risk of later developing multiple myeloma.
However, most people with risk factors never develop the disease, and many who do get the disease may have few or no known risk factors. Regular check-ups and discussions with a healthcare provider can help manage your risk and catch any potential problems early.
Diagnosing Multiple Myeloma
Diagnosing multiple myeloma effectively is crucial for early intervention and successful management of the disease. This cancer affects plasma cells, which are an essential part of the immune system, and it can lead to a variety of health issues if not identified and treated promptly.
Common Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
- Blood Tests: These are fundamental in checking for abnormal levels of monoclonal proteins (M proteins) produced by myeloma cells. The most common tests include the Complete Blood Count (CBC), Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP), and Immunofixation Electrophoresis (IFE).
- Urine Tests: Urine analysis can reveal Bence Jones proteins, which are small monoclonal proteins shed by myeloma cells, crucial for diagnosing myeloma.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: This invasive procedure involves extracting a small amount of bone marrow from the hip bone to detect myeloma cells directly.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, CT scans, and PET scans are utilized to identify bone damage or lesions caused by myeloma cells and help assess the extent of the disease.
- Genetic Tests: These tests are conducted on samples from blood, urine, or bone marrow to detect genetic abnormalities that may influence prognosis and treatment options.
The Role of Specialists in the Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
- Hematologists: These are physicians specializing in blood disorders who play a pivotal role in diagnosing and managing multiple myeloma. They interpret test results and develop the primary treatment strategies.
- Oncologists: Specialists in cancer treatment, oncologists work closely with hematologists to formulate and administer chemotherapy and other therapeutic regimens.
- Radiologists: These specialists help in the precise imaging diagnosis, crucial for detecting the extent of bone involvement by myeloma.
- Pathologists: They examine blood, urine, and bone marrow samples to confirm the presence of myeloma cells and assess their characteristics.
- Orthopedists: For patients experiencing bone damage or fractures, orthopedists are involved in managing skeletal issues and improving mobility.
Together, these specialists form a multidisciplinary team that ensures a comprehensive approach to treatment, from accurate diagnosis to effective management plans, improving the outcomes for patients with multiple myeloma.
Impact of Symptoms on Quality of Life for Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma, a type of cancer that affects plasma cells in the bone marrow, can significantly impact the quality of life for those diagnosed. Understanding how its symptoms affect daily activities and mental health is crucial for patients and their support networks.
Effects on Daily Life
- Fatigue: One of the most common symptoms of multiple myeloma is fatigue, which can be overwhelming and persistent. This exhaustion affects daily productivity and can limit patients’ ability to perform routine tasks, reducing their independence.
- Bone Pain and Fractures: The disease often leads to bone weakening, resulting in severe pain and increased risk of fractures. These conditions can restrict physical activity and mobility, making simple actions like walking or sitting uncomfortable and challenging.
- Infections: Due to a compromised immune system, patients are more susceptible to infections, which can frequently lead to hospital visits and a continuous cycle of health setbacks that disrupt normal life.
- Kidney Dysfunction: Impaired kidney function, a possible complication of multiple myeloma, can necessitate regular dialysis, impacting work schedules and personal life, and requiring significant lifestyle adjustments.
Impact on Mental Health
- Anxiety and Depression: The chronic pain, ongoing treatments, and uncertain prognosis associated with multiple myeloma can lead to anxiety and depression. The emotional toll of managing a chronic illness can be profound and pervasive, affecting mental well-being.
- Social Isolation: Symptoms like fatigue and pain may cause patients to avoid social interactions, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness, which can exacerbate stress and emotional distress.
Importance of Support and Resources
The challenges posed by multiple myeloma underline the importance of robust support and resources for patients:
- Medical Care: Access to specialized medical care and timely treatment can help manage symptoms effectively, improving quality of life.
- Support Groups: Engaging with support groups can provide emotional comfort and practical advice, offering a community that understands and shares the unique challenges faced by multiple myeloma patients.
- Informational Resources: Reliable information about the disease, treatment options, and management of side effects can empower patients and caregivers, enabling better decision-making and disease management.
- Mental Health Services: Professional counseling and psychiatric services can help address the psychological impacts of living with a chronic illness, aiding patients in coping with anxiety and depression.
However, understanding and addressing the multifaceted impacts of multiple myeloma symptoms on both physical and mental health are essential for enhancing the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Treatment Options for Managing Symptoms
Effective symptom management is crucial for enhancing patient quality of life and optimizing therapeutic outcomes. This section explores both the current approaches to managing symptoms and delves into emerging research that may influence future treatment modalities.
Current Approaches to Managing Symptoms
- Pharmacological Interventions: Medications remain the cornerstone of symptom management, with options tailored to specific conditions and symptoms. Commonly used drugs include pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, and symptom-specific treatments such as anticonvulsants for neurological symptoms or antihistamines for allergic reactions.
- Physical Therapy: For many physical symptoms, such as pain and mobility issues, physical therapy offers a non-pharmacological treatment option that can improve function and reduce discomfort.
- Dietary Modifications: Adjusting one’s diet can significantly affect various symptoms. For instance, low-inflammatory diets may benefit individuals with autoimmune diseases, while low-FODMAP diets can help manage irritable bowel syndrome symptoms.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This psychological intervention is used widely to manage symptoms related to mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression. CBT helps patients develop coping strategies to deal with their symptoms more effectively.
- Lifestyle Changes: Simple changes in daily routines, such as increased physical activity or improved sleep hygiene, can have profound effects on managing symptoms ranging from chronic pain to fatigue.
Emerging Research and Potential Future Treatments
- Gene Therapy: Research is increasingly focusing on gene therapy as a way to treat or even cure symptoms at their genetic roots. This approach has shown promise in treating hereditary diseases and conditions with known genetic components.
- Biologics: The development of biologic drugs, which target specific parts of the immune system, is revolutionizing the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. These treatments offer new ways to manage symptoms with potentially fewer side effects than traditional therapies.
- Neuromodulation Techniques: Techniques such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) are under investigation for their potential to treat a variety of neurological and psychological symptoms by altering nerve activity.
- Personalized Medicine: Leveraging genetic information to tailor treatments to individual patients promises more effective management of symptoms with minimized side effects. This approach is likely to become more prevalent as genetic testing becomes more accessible and affordable.
- Virtual Reality (VR) Therapy: Emerging as a novel tool in managing chronic pain, anxiety, and PTSD symptoms, VR therapy involves the use of virtual environments to provide therapeutic interventions in a controlled, immersive setting.
As research advances, these emerging therapies offer hope for more personalized and effective management strategies, tailored to the unique needs of each patient.
Prevention and Monitoring of Multiple Myeloma
Can Multiple Myeloma Be Prevented?
As of now, there is no proven way to prevent multiple myeloma. Since the exact causes of multiple myeloma remain unclear, specific prevention strategies are hard to define. However, understanding the risk factors and reducing exposure to potential carcinogens could be beneficial. For instance, minimizing radiation exposure and avoiding exposure to certain chemicals may decrease the risk of developing multiple myeloma.
Monitoring Strategies for Multiple Myeloma
Monitoring for multiple myeloma is crucial, especially for individuals at higher risk or those who have been diagnosed with precursor conditions like MGUS (monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance) or smoldering multiple myeloma. Regular monitoring can help detect any progression to multiple myeloma early, potentially improving outcomes. Here are key strategies for monitoring:
- Blood Tests: Regular complete blood counts (CBC) and serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) are essential. These tests can help track the levels of different types of proteins in the blood, which is vital for spotting abnormal monoclonal protein (M-protein) production—a hallmark of multiple myeloma.
- Urine Tests: A 24-hour urine test for Bence Jones proteins, which are light chains of immunoglobulins, can help in the detection of multiple myeloma.
- Bone Marrow Examination: Periodic bone marrow biopsies might be recommended for those at high risk to check for abnormal plasma cell growth.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans can be used to monitor bone health and detect any bone damage or lesions often caused by multiple myeloma.
Regular Health Checks: What Should They Include?
For individuals at risk of multiple myeloma or those aiming for general health maintenance, regular health checks should be comprehensive and tailored to catch various health issues, including early signs of multiple myeloma:
- Complete Physical Examination: This includes assessing general signs of health and checking for physical indicators of multiple myeloma such as bone tenderness.
- Blood and Urine Tests: As mentioned, these are crucial for detecting abnormal protein levels and kidney function, which can be affected by multiple myeloma.
- Bone Density Test: To assess bone strength and check for potential bone loss or lesions.
- Cancer Screenings: Depending on individual risk factors, additional screenings for other types of cancers may be advised.
- Consultation with Specialists: Regular consultations with a hematologist or an oncologist can provide specialized insights and proactive management strategies for those at increased risk.
By integrating these preventive and monitoring strategies into regular health care routines, individuals can better manage their risk and health concerning multiple myeloma. Regular consultations with health care providers will ensure that any changes in health status are promptly addressed.
FAQs about Multiple Myeloma Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma typically presents with varied symptoms that may evolve as the disease progresses. Common indicators include bone pain, particularly in the spine or chest, fatigue due to anemia, frequent infections, and kidney dysfunction. Some patients may also experience nausea, constipation, and loss of appetite.
How does multiple myeloma affect the bones?
Multiple myeloma can lead to bone weakening and increased risk of fractures. This is because the cancer cells accumulate in the bone marrow, leading to the production of osteoclasts (cells that break down bone), which surpass the activity of osteoblasts (cells that build bone), resulting in bone loss.
Can multiple myeloma cause kidney problems?
Yes, multiple myeloma can significantly affect kidney function. The disease can lead to the production of abnormal proteins that can clog the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste and fluids from the blood effectively.
Are there any early warning signs of multiple myeloma?
Early signs of multiple myeloma might be subtle and resemble less serious conditions. Symptoms such as fatigue, mild bone discomfort, and recurrent infections could be early indicators. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider if these symptoms persist.
What should I do if I suspect I have symptoms of multiple myeloma?
If you experience symptoms consistent with multiple myeloma, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly affect the management and prognosis of the disease.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms and causes of multiple myeloma is crucial for early detection and effective management of this complex condition. Recognizing signs such as bone pain, fatigue, and recurring infections can prompt timely medical consultations. It is imperative to be aware of the potential risk factors, including age, family history, and previous health issues, which might increase susceptibility to multiple myeloma.
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing these symptoms or who has risk factors to consult with healthcare providers. Early diagnosis can significantly improve the effectiveness of treatment options and enhance quality of life. Remember, your health is important, and proactive care is key to managing any medical condition effectively.
References
For further reading and validation of the information provided on the symptoms of Multiple Myeloma, the following sources are highly recommended. These reputable references offer a comprehensive overview and detailed insights into the condition, enhancing understanding and supporting the data mentioned:
- Mayo Clinic – A trusted resource for patient care and health information. Explore their detailed section on Multiple Myeloma, which covers symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Visit Mayo Clinic’s Multiple Myeloma Resource.
- American Cancer Society – Provides a wealth of information including symptom lists, treatment choices, and patient support resources for those diagnosed with Multiple Myeloma. Read about Multiple Myeloma at the American Cancer Society.
- National Cancer Institute – Features extensive articles on the symptoms, diagnosis, and management of Multiple Myeloma. This government resource is invaluable for detailed medical information and research updates. Explore Multiple Myeloma on the National Cancer Institute Website.
- WebMD – Offers easily digestible information on the signs and symptoms of Multiple Myeloma, making complex medical terms accessible to a general audience. Check Symptoms of Multiple Myeloma on WebMD.
- Leukemia & Lymphoma Society – Provides comprehensive guides and brochures on Multiple Myeloma, including symptoms, latest research findings, and therapy options. Learn More from the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
These sources are integral for those seeking a deeper understanding of Multiple Myeloma, its symptoms, and its treatment, ensuring that readers receive the most accurate and up-to-date information.