Microscopic Colitis Treatment: Microscopic colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects the colon and causes persistent watery diarrhea and abdominal pain.
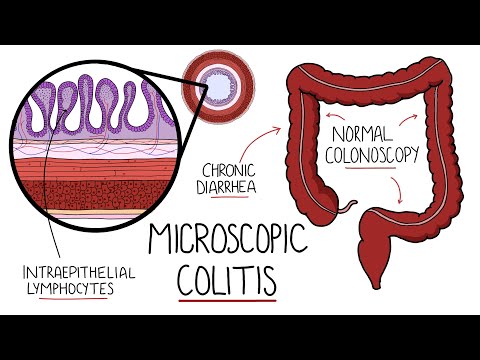
Unlike more widely known forms of colitis, microscopic colitis does not typically cause visible inflammation or ulcers on the colon’s surface. Instead, it can only be diagnosed by microscopic examination of colon tissue, hence the name.
This comprehensive guide explores the diagnosis and treatment options for microscopic colitis, aiming to provide a thorough understanding for patients and caregivers alike.
Understanding Microscopic Colitis
Microscopic colitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the colon that is only visible under a microscope. Unlike more common forms of colitis, there are no apparent changes or abnormalities on the surface of the colon when viewed with standard diagnostic tools like a colonoscopy. This condition can cause persistent diarrhea and discomfort, significantly impacting the quality of life.
Types of Microscopic Colitis
Microscopic colitis can be classified into two main types:
- Collagenous Colitis: This type involves a thick layer of collagen developing under the lining of the colon.
- Lymphocytic Colitis: In this form, there is an increase in lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) within the lining of the colon.
Both types share similar symptoms and can cause considerable discomfort and disruption to daily activities.
Common Symptoms and Affected Demographics
The symptoms of microscopic colitis can vary but commonly include:
- Chronic watery diarrhea
- Abdominal pain or cramps
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Fatigue
These symptoms can fluctuate, with periods of worsening followed by times when the symptoms may lessen or even disappear temporarily.
Who is Most Affected?
Microscopic colitis most frequently affects middle-aged and older adults, with a higher prevalence among women. It is especially common in individuals over the age of 50. Although the exact cause of microscopic colitis is not fully understood, it is believed to be associated with autoimmune conditions, certain medications, and genetic factors.
However, understanding microscopic colitis is crucial for those experiencing chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain, as these may be signs of this under-recognized condition. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Diagnosing Microscopic Colitis
Microscopic colitis, a condition characterized by chronic diarrhea and abdominal discomfort, is diagnosed primarily through medical history, physical examination, and specific diagnostic tests. Understanding this condition’s subtle presentation is crucial for effective diagnosis and management.
The Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
Medical history and physical examination are fundamental in the diagnosis of microscopic colitis. These initial steps help healthcare providers identify symptoms typical of the disease, such as chronic watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. A detailed medical history can reveal the duration and pattern of symptoms, potential triggers such as medication use (particularly NSAIDs, proton pump inhibitors, and SSRIs), and previous medical conditions that might suggest an alternative diagnosis. Physical examination, while often normal in microscopic colitis patients, helps exclude other causes of chronic diarrhea.
Key Diagnostic Tests
Several key diagnostic tests are essential for confirming microscopic colitis:
- Colonoscopy with Biopsy: This is the cornerstone of diagnosis. The colonoscopic appearance of the colon may be normal or show mild abnormalities, but histologic examination of multiple biopsies from throughout the colon is required to identify the characteristic inflammatory changes in the colon’s lining.
- Blood Tests: While not diagnostic for microscopic colitis, blood tests can rule out other causes of diarrhea and check for signs of inflammation or anemia.
- Stool Tests: These tests help exclude infections or inflammation that might mimic microscopic colitis.
Challenges in Diagnosing Microscopic Colitis
Diagnosing microscopic colitis presents several challenges:
- Subtle Symptoms: The symptoms of microscopic colitis can be subtle and intermittent, leading to delays in seeking medical attention or misdiagnosis.
- Normal Colonoscopic Appearance: The normal appearance of the colon during a colonoscopy can lead to overlooked diagnoses unless multiple biopsies are taken for histological examination.
- Variability in Presentation: The symptoms and biopsy findings of microscopic colitis can vary widely between individuals, complicating the diagnosis.
- Overlap with Other Digestive Disorders: Symptoms of microscopic colitis can overlap with those of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other inflammatory bowel diseases, which can complicate the diagnostic process.
However, understanding these challenges is crucial for healthcare providers to avoid misdiagnosis and to ensure appropriate management of patients with microscopic colitis.
Treatment Options for Microscopic Colitis
Fortunately, a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and understanding the impact of treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes and Diet
Managing microscopic colitis often begins with adjustments to your daily habits and diet:
- Hydration: Increase your water intake to counteract dehydration caused by diarrhea.
- Diet Modification: Identify and avoid foods that trigger symptoms. Common culprits include caffeine, dairy products, spicy foods, and fatty foods.
- Fiber Intake: A low-fiber diet helps some people, while others may benefit from a high-fiber diet. Tailoring fiber intake based on personal tolerance can be beneficial.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking can exacerbate symptoms, so quitting is recommended.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or counseling can help manage stress, which may trigger flare-ups.
Medications Commonly Used
Several medications are effective in treating microscopic colitis and are typically prescribed based on the severity of the symptoms:
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Budesonide is the most commonly prescribed steroid that helps reduce intestinal inflammation effectively.
- Antidiarrheal Agents: Over-the-counter medications like loperamide can control diarrhea, a common symptom of microscopic colitis.
- Immunosuppressant Drugs: For severe cases, drugs like azathioprine or methotrexate may be used to suppress the immune system’s activity.
- Bile Acid Binders: These can help if diarrhea is associated with bile acid malabsorption.
Impact of Treatment on Symptoms and Quality of Life
Effective management of microscopic colitis can lead to a significant improvement in symptoms and overall quality of life:
- Symptom Control: Most patients see a reduction in diarrhea and abdominal pain with the right treatment plan.
- Reduced Flare-ups: Lifestyle changes combined with medication can lead to fewer and less severe flare-ups.
- Improved Emotional Well-being: Controlling physical symptoms also helps improve emotional health, reducing feelings of anxiety and depression often associated with chronic illness.
However, regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
Advanced Treatment Strategies for Microscopic Colitis
As research progresses, new strategies are emerging to better manage and potentially alleviate this condition. Below, we explore some of the most promising advancements in the treatment of microscopic colitis.
Investigating Newer Pharmacological Treatments
Recent advancements in pharmacological treatments have shown promise in managing microscopic colitis more effectively. Researchers are exploring new classes of medications that target specific inflammatory pathways with fewer side effects than traditional therapies. These novel drugs aim to provide more targeted relief and improve the quality of life for patients with microscopic colitis.
The Potential of Biologics in Treating Microscopic Colitis
Biologics, which are therapies derived from living organisms, represent a cutting-edge approach in the treatment of microscopic colitis. These treatments work by specifically targeting molecules that play a key role in the inflammatory process. The potential of biologics lies in their ability to offer a more personalized treatment regimen, potentially leading to better management of symptoms and fewer systemic side effects.
Holistic Approaches and Alternative Medicine
In addition to conventional medical treatments, many patients are turning to holistic approaches and alternative medicine to manage microscopic colitis. These methods may include dietary changes, stress reduction techniques, and the use of supplements like probiotics, which can help maintain intestinal health. While these approaches should complement traditional treatments rather than replace them, they offer valuable support in managing the condition holistically.
By embracing a combination of these advanced strategies, healthcare providers can offer a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the diverse needs of patients with microscopic colitis.
Managing Flare-Ups in Microscopic Colitis
Effectively managing these episodes is crucial for maintaining quality of life and overall health. Here are some strategies to prevent and manage flare-ups, along with the importance of regular follow-ups with healthcare providers.
Strategies to Prevent and Manage Flare-Ups
- Dietary Adjustments: Identify and avoid foods that trigger symptoms. Common culprits include dairy, caffeine, spicy foods, and fatty foods. Consider keeping a food diary to track which foods exacerbate your condition.
- Medication Compliance: Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding medications. Some commonly prescribed medications for microscopic colitis include anti-inflammatory drugs and steroids.
- Stress Management: Since stress can exacerbate microscopic colitis, incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises into your daily routine.
- Stay Hydrated: Flare-ups often involve diarrhea, which can lead to dehydration. Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, helps maintain hydration.
- Avoid Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen and aspirin can worsen microscopic colitis symptoms. Use alternatives recommended by your healthcare provider.
Importance of Regular Follow-Ups with Healthcare Providers
Regular consultations with your healthcare provider are essential for managing microscopic colitis effectively. These follow-ups serve several critical purposes:
- Monitoring Disease Progression: Regular assessments can help monitor the effectiveness of your treatment plan and make adjustments as needed.
- Early Identification of Complications: Ongoing care allows for the early detection of any complications arising from the disease or its treatment.
- Support and Guidance: Regular interactions with healthcare professionals provide an opportunity to discuss concerns, get emotional support, and receive educational resources to better understand and manage your condition.
By adhering to these strategies and recognizing the value of consistent medical care, individuals living with microscopic colitis can lead a more comfortable and controlled life.
Living with Microscopic Colitis
Living with microscopic colitis means adapting to daily routines to manage symptoms effectively. Here are some strategies:
- Diet Adjustments: Identify and avoid foods that trigger symptoms. Common irritants include caffeine, dairy, spicy foods, and fatty foods. Keeping a food diary can help pinpoint specific triggers.
- Medication Compliance: Take prescribed medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs or steroids as directed by your healthcare provider to help control inflammation and manage symptoms.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to stay hydrated. Avoid alcoholic and caffeinated beverages that can exacerbate symptoms.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger or worsen symptoms. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can help manage stress levels.
- Regular Check-ups: Maintain regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
Support Systems and Resources for Patients
Navigating microscopic colitis is easier with the right support and resources:
- Healthcare Team: Build a supportive healthcare team, including a gastroenterologist who specializes in digestive disorders. Regular consultations can help manage the condition effectively.
- Support Groups: Join support groups where you can connect with others who understand the challenges you’re facing. These groups provide emotional support and practical tips from those who have similar experiences.
- Educational Resources: Utilize resources from reputable organizations like the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation, which offers educational materials, workshops, and seminars to help patients understand and manage their condition.
- Mental Health Support: Consider therapy or counseling to cope with the emotional impacts of living with a chronic illness. Mental health professionals can provide strategies to deal with stress and anxiety related to microscopic colitis.
- Online Communities: Engage with online forums and social media groups where you can share experiences and receive support from others with microscopic colitis, accessible from the comfort of your home.
By understanding and implementing these management strategies and utilizing available resources, individuals living with microscopic colitis can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition.
Future Directions in Research and Treatment
Current Research Trends in Microscopic Colitis
Recent advances in the study of microscopic colitis have primarily focused on understanding its pathogenesis and improving diagnostic accuracy. Researchers are investigating the role of genetics, environmental triggers, and the microbiome in its development. Additionally, there is a growing interest in identifying biomarkers that can aid in the early detection and differentiation of microscopic colitis from other inflammatory bowel diseases.
Potential Future Breakthroughs in Microscopic Colitis Treatment
Looking ahead, several promising breakthroughs are anticipated in the treatment of microscopic colitis. Innovations may include:
- Targeted Therapy: Development of treatments that specifically target the molecular pathways involved in microscopic colitis could offer more effective management with fewer side effects.
- Personalized Medicine: As our understanding of genetic factors improves, personalized treatment plans based on individual genetic profiles may become a reality, enhancing the efficacy of therapies.
- Microbiome Modulation: Treatments aimed at modifying the gut microbiome to maintain remission could revolutionize the management of microscopic colitis.
- Advanced Biologics: New biologic drugs that specifically address the immune response in microscopic colitis patients are under development, promising more precise intervention strategies.
These future directions not only hold the potential to enhance our understanding but also significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by microscopic colitis.
FAQs about Microscopic Colitis Treatment
What is Microscopic Colitis?
Microscopic colitis is an inflammatory bowel condition causing chronic, watery diarrhea. It is diagnosed through microscopic examination of colon tissue.
What are the treatment options for Microscopic Colitis?
Treatment options include dietary changes, medications like anti-inflammatory drugs, and probiotics. In severe cases, surgery may be considered.
How effective are medications in treating Microscopic Colitis?
Medications, such as budesonide and bismuth subsalicylate, are often highly effective in managing symptoms and reducing inflammation.
Are there any dietary changes that can help with Microscopic Colitis?
Yes, avoiding triggers like caffeine, dairy, and fatty foods can help. A low-FODMAP diet is also recommended to manage symptoms.
Can probiotics help with Microscopic Colitis?
Probiotics can aid in restoring gut flora balance, potentially reducing symptoms. Consult with a healthcare provider for recommendations.
Is surgery a common treatment for Microscopic Colitis?
Surgery is rare and typically considered only when other treatments fail. Most patients respond well to medication and lifestyle changes.
How long does it take to see improvement in symptoms?
Improvement can be seen within a few weeks of starting treatment, though this varies by individual. Consistent treatment and follow-up are key.
Conclusion
Microscopic colitis is a manageable condition with the right approach. Treatment options typically include dietary adjustments, medications, and lifestyle changes tailored to individual needs. Common medications like budesonide and anti-diarrheal agents help control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Patients are encouraged to collaborate closely with their healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans. Open communication and regular follow-ups are crucial for effective management. By working together, patients and healthcare professionals can achieve the best possible outcomes, ensuring a healthier, more comfortable life.
References
For further reading and to validate the information provided on Microscopic Colitis treatment, here are some reputable sources:
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – Offers comprehensive insights into Microscopic Colitis, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Read more.
- Mayo Clinic – Provides detailed information about Microscopic Colitis, its causes, risk factors, and treatment strategies. Learn more.
- WebMD – Features articles on Microscopic Colitis, covering topics such as symptoms, diagnosis, and management. Discover more.
- American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) – Publishes guidelines and research on the latest treatments and management practices for Microscopic Colitis. Explore further.
These sources provide reliable and up-to-date information to support your understanding and treatment of Microscopic Colitis.