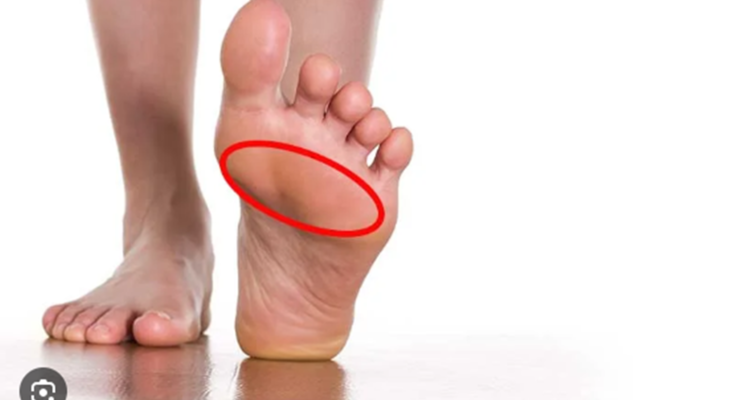
Metatarsalgia Symptoms: Metatarsalgia is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot.
This discomfort is typically concentrated around the metatarsal bones, which connect the toes and the arch of the foot.
Often referred to as a stone bruise, this ailment can affect individuals of various ages and activity levels.
What is Metatarsalgia?
Metatarsalgia is a medical condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot. This discomfort typically arises in the metatarsal region of the forefoot, where the bones connect to the toes. The pain, often described as a sharp ache or a burning sensation, can be exacerbated by standing, walking, or wearing unsuitable footwear. Metatarsalgia is not a disease itself but rather a symptom of various underlying issues that may affect foot mechanics, including overuse injuries, improper gait, or high-impact activities.
Who is Most at Risk for Developing Metatarsalgia?
Metatarsalgia can affect individuals of all ages, but certain groups are more susceptible due to specific lifestyle factors or physical conditions. Those most at risk include:
- Athletes: Particularly those who participate in high-impact sports such as running, football, or basketball, which place intense pressure on the feet.
- People with Foot Deformities: Conditions like hammertoes or bunions can alter foot mechanics and increase the risk.
- Individuals with High Arches or Flat Feet: These foot shapes can distribute weight unevenly across the foot, leading to excess pressure on the metatarsals.
- Overweight Individuals: Higher body weight can contribute to increased pressure on the foot structures during activities.
- Women who Frequently Wear High Heels: High heels elevate the pressure on the forefoot, potentially leading to metatarsalgia.
However, understanding these risk factors can help in managing or preventing the onset of metatarsalgia by adopting suitable footwear and engaging in appropriate foot care practices.
Symptoms of Metatarsalgia
Understanding the primary symptoms, their impact on daily activities, and knowing when to seek medical advice is essential for effective management and treatment.
Primary Symptoms Associated with Metatarsalgia
- Sharp, Aching Pain: The most notable symptom of metatarsalgia is a sharp or aching pain in the ball of the foot, particularly under the base of the second, third, and fourth toes.
- Burning Sensation: Many individuals experience a burning or tingling sensation in the affected area, which can indicate nerve involvement.
- Increased Pain When Standing or Walking: Activities that put pressure on the foot, such as standing, walking, or running, tend to exacerbate the pain.
- Pain that Worsens with Activity: Engaging in high-impact activities, especially those involving jumping or running, can intensify the discomfort.
- Numbness or Tingling in Toes: Alongside pain, there might be numbness or tingling in the toes, spreading from the ball of the foot.
Impact on Daily Activities
The discomfort associated with metatarsalgia can significantly impact daily life, including:
- Difficulty in Walking: The pain can make routine walking or prolonged standing very uncomfortable or even unbearable.
- Limitations on Physical Activities: Engaging in sports or exercises might become challenging, limiting one’s ability to participate in physical fitness or recreational activities.
- Footwear Restrictions: Individuals may find it difficult to wear certain types of shoes, such as high heels or tightly fitting shoes, which can exacerbate the pain.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider if:
- Persistent Pain: If the pain persists despite rest and over-the-counter pain relief measures, professional assessment is necessary.
- Symptoms Worsen: If symptoms worsen or new symptoms like increased swelling or changes in the skin color appear, it is important to seek medical attention.
- Impact on Mobility: If the pain significantly affects your ability to perform daily activities or reduces your quality of life, a medical evaluation can help determine the underlying causes and appropriate treatments.
However, recognizing these symptoms early and consulting with a healthcare professional can help manage metatarsalgia effectively, ensuring that this foot condition does not unduly affect your lifestyle.
Common Causes of Metatarsalgia
Understanding these can help in managing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. The causes of Metatarsalgia are generally categorized into internal factors, external factors, and activity-related causes.
Internal Factors
- Foot Structure: Individuals with high arches or a second toe longer than the big toe are more susceptible due to the uneven distribution of weight.
- Age: Aging causes the fat pad in the foot to thin, reducing cushioning, which can lead to increased pressure and pain.
- Weight: Excess body weight can put additional pressure on the metatarsals, leading to pain.
- Health Conditions: Diseases like arthritis, gout, or diabetes can contribute to foot problems, including Metatarsalgia.
External Factors
- Inappropriate Footwear: Shoes that are too tight, have high heels, or lack adequate padding can lead to Metatarsalgia.
- Poor Sock Padding: Insufficiently padded socks fail to absorb the impact while walking or running, increasing the stress on the metatarsals.
Activity-Related Causes
- High-Impact Sports: Activities such as running, tennis, or football, which involve significant running and jumping, can increase the risk of developing Metatarsalgia.
- Prolonged Standing: Jobs or activities that require standing for extended periods on hard surfaces can exacerbate foot pain.
- Overuse: Increasing activity levels too quickly without adequate conditioning can strain the metatarsals, leading to pain and inflammation.
By recognizing the specific causes linked to Metatarsalgia, individuals can better prevent or manage the condition through lifestyle adjustments, proper footwear, or seeking medical advice when necessary.
Diagnosing Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia, characterized by pain in the ball of the foot, can be diagnosed through various methods that healthcare professionals employ to understand and manage this condition effectively.
Common Diagnostic Techniques Used by Healthcare Professionals
- Physical Examination: Doctors typically begin with a thorough examination of the foot. They assess for tenderness in the metatarsal head region, the area just below the toes which is most often affected.
- Gait Analysis: Observing the patient’s walking pattern can help identify abnormalities in foot mechanics that might contribute to metatarsalgia.
- Pressure Tests: Applying pressure or having the patient engage in activities that provoke symptoms helps pinpoint the exact location and severity of the pain.
Role of Patient History and Physical Examination
- Review of Symptoms: Understanding when and how the pain occurs—during activities, following prolonged standing, or while wearing certain types of footwear—is crucial.
- Medical History: Discussing past foot injuries, surgeries, and overall health conditions that might influence foot mechanics.
- Lifestyle and Activity Levels: Analyzing the patient’s daily activities and physical demands can offer insights into potential causes of metatarsal pain.
Possible Tests
- X-rays: This common imaging test is used to rule out fractures and assess the alignment of the metatarsal bones.
- Ultrasound: An effective tool for visualizing soft tissue structures around the metatarsals to detect abnormalities like neuromas.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of both bone and soft tissues, including ligaments and tendons, which can help in diagnosing other conditions that might coexist with metatarsalgia.
- Blood Tests: Occasionally, if an underlying systemic condition such as rheumatoid arthritis is suspected, blood tests may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
However, each of these diagnostic approaches offers valuable information that aids in accurately identifying the causes of metatarsalgia, thus enabling effective treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Metatarsalgia
Below are the treatment options categorized into home remedies, medical treatments, and the role of physical therapy.
Initial Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Rest and Ice: Giving your feet a break can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Use ice packs on the affected area for 20 minutes several times a day to decrease inflammation.
- Proper Footwear: Choose shoes with good arch support and a wide toe box. Avoid high heels and tight shoes that can put additional pressure on the toes.
- Orthotic Inserts: Over-the-counter or custom-made orthotics can provide extra cushioning and support for the foot, distributing pressure more evenly.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the stress on the metatarsal bones.
- Elevation: Keep your feet elevated when sitting or lying down to reduce swelling.
Medical Treatments
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen or aspirin, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Steroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be recommended to relieve severe pain by reducing inflammation directly at the site of discomfort.
- Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the metatarsal bones and relieve pressure.
Role of Physical Therapy in Managing Symptoms
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing metatarsalgia by strengthening foot muscles, improving mobility, and reducing the likelihood of future injuries. Here’s how physical therapy can help:
- Stretching Exercises: These can help alleviate tightness in the foot and improve flexibility.
- Strengthening Exercises: Building strength in the foot and lower leg can help support the metatarsals and distribute foot pressure more effectively.
- Massage and Ultrasound Therapy: These techniques can help reduce inflammation and promote healing by improving blood flow to the affected area.
- Gait Analysis and Training: A physical therapist can analyze your walking pattern to identify and correct biomechanical issues that may be contributing to the pain.
Incorporating these treatments can significantly improve comfort and function for those suffering from metatarsalgia. Always consult a healthcare provider to tailor the treatment plan to your specific needs.
Prevention Tips for Metatarsalgia
Preventing this discomfort is crucial, especially for individuals who are at higher risk due to their lifestyle or foot structure. Here are some effective strategies to prevent metatarsalgia, focusing on proper footwear, foot care, lifestyle modifications, and the importance of regular foot assessments.
Recommendations for Footwear and Foot Care
- Choose the Right Footwear: Select shoes with a wide toe box that allows your toes to spread naturally without constriction. Ensure the footwear provides adequate arch support and a cushioned sole to reduce pressure on the ball of the foot.
- Use Orthotic Inserts: Consider using over-the-counter or custom-made orthotic inserts. These can help distribute pressure evenly across your foot, reducing the load on the metatarsal area.
- Maintain Foot Hygiene: Keep your feet clean and dry to prevent infections that could exacerbate foot pain. Regularly change your socks and use foot powder if necessary to keep feet dry.
- Moisturize Your Feet: Apply a good foot cream daily to prevent cracks and dry skin, which can make your feet more vulnerable to pain and infection.
Lifestyle Modifications for At-Risk Individuals
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body weight can increase the stress on your feet. Aim to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Limit High-Impact Activities: Activities that put excessive pressure on the feet, like running or jumping, should be moderated. Instead, opt for low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling.
- Take Breaks: If your job involves prolonged standing or walking, make sure to take regular breaks to rest your feet.
- Stretch Regularly: Incorporate foot and calf stretches into your daily routine to improve the flexibility and strength of your foot muscles, which can help prevent pain.
Importance of Regular Foot Assessments
- Schedule Regular Check-Ups: Visit a podiatrist annually for a comprehensive foot exam, especially if you have ongoing foot problems or conditions like diabetes that increase the risk of foot issues.
- Monitor Changes: Be vigilant about any changes in the shape, feel, or function of your feet. Early detection of potential problems can prevent the development of metatarsalgia.
- Follow Professional Advice: Adhere to any recommendations from your foot care specialist, including the use of specific footwear or orthotics and any suggested changes to your foot care routine.
Implementing these prevention tips can significantly reduce the risk of developing metatarsalgia, enabling you to lead an active and pain-free life. Prioritize your foot health through proactive care and make adjustments as needed to ensure your feet remain in excellent condition.
FAQs about Metatarsalgia Symptoms
What is metatarsalgia?
Metatarsalgia is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot. It commonly affects the area just behind the toes, where the metatarsal bones are located.
What are the common symptoms of metatarsalgia?
The most prevalent symptoms include sharp, aching, or burning pain in the ball of the foot, which may worsen when standing, walking, or running. Some individuals might also experience numbness or tingling in their toes.
What causes metatarsalgia to flare up?
Flare-ups can be triggered by excessive physical activity, wearing poorly fitting shoes, being overweight, or having an underlying foot deformity like a high arch or a bunion.
How can you relieve pain from metatarsalgia at home?
Home remedies include resting the foot, applying ice, using over-the-counter pain relievers, and wearing supportive footwear. Additionally, cushioned insoles or orthotics may help distribute pressure more evenly across the foot.
When should you see a doctor for metatarsalgia?
Consult a healthcare provider if pain persists despite home treatments, or if it interferes with daily activities. Persistent pain may require professional assessment to rule out other conditions and to receive targeted treatment.
Conclusion
In summary, metatarsalgia presents primarily with pain and discomfort in the ball of the foot, which may be exacerbated by activities like running or walking, especially in poorly fitting footwear. Causes range from high-impact sports to foot deformities and excess body weight, each contributing to the undue stress on the metatarsals.
If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms of metatarsalgia, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider. They can offer a thorough diagnosis and tailor a treatment plan that best suits your needs, helping you return to a pain-free lifestyle. Remember, timely medical advice is key to managing foot health effectively.
References
For further reading and validation of the information provided on Metatarsalgia symptoms, the following sources are highly recommended. These reputable references offer detailed insights and additional data that can be helpful for both healthcare professionals and patients:
- Mayo Clinic – This resource provides a comprehensive overview of Metatarsalgia, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Read more about Metatarsalgia at Mayo Clinic.
- WebMD – WebMD offers detailed information on the diagnosis and management of Metatarsalgia, helping readers understand the various aspects of the condition. Explore Metatarsalgia on WebMD.
- Healthline – Known for its clear and accessible health information, Healthline provides insights into the symptoms of Metatarsalgia and practical tips for alleviating discomfort. Visit Healthline for more on Metatarsalgia.
- OrthoInfo – American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons – This site offers in-depth medical articles on Metatarsalgia authored by orthopedic specialists, covering everything from early symptoms to advanced treatment techniques. Learn about Metatarsalgia at OrthoInfo.
These sources are excellent starting points for understanding Metatarsalgia and its impact on foot health. They provide reliable and up-to-date information that is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.