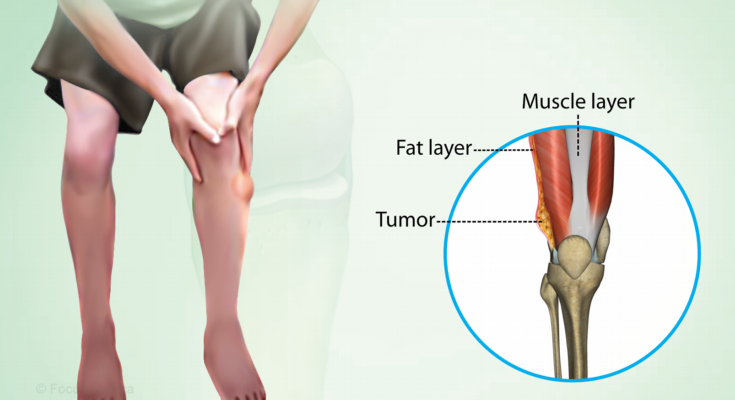
Liposarcoma Symptoms: Liposarcoma stands as one of the most prevalent types of soft tissue sarcoma, affecting thousands of individuals each year across the globe.
This malignancy arises in fatty tissues and can occur in almost any body part, though it most frequently manifests in the thighs, behind the knees, and in the abdomen.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of liposarcoma is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Understanding Liposarcoma
Liposarcoma is a type of cancer that arises in fat cells in deep soft tissue, such as that inside the thigh or in the belly. It is a rare form of cancer and is one of the many types of sarcoma. Understanding the types of liposarcoma and the demographics it affects can help in recognizing its impact and the importance of early diagnosis.
Types of Liposarcoma
Liposarcoma is classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics and behaviors. These include:
- Well-differentiated Liposarcoma: The most common type, often developing in the limbs or retroperitoneum (the abdominal space behind the intestines). It grows slowly and is considered low-grade, meaning it is less likely to spread.
- Myxoid Liposarcoma: Characterized by a gel-like consistency due to the presence of mucoid substance, this type tends to occur in the limbs. It is intermediate-grade and has a distinctive molecular marker that helps in its diagnosis.
- Round Cell Liposarcoma: This is a high-grade tumor that may behave more aggressively. It is often grouped with myxoid liposarcoma due to similar molecular features.
- Pleomorphic Liposarcoma: Known for its varied cell shapes and sizes, this type is rare and highly aggressive, typically occurring in the limbs of older adults.
- Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma: This type represents a progression from a well-differentiated liposarcoma into a more aggressive form. It can occur years after the initial diagnosis and behaves more aggressively.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Liposarcoma accounts for about 20% of all soft tissue sarcomas. Annually, approximately 2 to 3 cases occur per million people worldwide, which translates to around 1,000 to 1,500 new cases per year in the United States alone.
Demographic Insights:
- Age: Liposarcoma is most commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 40 and 60, but it can occur at any age.
- Gender: Studies suggest a slightly higher prevalence in males than in females.
- Geographical Variations: While liposarcoma occurs worldwide, the documented cases and reporting might vary significantly across different regions, often influenced by the availability of diagnostic and treatment facilities.
However, awareness and early diagnosis play key roles in improving the prognosis and outcome for those affected by liposarcoma.
Symptoms of Liposarcoma
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment, improving the overall prognosis.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of liposarcoma vary widely but generally include:
- A noticeable lump or swelling, which may or may not be painful. This lump might feel soft to the touch and can increase in size over time.
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area if the growing tumor presses on nerves or muscles.
- Numbness or tingling, especially if the tumor affects nerve tissues.
- Reduced mobility in the affected area, particularly if the liposarcoma develops near joints or within muscle groups.
Symptoms by Type and Location
Abdominal Liposarcoma:
- Abdominal pain which can be vague and nonspecific.
- Feeling of fullness or bloating, even without eating much.
- Changes in bowel habits such as constipation or diarrhea, sometimes accompanied by blood in the stool if the tumor impacts the gastrointestinal tract.
Retroperitoneal Liposarcoma:
- Back pain or pain on one side of the body.
- Weight loss that is unexplained by other health changes.
- Swelling in the legs or ankles due to lymphatic obstruction.
Liposarcoma in Limbs:
- Swelling or a mass that is initially painless.
- Decreased range of motion in the affected limb.
- Weakness in the limb, affecting daily activities.
Progression of Symptoms
As liposarcoma grows, symptoms tend to become more pronounced and can significantly impact quality of life. For example, a small, non-intrusive lump can evolve into a large mass that causes severe pain, functional impairment, and even visible deformity. Additionally, as the cancer progresses, it may metastasize to other parts of the body, leading to new symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and more severe systemic effects.
However, early medical consultation is crucial when any of these symptoms are observed, as early detection greatly enhances treatment efficacy.
Causes and Risk Factors of Liposarcoma
Here, we explore the recognized causes and risk factors, along with insights from recent research studies.
Causes of Liposarcoma
The exact causes of liposarcoma are not clearly understood. Like many cancers, liposarcoma develops when mutations occur in the genetic material of fat cells. These mutations cause the cells to multiply uncontrollably, forming a mass of abnormal cells that can invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body. However, specific triggers for these mutations are not well-defined in medical research.
Risk Factors of Liposarcoma
While the direct causes are elusive, several risk factors have been identified that may increase a person’s likelihood of developing liposarcoma:
- Age: Liposarcoma is most commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 50 and 65. It is rare in children.
- Genetic Factors: Certain inherited genetic conditions, such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome and hereditary retinoblastoma, are linked to a higher risk of developing liposarcoma.
- Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation treatment for other cancers can increase the risk of developing liposarcoma. The risk typically increases with higher doses of radiation.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as vinyl chloride and dioxin, may be linked to an increased risk of liposarcoma, although more research is needed to confirm these associations.
- Lifestyle Factors: While less directly linked than other cancers, lifestyle factors that lead to general poor health can theoretically increase the risk due to their impact on overall cellular health.
Insights from Recent Research
Recent studies continue to explore the molecular and genetic bases of liposarcoma to better understand its causes. For instance, research has identified that deletions or amplifications of certain genes (like CDK4, MDM2) are common in liposarcoma cells. These genetic changes can guide the development of targeted therapies.
Additionally, ongoing research aims to identify biomarkers that can predict the development of liposarcoma, which would aid in early diagnosis and treatment. Studies investigating the role of the immune system in controlling or promoting tumor growth are also promising, potentially leading to new immunotherapeutic approaches for treatment.
Diagnosing Liposarcoma
Below, we outline the key diagnostic steps, common tests, and imaging techniques used in the diagnosis of liposarcoma, emphasizing the importance of early detection.
Diagnostic Processes for Detecting Liposarcoma
The process of diagnosing liposarcoma typically begins with a detailed patient history and physical examination, followed by a series of specialized tests. These steps are designed to differentiate liposarcoma from other types of soft tissue tumors and to ascertain the exact type and stage of the tumor:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Doctors start by gathering information about the patient’s health history and any symptoms experienced. A physical exam can help identify unusual growths or lumps.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques play a pivotal role in visualizing the location and size of the tumor, as well as in determining whether the cancer has spread.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is the definitive way to diagnose liposarcoma. A sample of tissue is removed from the tumor and examined under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
Common Tests and Imaging Techniques
Several tests and imaging modalities are crucial in diagnosing liposarcoma effectively:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI is particularly useful for examining soft tissue tumors. It provides detailed images and can help in assessing the tumor’s size and depth, crucial for treatment planning.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): CT scans can help determine the location of the tumor and check if the disease has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs.
- Ultrasound: Sometimes used in the initial assessment to distinguish between a solid tumor and a fluid-filled cyst.
- PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography): This may be used to gauge the metabolic activity of the tumor and to check for metastasis.
- Biopsy Techniques: Depending on the tumor’s location, different types of biopsy techniques, such as fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, or surgical biopsy, may be used.
Importance of Early Detection
Detecting liposarcoma at an early stage is critical as it greatly enhances the effectiveness of treatment. Early detection can lead to successful surgical removal of the tumor before it metastasizes or grows too large, making surgery more complicated. Additionally, when liposarcoma is identified and treated early, patients have a higher likelihood of favorable outcomes and reduced risk of recurrence.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis not only facilitates better management options but also significantly improves the overall quality of life for patients, underscoring the need for awareness and timely medical consultation when symptoms first appear.
By employing a combination of detailed medical examination and advanced imaging techniques, healthcare professionals can effectively diagnose liposarcoma, enabling them to tailor a treatment plan that offers the best chance for recovery and long-term management of the disease.
Treatment Options for Liposarcoma
Here, we explore the established treatment modalities, new and emerging treatments, and the importance of personalized treatment plans.
Established Treatment Modalities
- Surgery: The primary treatment for liposarcoma is surgical removal of the tumor. The goal is to completely remove the cancer along with a margin of healthy tissue around it. Sometimes, in cases where the tumor affects critical structures, complete removal might be challenging.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is often used before surgery to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove, or after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Although liposarcoma is often resistant to chemotherapy, certain types might still respond to it. Chemotherapy may be used in cases of more aggressive or advanced liposarcoma, especially if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Targeted Therapy: This involves drugs that specifically target unique aspects of cancer cells, such as specific genetic mutations. For example, drugs that inhibit the growth of blood vessels that supply nutrients to the tumor (anti-angiogenic therapy) can be effective in some cases.
New and Emerging Treatments
Research into liposarcoma treatments continues to evolve, offering new hope:
- Immunotherapy: This treatment leverages the body’s immune system to fight the cancer. New immunotherapeutic agents are being tested in clinical trials and have shown promise in treating some types of liposarcoma.
- Molecularly Targeted Therapy: Advances in understanding the genetic makeup of liposarcomas have led to the development of drugs that target specific molecular pathways involved in tumor growth and progression.
- Gene Therapy: Experimental treatments that involve altering the genes inside cancer cells to stop them from growing are currently under research and could provide new treatment options in the future.
Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Personalized treatment plans are critical in the management of liposarcoma due to the diverse nature of the disease. Personalized medicine involves:
- Genetic Testing: Identifying specific mutations in the tumor can help tailor treatment options that are more effective for the individual patient.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Treatment often involves a team of specialists, including oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and pathologists, who work together to create a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Regular Follow-ups: Monitoring the patient regularly to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and make adjustments as necessary is crucial for achieving the best outcomes.
However, patients are encouraged to discuss these options with their healthcare provider to determine the most effective treatment strategy based on their specific condition.
Prevention and Management of Liposarcoma
Effective management and potential prevention strategies can be vital for those at risk. Below are guidelines and tips for managing symptoms and lifestyle recommendations that may help those affected by or at risk for liposarcoma.
Managing Symptoms of Liposarcoma
The management of liposarcoma symptoms plays a critical role in improving the quality of life for patients. Here are some key strategies:
- Pain Management: Regular consultation with a pain specialist can help manage the pain associated with tumor growth, using both medication and non-pharmacological methods.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in tailored physical therapy can help maintain mobility and function, which might be affected by tumors in limbs.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent medical check-ups are crucial to monitor the growth and spread of the tumor. Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans are commonly used.
- Nutritional Support: Consulting a dietitian to ensure proper nutrition can help maintain strength and overall health, which is particularly important during treatment.
- Psychological Support: Accessing psychological or counseling services to address the emotional and mental health challenges posed by a chronic condition like liposarcoma.
Can Liposarcoma Be Prevented?
Currently, there are no proven methods to prevent liposarcoma as its exact causes are not fully understood and are thought to involve genetic factors beyond individual control. However, awareness of the disease and early detection through regular medical check-ups can aid in early treatment, which is often more effective.
Lifestyle Changes and Monitoring for At-Risk Individuals
For individuals at risk of liposarcoma, or for those who want to adopt a lifestyle that supports overall health, consider the following:
- Regular Screenings: For those with a family history of liposarcoma or other risk factors, regular screenings can help in early detection.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: While there’s no direct link between obesity and liposarcoma, maintaining a healthy weight supports overall well-being.
- Avoid Exposure to Chemicals: Some studies suggest that exposure to certain chemicals may increase cancer risk, so minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals, like certain herbicides and aerosols, could be prudent.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise helps maintain overall health and can improve recovery outcomes if you become ill.
- No Smoking: Avoid smoking, as tobacco use is linked with many types of cancer, although direct links with liposarcoma are not established.
Please Note: Some of these strategies may not directly prevent liposarcoma, they do contribute to a healthier lifestyle that can enhance your ability to cope with diseases and improve your overall health status.
FAQs about Liposarcoma Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of liposarcoma?
Liposarcoma often develops silently and may not show noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Common symptoms include a growing lump or swelling which may be painful, fatigue, and weight loss. These tumors typically appear in the thighs, legs, or abdomen, and the discomfort can increase as they press against nearby nerves or organs.
Can liposarcoma symptoms be easily confused with other conditions?
Yes, the symptoms of liposarcoma can be quite generic and similar to less serious conditions, such as lipomas (benign fatty tumors). The presence of a painless lump is the most common symptom, which is why medical evaluation is essential for an accurate diagnosis, particularly if the lump grows or becomes painful.
Do liposarcoma symptoms vary by the tumor’s location?
Absolutely. Liposarcomas can vary in symptomatology depending on their location. For example, tumors in the abdomen may lead to abdominal pain, feelings of fullness, or constipation, while those in the limbs might only present as swelling without significant pain until they grow large.
What are the red flags for liposarcoma that warrant immediate medical attention?
Red flags for liposarcoma include an increase in the size of a lump, a lump that becomes painful, noticeable weight loss, and persistent pain in the abdomen or limbs. Any of these symptoms should prompt immediate consultation with a healthcare provider.
How is liposarcoma diagnosed following the observation of symptoms?
Diagnosis of liposarcoma typically begins with a physical examination, followed by imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to view the detailed structure of the lump. A definitive diagnosis is usually made via a biopsy, where a sample of the tumor is examined under a microscope.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of liposarcoma is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. If you notice any unusual lumps or pain in your body, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider.
Regular check-ups can help detect this rare cancer at an early stage, increasing the likelihood of successful treatment. Remember, your health is important, and being proactive about any symptoms can make a significant difference in your treatment journey.
Do not hesitate to reach out to medical professionals if you have any concerns about your health.
References
For additional information and further validation of the details discussed regarding liposarcoma symptoms, consider exploring the following reputable sources. These references are chosen for their credibility and depth of research, providing readers with comprehensive insights into liposarcoma:
- Mayo Clinic – Offers detailed overviews of symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for liposarcoma. Visit Mayo Clinic’s Liposarcoma Page.
- American Cancer Society – Provides extensive information on the types of liposarcoma, how they are diagnosed, and what treatments are available. Read more at American Cancer Society.
- National Cancer Institute – A resource for in-depth research articles and data on liposarcoma, including symptoms and patient care guidelines. Explore the National Cancer Institute Resources.
These links are a great starting point for anyone looking to understand more about liposarcoma, its symptoms, and the latest treatments and research in the field.