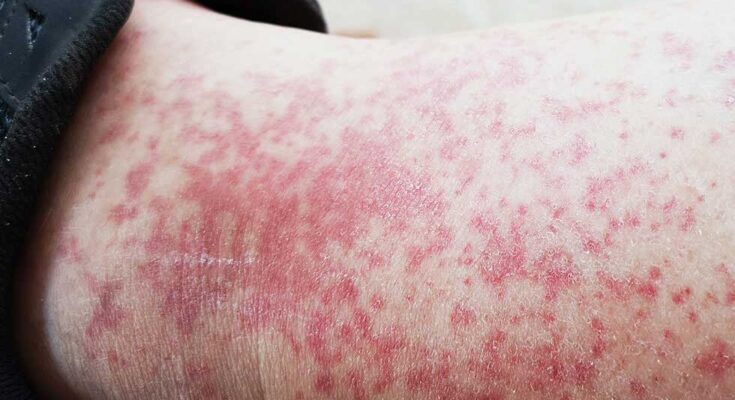
Lichen Planus Treatment: Lichen Planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the skin, hair, nails, and mucous membranes.
It is characterized by itchy, purple, polygonal bumps that typically manifest along the wrists, lower legs, back, and in oral or genital mucosa.
The exact cause of Lichen Planus is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve an immune-mediated response triggered by various factors such as viruses, allergens, or genetic predisposition.
Understanding Lichen Planus
Lichen Planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the skin, hair, nails, and mucous membranes. It is known for its characteristic itchy, purple bumps, which can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. Understanding the incidence, causes, types, and risk factors associated with Lichen Planus can help individuals manage and seek appropriate treatment for this condition.
Incidence and Demographics Affected
- Prevalence: Lichen Planus affects approximately 1% of the population worldwide. Although it can occur at any age, it is most commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 30 and 60.
- Gender Distribution: Women are slightly more likely to develop Lichen Planus than men.
- Geographical Variation: The condition is observed globally, with no specific geographical concentration.
- Ethnic Impact: Some studies suggest that Lichen Planus might be more prevalent or more severe in certain ethnic groups, though more research is needed to clarify these trends.
Causes and Risk Factors of Lichen Planus
Lichen Planus is considered to be an autoimmune disorder, but the exact causes remain unclear. Several factors, however, are thought to increase the risk of developing the condition:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of Lichen Planus can increase one’s risk.
- Viral Infections: Hepatitis C infection has been linked to a higher incidence of Lichen Planus.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including some antimalarials and medications used in the treatment of heart disease, have been associated with triggering Lichen Planus.
- Stress: Emotional stress is believed to exacerbate the condition.
- Chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals used in photography and the manufacturing of color film has been implicated.
Types of Lichen Planus
Lichen Planus manifests in several distinct forms, each affecting the body in different ways:
- Cutaneous Lichen Planus: The most common form, characterized by itchy, purple, flat-topped bumps on the skin.
- Oral Lichen Planus: Affects the mucous membranes inside the mouth, causing white patches, redness, and ulcers.
- Genital Lichen Planus: Involves the mucous membranes of the genitalia, leading to soreness and erosive lesions.
- Scalp Lichen Planus (Lichen Planopilaris): Can cause hair loss and permanent scarring on the scalp.
- Nail Lichen Planus: Affects the nails, leading to abnormal growth, ridges, and sometimes complete loss of the nail.
If you suspect you might have Lichen Planus, consulting a healthcare professional for an evaluation and appropriate treatment is advisable.
Symptoms and Signs of Lichen Planus
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Here, we detail the common symptoms of Lichen Planus and explain how these symptoms can vary between different types of LP.
Common Symptoms of Lichen Planus
Lichen Planus typically presents with several distinct symptoms, which can affect different parts of the body:
- Purple-Colored Lesions or Rashes: These are usually itchy and can have flat-topped bumps.
- Itching: This is one of the most common symptoms, ranging from mild to severe.
- Lacy White Patches: Often found in the mouth, these can also appear on other mucous membranes.
- Painful Sores: These can occur in the mouth or on the vulva and may be accompanied by burning sensations.
- Hair Loss and Scalp Changes: In cases affecting the scalp (Lichen Planopilaris), it can lead to hair thinning and permanent hair loss.
- Nail Damage: Nails may become thin, ridged, or split, and in severe cases, nail loss can occur.
Variation in Symptoms Among Different Types of Lichen Planus
The symptoms of Lichen Planus can vary significantly depending on the type involved:
- Cutaneous Lichen Planus: This type primarily affects the skin, leading to the purple, itchy, flat-topped lesions typically associated with the disorder.
- Oral Lichen Planus: Affecting the mucous membranes inside the mouth, this form manifests as white, lacy patches or red, swollen tissues, and can cause painful sores.
- Genital Lichen Planus: This form can cause severe itching, redness, and soreness around the genital area, impacting both men and women.
- Lichen Planopilaris: Specifically affecting hair follicles, this subtype can lead to scalp lesions, hair loss, and sometimes scarring.
- Erosive Lichen Planus: Particularly aggressive, this variant involves painful, raw lesions on mucous membranes, often in the mouth or genitals, and can significantly impair quality of life.
However, understanding these variations is essential for healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively and for patients to manage their symptoms appropriately.
Diagnosing Lichen Planus
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment. Below, we delve into the primary diagnostic procedures and criteria, as well as the challenges faced in diagnosing Lichen Planus.
Diagnostic Procedures and Criteria for Lichen Planus
1. Clinical Evaluation:
- Symptoms Review: Doctors start by examining the skin, mouth, scalp, and nails for the characteristic rashes and lesions of Lichen Planus. A detailed medical history helps differentiate it from similar conditions.
- Physical Examination: Special attention is given to the typical purple, flat-topped lesions that often appear in symmetrical patterns.
2. Biopsy: A small sample of affected tissue may be taken and examined under a microscope. This helps confirm the presence of the lichenoid tissue reaction typical of Lichen Planus.
3. Histopathological Examination: This involves looking at the biopsy sample to identify specific microscopic features of Lichen Planus, such as a thickened epidermal layer and a band-like infiltration of white blood cells.
4. Direct Immunofluorescence: This test is used to check for specific immune proteins often present in Lichen Planus lesions, aiding in differential diagnosis from other dermatological conditions.
5. Blood Tests and Allergy Testing: While not specific to Lichen Planus, these tests can help rule out other causes of the symptoms, such as hepatic conditions that are sometimes linked to the disease.
Challenges in Diagnosing Lichen Planus
Diagnosing Lichen Planus comes with its own set of challenges:
1. Similarity to Other Skin Conditions: Lichen Planus can be easily confused with conditions like psoriasis, eczema, or other lichenoid dermatoses, making accurate diagnosis challenging.
2. Variability of Symptoms: Symptoms can vary widely from one patient to another, especially since Lichen Planus can affect the skin, mouth, scalp, nails, and even genitalia, each of which may present differently.
3. Occurrence of Lesions in Hidden Areas: Lesions may appear in less visible areas such as the scalp or inside the mouth and genitals, which can delay diagnosis.
4. Lack of Awareness and Misdiagnosis: Due to its relatively rare occurrence and the variability of its presentation, Lichen Planus may be unfamiliar to some healthcare providers, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
However, regular follow-ups and a comprehensive approach to treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected.
Treatment Options for Lichen Planus
While there is no cure, effective management strategies can alleviate symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Below, we explore the various treatment options available for Lichen Planus, the role of light therapy and other physical treatments, as well as emerging therapies and ongoing research in this field.
Conventional Treatment Methods
- Topical Corticosteroids: The most common treatment for Lichen Planus involves topical corticosteroids which reduce inflammation and alleviate itching.
- Systemic Corticosteroids: In severe cases, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for a short duration to control symptoms.
- Retinoids: Both topical and oral retinoids are used to treat severe or persistent Lichen Planus.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like cyclosporine can be used to suppress the immune system’s activity, reducing the severity of the symptoms.
- Antihistamines: These are often recommended to reduce itching, particularly in cases where itching disrupts sleep.
Role of Light Therapy and Other Physical Treatments
Light therapy, or phototherapy, has shown promise in treating Lichen Planus, particularly in cases resistant to topical treatments. The most common forms include:
- UVB Phototherapy: Narrowband UVB light can help reduce lesions and alleviate symptoms.
- PUVA Therapy: This involves the use of a plant-derived compound called psoralen combined with UVA light exposure, which can be effective for more extensive skin involvement.
Other physical treatments include:
- Laser Therapy: For resistant lesions, laser treatment can be beneficial in reducing the thickness and discomfort of plaques.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the lesions with liquid nitrogen can help remove them, though it’s generally used for fewer and isolated lesions.
Emerging Therapies and Research
Research into new treatments for Lichen Planus is ongoing, with several promising areas:
- Biologic Therapies: These are targeted drugs that affect specific parts of the immune system. Drugs like etanercept and ustekinumab are under investigation for their potential in treating Lichen Planus.
- Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors: These medications interfere with the pathway that leads to inflammation and have shown potential in early trials.
- Microbiome Therapies: Emerging research suggests that the skin and oral microbiome may play a role in the inflammation characteristic of Lichen Planus, pointing towards probiotic treatments as a potential therapy.
However, as research progresses, the hope for more targeted and effective treatments grows, promising better management of this complex condition.
Managing Lichen Planus
Effective management involves lifestyle modifications, dietary considerations, psychological support, and leveraging patient resources. Here’s a detailed guide to help individuals cope with Lichen Planus.
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
To alleviate symptoms and manage Lichen Planus effectively, consider the following lifestyle adjustments and home remedies:
- Skin Care: Use mild, unscented soaps and lotions to minimize irritation. Moisturizing regularly can help soothe affected areas.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that exacerbate your symptoms, such as certain chemicals and medications.
- Sun Protection: Protect skin from excessive sun exposure by wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen, which can prevent flare-ups.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can reduce stress, which may trigger or worsen symptoms.
Importance of Diet and Nutrition
Nutrition plays a vital role in managing Lichen Planus:
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties, such as berries, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens.
- Avoid Irritants: Some individuals may find that spicy foods, citrus fruits, and acidic items can irritate oral lichen planus.
- Vitamin Rich Diet: Ensuring a diet high in vitamins, especially vitamin A, C, and zinc, can support skin health and potentially reduce symptoms.
Psychological Impact of Lichen Planus and Coping Strategies
Living with Lichen Planus can be challenging not just physically but also mentally:
- Emotional Support: It’s important to seek support from friends, family, or professional counselors to manage the emotional stress.
- Coping Mechanisms: Engage in activities that you enjoy and that relax you to divert attention from persistent discomfort.
- Education: Understanding your condition can alleviate fears and misconceptions, helping you manage your condition more effectively.
Patient Support and Resources
Accessing reliable support and resources can greatly assist in the management of Lichen Planus:
- Support Groups: Join online forums and local support groups where experiences and coping strategies are shared among sufferers.
- Professional Help: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers who specialize in skin disorders can provide personalized advice and treatment plans.
- Educational Resources: Websites like the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) offer valuable information and updates on managing skin conditions.
By adopting comprehensive management strategies, individuals living with Lichen Planus can lead a healthier and more comfortable life.
Prognosis and Long-Term Management of Lichen Planus
Lichen Planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the skin, hair, nails, and mucous membranes. While it can be uncomfortable and persistent, the prognosis for most patients is generally positive, especially with effective management.
Typical Prognosis for Patients with Lichen Planus
For many individuals, Lichen Planus is a self-limiting disease, which means it may resolve on its own without treatment within a couple of years. However, symptoms can recur. The prognosis varies based on the severity and location of the outbreak. Skin lesions typically resolve without scarring, but lesions on mucous membranes, such as the mouth or genitals, can be more persistent and challenging to treat.
Potential Complications and How to Manage Them
Lichen Planus can lead to several complications, particularly if it affects the mucous membranes. Persistent oral Lichen Planus can increase the risk of oral cancer, so regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is crucial. Scarring and permanent hair loss can occur when the scalp is involved. Emotional and psychological impacts, such as stress or depression, are also common due to the chronic nature of the disease and its effect on appearance.
Management strategies for complications include:
- Regular Screening: Regular dental check-ups and screenings for skin health are recommended to catch any malignant changes early.
- Symptom Management: Topical steroids, retinoids, or immunosuppressants can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of scarring.
- Supportive Care: Psychological support or counseling can be beneficial for those dealing with the emotional effects of chronic illness.
Monitoring and Long-Term Care Strategies
Effective long-term management of Lichen Planus involves regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment as needed. Here are key strategies:
- Regular Follow-Ups: Schedule regular visits with a dermatologist to monitor the condition’s progress and response to treatment.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Patients are advised to avoid triggers known to exacerbate symptoms, such as certain medications, allergens, or stress.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about the nature of the disease and the importance of adherence to treatment plans is crucial for management.
However, while Lichen Planus can be a persistent and sometimes debilitating condition, with the right strategies and ongoing care, most individuals can manage their symptoms and lead healthy lives.
FAQs about Lichen Planus Treatment
1. What is the most effective treatment for lichen planus?
The most effective treatment for lichen planus can vary depending on the individual’s symptoms and the severity of their condition. Typically, corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve itching. Topical ointments, oral medications, or injections may be used. For more severe cases, treatments like retinoids, immunosuppressants, or light therapy may be recommended. Always consult a healthcare professional for a tailored treatment plan.
2. Are there any home remedies that can help with lichen planus?
While home remedies are not a substitute for professional medical treatment, some may help alleviate symptoms. Aloe vera, coconut oil, and oatmeal baths can soothe itching and inflammation. However, it’s important to discuss these with a healthcare provider before starting them to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your condition.
3. How long does it take for lichen planus to go away with treatment?
The duration of treatment for lichen planus can vary. Some patients may see improvement within a few weeks, while others might take several months. The response to treatment can differ based on the type of lichen planus and the individual’s overall health and response to therapy.
4. Can lichen planus be cured permanently?
Lichen planus is considered a chronic condition, and while treatment can alleviate symptoms and possibly lead to remission, there is currently no permanent cure. Recurrences can occur, and ongoing management might be necessary.
5. Are there any side effects of lichen planus treatments?
Yes, treatments for lichen planus, particularly those involving steroids and immunosuppressants, can have side effects. Common side effects include skin thinning, increased susceptibility to infections, and potential liver damage with certain medications. Discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider to understand the risks and benefits of your treatment plan.
6. Is diet linked to lichen planus flare-ups?
While there’s no definitive link between diet and lichen planus, some individuals might find that certain foods exacerbate their symptoms. Foods that can trigger allergic reactions or are highly acidic might worsen symptoms for some people. Keeping a food diary and consulting with a healthcare professional about potential food triggers can be beneficial.
Conclusion
In summary, diagnosing and treating Lichen Planus involves recognizing its distinct signs, such as purple, itchy, flat bumps on the skin, and possibly white patches or soreness in the mouth. Effective management typically requires a combination of medical evaluations and tailored treatments, which may include topical corticosteroids, oral medications, or light therapy, depending on the severity and location of the symptoms.
If you suspect that you have symptoms of Lichen Planus, it is crucial to consult with healthcare providers. They can offer a proper diagnosis and create an appropriate treatment plan suited to your specific needs. Remember, early intervention can help manage the symptoms more effectively and improve your quality of life. Therefore, don’t hesitate to reach out to a medical professional for guidance and treatment.
References
For those seeking additional information or wishing to validate the details provided on the treatment of lichen planus, the following reputable sources are highly recommended. These links lead to well-respected medical journals and websites that offer further reading and in-depth research on the subject:
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – Explore comprehensive resources on the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for lichen planus available on the AAD’s official website. Read more about Lichen Planus on AAD.
- National Health Service (NHS) – The NHS provides detailed patient-oriented information on lichen planus, including self-care tips and medical treatment approaches. Visit NHS Lichen Planus Page.
- Mayo Clinic – A trusted resource for patient care and health information, the Mayo Clinic offers an in-depth look at lichen planus, including diagnosis and treatment. Learn about Lichen Planus at Mayo Clinic.
- PubMed Central – For those interested in the scientific and medical study of lichen planus, PubMed Central provides access to numerous research articles and clinical study reports. Search for Lichen Planus Studies on PubMed.
Each of these sources has been selected for their authority and reliability in the field of dermatology and medicine, offering readers a thorough understanding of lichen planus and its treatments.