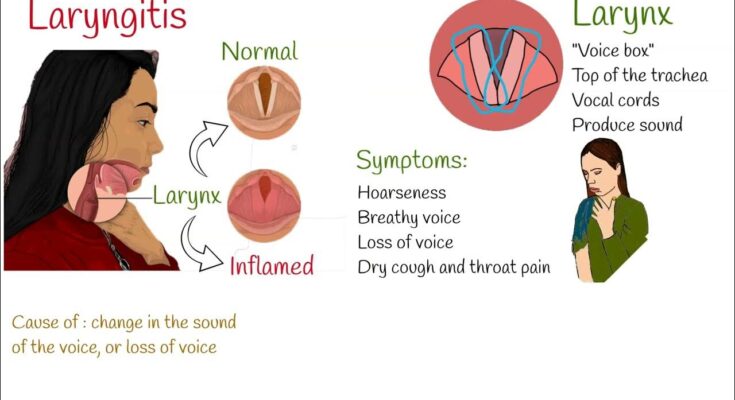
Laryngitis Symptoms: Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx, commonly known as the voice box, which is situated in the upper part of the respiratory tract.
This condition can affect anyone, from young children to adults, leading to various symptoms that may impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of laryngitis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Understanding Laryngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx, commonly known as the voice box, located at the top of the windpipe (trachea). This condition leads to hoarseness, loss of voice, and often a sore throat, typically resulting from overuse, irritation, or infection.
Prevalence and Demographics
Laryngitis is a widespread condition that affects millions of people annually across all age groups and demographics. It is particularly common among teachers, singers, and others who use their voice extensively, making them more susceptible to strain and vocal cord inflammation. Viral infections, such as the common cold or flu, are the most frequent causes, making laryngitis prevalent in colder seasons. However, anyone can develop laryngitis from a variety of causes at any time of the year.
Symptoms of Laryngitis
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for recognizing when to seek medical attention.
Primary Symptoms of Laryngitis
The primary symptoms of laryngitis are often immediately noticeable and can significantly affect your ability to speak. These include:
- Hoarseness: A raspy or weak voice is one of the first signs of laryngitis.
- Loss of Voice: In severe cases, laryngitis can cause complete loss of voice, making it difficult to speak above a whisper.
- Throat Pain: There may be a constant ache or discomfort in the throat area.
- Dry Throat: A sensation of dryness or scratchiness in the throat is common.
Secondary Symptoms of Laryngitis
In addition to the primary symptoms, there are several secondary symptoms that may develop, including:
- Cough: A dry, persistent cough is often associated with laryngitis.
- Sore Throat: The throat may feel raw or irritated.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Some people may experience pain or discomfort when swallowing.
- Swollen Glands: The lymph nodes in your neck may swell.
Acute vs. Chronic Laryngitis Symptoms
The symptoms of laryngitis can vary depending on whether the condition is acute or chronic:
- Acute Laryngitis: Typically develops suddenly and is usually caused by a viral infection or vocal strain. It lasts no more than a few weeks. Symptoms are primarily those of hoarseness or voice loss and may be accompanied by a mild fever.
- Chronic Laryngitis: Develops over a longer period and is often due to factors such as prolonged exposure to irritants, smoking, or acid reflux. Chronic laryngitis may involve more persistent hoarseness and frequent throat clearing.
When to Seek Medical Help
It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- Symptoms that last longer than two weeks, which might indicate chronic laryngitis.
- Difficulty breathing or severe pain, suggesting more serious conditions.
- Symptoms accompanied by high fever or pus in the throat.
- Frequent episodes of laryngitis, as they can signify underlying health issues.
However, regular voice rest and avoiding irritants may also help alleviate symptoms. If you’re concerned about your symptoms, it’s best to contact a healthcare professional.
Causes of Laryngitis
Understanding these causes is essential for effective management and prevention. Below, we explore the most common causes of laryngitis, which range from infections to environmental exposures.
Viral Infections: The Most Common Culprit
Viral infections are the leading cause of laryngitis. Common viruses that lead to laryngitis include those causing the cold and flu. These viruses inflame the larynx, leading to symptoms such as hoarseness or loss of voice.
Bacterial Infections
While less common than viral infections, bacterial infections can also cause laryngitis. Such infections typically require antibiotic treatment, unlike viral laryngitis, which often resolves on its own.
Strain and Overuse of the Voice
Vocal strain from yelling, prolonged talking, or singing can cause temporary laryngitis. Vocal cords become irritated and swollen, leading to altered voice quality or temporary voice loss.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to extreme environmental conditions, such as cold or dry air, can irritate the larynx and result in laryngitis.
Irritants: Smoke and Chemicals
Exposure to smoke, chemical fumes, and other irritants can severely inflame the vocal cords. This is especially common in individuals exposed to secondhand smoke or pollutants in occupational settings.
Allergies
Allergic reactions can cause swelling and irritation of the larynx as part of a broader allergic response, which may include laryngitis.
Underlying Health Conditions
Several health conditions can predispose individuals to develop laryngitis:
- GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease): This condition, where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, can irritate and damage the vocal cords when the acid reaches the larynx.
- Sinusitis: Inflammation or infection of the sinuses can lead to postnasal drip, which irritates the throat and larynx.
- Other Respiratory Infections: Infections like bronchitis and pneumonia can also involve the larynx and lead to laryngitis.
Identifying the underlying cause of laryngitis is crucial for treatment and recovery. In cases where laryngitis persists or recurs frequently, it is advisable to seek medical advice to investigate potential underlying conditions.
Risk Factors for Laryngitis
Understanding the risk factors associated with laryngitis is crucial for prevention and effective management. Here are some key factors that can increase your likelihood of developing laryngitis:
- Smoking: Smoking is one of the primary risk factors for laryngitis. Tobacco smoke irritates the mucous membranes of the throat and larynx, leading to inflammation. This not only increases the risk of laryngitis but also prolongs recovery times for those affected.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can cause irritation and swelling in the throat and larynx. Regular heavy drinking exacerbates this effect, increasing the risk of developing laryngitis. Alcohol also has a dehydrating effect on the body, which can dry out the throat and make the tissues more susceptible to irritation.
- Exposure to Irritants: Exposure to environmental irritants such as dust, chemical fumes, and allergens can lead to laryngitis. People who work in environments with high levels of air pollution or chemical exposure are particularly at risk. Additionally, professional singers or speakers who frequently use their voices intensely are more susceptible to irritation that can lead to laryngitis.
- Recent Respiratory Infection or Cold: A recent bout of a cold, flu, or other respiratory infection is a common precursor to laryngitis. These infections can spread to the larynx, causing direct inflammation and irritation, which may result in voice loss or hoarseness.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of laryngitis, especially if they persist beyond a couple of weeks, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Preventive Measures for Laryngitis
Laryngitis can be a frustrating condition, but there are several proactive steps you can take to prevent its onset and reduce your risk. By integrating simple lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits, you can keep your vocal cords in optimal condition. Here’s how:
Tips to Prevent Laryngitis
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water keeps your vocal cords hydrated and less prone to irritation. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water a day, especially if you use your voice extensively.
- Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke: Smoke irritates the vocal cords. If you smoke, consider quitting, and try to avoid environments where you might be exposed to secondhand smoke.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Both alcohol and caffeine can dehydrate your body, including your vocal cords. Reducing your intake of these substances can help maintain vocal health.
- Manage Acid Reflux: Acid reflux can damage your vocal cords if the stomach acid travels up to your throat. Manage your diet by avoiding spicy and fatty foods and consider talking to a healthcare provider for effective treatment.
- Rest Your Voice: Overuse of your voice can lead to strain. Give your voice a break by avoiding shouting or speaking loudly for long periods. Use amplification tools when needed.
- Practice Good Vocal Hygiene: Warm up your voice before extensive use and avoid whispering, which can strain the vocal cords more than speaking softly.
- Maintain General Health: A strong immune system can help you avoid infections that might lead to laryngitis. Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get sufficient sleep.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Risk
- Adopt a Healthy Diet: Foods rich in vitamins A, E, and C support mucous membrane health. Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your daily meals.
- Increase Indoor Humidity: Dry air can irritate the throat and vocal cords. Use a humidifier in your home, especially during winter months when indoor air tends to be drier.
- Stay Physically Active: Regular physical activity improves overall health and boosts the immune system, reducing the risk of infections that can cause laryngitis.
- Regular Hand Washing: Since viruses or bacteria often cause laryngitis, regular hand washing is a simple and effective way to prevent these infections.
- Avoid Vocal Strain: Be mindful of your vocal limits. Avoid speaking or singing when your voice feels strained or tired, and seek professional advice if you use your voice professionally.
By implementing these preventive measures and lifestyle changes, you can significantly lower your risk of developing laryngitis and maintain a healthy voice. These habits not only benefit your vocal health but also enhance your overall well-being.
When to See a Doctor for Laryngitis
There are specific scenarios when seeking medical attention is crucial. Understanding when to see a doctor can help ensure proper treatment and prevent complications.
Symptoms That Require Medical Attention
Immediate medical consultation is advisable if you experience any of the following symptoms alongside laryngitis:
- Persistent Symptoms: If hoarseness or other laryngitis symptoms last longer than two weeks, it’s essential to consult a doctor to rule out more serious conditions.
- Difficulty Breathing: Any signs of breathing difficulty, such as noisy breathing (stridor), are urgent symptoms that need immediate medical attention.
- Painful Swallowing: Severe pain when swallowing can indicate an infection or an abscess, which requires prompt medical treatment.
- Fever: A high fever alongside throat symptoms could suggest a bacterial infection that might need antibiotic treatment.
- Blood in Saliva: This could be a sign of more severe issues such as injury to the throat or larynx, requiring immediate medical evaluation.
- Voice Loss: Complete loss of voice or whispering for more than a few days can indicate serious damage to your vocal cords.
What to Expect During a Doctor’s Visit
When you visit the doctor for laryngitis, here’s what you can typically expect:
- Medical History Review: The doctor will ask about your symptoms’ duration, severity, and any accompanying issues like fever or pain.
- Physical Examination: This includes checking your throat for inflammation, redness, and other abnormalities. The doctor might also examine your ears, nose, and neck.
- Laryngoscopy: In cases where the cause of your symptoms is unclear, or if symptoms are severe or persistent, your doctor might perform a laryngoscopy. This procedure involves using a small mirror or a fiber-optic camera to view your vocal cords and larynx directly.
- Discussion of Treatment Options: Based on the diagnosis, treatment may include recommendations for voice rest, hydration, humidifiers, or medications such as antibiotics or corticosteroids.
- Guidance on Follow-Up Care: The doctor will provide instructions on how to care for your voice and throat, and schedule follow-up visits if necessary to monitor your recovery.
However, always consult a healthcare provider if your symptoms do not improve with basic home care or if severe symptoms develop.
FAQs about Laryngitis Symptoms
What are the most common symptoms of laryngitis?
The most common symptoms of laryngitis include hoarseness, a weak or absent voice, a sore throat, and a dry cough. Some people may also experience a tickling sensation and discomfort in their throat.
How quickly do laryngitis symptoms appear?
Laryngitis symptoms can appear quite suddenly, often within hours. Acute laryngitis typically develops rapidly and is usually caused by a viral infection or vocal strain.
Can laryngitis symptoms vary in severity?
Yes, symptoms of laryngitis can vary widely from mild to severe. In severe cases, the voice may be completely lost, and there might be significant pain when trying to speak.
Are there any symptoms that might indicate a more serious condition?
Yes, if laryngitis symptoms are accompanied by difficulty breathing, blood in the saliva, persistent fever, or an inability to swallow, it is important to seek medical attention immediately as these could indicate a more serious condition.
How long do laryngitis symptoms typically last?
For acute laryngitis, symptoms usually last less than two weeks. If symptoms persist beyond two weeks, it may be considered chronic laryngitis, and further evaluation by a healthcare provider is recommended.
Can children and adults experience different symptoms?
Generally, the symptoms of laryngitis are similar in both children and adults. However, children may be less able to describe their symptoms and may appear more irritable, especially if they are experiencing discomfort.
What can be done to alleviate the symptoms of laryngitis?
Resting your voice, staying hydrated, and using humidifiers can help alleviate symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers and throat lozenges may also provide relief. Avoiding irritants like smoke and allergens is also beneficial.
When should you consult a doctor for laryngitis symptoms?
It’s advisable to consult a doctor if symptoms do not improve after two weeks, if they worsen rapidly, or if you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or swallowing.
Conclusion
In summary, laryngitis, characterized by symptoms such as hoarseness, a weak voice, or complete loss of voice, sore throat, and a dry cough, can arise from various causes including viral infections, vocal strain, or exposure to irritants. Understanding these triggers is essential in both preventing and managing the condition effectively.
To safeguard your vocal health, consider adopting preventive measures such as staying hydrated, avoiding excessive vocal strain, and quitting smoking. If symptoms persist or you experience severe discomfort, it is crucial to seek professional medical advice to rule out more serious conditions. Remember, early intervention is key to a quick and effective recovery from laryngitis.
References
For those seeking more detailed information and confirmation of the facts presented about laryngitis symptoms, here are some reputable sources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC provides comprehensive guides on various health conditions, including laryngitis. Their resources offer insights into symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Learn more about laryngitis on the CDC website.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its thorough medical articles, Mayo Clinic offers an in-depth look at laryngitis, detailing symptoms, preventive measures, and when to see a doctor. Explore the Mayo Clinic’s article on laryngitis.
- WebMD – WebMD is a trusted source for medical information, providing an easy-to-understand overview of laryngitis, including its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Read more about laryngitis at WebMD.
- Healthline – Healthline covers a wide range of medical topics, including laryngitis. Their content is reviewed by medical professionals to ensure accuracy. Visit Healthline for comprehensive information on laryngitis.
These sources are excellent for anyone looking to verify information or learn more about laryngitis and its symptoms in a detailed and accessible manner.