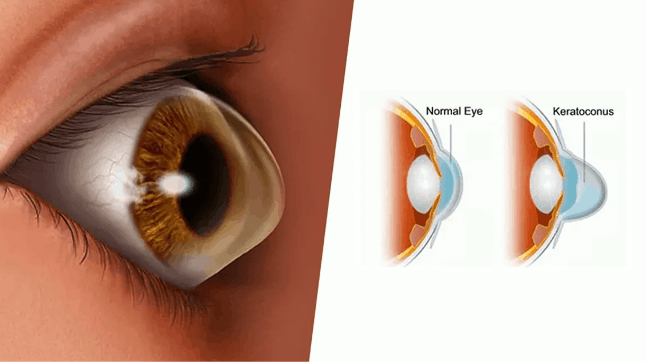
Keratoconus Symptoms: Keratoconus is a progressive eye condition that affects the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped front surface of the eye.
Over time, the cornea thins and gradually bulges outward into a cone shape, which distorts vision.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the symptoms and causes of keratoconus, aiming to educate patients and guide them towards timely and effective treatment options.
What is Keratoconus?
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disease in which the normally round cornea thins and begins to bulge into a cone-like shape. This deformation deflects light as it enters the eye on its way to the light-sensitive retina, causing distorted vision. Common symptoms of keratoconus include blurring and distortion of vision, increased sensitivity to light, and the frequent need for changes in eyeglass prescription. The condition typically first appears in individuals during their late teens or early twenties and can affect one or both eyes.
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Keratoconus
Keratoconus is relatively uncommon, affecting approximately one in every 2,000 people globally. However, the incidence can vary by region and demographic factors. The disease is generally diagnosed in the adolescent years and can progress for 10 to 20 years before slowing or stabilizing.
Risk factors for developing keratoconus include:
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of keratoconus significantly increases the risk, suggesting a genetic component to the disease.
- Environmental influences: Chronic eye rubbing is strongly associated with the progression of keratoconus, potentially exacerbated by allergic eye diseases.
- Hormonal factors: The onset of keratoconus often coincides with puberty, indicating that hormonal changes may influence its development.
- Ethnicity: Some studies suggest that keratoconus may be more prevalent among certain ethnic groups, such as those of Asian and Middle Eastern descent.
However, early detection and treatment are crucial in managing keratoconus effectively, as the condition can lead to significant visual impairment if left untreated.
Symptoms of Keratoconus
Understanding the symptoms of keratoconus is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Here, we explore the early signs, progression of symptoms, and their impact on daily activities.
Early Signs of Keratoconus
The initial symptoms of keratoconus are often subtle and can be easily mistaken for common vision issues. Early detection is key, and individuals should look out for the following early signs:
- Slight blurring of vision: Vision may begin to appear slightly blurred, making it difficult to see details clearly.
- Distortion of vision: Straight lines might appear bent or wavy, a symptom often confused with astigmatism.
- Increased light sensitivity: There may be increased discomfort in bright light or glare, which can make driving at night particularly challenging.
- Frequent changes in eye prescription: A rapid change in the power of glasses or contact lenses needed to correct vision might be noted.
- Ghosting or multiple images: In low light, one might notice ‘ghost’ images or double vision when looking with one eye.
Progression of Symptoms
As keratoconus progresses, the symptoms typically become more pronounced and can significantly impair visual quality:
- Worsening vision distortion: The distortion of vision becomes more noticeable, and regular prescription glasses may no longer correct it effectively.
- Increased astigmatism: As the cornea bulges more, astigmatism increases, leading to further distortion.
- Difficulty wearing contact lenses: It may become challenging to fit contact lenses comfortably due to the irregular shape of the cornea.
- Sharpened sensitivity to light: Sensitivity to light can intensify, making exposure to sunlight or bright indoor lights uncomfortable.
- Noticeable thinning of the cornea: Advanced stages can show a visible thinning of the cornea when examined by an eye care professional.
Impact on Daily Activities
The symptoms of keratoconus can affect various aspects of daily life, impacting performance and quality of life:
- Driving challenges: Distorted and blurred vision can make driving unsafe, especially at night due to glare and halos around lights.
- Difficulty reading: Fluctuations in vision can make reading text on both print and digital screens strenuous.
- Impaired outdoor activities: Activities that require sharp vision, like sports, can become difficult, and sensitivity to light may limit outdoor exposure.
- Visual fatigue: Eye strain from struggling to focus can lead to frequent headaches and visual fatigue, reducing productivity and daily comfort.
- Emotional stress: Coping with the uncertainty of vision quality and the frequent need for new corrective lenses can cause significant emotional distress.
Regular check-ups with an eye care professional are essential for monitoring the progression of the condition and discussing the most effective treatment options.
Causes of Keratoconus
Understanding the causes of keratoconus is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. The causes are generally classified into genetic factors, environmental influences, and other risk factors.
Genetic Factors
Research has shown that genetics play a significant role in the development of keratoconus. Some key genetic factors include:
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of keratoconus are at a higher risk, suggesting a hereditary component.
- Genetic Disorders: Certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, are associated with an increased incidence of keratoconus.
- Ethnicity: Some studies suggest that keratoconus may be more prevalent in certain ethnic groups, indicating potential genetic predispositions.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors also contribute significantly to the onset and progression of keratoconus. Important environmental influences include:
- Chronic Eye Rubbing: Persistent eye rubbing can induce mechanical stress on the cornea, exacerbating thinning and bulging.
- Exposure to UV Light: Ultraviolet light exposure can contribute to the weakening of corneal tissues, promoting the development of keratoconus.
- Contact Lens Wear: Improper or overly tight-fitting contact lenses can cause mechanical trauma to the cornea, potentially leading to keratoconus.
Other Risk Factors
Besides genetic and environmental factors, other risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing keratoconus, such as:
- Age: Keratoconus typically begins at puberty and progresses into the mid-30s. Younger age at onset can predict a more severe progression.
- Allergic Conditions: Conditions like asthma and eczema are frequently associated with keratoconus, possibly due to the link between allergies and eye rubbing.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, may influence the structural integrity of the cornea and contribute to the development of keratoconus.
By recognizing these factors early, individuals at risk can seek prompt evaluation and management to slow the progression of keratoconus and maintain optimal visual health.
Diagnosing Keratoconus
Diagnosing keratoconus early is crucial as it can help manage the condition effectively and prevent progression that might lead to severe vision impairment. This section outlines the common diagnostic tests and procedures used to detect keratoconus and discusses the importance of early diagnosis.
Common Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
- Corneal Topography: This is the most critical test for diagnosing keratoconus. It creates a detailed map of the curvature of the cornea, showing distortions and thinning characteristic of keratoconus.
- Pachymetry: This procedure measures the thickness of the cornea. Thinning corneas can indicate the presence of keratoconus.
- Computerized Videokeratography: Also known as corneal mapping, this test provides detailed images of the cornea’s surface, allowing doctors to detect early signs of keratoconus.
- Slit-lamp Examination: Under a microscope, a doctor examines the eyes to look for structural changes in the cornea typical of keratoconus, such as thinning or a cone-like shape.
- Refraction Test: This eye examination tests the eyes’ ability to focus light rays to form an image on the retina, which can be affected by the irregular cornea shape caused by keratoconus.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Detecting keratoconus early is vital for several reasons:
- Prevention of Progression: Early diagnosis allows for interventions that can slow the progression of the condition, such as corneal collagen cross-linking.
- Better Visual Outcomes: Early treatment can help maintain better vision over time and reduce the likelihood of needing corneal transplants.
- Customized Treatment Plans: With early detection, eye care specialists can design a treatment plan that is tailored to the severity and specific characteristics of the keratoconus in each patient.
- Lifestyle Management: Early diagnosis provides patients with the knowledge to adjust their lifestyle to manage their condition better, including avoiding eye-rubbing, which can worsen the condition.
However, regular eye examinations are recommended for those at risk or those who experience symptoms like blurry vision, increased light sensitivity, or rapidly changing prescriptions.
Managing and Treating Keratoconus
Effective management and treatment of keratoconus are crucial for improving vision and slowing the progression of the disease. Treatment options can be broadly categorized into non-surgical treatments, surgical options, and lifestyle adjustments. Here’s a detailed look at each category.
Non-surgical Treatments
Non-surgical interventions are typically the first line of treatment for keratoconus and are aimed at correcting vision and preventing further progression of the corneal bulging. These include:
- Eyeglasses or Soft Contact Lenses: In the early stages, simple eyeglasses or soft contact lenses may help to correct the mild distortion caused by keratoconus.
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Contact Lenses: These lenses are more effective than soft lenses because they maintain their shape, rather than conforming to the conical shape of the cornea, providing clearer vision.
- Hybrid Contact Lenses: These lenses feature a rigid gas permeable center surrounded by a soft lens ring. They provide the clarity of RGP lenses with the comfort of soft lenses.
- Scleral and Semi-Scleral Lenses: These larger contact lenses vault over the cornea and rest on the sclera, the white part of the eye, which helps to mask the irregularities in the cornea’s shape.
- Collagen Cross-Linking (CXL): This treatment helps to strengthen the corneal tissue to halt bulging of the eye’s surface. It involves applying vitamin B2 (riboflavin) to the cornea and then activating it with UV light.
Surgical Options
When non-surgical treatments are not sufficient to improve vision or if the keratoconus continues to progress, surgical options may be considered:
- Corneal Inserts or Intacs: These are small plastic rings inserted into the cornea to flatten the cornea’s cone shape, improving vision.
- Corneal Transplant: In severe cases, when the cornea becomes extremely thin or when scarring has occurred, a corneal transplant may be necessary. This involves replacing the damaged cornea with a healthy donor cornea.
- Topography-guided Conductive Keratoplasty: This newer procedure uses radio frequency energy to reshape the cornea based on detailed corneal topography maps.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing Symptoms
In addition to medical treatments, making some lifestyle adjustments can help manage the symptoms of keratoconus:
- Avoid Rubbing Eyes: Rubbing your eyes can exacerbate the thinning of the corneal tissue, worsening keratoconus.
- Use Protective Eyewear: This can help to shield the eyes from UV rays and protect them from debris and other harmful substances, especially in windy and sunny conditions.
- Maintain Regular Eye Check-ups: Frequent monitoring of the eyes can help catch any changes in the condition early, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment.
- Manage Allergies: Controlling allergies that cause itching can help to minimize eye rubbing, reducing the risk of progressing the disease.
However, with the right combination of treatments and lifestyle adjustments, many individuals with keratoconus can manage their condition effectively and maintain active lifestyles.
Prevention Tips for Keratoconus
While it is not possible to prevent keratoconus entirely, there are several strategies that can help manage and slow its progression, ensuring better eye health and vision quality. Below are key preventive measures to consider:
1. Avoid Rubbing Your Eyes
- Why It’s Important: Eye rubbing can significantly contribute to the progression of keratoconus by exerting pressure on the cornea, potentially worsening its thinning and bulging.
- What to Do: If you experience itchiness or irritation, address the cause with suitable treatments such as antihistamines or lubricating eye drops and try to keep your hands away from your eyes.
2. Wear UV-Protective Sunglasses
- Why It’s Important: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays can damage the eyes and may exacerbate keratoconus symptoms.
- What to Do: Opt for sunglasses that offer 100% UV protection to shield your eyes from harmful rays and reduce the risk of further damage.
3. Use Appropriate Eye Protection
- Why It’s Important: Physical injury to the eye can accelerate the progression of keratoconus.
- What to Do: Wear protective eyewear during activities that pose a risk of injury, such as sports or working with hazardous materials.
4. Maintain a Healthy Diet
- Why It’s Important: Nutritional factors influence overall eye health. A diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, can support the health of your cornea.
- What to Do: Incorporate foods like carrots, spinach, fish, and nuts into your daily diet.
5. Manage Allergies Effectively
- Why It’s Important: Allergies can lead to eye rubbing, which can worsen keratoconus.
- What to Do: Consult with a healthcare provider to effectively manage your allergies with the right medications or strategies.
Importance of Regular Eye Check-ups
Regular eye examinations are crucial for individuals with keratoconus, regardless of whether symptoms are present:
- Early Detection: Routine check-ups can help detect keratoconus in its earliest stages, even before symptoms manifest.
- Monitoring Progression: Regular visits allow your eye care provider to monitor the progression of the disease and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
- Optimizing Vision: Eye doctors can provide prescriptions for corrective lenses or suggest other interventions such as corneal cross-linking to help maintain the best possible vision.
- Preventing Complications: Early and regular intervention can prevent complications associated with keratoconus, such as acute corneal hydrops, where the cornea suddenly swells due to fluid buildup.
Incorporating these preventive measures and ensuring consistent eye care can greatly contribute to managing keratoconus effectively, maintaining eye health, and preserving quality of vision.
FAQs about Keratoconus Symptoms
What is keratoconus?
Keratoconus is an eye condition where the normally round, dome-shaped cornea progressively thins and begins to bulge into a cone-like shape. This deformation deflects light as it enters the eye, causing distorted vision.
What are the early signs of keratoconus?
Early signs of keratoconus include slight blurring of vision, increased sensitivity to light and glare, and mild eye irritation. Many people initially attribute these symptoms to more common issues, such as eye strain or allergies.
How does keratoconus affect vision over time?
As keratoconus progresses, the vision distortion and blurriness increase. This can lead to significant changes in how well one can see details, and it may cause frequent updates in prescription lenses. Advanced stages may lead to significant vision impairment.
Can keratoconus cause pain?
Keratoconus itself typically does not cause pain. However, the strain and stress on the eyes from trying to focus with a distorted cornea can lead to eye fatigue and discomfort. In rare cases, acute hydrops, where the cornea suddenly swells, can cause pain and sudden vision loss.
Is keratoconus linked to any other conditions?
Keratoconus is often associated with other allergic conditions like asthma and eczema. Eye rubbing, a common response to the itchiness caused by allergies, is considered a risk factor for the development or worsening of keratoconus.
How is keratoconus diagnosed?
Keratoconus is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam. Specialized tests, such as corneal topography, which maps the shape of the cornea, are essential in identifying the cone-like shape typical of keratoconus.
Can keratoconus be cured?
While there is no cure for keratoconus, treatments are available that can help manage symptoms and improve vision. These include eyeglasses, specially designed contact lenses, and corneal cross-linking, a procedure that can help stop the progression of the condition.
Conclusion
In summary, keratoconus is a progressive eye disorder characterized by the thinning and bulging of the cornea into a cone-like shape, which can lead to distorted vision. Key symptoms include blurred and distorted vision, increased sensitivity to light, and difficulty with night vision. Causes of keratoconus are still not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
If you experience any symptoms of keratoconus, such as sudden changes in vision or persistent visual disturbances, it is crucial to consult with an eye care professional. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital in managing the condition effectively and preventing further deterioration of vision. Remember, timely professional advice can make a significant difference in maintaining your eye health and quality of life.
References
For additional information and to validate the content discussed in our article on Keratoconus symptoms, we recommend consulting the following reputable sources:
- National Keratoconus Foundation – A comprehensive resource offering detailed information on the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Keratoconus. Visit the National Keratoconus Foundation.
- Mayo Clinic – A respected medical institution providing in-depth health articles, including one on Keratoconus that covers various aspects of the condition. Read more at Mayo Clinic.
- American Academy of Ophthalmology – Offers a wide range of medical articles and studies about Keratoconus, including symptom management and innovative treatment approaches. Explore the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
- PubMed Central – An invaluable resource for accessing peer-reviewed scientific papers, including those on the latest research in Keratoconus treatment and symptoms. Search PubMed Central.
Each of these sources provides a wealth of information that can be useful for both patients and healthcare professionals interested in learning more about Keratoconus. By exploring these links, you can enhance your understanding of the condition and stay updated on the latest research and treatment techniques.