Keratitis Symptoms: Keratitis, a significant eye condition affecting numerous individuals globally, necessitates a deeper understanding due to its impact on vision health.
This detailed article aims to shed light on the various symptoms and causes of keratitis, offering valuable insights for both patients and healthcare providers.
What is Keratitis?
Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. This condition can vary in severity, ranging from mild irritation to serious infections that could potentially threaten one’s vision if not treated promptly. Understanding keratitis is crucial for timely diagnosis and management, ensuring the preservation of eye health and function.
Types of Keratitis
Keratitis can be categorized into several types, each with distinct causes and treatment approaches:
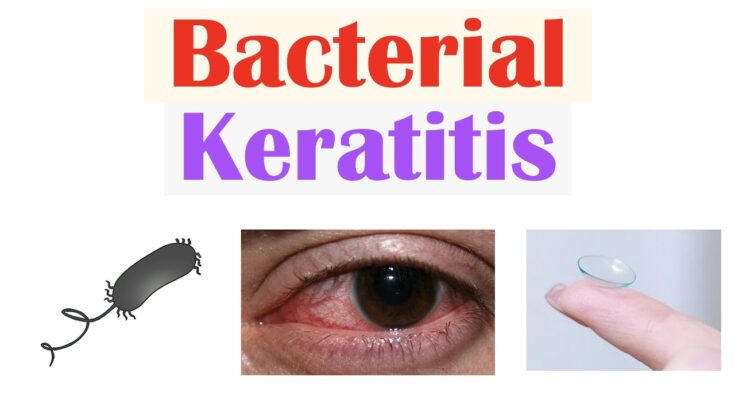
- Bacterial Keratitis: Often related to the misuse of contact lenses or injury, this type involves bacterial infection that requires immediate antibiotic treatment.
- Viral Keratitis: Commonly caused by the herpes simplex virus, this form is recurrent and can lead to more severe eye conditions if not managed properly.
- Fungal Keratitis: This less common type typically occurs after a corneal injury involving plant materials, necessitating antifungal therapy.
- Acanthamoeba Keratitis: Particularly associated with contact lens wearers, this rare but serious infection is caused by amoebae found in water and soil.
- Photokeratitis: Caused by exposure to intense ultraviolet (UV) radiation, this type of keratitis is essentially a sunburn of the eye, often seen in skiers or welders without proper eye protection.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Keratitis affects a significant number of individuals worldwide, with bacterial and viral keratitis being the most common types encountered in clinical settings. While anyone can develop keratitis, certain groups are at a higher risk:
- Contact Lens Wearers: The risk increases with poor hygiene, such as sleeping in lenses or using inadequate lens solutions.
- Individuals with Reduced Immune Function: People with diabetes, those on corticosteroids, or with general immune deficiencies are more susceptible.
- Outdoor Workers and Athletes: Exposure to environmental factors and potential injuries can elevate the risk for various types of keratitis.
However, awareness of the signs, potential complications, and preventive measures are key to managing and reducing the incidence of keratitis, thereby safeguarding vision.
Symptoms of Keratitis
Identifying the symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment and to prevent potential complications. Here, we detail the primary symptoms of keratitis and offer guidance on how to distinguish them from symptoms of other eye conditions.
Primary Symptoms of Keratitis
The most common signs of keratitis include:
- Eye Redness: The eye may appear visibly red or irritated.
- Pain and Discomfort: Individuals often report a significant amount of pain in the affected eye. This discomfort may be persistent and worsen with time.
- Blurred Vision: Vision may become blurry as the cornea becomes inflamed.
- Increased Sensitivity to Light: This condition, known as photophobia, involves a heightened sensitivity to light, which can be painful or uncomfortable.
- Excessive Tearing or Discharge: The eye might produce an unusual amount of tears, or there might be a noticeable discharge, which can be clear or pus-like.
- Feeling of a Foreign Body in the Eye: Patients often feel like there’s something in their eye, which is an effect of the inflammation of the cornea.
Distinguishing Keratitis Symptoms from Other Eye Conditions
While many eye conditions can cause symptoms like redness and discomfort, certain features of keratitis are distinctive:
- Pain Severity: The pain associated with keratitis is typically more intense than that caused by common conditions like dry eyes or mild conjunctivitis.
- Visual Impact: Unlike general eye irritation, keratitis often leads to noticeable changes in vision, such as blurriness or haze, due to the cornea’s inflammation.
- Sensitivity to Light: While other conditions can increase light sensitivity, the degree in keratitis is often severe and debilitating.
- Corneal Appearance: In keratitis, the cornea may appear more cloudy or have visible marks, which are less common in conditions like pink eye (conjunctivitis).
However, always seek professional advice to accurately distinguish keratitis from other eye conditions based on symptoms and clinical examination.
Causes of Keratitis
Understanding the specific causes can help in effective prevention and treatment. Here’s a detailed look at each type:
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial keratitis is often associated with the improper use of contact lenses. Common bacteria responsible for this condition include Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These bacteria can enter the corneal layer through minor scratches or improper lens hygiene, leading to rapid inflammation and discomfort.
Viral Infections
Viral infections are a leading cause of keratitis, with the herpes simplex virus (HSV) being the most prevalent. HSV keratitis can occur in individuals who have oral or genital herpes infections that spread to the eye. Other viruses that can cause keratitis include the varicella-zoster virus, which is linked to chickenpox and shingles.
Fungal Infections
Fungal keratitis typically arises after the cornea is damaged by an injury involving plant material or after the eye comes into contact with contaminated organic matter. Fungi such as Fusarium, Aspergillus, and Candida are common culprits. These organisms find a conducive environment in the eye, especially when the immune response is compromised.
Parasitic Infections
Acanthamoeba keratitis is caused by a parasite that is commonly found in water. This type of infection is rare but serious and primarily affects contact lens wearers who expose their lenses to water. Symptoms can be severe and may lead to significant vision loss if not treated promptly.
Environmental and Behavioral Risk Factors
Several environmental and behavioral factors can increase the risk of developing keratitis:
- Contact Lens Wear: Improper use or poor hygiene of contact lenses is one of the most significant risk factors. Not cleaning lenses properly, wearing them longer than recommended, or sleeping in contact lenses can greatly increase the risk of infection.
- Exposure to Contaminated Water: Swimming or using hot tubs while wearing contact lenses can expose the eyes to pathogens that cause keratitis.
- Eye Injuries or Foreign Bodies: Physical damage to the cornea from injuries or small particles can make the eye more susceptible to infections.
- Reduced Immunity and Other Underlying Health Conditions: Individuals with weakened immune systems or other health conditions like diabetes are at higher risk for infections, including keratitis.
By understanding and mitigating these risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing keratitis and ensure prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Complications of Untreated Keratitis
Understanding the potential risks associated with untreated keratitis is crucial for preventing long-term damage to the eye. Here are some of the significant complications that can arise:
- Corneal Scarring: One of the most common complications of untreated keratitis is scarring of the cornea. Scarring can result in blurred vision or permanent vision impairment, depending on the severity and location of the scar.
- Chronic Inflammation: Without adequate treatment, keratitis can become chronic, leading to persistent inflammation that may require long-term treatment strategies and could result in fluctuating vision problems.
- Infection Spread: If keratitis is caused by an infectious agent, such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses, there is a risk that the infection could spread deeper into the eye, affecting other structures like the iris or the lens, and potentially leading to more severe conditions such as endophthalmitis.
- Corneal Ulceration: Prolonged inflammation can lead to the development of corneal ulcers. These ulcers are not only painful but also increase the risk of further infection and can cause severe vision loss if they become deep or large.
- Vision Loss: In severe cases, untreated keratitis can lead to significant loss of vision or even blindness, especially if the central part of the cornea is affected or if there is substantial scarring.
- Secondary Glaucoma: Inflammatory processes associated with keratitis can lead to increased intraocular pressure, a condition known as secondary glaucoma. This increase in pressure can damage the optic nerve, potentially leading to irreversible vision loss.
However, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage and help preserve vision.
Diagnosing Keratitis
Keratitis, an inflammation of the cornea, can vary widely in severity and cause, making accurate diagnosis essential for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals employ several tools and tests to diagnose this condition, ensuring they tailor treatment to the specific type of keratitis present.
Tools and Tests Used in Diagnosing Keratitis
- Slit Lamp Examination: A fundamental tool in diagnosing keratitis is the slit lamp. This binocular microscope allows doctors to examine the eye under high magnification. During the examination, different layers of the cornea are inspected for signs of inflammation, infection, or damage.
- Corneal Staining: To further assess the extent of corneal damage, doctors often use a dye like fluorescein. This dye is dropped into the eye, adhering to areas of tissue damage and appearing green under blue light. This test helps in identifying patterns specific to different types of keratitis.
- Visual Acuity Test: This test measures how well a patient can see at various distances. Changes in visual acuity can help gauge the impact of keratitis on vision.
- Culture Tests: If an infectious cause is suspected, samples from the cornea may be taken for culture tests. This involves growing the sample in a lab to identify the presence of bacteria, viruses, or fungi, which helps in determining the appropriate antimicrobial treatment.
- Confocal Microscopy: This non-invasive imaging test provides high-resolution images of the cornea, enabling detailed visualization of the cellular structure. It’s particularly useful for diagnosing fungal keratitis and differentiating it from other microbial infections.
- Topography and Pachymetry: Corneal topography maps the surface curvature of the eye, useful in assessing the corneal shape and detecting irregularities. Pachymetry measures the thickness of the cornea, which can indicate swelling associated with keratitis.
Importance of Timely Diagnosis
Early and accurate diagnosis of keratitis is crucial to managing the condition effectively and preventing potential complications, such as corneal scarring or vision loss. By utilizing these specialized tools and tests, healthcare professionals can develop a precise treatment plan tailored to the needs of each patient. This targeted approach helps in resolving symptoms more efficiently and restoring normal vision.
However, diagnosing keratitis involves a comprehensive evaluation using several sophisticated tools and tests. This ensures that the treatment not only addresses the symptoms but also targets the underlying cause of the inflammation, leading to better outcomes for patients.
Treatment Options for Keratitis
Effective treatment is crucial for alleviating symptoms and preventing further damage to the eye. Here, we explore the various treatment options available, focusing on medications typically used, as well as the role of eye care and home remedies in managing symptoms.
Medications Typically Used in Treating Keratitis
The choice of medication for keratitis depends on the underlying cause of the inflammation. Here are some commonly prescribed medications:
- Antibiotic Eye Drops or Ointments: These are primarily used if the keratitis is bacterial in origin. Specific antibiotics are prescribed based on the type of bacteria identified or most likely to be causing the infection.
- Antiviral Medications: In cases where the keratitis is caused by a virus, such as herpes simplex, doctors may prescribe antiviral eye drops or oral antiviral medications to reduce the viral load and alleviate symptoms.
- Antifungal Treatments: For fungal keratitis, antifungal eye drops or systemic medication may be necessary to combat the fungal infection effectively.
- Corticosteroid Eye Drops: These may be used to reduce inflammation in certain cases of non-infectious keratitis or following the control of an infectious cause. Their use is carefully monitored by healthcare professionals to avoid potential complications.
- Cycloplegic Eye Drops: These drops help relieve pain associated with keratitis by temporarily paralyzing the ciliary muscle of the eye, thus providing comfort during healing.
It’s important to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure proper treatment and to avoid exacerbating the condition.
The Role of Eye Care and Home Remedies in Managing Keratitis Symptoms
In addition to medical treatment, proper eye care and certain home remedies can be beneficial in managing the symptoms of keratitis:
- Avoid Wearing Contact Lenses: During treatment, it’s crucial to stop wearing contact lenses to allow the cornea to heal and prevent further irritation or infection.
- Apply Warm or Cool Compresses: Depending on what feels more soothing, you can apply warm or cool compresses to the closed eyelids to reduce discomfort and swelling.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands before touching the eyes, is essential to prevent the spread of infection.
- Use Lubricating Eye Drops: Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops can help relieve dryness and irritation, provided they are preservative-free to avoid further irritation.
- Wear Sunglasses: Protecting your eyes from harsh sunlight and wind when going outdoors can help reduce symptoms and prevent further irritation.
- Follow a Healthy Diet: Nutrients like vitamins A, C, and E, along with omega-3 fatty acids, can promote eye health and aid in recovery.
While these home remedies can help manage symptoms, they should not replace professional medical treatment. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for treating keratitis.
Implementing these treatment options can significantly improve comfort and outcomes in individuals suffering from keratitis, ensuring a quicker recovery and preventing long-term complications.
Prevention Tips for Keratitis
Preventing keratitis involves diligent care and hygiene practices. Here are some effective tips tailored specifically for contact lens users:
1. Maintain Impeccable Hygiene
- Handwashing: Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling contact lenses.
- Lens Cleaning: Use only recommended solutions for cleaning and storing contact lenses. Avoid using water or saliva to wet your lenses.
- Proper Storage: Ensure that the lens storage case is clean and replace it regularly, at least every three months.
2. Follow Contact Lens Guidelines
- Wear Schedule: Adhere strictly to the wear schedule prescribed by your eye care professional. Do not wear lenses longer than recommended.
- Overnight Wear: Avoid sleeping in contact lenses unless they are specifically designed for overnight use. Overnight wear significantly increases the risk of developing keratitis.
3. Use Quality Lens Care Products
- Approved Solutions: Always use the lens care products recommended by your optometrist. Substituting products can lead to lens contamination.
- No Tap Water: Never rinse your lenses or lens cases with tap water. Microorganisms in tap water can lead to infections.
4. Regular Eye Check-ups
- Routine Examinations: Schedule regular check-ups with your eye care provider. These visits are crucial for catching and preventing issues before they escalate.
- Monitor for Symptoms: Be vigilant about any signs of irritation, redness, blurred vision, or pain, and consult your eye care professional immediately if these occur.
5. Educate Yourself About Lens Safety
- Product Recalls and Safety Notices: Stay informed about any recalls or safety notices regarding contact lens solutions or lenses.
- Updates in Eye Care: Keep up-to-date with the latest in eye health care and lens technology to ensure you are using the safest products.
Remember, the cornerstone of keratitis prevention lies in strict adherence to eye hygiene and regular professional eye care. Prioritize your eye health to maintain clear and comfortable vision.
FAQs about Keratitis Symptoms
What is keratitis?
Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped tissue on the front of your eye that covers the pupil and iris. It can be caused by infections, injury, environmental factors, or contact lens wear.
What are the common symptoms of keratitis?
Common symptoms of keratitis include:
- Redness and pain in the eye
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Blurred or decreased vision
- Excessive tearing or discharge from the eye
- A feeling of something in the eye (foreign body sensation)
Can keratitis cause permanent vision damage?
Yes, if not treated promptly and effectively, keratitis can lead to complications that may result in permanent vision loss or damage to the eye. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
How quickly do symptoms of keratitis develop?
Symptoms of keratitis can develop rapidly, especially if caused by an infection. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as symptoms are noticed to prevent complications.
Is keratitis contagious?
Keratitis caused by an infectious agent, such as bacteria or viruses, can be contagious. It is important to practice good hygiene, avoid sharing personal items like towels or eye makeup, and follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations to prevent spreading the infection.
What should I do if I suspect I have keratitis?
If you suspect you have keratitis, you should seek medical attention immediately. Avoid wearing contact lenses and do not attempt to treat the condition on your own with over-the-counter medications.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of keratitis early is crucial for effective treatment and preventing complications that could impact your vision. Symptoms such as redness, pain, excessive tearing, blurred vision, or sensitivity to light should prompt immediate action.
We urge anyone experiencing these signs to consult a healthcare professional without delay. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention can significantly improve outcomes, ensuring your eye health is preserved.
Remember, when it comes to your eyes, it’s better to be safe than sorry. Seek professional advice at the first sign of discomfort.
References
For those seeking more detailed information on keratitis and its symptoms, or wishing to validate the information provided here, consider exploring the following reputable sources. These resources offer extensive insights and are maintained by credible institutions known for their expertise in eye health.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC provides comprehensive guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of keratitis. Learn more about keratitis at the CDC.
- American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) – The AAO offers a detailed overview of keratitis, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options. This resource is particularly valuable for understanding the various types of keratitis. Read about keratitis on the AAO website.
- Mayo Clinic – Renowned for its patient-friendly material, the Mayo Clinic provides easily understandable information on keratitis symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures. Visit the Mayo Clinic’s page on keratitis.
- National Health Service (NHS) UK – The NHS UK site offers practical advice and information on keratitis, tailored for patients and healthcare professionals alike. Explore keratitis information at NHS UK.
- PubMed Central – For those interested in the scientific and medical research aspects of keratitis, PubMed Central provides access to numerous research articles and clinical studies. Search for keratitis studies on PubMed Central.
These sources are continually updated to reflect the latest research and guidelines in eye health, ensuring that readers receive the most current and accurate information available.