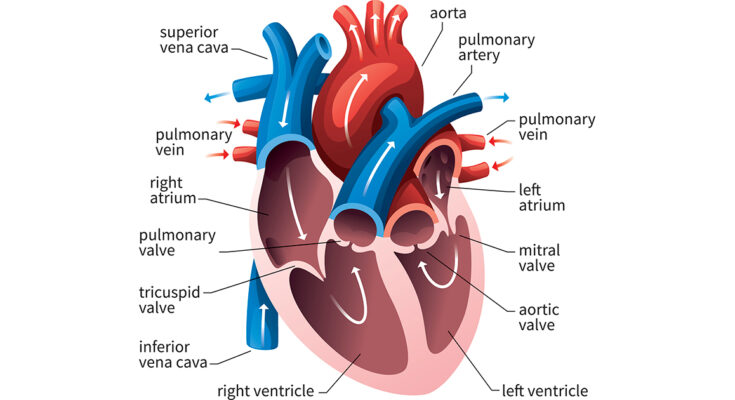
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Treatment: Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a condition characterized by the abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, particularly affecting the ventricles.
This thickening can lead to various complications, including obstruction of blood flow, arrhythmias, and even sudden cardiac death.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for HCM is crucial for managing this potentially life-threatening condition.
What is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a condition characterized by the abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, particularly the ventricles. This thickening can make it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively. HCM is often undiagnosed as many people with the condition may not exhibit symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations, and fainting, especially during physical activity. In severe cases, HCM can lead to heart failure or sudden cardiac death.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy affects approximately 1 in 500 people globally, making it one of the most common genetic heart conditions. The risk factors for developing HCM include:
- Family History: A family history of HCM significantly increases the risk, as it is often inherited.
- Age: While HCM can occur at any age, it is often diagnosed in adolescence or young adulthood.
- Sex: Men and women are equally affected, though the condition may present differently between sexes.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can contribute to the development or worsening of HCM.
- Lifestyle: Sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity can exacerbate the condition.
Genetic and Environmental Causes
Genetic Causes
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy is primarily a genetic disorder. It is usually inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning a single copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. Several genes have been implicated in HCM, most of which are involved in the production of proteins essential for heart muscle contraction. The most commonly affected genes include:
- MYH7: Encodes the beta-myosin heavy chain.
- MYBPC3: Encodes the cardiac myosin-binding protein C.
- TNNT2: Encodes the cardiac troponin T protein.
Mutations in these genes disrupt the normal structure and function of the heart muscle, leading to hypertrophy.
Environmental Causes
While genetic factors play a predominant role in HCM, environmental factors can influence the severity and progression of the condition. These include:
- Physical Activity: Intense exercise can exacerbate symptoms and trigger complications in individuals with HCM.
- Diet and Nutrition: Poor dietary habits and nutritional deficiencies can affect heart health.
- Substance Use: Alcohol and recreational drugs can worsen heart muscle function and contribute to the severity of HCM.
- Stress: Chronic stress can have a detrimental effect on cardiovascular health, potentially aggravating HCM symptoms.
However, understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors is crucial for managing and treating Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy effectively. Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments can help mitigate the risks associated with this condition.
Symptoms of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a condition characterized by the abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, which can significantly impact daily life. The common symptoms include:
- Shortness of Breath: This is often experienced during physical activities or even at rest, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks or exercise.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest can occur, particularly during or after physical exertion, which can limit participation in sports or strenuous activities.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy are common, affecting the ability to work, engage in social activities, or carry out household chores.
- Dizziness or Fainting: Episodes of dizziness or fainting, especially during physical activity or after standing up quickly, can be dangerous and hinder daily functioning.
- Palpitations: The sensation of a rapid or irregular heartbeat can cause anxiety and discomfort, impacting sleep and overall well-being.
Importance of Recognizing Early Signs
Early detection of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is crucial for managing the condition and preventing serious complications. Recognizing the early signs, such as unexplained shortness of breath, chest pain, or episodes of fainting, can prompt timely medical intervention. Early diagnosis allows for better management through lifestyle modifications, medications, and potentially, surgical interventions. This proactive approach can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the risk of severe outcomes, such as sudden cardiac arrest.
By being aware of the symptoms and understanding their impact, individuals can seek medical advice promptly, ensuring better health outcomes and maintaining a higher quality of life.
Diagnosing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Initial Medical History and Physical Examination
Diagnosing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. During this initial assessment, the doctor will ask about symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting, or palpitations. They will also inquire about any family history of heart conditions, as HCM is often hereditary. A thorough physical examination will be conducted to detect any abnormal heart sounds or murmurs, which can indicate the presence of HCM.
Diagnostic Tests
After the initial assessment, several diagnostic tests are typically performed to confirm the diagnosis of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. These include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the electrical activity of the heart and can detect abnormal rhythms or other changes indicative of HCM.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound of the heart provides detailed images of the heart’s structure and function, allowing doctors to see the thickening of the heart muscle characteristic of HCM.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI offers a more detailed view of the heart’s structure and can be especially useful in complex cases or when the echocardiogram results are inconclusive.
Genetic Testing and Its Role in Diagnosis
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, especially given its hereditary nature. Identifying genetic mutations associated with HCM can not only confirm the diagnosis but also help in screening family members who might be at risk. Early detection through genetic testing can lead to timely Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy treatment and management, potentially preventing severe complications.
By combining these diagnostic methods, doctors can accurately diagnose HCM and develop an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
Treatment Options for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
When it comes to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment, several effective strategies can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These treatment options include medications and lifestyle modifications.
Medications
- Beta-blockers: Beta-blockers are commonly prescribed for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment. They help slow the heart rate, reduce the force of heart contractions, and alleviate symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Calcium channel blockers: These medications work by relaxing the heart’s muscles and lowering blood pressure. They can be particularly beneficial in reducing symptoms and improving exercise tolerance in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs: Antiarrhythmic medications help control irregular heart rhythms, a common issue in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. By maintaining a stable heart rhythm, these drugs can prevent complications and enhance overall heart function.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Exercise and activity recommendations: Regular, moderate exercise is an essential component of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling can help maintain cardiovascular health without overexerting the heart. It is crucial to follow a healthcare provider’s guidelines on safe levels of activity.
- Diet and nutrition: A heart-healthy diet is vital for managing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. This includes consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting salt, sugar, and saturated fats. Proper nutrition can help control weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, all of which are important for heart health.
By incorporating these treatment options, individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can lead healthier, more active lives. It is always essential to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan that meets individual needs and circumstances.
Advanced Treatment Approaches for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Advanced treatment approaches are designed to manage symptoms, reduce complications, and improve the quality of life for patients. These approaches can be broadly categorized into surgical and non-surgical options.
Surgical Options
- Septal Myectomy: This open-heart surgery involves removing a portion of the thickened septal wall to improve blood flow from the heart. It is often recommended for patients with severe symptoms that do not respond to other treatments.
- Mitral Valve Surgery: In cases where the mitral valve is affected, surgery to repair or replace the valve may be necessary. This can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): An ICD is a device implanted in the chest to monitor and regulate heart rhythms. It can deliver shocks to correct potentially life-threatening arrhythmias, significantly reducing the risk of sudden cardiac death in HCM patients.
Non-Surgical Procedures
- Alcohol Septal Ablation: This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting alcohol into the septal artery to induce a controlled heart muscle infarction, reducing the thickness of the septal wall and improving blood flow. It is often used as an alternative to septal myectomy for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery.
- Medications: Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic drugs are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and arrhythmias. These medications can help improve heart function and reduce the risk of complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients are often advised to make lifestyle changes, such as avoiding intense physical activities, adopting a heart-healthy diet, and managing stress. These modifications can help control symptoms and improve overall heart health.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: A structured program of exercise and education designed to help patients improve their cardiovascular health under medical supervision. It can be particularly beneficial for patients recovering from surgery or experiencing chronic symptoms.
By understanding and utilizing these advanced treatment approaches, patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can better manage their condition and enhance their quality of life.
Advanced Treatment Approaches for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Advanced treatment approaches are designed to manage symptoms, reduce complications, and improve the quality of life for patients. These approaches can be broadly categorized into surgical and non-surgical options.
Surgical Options
- Septal Myectomy: This open-heart surgery involves removing a portion of the thickened septal wall to improve blood flow from the heart. It is often recommended for patients with severe symptoms that do not respond to other treatments.
- Mitral Valve Surgery: In cases where the mitral valve is affected, surgery to repair or replace the valve may be necessary. This can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): An ICD is a device implanted in the chest to monitor and regulate heart rhythms. It can deliver shocks to correct potentially life-threatening arrhythmias, significantly reducing the risk of sudden cardiac death in HCM patients.
Non-Surgical Procedures
- Alcohol Septal Ablation: This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting alcohol into the septal artery to induce a controlled heart muscle infarction, reducing the thickness of the septal wall and improving blood flow. It is often used as an alternative to septal myectomy for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery.
- Medications: Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic drugs are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and arrhythmias. These medications can help improve heart function and reduce the risk of complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients are often advised to make lifestyle changes, such as avoiding intense physical activities, adopting a heart-healthy diet, and managing stress. These modifications can help control symptoms and improve overall heart health.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: A structured program of exercise and education designed to help patients improve their cardiovascular health under medical supervision. It can be particularly beneficial for patients recovering from surgery or experiencing chronic symptoms.
By understanding and utilizing these advanced treatment approaches, patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can better manage their condition and enhance their quality of life.
FAQs about Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Treatment
What is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a genetic condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick, making it harder for the heart to pump blood.
What are the symptoms of HCM?
Common symptoms of HCM include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and fainting, especially during exercise. Some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
How is HCM diagnosed?
HCM is diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, patient history, and diagnostic tests such as echocardiograms, MRIs, and genetic testing.
What are the treatment options for HCM?
Treatment options for HCM include medications to manage symptoms, lifestyle changes, and surgical procedures like septal myectomy or alcohol septal ablation. In some cases, an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) may be recommended.
Can HCM be cured?
There is no cure for HCM, but with proper treatment and management, many people with HCM can lead normal, active lives.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage HCM?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding strenuous exercise, managing stress, and following a heart-healthy diet can help manage symptoms and improve overall heart health.
How often should someone with HCM see a doctor?
Regular check-ups with a cardiologist are essential for managing HCM. The frequency of visits depends on the severity of the condition and the treatment plan. Typically, patients should have follow-up appointments every 6 to 12 months.
Can HCM be inherited?
Yes, HCM is a genetic condition and can be inherited. If you have a family history of HCM, it is important to inform your doctor and consider genetic testing for early detection and management.
Conclusion:
Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in the effective management of HCM. It enables timely intervention, which can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications such as sudden cardiac death and heart failure. Comprehensive treatment following early diagnosis can also help in monitoring the progression of the disease and adjusting treatments as necessary.
In essence, the integration of early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary treatment approach is vital for managing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy effectively. Patients are encouraged to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and circumstances. This collaborative approach ensures that each patient receives the best possible care, highlighting the importance of patient-centered strategies in the management of HCM.
References
To further explore and validate the information provided in this guide on Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Treatment, we recommend consulting the following reputable sources:
- American Heart Association: An authoritative source for cardiovascular diseases, including the latest research and treatment options for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Read more.
- Mayo Clinic: Offers comprehensive information on symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment strategies for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Read more.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): Provides detailed insights into the causes, symptoms, and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Read more.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine: Features expert opinions and detailed articles on the latest advancements in the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Read more.
By referencing these trusted sources, you can ensure that you are getting accurate and up-to-date information on the management and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.