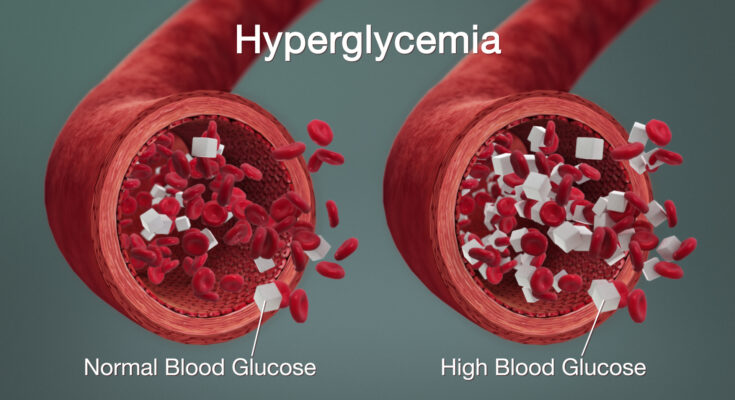
Hyperglycemia in Diabetes Treatment: Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that impairs the body’s ability to regulate blood glucose levels. Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is a common and potentially dangerous complication of diabetes.
This article delves into the intricacies of hyperglycemia, including its diagnosis, underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Understanding Hyperglycemia in Diabetes
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is a critical aspect of diabetes management. It’s essential to understand how hyperglycemia fits into the broader context of diabetes and recognize the common causes and risk factors. This knowledge can help in better managing the condition and preventing complications.
How Hyperglycemia Fits into the Broader Context of Diabetes
- Core Symptom: Hyperglycemia is a hallmark symptom of both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use insulin effectively, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
- Indicator of Poor Control: Persistent hyperglycemia is an indicator of poor diabetes control and can lead to serious long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision problems.
- Short-term Complications: Acute episodes of hyperglycemia can lead to immediate health issues like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in Type 1 diabetes or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) in Type 2 diabetes, both of which are medical emergencies.
- Monitoring and Management: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial for diabetes management. Hyperglycemia requires adjustments in diet, physical activity, and medications to bring blood sugar levels back to the target range.
Common Causes and Risk Factors for Hyperglycemia in Diabetics
- Dietary Choices: Consuming foods high in carbohydrates and sugars can cause blood sugar levels to spike. It’s important for diabetics to follow a balanced diet that regulates carbohydrate intake.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of physical activity can lead to higher blood sugar levels. Regular exercise helps the body use insulin more efficiently and can lower blood glucose.
- Insufficient Insulin or Medication: For those on insulin therapy or other diabetes medications, missing doses or not taking enough can result in hyperglycemia.
- Illness or Infection: When the body is fighting an illness or infection, it releases stress hormones that can raise blood glucose levels.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can cause the body to release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase blood sugar levels.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, like steroids or diuretics, can interfere with blood sugar control and lead to hyperglycemia.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women during menstrual cycles or pregnancy, can affect blood sugar levels.
By identifying and mitigating the risk factors, diabetics can maintain better control over their blood glucose levels and overall health.
Signs and Symptoms of Hyperglycemia in Diabetes
Here’s a detailed description of the symptoms associated with hyperglycemia, how they differ from other diabetes-related conditions, and when to seek medical advice.
Detailed Description of Symptoms Associated with High Blood Sugar
- Increased Thirst (Polydipsia): One of the earliest signs of hyperglycemia is excessive thirst. This occurs because the body tries to flush out the excess sugar through urine, leading to dehydration.
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria): High blood sugar levels force the kidneys to work harder to eliminate the excess glucose, resulting in frequent urination.
- Fatigue: When cells are unable to absorb glucose due to insulin resistance or lack of insulin, the body lacks energy, causing fatigue and weakness.
- Blurred Vision: Excess glucose can affect the lenses in the eyes, leading to swelling and changes in vision.
- Headaches: Fluctuating blood sugar levels can cause headaches, which might range from mild to severe.
- Difficulty Concentrating: High blood sugar can impact brain function, making it hard to focus or think clearly.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite eating normally, individuals may lose weight because the body starts burning fat for energy when it can’t access glucose.
- Slow-Healing Sores or Cuts: High glucose levels can impair blood flow and delay healing, making infections and sores more common and harder to treat.
- Recurrent Infections: Elevated blood sugar levels create an environment where bacteria and fungi can thrive, leading to frequent infections, especially in the skin, gums, and urinary tract.
How These Symptoms Differ from Other Diabetes-Related Conditions
While hyperglycemia shares some symptoms with other diabetes-related conditions, there are key differences:
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Symptoms such as shakiness, sweating, dizziness, and confusion are more indicative of hypoglycemia rather than hyperglycemia.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): This severe condition often presents with symptoms similar to hyperglycemia but includes additional signs like fruity-smelling breath, rapid breathing, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- General Diabetes Symptoms: Symptoms like increased thirst and frequent urination are common in both hyperglycemia and general diabetes onset. However, the severity and combination of these symptoms can help distinguish hyperglycemia.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s crucial to seek medical advice if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent High Blood Sugar Readings: If your blood sugar levels remain above 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L) for several days, despite following your diabetes management plan.
- Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: If you experience symptoms like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fruity-smelling breath, or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention.
- Frequent Episodes of Hyperglycemia: Regular episodes of high blood sugar require medical evaluation to adjust your treatment plan.
- Signs of Infection: If you have sores or cuts that are slow to heal, or frequent infections, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider.
Early detection and management of hyperglycemia can prevent complications and improve overall health. If you notice any signs or symptoms, contact your healthcare provider promptly for guidance and treatment adjustments.
Diagnosing Hyperglycemia in Diabetes
Diagnosing hyperglycemia, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Understanding the various diagnostic methods can help individuals and healthcare providers monitor and control blood sugar levels more efficiently. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the diagnostic techniques used to identify hyperglycemia in diabetes.
List of Diagnostic Methods for Hyperglycemia in Diabetes
- Fasting Blood Glucose Test: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. A fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher on two separate occasions typically indicates diabetes.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): The OGTT measures blood glucose after a fasting period, followed by consuming a glucose-rich drink. Blood sugar levels are then tested several times over a few hours. A reading above 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) after two hours suggests diabetes.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test: This test provides an average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher is indicative of diabetes. It’s particularly useful as it does not require fasting and can give a broader view of glucose control.
- Random Blood Sugar Test: A blood sample is taken at a random time, regardless of when the person last ate. Blood glucose levels of 200 mg/dL or higher can suggest diabetes if accompanied by symptoms of hyperglycemia.
Blood Tests and Their Significance
Each of these tests plays a vital role in the diagnosis of hyperglycemia:
- Fasting Blood Glucose Test helps determine how well the body manages blood sugar levels without intake of food.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test assesses the body’s response to sugar and can help identify cases of impaired glucose tolerance.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test provides insight into the overall effectiveness of diabetes management strategies over a quarter of a year.
- Random Blood Sugar Test offers a quick, though less specific, diagnostic snapshot, useful for urgent assessments.
The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Other Technologies
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems are revolutionary in the management of diabetes, offering real-time insights into glucose levels throughout the day. These devices track glucose levels in the interstitial fluid every few minutes, providing trends and patterns that can inform better treatment decisions and lifestyle adjustments.
Other technologies include:
- Flash Glucose Monitoring: Like CGM, this technology uses a sensor placed on the body to record blood sugar levels continuously. However, data is obtained on demand when the user scans the sensor, rather than automatically sending it to a device.
- Smart Insulin Pens: These devices record the time and amount of insulin administered, syncing this data with smartphone apps to optimize dosage and timing.
- Digital Apps and Health Platforms: Many apps now offer ways to track blood glucose levels, dietary habits, and medication adherence, which can help in fine-tuning the management of diabetes.
Together, these diagnostic methods and technologies provide comprehensive tools for detecting and managing hyperglycemia in diabetes, ensuring patients can maintain an optimal quality of life.
Treatment Options for Hyperglycemia in Diabetes
Managing hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications and maintain overall health. Here’s a comprehensive review of the primary treatment strategies:
Medications
- Insulin Therapy: Essential for type 1 diabetes and often prescribed for type 2 diabetes, insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Oral Medications: Includes metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, and SGLT2 inhibitors, which help control blood sugar levels in various ways.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These injectable medications help the pancreas release insulin and can also aid in weight loss.
- Amylinomimetics: Used alongside insulin, these drugs slow down food digestion to prevent spikes in blood sugar.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity such as walking, cycling, or swimming helps the body use insulin more efficiently.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly improve blood sugar control.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can reduce stress, which may help lower blood sugar levels.
Advanced Treatments
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): This technology provides real-time blood sugar readings, helping individuals make informed decisions about their treatment.
- Insulin Pumps: These devices deliver a continuous supply of insulin, closely mimicking the body’s natural insulin release.
- Bariatric Surgery: For individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes, bariatric surgery can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control.
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: These advanced devices automate insulin delivery based on CGM readings, offering a more precise and less burdensome way to manage diabetes.
By combining these treatment options, individuals with diabetes can achieve better blood sugar control and improve their quality of life. Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential to tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
Complications of Unmanaged Hyperglycemia
Unmanaged hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar levels, can lead to a range of short-term and long-term health complications. Understanding these risks is crucial for effective diabetes management and overall well-being.
Short-term Health Risks
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): A severe condition that occurs when the body starts breaking down fats at an excessive rate, leading to a buildup of acids in the bloodstream called ketones. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, which require immediate medical attention.
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS): This is a life-threatening condition that often affects older adults. It involves extreme dehydration and very high blood sugar levels, which can lead to seizures, coma, or even death if untreated.
Long-term Health Risks
- Cardiovascular Disease: Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure.
- Neuropathy: High blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, leading to symptoms like pain, tingling, or loss of feeling, especially in the hands and feet.
- Nephropathy: Hyperglycemia can damage the kidneys’ filtering system, leading to chronic kidney disease and, in severe cases, kidney failure.
- Retinopathy: Persistent high blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, potentially causing vision problems and even blindness.
- Foot Complications: Reduced blood flow and nerve damage in the feet increase the risk of infections, ulcers, and, in severe cases, amputation.
Impact on Overall Health and Diabetes Management
Hyperglycemia negatively impacts overall health, making diabetes management more challenging. It can lead to frequent infections, slow healing wounds, and general fatigue, all of which lower the quality of life. Effective diabetes management becomes more complicated as uncontrolled blood sugar levels can cause fluctuations that are hard to predict and control.
Preventative Measures and Regular Monitoring
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps to regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Medication Adherence: Taking prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare provider is essential for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels.
- Frequent Monitoring: Regular blood sugar testing helps in keeping track of glucose levels and making necessary adjustments in diet, exercise, or medication.
- Routine Check-ups: Regular visits to healthcare professionals for comprehensive diabetes management, including eye exams and kidney function tests, are crucial.
By understanding the complications associated with unmanaged hyperglycemia and adopting preventative measures, individuals can better manage their diabetes and lead healthier lives.
Case Studies and Patient Success Stories
Real-Life Examples of Effective Management of Hyperglycemia
In our case studies, we explore real-life examples of patients successfully managing hyperglycemia. One patient, John, was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and struggled with high blood sugar levels. Through personalized treatment plans and lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, John was able to maintain his blood glucose levels within a healthy range. His story highlights the effectiveness of individualized care in managing hyperglycemia.
Discussion on Patient Adherence to Treatment Protocols
Patient adherence to treatment protocols is crucial for effective hyperglycemia management. Many patients find it challenging to stick to their prescribed regimens. Our success stories demonstrate that consistent follow-up, education, and support can significantly improve adherence. For instance, Sarah, another patient, benefited from regular check-ins with her healthcare team, which kept her motivated and informed about her progress. This consistent support helped her stay on track with her medication and lifestyle modifications.
The Role of Healthcare Teams in Supporting Patient Outcomes
Healthcare teams play a vital role in supporting patient outcomes. Multidisciplinary teams, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators, provide comprehensive care that addresses all aspects of hyperglycemia management. By working collaboratively, these teams ensure that patients receive the best possible care. Our case studies underscore the importance of a team-based approach in achieving optimal patient outcomes. For example, Michael’s success in managing his hyperglycemia was largely due to the coordinated efforts of his healthcare team, which provided him with a tailored treatment plan, ongoing education, and emotional support.
These case studies and patient success stories illustrate the critical components of effective hyperglycemia management and the positive impact of patient adherence and healthcare team support.
Latest Advances in Hyperglycemia Treatment
Update on New Research and Developments
Hyperglycemia, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, continues to be a significant challenge in diabetes management. Recent research has led to promising developments that could transform treatment approaches. Scientists are focusing on understanding the molecular mechanisms of hyperglycemia, leading to innovative therapies that target the root causes rather than just the symptoms.
Emerging Drugs and Technologies
Several new drugs are showing potential in hyperglycemia treatment. For instance, SGLT2 inhibitors, which help the kidneys remove glucose from the blood, are gaining attention for their dual benefits in managing blood sugar and protecting heart health. Additionally, GLP-1 receptor agonists, which stimulate insulin secretion and suppress appetite, are proving effective in controlling hyperglycemia and supporting weight loss.
In the realm of technology, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and advanced insulin pumps are revolutionizing diabetes care. These devices offer real-time blood sugar tracking and automated insulin delivery, significantly enhancing patient convenience and glucose control.
Future Prospects in the Management of Diabetes-Related Hyperglycemia
The future of hyperglycemia treatment looks promising with ongoing advancements in personalized medicine. Researchers are exploring gene therapies and beta-cell regeneration techniques to provide long-term solutions for diabetes. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence in diabetes management tools is expected to optimize treatment plans, making them more precise and effective.
As these emerging drugs and technologies continue to evolve, they hold the potential to greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with hyperglycemia, offering more effective and tailored treatment options.
FAQs about Hyperglycemia in Diabetes Treatment
What is Hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, occurs when there’s too much glucose in the blood. It’s a common issue for people with diabetes and can lead to serious health problems if not managed properly.
What Causes Hyperglycemia in Diabetes?
Several factors can cause hyperglycemia, including eating too many carbohydrates, not taking enough insulin or diabetes medication, illness, stress, and lack of physical activity.
What Are the Symptoms of Hyperglycemia?
Symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, and headaches. If left untreated, it can lead to more severe conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis.
How Can Hyperglycemia Be Prevented?
To prevent hyperglycemia, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, follow your meal plan, take medications as prescribed, stay active, and manage stress effectively.
What Should I Do If I Experience Hyperglycemia?
If you experience hyperglycemia, check your blood sugar levels, take your medication as directed, drink water to stay hydrated, and engage in light physical activity. If your blood sugar remains high, contact your healthcare provider for guidance.
When Should I Seek Emergency Help?
Seek immediate medical attention if you have symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis, such as fruity-smelling breath, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, or confusion. These symptoms indicate a medical emergency.
Can Hyperglycemia Be Managed with Diet Alone?
While diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels, it often needs to be combined with medication and physical activity for effective hyperglycemia management. Always consult your healthcare provider for a comprehensive treatment plan.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored the key strategies for managing diabetes and hyperglycemia effectively. Integrated care plays a crucial role in this process, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive, coordinated support from various healthcare professionals. By working together, these experts can provide personalized treatment plans that address all aspects of diabetes care.
We emphasize the importance of integrated care in achieving better health outcomes for individuals with diabetes. Coordinated efforts help to manage blood sugar levels, reduce complications, and improve overall quality of life.
If you or a loved one is dealing with diabetes or hyperglycemia, we strongly encourage you to consult with your healthcare providers. They can offer valuable guidance and support tailored to your unique needs. Remember, effective management starts with a team approach and proactive engagement in your health journey.
References
For further reading and validation of the information provided on hyperglycemia treatment in diabetes, refer to the following reputable sources:
- American Diabetes Association: Comprehensive guidelines and resources on diabetes management. American Diabetes Association
- Mayo Clinic: Detailed explanations of hyperglycemia symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Mayo Clinic – Hyperglycemia
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): Research-backed information on diabetes and hyperglycemia. NIDDK – Diabetes
- WebMD: Easy-to-understand articles on managing high blood sugar levels in diabetes. WebMD – Hyperglycemia
These sources provide valuable insights and up-to-date research, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of hyperglycemia management in diabetes.