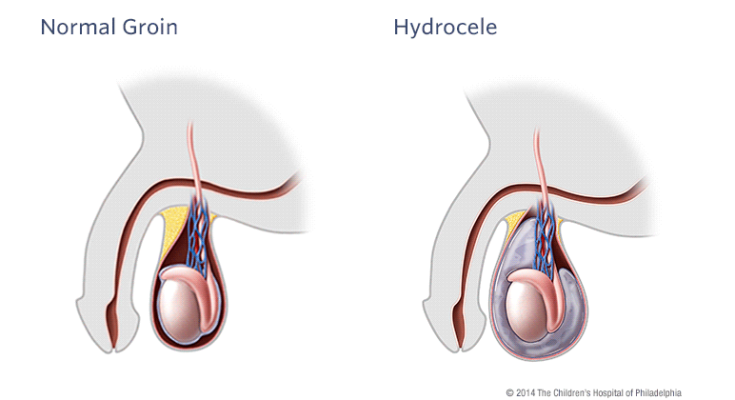
Hydrocele Treatment: A hydrocele is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the sac around the testicle, causing swelling in the scrotum. Although typically painless, hydroceles can cause discomfort due to their size.
They are common in newborns but can also affect adult men. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hydroceles is crucial for effective management.
What is a Hydrocele?
A hydrocele is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the sac surrounding the testicles, causing swelling in the scrotum. This condition is commonly seen in newborns but can also occur in older males due to injury, inflammation, or other underlying health issues. Though generally painless and harmless, a hydrocele can sometimes indicate more serious problems that require medical attention.
Types of Hydrocele
- Communicating Hydrocele: This type occurs when the channel through which the testicles descend into the scrotum does not close properly, allowing fluid to flow back and forth between the abdomen and the scrotum.
- Non-Communicating Hydrocele: This type develops when the channel is closed, but the sac around the testicles retains fluid. This form is more common in adults and is usually caused by an imbalance in the production and absorption of fluid.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
- Congenital Hydrocele: Present at birth, often due to incomplete closure of the processus vaginalis.
- Injury or Trauma: Damage to the scrotum can lead to fluid accumulation.
- Infections: Conditions such as epididymitis or orchitis can cause inflammation and fluid buildup.
- Tumors: Testicular tumors can lead to fluid accumulation around the testicles.
- Surgery: Previous surgeries in the scrotal area or groin can result in hydrocele formation.
- Age: Older age increases the risk, especially in men over 40.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions like heart failure or kidney disease that cause generalized fluid retention can also lead to hydrocele.
If you notice any unusual swelling in the scrotum, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate assessment and appropriate care.
Symptoms of Hydrocele
Recognizing the symptoms early can help in managing the condition effectively. Here are the common symptoms associated with hydrocele:
- Swelling in the Scrotum: The most noticeable symptom is a painless swelling in one or both sides of the scrotum. The swelling may vary in size and can become more prominent over time.
- Feeling of Heaviness: Some individuals may experience a sensation of heaviness in the scrotum due to the fluid accumulation.
- Discomfort or Pain: While hydrocele is generally painless, some men may feel discomfort or a dull ache, especially if the swelling becomes significant.
- Changes in Size: The size of the swelling may fluctuate, often becoming larger during the day and reducing in size at night or when lying down.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Hydrocele Symptoms
While hydrocele is usually not a serious condition, it is important to seek medical advice if you notice any of the following:
- Persistent or Increasing Swelling: If the swelling continues to grow or does not decrease over time, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider.
- Severe Pain: If you experience severe pain in the scrotum, it could indicate a more serious condition, such as an infection or testicular torsion, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Redness or Warmth: Redness, warmth, or tenderness in the scrotum could be signs of an infection, necessitating prompt medical evaluation.
- Difficulty Urinating: Any issues with urination, such as difficulty starting or a weak stream, should be discussed with a doctor as they may be related to underlying conditions.
- Changes in Testicular Shape or Consistency: Noticing changes in the shape or feel of the testicle warrants a medical examination to rule out other potential issues, such as tumors.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early detection and intervention can help prevent complications and ensure better health outcomes.
Diagnosing Hydrocele
Diagnosing hydrocele involves a combination of physical examinations and diagnostic tests. Here’s a detailed look at how healthcare providers diagnose hydrocele:
Common Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
1. Physical Examination:
- Inspection and Palpation: The doctor will visually inspect the scrotum and feel for any abnormal swelling or tenderness. This initial step helps in assessing the extent of the fluid accumulation and ruling out other conditions.
- Transillumination: During this test, the healthcare provider shines a light through the scrotum. If the scrotum is filled with clear fluid, the light will pass through, indicating a hydrocele. This simple yet effective test helps differentiate hydrocele from other scrotal masses.
2. Ultrasound:
- Scrotal Ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the scrotum and testicles. This non-invasive test provides detailed information about the structure of the scrotum, confirming the presence of fluid and ruling out other conditions such as tumors or hernias.
3. Blood and Urine Tests:
- Laboratory Tests: Blood and urine tests may be conducted to check for signs of infection or other underlying conditions. While these tests are not specific for hydrocele, they help in providing a comprehensive health assessment and ruling out other potential causes of scrotal swelling.
4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- MRI Scan: In rare cases, an MRI might be recommended for a more detailed view of the scrotal area. This imaging technique is typically used when ultrasound results are inconclusive or when there is a suspicion of more complex underlying issues.
5. Clinical History Review:
- Patient History: The healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history, including any previous injuries, surgeries, or infections. Understanding the patient’s medical background helps in identifying potential causes and associated risk factors for hydrocele.
By combining these diagnostic tests and procedures, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose hydrocele and differentiate it from other conditions with similar symptoms. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management of hydrocele, ensuring better health outcomes for patients.
Treatment Options for Hydrocele
While hydroceles are often painless and may resolve on their own, particularly in infants, treatment may be necessary if they persist or cause discomfort. Below are the non-surgical and surgical treatment options available for managing hydrocele, along with the latest advancements in this field.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Hydrocele
- Observation: Often recommended for infants, as many hydroceles resolve without intervention by the age of one year. In adults, if the hydrocele is small and not causing any discomfort, monitoring the condition might be all that is required.
- Aspiration: This involves using a needle to drain the fluid from the hydrocele. It is a minimally invasive procedure but is less frequently used due to high rates of fluid recurrence. Aspiration may be accompanied by the injection of a sclerosing agent that helps to close off the space and prevent fluid from reaccumulating.
- Compression Garments: For mild discomfort or swelling, wearing supportive underwear or compression garments can help alleviate symptoms by providing scrotal support.
Surgical Treatments for Hydrocele
- Hydrocelectomy: This is the standard surgery for adult hydrocele and involves making a small incision in the scrotum or lower abdomen to remove the fluid and part of the hydrocele sac. This procedure is highly effective with a low risk of recurrence.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive alternative to traditional hydrocelectomy, laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions and the use of a camera to guide the surgery. This option leads to quicker recovery and less postoperative pain.
- Plication Procedures: Techniques such as the Lord or Jaboulay plication involve folding and stitching the hydrocele sac to prevent fluid accumulation. These are considered less invasive and can be suitable for patients with higher surgical risks.
Latest Advancements in Hydrocele Treatment
Recent advancements in hydrocele treatment primarily focus on enhancing surgical techniques and reducing recovery time. One of the innovative approaches includes the use of robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery, which allows for greater precision and potentially shorter healing times compared to traditional methods. Additionally, there is ongoing research into new sclerosing agents that could improve the effectiveness of aspiration procedures by reducing the likelihood of fluid reaccumulation, making it a more viable option for more patients.
However, the treatment for hydrocele ranges from simple observation and non-invasive procedures to more advanced surgical interventions. The choice of treatment depends on factors like the age of the patient, the severity of symptoms, and the presence of any underlying health conditions. It’s important for individuals to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on their specific circumstances.
Preparing for Your Doctor’s Visit
What to Expect During a Consultation for Hydrocele
When you visit your doctor to discuss hydrocele, it’s essential to know what to expect. Your consultation will likely begin with a discussion of your medical history and any symptoms you’re experiencing. Be prepared to answer questions about the duration and severity of your symptoms, any discomfort or pain, and how it affects your daily activities.
Your doctor will then perform a physical examination, focusing on the affected area. They may use a technique called transillumination, where a light is shined through the scrotum to help distinguish a hydrocele from other conditions, such as hernias or tumors. In some cases, an ultrasound may be recommended to get a clearer view of the fluid accumulation and to rule out other underlying issues.
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider About Hydrocele Treatment
To make the most of your consultation, it’s helpful to have a list of questions ready. Here are some important questions to consider:
1. What is the cause of my hydrocele?
Understanding the underlying cause can help in determining the best treatment approach.
2. What treatment options are available?
Your doctor can explain the different treatments, from watchful waiting to surgical intervention, and help you understand which option is most suitable for your situation.
3. What are the risks and benefits of each treatment option?
Knowing the potential outcomes and side effects can help you make an informed decision.
4. How long will recovery take if I need surgery?
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the recovery process and any post-surgery care you might need.
5. Are there any lifestyle changes I should make?
Your doctor may suggest modifications to your daily routine to help manage symptoms or prevent complications.
6. How often should I have follow-up appointments?
Regular check-ups can be crucial in monitoring your condition and ensuring that your treatment plan is effective.
Preparing for your doctor’s visit with these questions in mind can help you feel more confident and informed about your hydrocele treatment options.
Recovery and Management Post-Treatment
Recovery Process After Hydrocele Treatment
The recovery process after hydrocele treatment typically involves a few key steps to ensure proper healing and a return to normal activities. Here’s what to expect:
- Immediate Post-Operative Care: Right after the surgery, you may experience some discomfort and swelling. Your doctor will likely prescribe pain medications to help manage this. It’s crucial to rest and avoid strenuous activities for the first few days.
- Incision Care: Keeping the surgical site clean and dry is essential to prevent infections. Follow your doctor’s instructions on how to care for the incision, which may include changing dressings and looking out for signs of infection.
- Gradual Return to Activities: Most patients can return to light activities within a week but should avoid heavy lifting and vigorous exercise for several weeks. Follow your healthcare provider’s guidance on when it’s safe to resume normal activities.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up visits with your doctor to ensure the healing process is on track and to address any concerns or complications that may arise.
Tips for Managing Symptoms and Preventing Recurrence
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can aid in recovery and prevent recurrence. This includes eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular, moderate exercise to improve overall health and circulation. However, avoid high-impact activities that could strain the surgical area until fully healed.
- Weight Management: Keeping a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the lower abdomen and scrotum, which may help prevent the recurrence of a hydrocele.
- Proper Support: Wearing supportive underwear can provide comfort and support during the recovery period. It can also help in reducing swelling.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water aids in the healing process and helps maintain overall health.
- Monitor for Symptoms: Be vigilant about any new symptoms or changes in your condition. If you notice increased pain, swelling, or signs of infection, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
By following these recovery guidelines and management tips, you can enhance your healing process and reduce the likelihood of hydrocele recurrence. Always consult your doctor for personalized advice tailored to your specific condition and recovery progress.
FAQs About Hydrocele Treatment
What is a hydrocele?
A hydrocele is a fluid-filled sac around a testicle, often causing swelling in the scrotum. It’s typically painless and harmless, but it can cause discomfort and lead to other issues if left untreated.
What are the common symptoms of a hydrocele?
The main symptom is a swollen scrotum. The swelling may be more noticeable in the evening or after physical activity. In some cases, it may cause a feeling of heaviness or discomfort.
How is a hydrocele diagnosed?
A hydrocele is usually diagnosed through a physical examination. Your doctor may shine a light through the scrotum to see if the swelling is translucent. An ultrasound may also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for a hydrocele?
Treatment options include watchful waiting, aspiration, and surgery. Watchful waiting is often recommended if the hydrocele is small and not causing symptoms. Aspiration involves draining the fluid with a needle. Surgery, known as hydrocelectomy, is the most effective treatment and involves removing the hydrocele.
Is hydrocele surgery safe?
Yes, hydrocele surgery is generally safe and effective. As with any surgery, there are risks, such as infection or reaction to anesthesia, but complications are rare. Most patients recover quickly and return to normal activities within a few weeks.
Can a hydrocele recur after treatment?
While recurrence is uncommon, it can happen. Following your doctor’s post-treatment advice and attending follow-up appointments can help monitor for any signs of recurrence.
What can I expect during recovery from hydrocele surgery?
Recovery from hydrocele surgery typically involves a few days of rest and avoiding strenuous activities. Your doctor may recommend wearing supportive underwear and using ice packs to reduce swelling. Most patients return to normal activities within two weeks.
When should I see a doctor about a hydrocele?
If you notice any swelling in your scrotum, it’s important to see a doctor to determine the cause. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, fever, or redness, as these may be signs of an infection or other serious condition.
Conclusion
Timely diagnosis and effective treatment of hydrocele are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring optimal health. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking professional medical advice can lead to a straightforward and successful treatment process.
Don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best treatment options for your condition. Following through with professional medical advice not only aids in a faster recovery but also provides peace of mind.
Your health is paramount—take the necessary steps today to ensure a healthier tomorrow.
References
For further reading and to validate the information provided in our guide on Hydrocele Treatment, we recommend consulting the following reputable sources:
- Mayo Clinic: Hydrocele Treatment – The Mayo Clinic offers detailed information about hydroceles, including symptoms, causes, and various treatment options. Read more on the Mayo Clinic website.
- WebMD: Understanding Hydrocele – WebMD provides a comprehensive overview of hydroceles, their diagnosis, and the treatments available. Explore more on WebMD.
- Healthline: Hydrocele Treatment and Symptoms – Healthline covers the essential aspects of hydroceles, including treatment procedures and symptom management. Find out more on Healthline.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine: Hydrocele – Johns Hopkins Medicine explains the condition in detail, offering insights into surgical and non-surgical treatments. Learn more on the Johns Hopkins Medicine website.
These sources provide in-depth and trustworthy information that can help enhance your understanding of hydrocele treatment options.