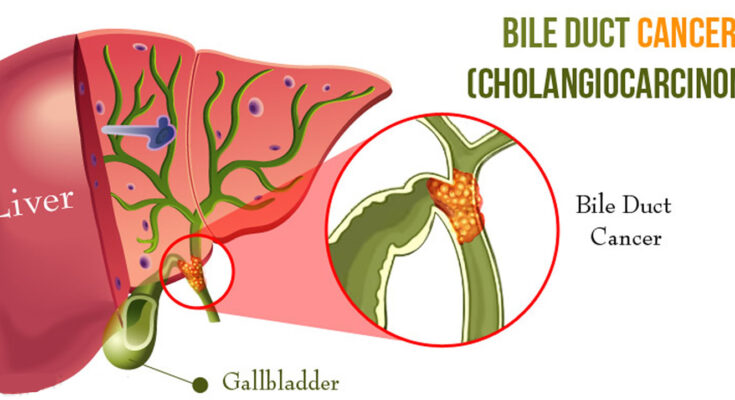
Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma Treatment: Hilar cholangiocarcinoma, also known as Klatskin tumor, is a rare and aggressive cancer that originates in the bile ducts, specifically at the confluence of the right and left hepatic ducts.
This malignancy presents significant challenges in diagnosis and treatment due to its location and biological behavior.
However, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the diagnosis and treatment options for hilar cholangiocarcinoma, offering valuable insights for medical professionals and patients alike.
What is Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma?
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma, also known as Klatskin tumor, is a type of cancer that originates in the bile ducts, specifically at the junction where the left and right hepatic ducts meet to form the common hepatic duct. This area, known as the hilum, is crucial for bile transportation from the liver to the small intestine. Hilar cholangiocarcinoma obstructs this flow, leading to various symptoms and complications.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma is a relatively rare cancer, accounting for about 50-60% of all cholangiocarcinoma cases. The incidence rate varies by region but is generally higher in Southeast Asia compared to Western countries. This difference is attributed to the higher prevalence of liver fluke infections in these areas, which is a significant risk factor. The disease predominantly affects individuals over the age of 50, with a slight male predominance.
Risk Factors Associated with Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma
Several risk factors contribute to the development of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, often due to primary sclerosing cholangitis or liver fluke infections, significantly increases the risk. Other risk factors include:
- Biliary Tract Diseases: Conditions such as choledochal cysts and Caroli’s disease.
- Hepatitis B and C Infections: Chronic viral hepatitis can lead to liver cirrhosis, increasing cancer risk.
- Liver Cirrhosis: Regardless of its cause, cirrhosis is a significant risk factor.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Exposure to toxins like dioxins and nitrosamines.
- Obesity and Diabetes: These metabolic conditions are associated with an increased risk of various cancers, including cholangiocarcinoma.
However, understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention strategies in high-risk populations.
Symptoms of Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma
It’s crucial to recognize these early signs to seek prompt medical attention. Here are the common symptoms to watch for:
- Jaundice: One of the most noticeable signs is yellowing of the skin and eyes, caused by a buildup of bilirubin in the blood.
- Itchy Skin: This can accompany jaundice and is a result of the bile duct obstruction.
- Dark Urine and Pale Stools: Changes in urine and stool color can indicate bile flow issues.
- Abdominal Pain: Persistent pain in the upper right side of the abdomen can be a symptom.
- Unintended Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying can be a warning sign.
- Fever and Chills: These can occur if the bile duct is infected.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can result from digestive system disruptions.
Staging and Its Importance in Treatment Planning
Staging of hilar cholangiocarcinoma is a critical step in the treatment planning process. It involves determining the extent of cancer spread, which helps doctors devise the most effective treatment strategy. The staging is generally classified into the following stages:
- Stage I: Cancer is localized to the bile duct.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
- Stage III: Cancer has invaded major blood vessels or multiple lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: Cancer has metastasized to distant organs.
Understanding the stage of hilar cholangiocarcinoma is essential for several reasons:
- Treatment Decisions: Different stages require different treatment approaches, such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
- Prognosis Estimation: Staging helps estimate the likely course and outcome of the disease.
- Planning Clinical Trials: It assists in determining eligibility for clinical trials that might offer new treatment options.
- Tailoring Patient Care: It allows for personalized care plans that consider the patient’s overall health and specific cancer characteristics.
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.
Diagnosing Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma: Techniques and Challenges
Techniques Used for Diagnosis
Diagnosing hilar cholangiocarcinoma, also known as Klatskin tumor, involves a combination of imaging studies, laboratory tests, and sometimes invasive procedures. Here are the primary techniques used:
1. Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound: Often the first imaging test used. It helps detect any abnormalities in the bile ducts.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Provides detailed images of the bile ducts and surrounding structures.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Offers a detailed view of the bile ducts and liver, often with MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography) for better visualization.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): Combines endoscopy and X-ray to visualize bile ducts, with the possibility of taking biopsies.
2. Laboratory Tests:
- Blood Tests: To check for liver function and tumor markers such as CA 19-9 and CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen).
3. Biopsy:
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): Obtains cells for microscopic examination.
- Brush Cytology: During ERCP, a brush is used to collect cells from the bile duct for analysis.
4. Cholangioscopy: Direct visualization of the bile ducts using a special endoscope, allowing for targeted biopsies.
Challenges in Diagnosing Based on Symptoms Alone
Diagnosing hilar cholangiocarcinoma based solely on symptoms presents significant challenges:
- Non-specific Symptoms: Early symptoms are often vague and can mimic other less severe conditions. These include jaundice, abdominal pain, weight loss, and itching.
- Delayed Onset: Symptoms typically appear only after significant disease progression, making early diagnosis difficult.
- Overlapping Symptoms: Many symptoms overlap with other hepatobiliary diseases, such as gallstones, hepatitis, and pancreatitis, leading to potential misdiagnosis.
However, early and accurate diagnosis of hilar cholangiocarcinoma is crucial for effective treatment. Thus, relying on a combination of advanced diagnostic techniques is essential to overcome the limitations posed by symptom-based diagnosis alone.
Treatment Options for Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma
Managing this type of cancer requires a comprehensive approach, involving surgical, non-surgical, and emerging treatment modalities. Below, we explore these options to provide patients and caregivers with a clear understanding of the available treatments.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical intervention is often considered the most effective treatment for hilar cholangiocarcinoma, particularly when the cancer is detected early and hasn’t spread beyond the liver. The main goal of surgery is to remove the tumor entirely, which can significantly improve the prognosis. The types of surgical treatments include:
- Resection: This involves the removal of the bile duct along with any affected liver tissue. Depending on the tumor’s location, this might also require the removal of part of the pancreas and small intestine.
- Liver Transplant: In cases where the tumor is confined but resection is not feasible, a liver transplant may be considered. This option is usually reserved for patients without metastasis and who meet specific criteria to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Non-Surgical Treatments
When surgery is not an option due to the advanced stage of the disease or poor health of the patient, non-surgical treatments play a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. These include:
- Biliary Drainage: This procedure relieves jaundice caused by bile duct blockage. Techniques such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC), or the placement of biliary stents help maintain bile flow.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy can help shrink tumors, delay progression, and manage symptoms. It is often used in combination with radiation therapy to control the disease in patients who cannot undergo surgery.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It is typically used to alleviate symptoms and control tumor growth in inoperable cases.
Emerging Treatments
Research into hilar cholangiocarcinoma is ongoing, with new treatments being developed to provide better outcomes for patients. Emerging treatment options include:
- Targeted Therapy: These drugs target specific molecules involved in tumor growth and spread, offering a more focused treatment approach that can be less harmful to normal cells than traditional chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy: Leveraging the body’s immune system to fight cancer, immunotherapy shows promise in treating various cancers, including hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate its efficacy and safety in this specific cancer type.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): This is a two-step treatment that involves injecting a light-sensitive drug into the bloodstream, which is absorbed by all cells but remains longer in cancer cells. A light source is then directed at the tumor, activating the drug and destroying cancer cells.
For patients diagnosed with hilar cholangiocarcinoma, a multidisciplinary team approach is crucial to tailor treatment plans that best suit individual conditions and disease stages. Consulting with oncologists, hepatologists, and other specialists is essential for optimal care and management of this challenging cancer.
Factors Influencing Treatment Decisions of Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma
Tumor Size and Location
The size and precise location of the tumor are critical factors in determining the appropriate treatment for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Larger tumors may require more aggressive treatment, while smaller tumors might be managed with less invasive options. The tumor’s position relative to vital structures such as bile ducts, blood vessels, and nearby organs can also influence the choice of surgical techniques and other therapies.
Patient’s Overall Health and Medical History
A patient’s overall health and medical history play a significant role in treatment decisions for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Physicians assess the patient’s physical condition, underlying health issues, and previous medical treatments to tailor the most effective treatment plan. Factors such as age, liver function, and co-existing conditions like diabetes or cardiovascular disease can impact the patient’s ability to tolerate certain treatments, including surgery and chemotherapy.
Potential Complications and Side Effects
Potential complications and side effects of various treatment options must be carefully considered. Treatments such as surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy can have significant side effects that may affect the patient’s quality of life. Physicians must weigh the potential benefits of each treatment against the possible risks and complications. For instance, surgery might offer the best chance for a cure but could come with higher immediate risks and a longer recovery period. Understanding these factors helps ensure that the chosen treatment aligns with the patient’s preferences and overall health goals.
By thoroughly evaluating these factors, healthcare providers can make informed treatment decisions that optimize outcomes for patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma.
Prognosis and Survival Rates of Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma
Factors Affecting Prognosis
The prognosis for patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma, a rare and aggressive bile duct cancer, depends on several key factors. One of the most critical is the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed. Early-stage detection often leads to better outcomes, while advanced stages are associated with poorer prognoses. Tumor size and location also play a significant role, with smaller, localized tumors offering a better chance for successful treatment.
Additionally, the patient’s overall health and ability to undergo surgery impact prognosis. Surgical resection, often combined with chemotherapy or radiation, can significantly improve survival rates. However, the presence of underlying liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, can complicate treatment and negatively affect outcomes. Genetic factors and the specific characteristics of the tumor, including its growth rate and response to treatment, are also important considerations.
Statistics on Survival Rates
Survival rates for hilar cholangiocarcinoma vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. On average, the five-year survival rate for this type of cancer is relatively low, ranging from 10% to 40%. For patients who undergo successful surgical resection, the five-year survival rate can increase to approximately 30% to 50%. However, for those with inoperable tumors or advanced disease, the prognosis is less favorable, with a median survival time of less than one year.
Importance of Follow-up Care
Follow-up care is crucial for patients treated for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Regular monitoring through imaging tests, blood work, and physical exams helps detect any recurrence of cancer early, which is vital for prompt intervention. Follow-up care also includes managing any side effects from treatment, monitoring liver function, and addressing any complications that may arise.
Adherence to a follow-up care plan can improve quality of life and potentially extend survival. It provides an opportunity for healthcare providers to offer supportive care, address concerns, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Patients are encouraged to maintain open communication with their healthcare team and attend all scheduled appointments to ensure optimal outcomes.
However, the prognosis and survival rates for hilar cholangiocarcinoma depend on multiple factors, including early detection, the feasibility of surgical intervention, and the patient’s overall health. While the statistics highlight the challenges associated with this cancer, diligent follow-up care plays a vital role in managing the disease and improving patient outcomes.
FAQs about Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma Treatment
What is Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma?
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma, also known as Klatskin tumor, is a type of cancer that forms in the bile ducts near the liver. It is a rare but aggressive form of cancer that requires specialized treatment.
What are the symptoms of Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma?
Common symptoms include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), itching, abdominal pain, weight loss, and fever. Early detection is crucial for better treatment outcomes.
How is Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests such as MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds. A biopsy may also be performed to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
What are the treatment options for Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma?
Treatment options vary depending on the stage of the cancer. They may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. In some cases, liver transplantation may be considered.
Can Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma be cured?
The prognosis for hilar cholangiocarcinoma depends on the stage at which it is diagnosed and the effectiveness of the treatment. Early-stage cancers that are surgically resectable have a better chance of being cured.
What is the recovery process like after treatment?
Recovery varies based on the type of treatment received. Post-surgery, patients may need several weeks to months to fully recover. Follow-up care is essential to monitor for any signs of recurrence.
Are there any clinical trials available for Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma?
Yes, clinical trials may be available for patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma. These trials offer access to new and potentially more effective treatments. Consult with your healthcare provider to explore these options.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma are crucial for improving patient outcomes and enhancing quality of life. By identifying this rare and aggressive cancer in its initial stages, healthcare providers can implement more effective treatment plans, increasing the chances of successful management and potentially extending patient survival. Comprehensive treatment strategies, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, tailored to the individual’s needs, play a vital role in combating this disease.
If you or a loved one experience symptoms such as jaundice, unexplained weight loss, or abdominal pain, it is essential to seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention can make a significant difference in the prognosis and treatment success of Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma. Don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any concerning symptoms, as timely medical attention is key to addressing this challenging condition.
References
For further reading and validation of the information provided on Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma treatment, we recommend the following reputable sources:
- National Cancer Institute: Detailed information about cholangiocarcinoma, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Visit the National Cancer Institute
- American Cancer Society: Comprehensive guide on liver cancer, including bile duct cancer, with sections on prevention, early detection, and treatment. Visit the American Cancer Society
- Johns Hopkins Medicine: Insights into the latest research, clinical trials, and treatment advancements for bile duct cancer. Visit Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Mayo Clinic: Overview of cholangiocarcinoma, including risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Visit the Mayo Clinic
These sources offer a wealth of information to help you understand Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma and explore various treatment options.