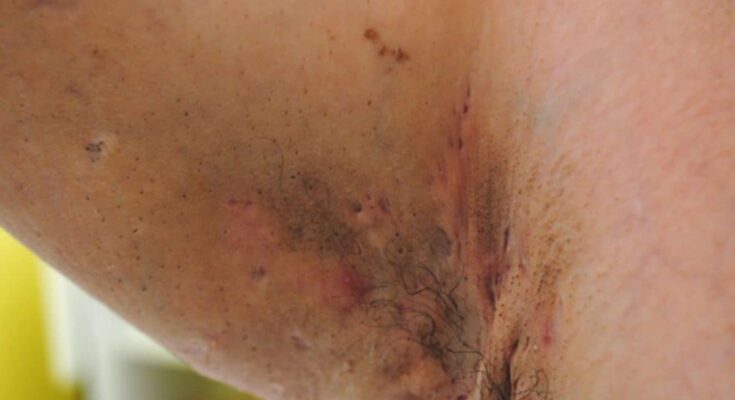
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Symptoms: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition characterized by the appearance of painful lumps under the skin.
The lumps typically occur near hair follicles where there are sweat glands, often around the armpits, groin, buttocks, and breasts. This debilitating condition can cause severe discomfort and has a significant impact on the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of hidradenitis suppurativa is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition characterized by the appearance of painful lumps under the skin. These lumps, typically found in areas where the skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts, can break open or become inflamed, often leading to scarring. The exact cause of HS is not well understood, but it involves inflammation of the hair follicles and can be significantly influenced by hormonal, genetic, and environmental factors.
Who Does Hidradenitis Suppurativa Commonly Affect?
HS most commonly affects individuals in the following groups:
- Age Group: The condition typically begins after puberty and is most commonly diagnosed in individuals between the ages of 20 and 30.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop HS than men, with studies suggesting nearly three times the prevalence in females.
- Family History: Those with a family history of HS are at a higher risk, indicating a possible genetic link.
- Smokers and Overweight Individuals: Smoking and obesity are strong risk factors for HS, with both conditions believed to exacerbate the severity of the disease.
Prevalence of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
HS affects approximately 1 to 4 percent of the global population, making it relatively uncommon but still significant. The prevalence can vary widely by region and population, and due to its often private and sensitive nature, HS may be underreported. The impact of this condition on quality of life can be profound, affecting both physical health and emotional well-being.
However, understanding HS and its effects on various demographics is crucial in managing and treating this challenging skin condition effectively. By recognizing its signs early and seeking appropriate medical consultation, individuals can manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Recognizing the early signs and understanding the progression of symptoms are crucial for timely and effective management. Here’s a breakdown of the common symptoms, their physical manifestations, and how they can evolve over time.
Early Signs and Symptoms
The initial signs of Hidradenitis Suppurativa may be subtle and easy to overlook. Early symptoms typically include:
- Persistent Skin Irritation: Early stages often begin with mild irritation, redness, and discomfort in areas prone to friction or sweat, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts.
- Formation of Small Lumps: Small, pimple-like bumps appear under the skin. These can be tender to the touch and may persist or recur in the same locations.
- Mild Pain or Discomfort: The affected areas may be painful, especially when touched or during movement.
It’s important to note these symptoms early, as prompt treatment can help manage the condition and prevent severe complications.
Description of the Physical Manifestations
As HS progresses, the physical symptoms become more pronounced and can include:
- Lumps and Abscesses: The small bumps can evolve into larger, painful lumps and deep-seated abscesses. These are often filled with pus and can be extremely painful.
- Sinus Tracts and Scarring: Chronic or recurring abscesses lead to the formation of sinus tracts—abnormal channels in the skin that can leak pus and other fluids. This can result in significant scarring.
- Skin Changes: The repeated cycle of inflammation and healing can cause the skin to become thick and scarred, limiting movement and causing chronic pain.
Stages of Symptom Progression
Hidradenitis Suppurativa symptoms typically progress through three stages:
- Stage I: Characterized by the presence of solitary or multiple isolated abscesses without sinus tracts or scarring. This stage often resembles simple acne and is the best stage at which to initiate treatment.
- Stage II: At this stage, recurrent abscesses are evident, and they are connected by sinus tracts. Scarring may begin to appear, and flare-ups are more frequent and painful.
- Stage III: The most severe stage, featuring extensive abscesses and sinus tract formation. This stage includes significant scarring and may involve multiple areas of the body. Chronic pain and mobility issues are common, severely affecting patients’ lifestyle and mental health.
However, understanding these stages helps in monitoring the progression of the disease and can guide therapeutic decisions aimed at managing symptoms and improving life quality. Early diagnosis and intervention remain key in managing Hidradenitis Suppurativa effectively.
Causes and Risk Factors of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
The exact causes of HS are not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Understanding these can help in managing symptoms and reducing flare-ups.
Genetic Factors
Research indicates that HS may have a genetic component. It is more common in individuals who have a family history of the condition. Specific genes associated with inflammation and the immune system may play a role in developing HS, suggesting a hereditary pattern that predisposes individuals to the condition.
Environmental Factors
Environmental triggers can exacerbate HS symptoms. These include:
- Friction from Clothing: Tight clothing can irritate the skin by causing friction, especially in areas like the armpits, groin, and under the breasts.
- Excessive Sweating: High levels of sweating can worsen symptoms, as moisture can lead to further irritation and infection in the affected areas.
- Smoking: Smoking is strongly linked to HS. It can increase the severity of the condition and may also delay healing.
- Weight: Higher body weight can increase the risk of developing HS, likely due to increased skin friction and hormone variations.
Triggers that Exacerbate Symptoms
Individual triggers may vary, but common ones include:
- Stress: Emotional stress is known to trigger flare-ups in many chronic dermatological conditions, including HS.
- Hormonal Changes: Women often report worsening symptoms during menstrual periods, pregnancy, or menopause, indicating a hormonal influence on HS.
Role of Hormones and Lifestyle Choices
Hormones play a significant role in HS, especially sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone, which influence skin and hair follicle behavior. Fluctuations in these hormones can trigger or worsen symptoms.
Lifestyle choices also have a substantial impact on HS management:
- Diet: While no specific diet causes HS, certain foods might trigger flare-ups in some people. Foods high in dairy and refined sugars have been reported to exacerbate symptoms.
- Exercise: Regular, gentle exercise can help manage weight and reduce stress, potentially helping to control symptoms. However, care should be taken to avoid excessive friction and ensure proper hygiene to prevent exacerbations.
However, understanding these factors can help individuals with HS make informed choices about their health and lifestyle, potentially leading to better management of their symptoms.
Complications Associated with Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Understanding these complications is essential for those managing the condition and for healthcare providers aiming to offer comprehensive care.
Potential Complications of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Infections: The open wounds and abscesses associated with HS can become gateways for bacterial infections. These infections can be recurrent and may require antibiotic treatment, which can further complicate the condition.
- Scarring and Skin Changes: Chronic HS leads to significant scarring. Keloid scars, which are thick, puckered, itchy clusters of scar tissue that grow beyond the edges of the wounds, are particularly common. These scars can cause restricted movement when located near joints and can be cosmetically distressing.
- Restricted Movement: Severe scarring can reduce skin elasticity, limiting the range of motion and impacting daily activities. This is especially common in areas like the armpits, groin, and under the breasts.
- Formation of Sinus Tracts: One of the hallmark complications of HS is the development of sinus tracts, or tunneling wounds beneath the skin that can leak pus and are extremely painful.
- Lymphedema: Persistent inflammation from HS can lead to lymphedema — a condition characterized by swelling due to a blockage in the lymphatic system, which occurs commonly in the arms and legs but can also affect areas around HS lesions.
- Anemia: Chronic inflammation can also lead to anemia, which is a reduction in red blood cells or hemoglobin, causing fatigue, weakness, and other systemic symptoms.
- Increased Risk of Squamous Cell Carcinoma: In rare cases, long-standing HS can lead to the development of squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer, in the affected areas.
Impact on Mental Health and Quality of Life
The impact of HS on mental health and quality of life cannot be overstated:
- Chronic Pain: Constant, intense pain affects all aspects of life, limiting mobility and activity levels and reducing overall life satisfaction.
- Emotional Distress: The visibility of the condition can lead to self-esteem issues, social withdrawal, and depression. Anxiety and depression are significantly higher in individuals with HS compared to the general population.
- Social Stigma and Isolation: Due to the misunderstanding of the condition, individuals may face social stigma and isolation. The chronic nature of the disease and its symptoms, such as odor and visible lesions, can impair social interactions and intimate relationships.
- Impact on Employment: Frequent medical appointments and sick days can jeopardize employment and financial stability. The physical symptoms can also limit the types of jobs individuals with HS are able to perform.
- Sleep Disturbances: Pain and discomfort can disrupt sleep, leading to chronic fatigue and affecting overall well-being and mental health.
However, effective management, supportive therapies, and compassionate care are essential to help individuals cope with the challenges posed by Hidradenitis Suppurativa.
Diagnosis of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Early diagnosis is crucial as it can significantly affect the management and prognosis of the condition. Here, we explore the methods used by healthcare professionals to diagnose HS, underline the importance of early detection, and discuss the challenges involved in diagnosing the condition accurately.
Methods of Diagnosing Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Diagnosis of HS typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and medical history assessment. Here are some common steps and methods used:
- Physical Examination: The first step in diagnosing HS is a thorough physical exam. Doctors look for the characteristic signs of HS such as blackheads, red, tender bumps (nodules), and abscesses. The pattern of these skin changes and their specific locations are key indicators.
- Medical History: A detailed medical history helps doctors understand the duration and progression of symptoms. Patients are often asked about pain, odor, drainage from the bumps, and how these symptoms affect their daily activities and quality of life.
- Symptom Tracking: Patients may be asked to keep a symptom diary to track flare-ups and any factors that might trigger them, such as stress or heat.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: Since symptoms of HS can resemble those of acne, folliculitis, and other infections, doctors often need to rule out these other conditions. This might involve swab tests to exclude bacterial infections or other relevant tests.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, doctors may recommend ultrasound scans to better understand the depth and extent of the affected areas. Advanced imaging like MRI can be useful in assessing the involvement of deeper tissues.
- Dermatology Referral: If the diagnosis is uncertain, or if the treatment becomes complex, referral to a dermatologist or a specialist HS clinic is common.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of HS is vital for several reasons:
- Early treatment can slow progression: Starting treatment early in the disease can help manage symptoms more effectively and may prevent the formation of severe scars and complications.
- Improves quality of life: Effective management of symptoms can significantly improve the quality of life and mental health of patients, reducing the social and psychological burden of the disease.
- Prevents complications: Early and aggressive treatment can prevent the formation of tunnels under the skin—a common complication of advanced HS.
Challenges in Early Diagnosis
Despite the importance of early diagnosis, several challenges exist:
- Lack of awareness: Both patients and healthcare providers may not be familiar with HS, leading to significant delays in diagnosis.
- Misdiagnosis: Symptoms of HS are often mistaken for those of other common skin conditions, which can lead to inappropriate treatments.
- Variable presentation: The symptoms of HS can vary greatly from one patient to another, and even in the same patient over time, complicating the diagnosis process.
Awareness and education about HS among both the public and healthcare providers are essential to improve early detection and management of this challenging condition.
Management and Treatment Options for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Managing and treating HS effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical interventions, lifestyle adjustments, and home remedies. Below, we explore current treatment strategies and lifestyle modifications that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Current Treatment Strategies for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
1. Medications:
- Antibiotics: Often used to treat and prevent infections and reduce inflammation. They can be taken orally or applied topically.
- Corticosteroids: Injections or oral steroids can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Hormonal Therapies: Such as oral contraceptives or anti-androgens, can be effective in managing HS, particularly in women.
- Biologics: Medications like adalimumab (Humira) are approved for severe cases of HS and can significantly reduce symptoms by targeting specific parts of the immune system.
- Retinoids: Oral retinoids, like acitretin, may be used in severe or persistent cases.
2. Surgery:
- Incision and Drainage: Primarily used to relieve pain from severe flare-ups, but not a long-term solution as it does not prevent recurrence.
- Excision: Surgical removal of the affected skin areas; this method can be effective in reducing recurrence but may require significant recovery time.
- Laser Therapy: Used to reduce hair follicles and inflammation; it can be an effective adjunct treatment for HS.
3. Pain Management:
- Pain related to HS can be severe. Options include over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription pain medications, and local anesthetic injections.
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
1. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the friction between skin folds, decreasing the severity of symptoms.
2. Dietary Changes: Some individuals may find relief by avoiding inflammatory foods such as dairy and brewer’s yeast. A balanced, anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may also help.
3. Wound Care: Keeping affected areas clean and applying warm compresses can help soothe pain and promote drainage of the lesions.
4. Clothing Choices: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing to reduce irritation and moisture buildup, which can exacerbate symptoms.
5. Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage the emotional stress associated with living with a chronic condition.
6. Quitting Smoking and Limiting Alcohol Intake: Smoking and heavy alcohol use can worsen symptoms. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption can improve overall health and potentially reduce HS flare-ups.
7. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help manage weight, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being.
It’s important for individuals with HS to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific symptoms and needs.
Prevention Tips for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Here are some essential tips to keep in mind for those seeking to control their symptoms and reduce the occurrence of new outbreaks.
1. Maintain Good Hygiene
Keeping the affected areas clean and dry is crucial in managing HS. Use a gentle, non-irritating soap and lukewarm water to cleanse the skin daily. Avoid scrubbing the areas harshly as this can irritate the skin and exacerbate symptoms.
2. Wear Loose and Breathable Clothing
Tight clothing can irritate your skin, leading to flare-ups. Opt for loose-fitting, breathable fabrics like cotton that allow air circulation and reduce friction on the skin.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking is strongly linked to the severity and frequency of HS flare-ups. Quitting smoking can significantly improve your symptoms and overall health. If quitting is challenging, seek help from medical professionals for cessation programs and resources.
4. Manage Your Weight
Excess body weight increases the risk of developing HS and can exacerbate symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise can significantly reduce flare-ups and relieve pain.
5. Avoid Trigger Foods
Some individuals may notice that certain foods, like dairy and processed foods, trigger their symptoms. Keeping a food diary to track what you eat and how it affects your symptoms can be beneficial. It may help to consult a nutritionist who can guide you in identifying potential food triggers and creating a diet plan that suits your needs.
6. Reduce Stress
Stress is a known trigger for many inflammatory diseases, including HS. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises. Regular physical activity can also help reduce stress.
7. Regular Medical Check-Ups
Staying in regular contact with your healthcare provider is essential for managing HS. They can monitor the progression of your condition, adjust treatments, and provide support and advice. Early intervention can prevent complications and manage symptoms more effectively.
8. Practice Self-Care
Taking time for self-care is crucial. This can include skincare routines, sufficient rest, and engaging in activities that you enjoy and find relaxing. Self-care practices can improve your quality of life and mental health, which is vital in managing chronic conditions like HS.
By integrating these prevention tips into your daily routine, you can manage hidradenitis suppurativa more effectively and improve your quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your lifestyle, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and recognizing the symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) early cannot be overstated. Early identification of the signs, such as painful lumps under the skin, recurring abscesses, and scarring, plays a critical role in managing the condition effectively. Early intervention may help mitigate the severity of the symptoms and improve quality of life.
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing symptoms of HS to seek medical advice promptly. Consulting with a healthcare provider can lead to a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Living with HS can be challenging, but with the right medical support and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Remember, you are not alone, and help is available. Seeking support from medical professionals and connecting with others who understand what you are going through can provide both medical and emotional benefits.
References
For further reading and to validate the information discussed regarding the symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, the following resources offer comprehensive insights and reputable data. These sources are essential for patients, healthcare providers, and researchers interested in understanding the complexities of this condition.
- Mayo Clinic – Provides a detailed overview of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Explore more at Mayo Clinic’s Hidradenitis Suppurativa page.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) – Offers in-depth information on rare diseases, including Hidradenitis Suppurativa. For a thorough exploration, visit NORD’s Hidradenitis Suppurativa resource.
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – Provides guidance and educational materials on various skin conditions, including Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Learn more at American Academy of Dermatology’s webpage.
These sources are reliable and can provide additional support and information to those looking to learn more about Hidradenitis Suppurativa.
Feel free to visit these links to enhance your understanding of the condition and its implications on health.