Hepatitis C Treatment: Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver, leading to inflammation and significant liver damage.
The Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is transmitted through contact with contaminated blood, often via shared needles or inadequate sterilization of medical equipment.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for Hepatitis C is crucial for managing and potentially curing this chronic infection.
Understanding Hepatitis C
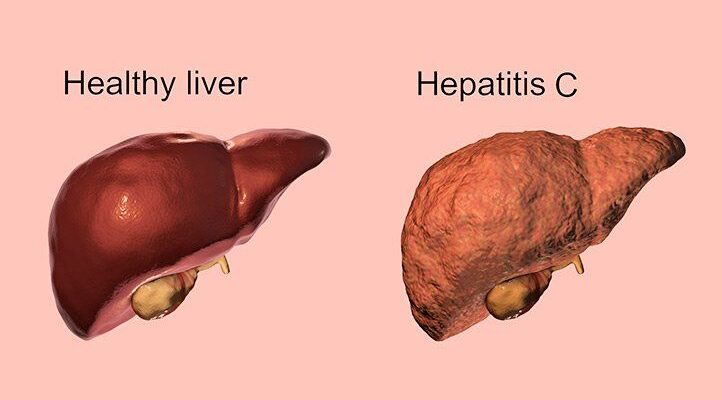
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver, leading to inflammation and significant liver damage. This infection is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a chronic, lifelong illness that can lead to serious liver problems, including cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) or liver cancer.
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus, a bloodborne virus that infects liver cells. The disease progresses slowly, often without any symptoms, which makes it particularly dangerous because many people are unaware they are infected. Over time, chronic hepatitis C can cause severe damage to the liver, impairing its ability to function properly.
How is Hepatitis C Transmitted?
Hepatitis C is primarily transmitted through exposure to infected blood. The most common modes of transmission include:
- Sharing needles or syringes: This is the most common route of transmission, especially among individuals who inject drugs.
- Unregulated tattooing and piercing: Equipment that is not properly sterilized can pose a risk.
- Blood transfusions and organ transplants: Before widespread screening of the blood supply began in 1992 in the United States, hepatitis C was commonly spread through transfusions and transplanted organs. Today, this is rare in countries that have effective screening procedures.
- Sharing personal items: Items such as razors or toothbrushes that might have come into contact with an infected person’s blood can transmit the virus.
- Healthcare exposures: Improper sterilization of medical equipment in healthcare settings can lead to transmission.
- Mother to baby during childbirth: While less common, a mother with hepatitis C can transmit the virus to her child during birth.
Common Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Many people with hepatitis C do not experience symptoms and may not know they are infected. When symptoms do occur, they can be mild and flu-like, including:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Joint pain
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment, potentially mitigating the long-term damage to the liver. Regular medical check-ups and screenings are essential for those who may be at risk of hepatitis C.
Diagnosis of Hepatitis C
Diagnosing Hepatitis C accurately and promptly is crucial for effective management and treatment of the disease. Understanding who needs testing, the types of tests available, and the interpretation of these tests can guide patients and healthcare providers through the diagnosis process efficiently.
Screening and Early Detection: Who Should Get Tested?
Screening for Hepatitis C is essential because many people with the infection may not show symptoms for many years. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that all adults aged 18 years and older should get screened at least once in their lifetime. High-risk individuals, including those who have ever injected drugs, received blood transfusions or organ transplants before July 1992, or have HIV, should consider more frequent testing.
Types of Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis C
Blood Tests
- HCV Antibody Test: This test checks for antibodies to the Hepatitis C virus and can indicate if a person has been exposed to the virus at some point. A non-reactive or negative test means that a person has not been infected with Hepatitis C. A reactive or positive result requires further testing to confirm active infection.
- HCV RNA Test: This test detects the presence of the virus’s RNA in the blood and can confirm an active infection. It’s used after a positive antibody test to verify if the virus is currently in the bloodstream.
Additional Tests
- Liver Function Tests: These tests assess liver damage and how well the liver is functioning. They measure levels of liver enzymes in the blood which can indicate liver inflammation or damage.
- Imaging Tests: Techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs are used to visually assess the liver and check for the extent of liver damage.
Interpretation of Test Results
Interpreting the results of Hepatitis C testing involves several steps:
- A positive antibody test with a negative RNA test suggests a past infection that has resolved.
- A positive RNA test indicates an active infection and will lead to further assessment and possible treatment options.
- Liver function tests and imaging help determine the degree of liver damage, which is critical for treatment decisions.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in the Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in the diagnosis of Hepatitis C. They are responsible for recommending who gets tested based on CDC guidelines, interpreting the results of diagnostic tests, and guiding patients through subsequent steps if tests are positive. They also provide crucial support in managing the condition if a diagnosis is confirmed, coordinating further diagnostics, and treatment procedures.
However, the effective diagnosis of Hepatitis C involves a combination of strategic screening, comprehensive testing, and professional interpretation of results, all guided by skilled healthcare providers. Early detection and accurate diagnosis are key to managing and potentially curing Hepatitis C.
Treatment Options for Hepatitis C
Understanding these options can lead to more effective management of the condition and improved patient outcomes.
List of Current Treatment Methods
Modern treatment for hepatitis C primarily involves the use of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs). These medications have revolutionized hepatitis C care by offering cure rates above 90%. DAAs work by directly targeting the virus’s ability to replicate, effectively clearing the virus from the bloodstream within 8 to 12 weeks. The specific regimen recommended can vary depending on the genotype of the virus, the presence of existing liver damage, prior treatments, and other individual health factors.
- Pan-genotypic regimens: These are effective against all genotypes of the hepatitis C virus and include drugs like sofosbuvir/velpatasvir and glecaprevir/pibrentasvir.
- Genotype-specific regimens: These treatments are tailored to specific HCV genotypes, such as sofosbuvir/ledipasvir for genotypes 1 and 4.
Additionally, supportive treatments might include:
- Ribavirin: Sometimes used in combination with DAAs for certain cases, such as patients with advanced liver disease or those who have had previous treatment failures.
- Liver transplant: In severe cases, particularly where cirrhosis has led to liver failure, a transplant may be necessary.
Monitoring and Managing Treatment Response
Monitoring the effectiveness of hepatitis C treatment involves regular medical check-ups and blood tests. These tests measure the virus’s RNA in the blood to confirm if the virus is being cleared effectively, known as a sustained virological response (SVR). Achieving SVR usually indicates that the treatment has been successful and the virus has been eradicated.
- During treatment: Patients will undergo periodic blood tests to monitor liver function and viral load.
- Post-treatment: Follow-up tests are crucial to ensure the virus has been completely cleared from the body.
Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Personalized treatment plans are vital in managing hepatitis C effectively. Each patient’s plan should be tailored based on the specific characteristics of the virus they are infected with, their overall health status, and any other medical conditions they may have. Personalized plans can significantly impact the success rate of treatments and help in managing side effects.
Factors influencing treatment decisions include:
- Genotype of the virus: Different regimens may be more effective for specific genotypes.
- Stage of liver disease: Patients with advanced liver disease may require different therapeutic approaches.
- Previous treatment history: This can affect resistance to certain drugs.
- Comorbid conditions: Other health issues, such as kidney disease or heart conditions, can influence the choice of medication.
However, the treatment of hepatitis C has become more effective with the advent of DAAs, but it requires a careful approach that considers the unique aspects of each patient’s condition. Regular monitoring and personalized treatment plans ensure the best outcomes and help patients lead a healthier life post-treatment.
Challenges in Hepatitis C Treatment
Treating Hepatitis C (HCV) presents various challenges that can affect the choice and effectiveness of treatment methods. Understanding these challenges is crucial for healthcare providers and patients aiming to manage and overcome this liver disease effectively.
Factors Influencing Treatment Choice and Effectiveness
The decision on which Hepatitis C treatment to use is influenced by several factors. These include the genotype of the virus, the patient’s previous treatment history, and the presence of liver damage like cirrhosis. Additionally, patient-specific factors such as age, comorbidities, and even socioeconomic status can influence treatment decisions. Advances in medical research have led to the development of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) which have significantly improved treatment success rates. However, selecting the right treatment regimen remains complex and must be personalized to each patient’s circumstances.
Side Effects of Treatment
While the newer DAAs have fewer side effects compared to older treatments like interferon, they are not entirely free from adverse effects. Common side effects of DAAs include headache, fatigue, and nausea. In some rare cases, these medications can lead to more severe health issues such as liver failure or reactivation of hepatitis B in patients co-infected with hepatitis B virus. Managing these side effects is a critical aspect of the treatment process, as it can influence patient adherence to the medication regimen.
Addressing Treatment Resistance
Treatment resistance remains a significant hurdle in the fight against Hepatitis C. The virus can mutate, leading to variants that are resistant to current drugs. This challenge is particularly daunting when dealing with patients who have experienced treatment failure. Ongoing research and the development of new drugs aim to address these resistant strains, but this area remains a critical focus for improving treatment outcomes.
The Impact of Co-existing Conditions
The presence of co-existing conditions such as HIV significantly complicates the treatment of Hepatitis C. HIV co-infection can accelerate the progression of liver disease and affect the body’s response to HCV treatment. Treating HCV in HIV-positive patients requires a careful selection of drugs to avoid drug interactions and to manage both conditions effectively. It is essential for treatment plans to be coordinated across specialties to ensure comprehensive care.
However, the challenges in treating Hepatitis C are significant and multifaceted. Addressing these challenges requires a careful and personalized approach to treatment, considering the unique circumstances of each patient. By overcoming these obstacles, healthcare providers can improve treatment outcomes and enhance the quality of life for those affected by Hepatitis C.
Advancements in Hepatitis C Treatment
Hepatitis C, a significant global health issue, has seen transformative advancements in treatment options over the past few years. These breakthroughs have drastically improved the prognosis for individuals affected by the virus, turning what was once a potentially chronic, debilitating condition into one that is highly manageable and often curable.
Recent Breakthroughs and Innovations in Treatment
The landscape of Hepatitis C treatment has evolved with the introduction of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs). These drugs target the virus directly, offering a cure rate of over 90% in most cases. The newest generation of DAAs is not only more effective but also boasts a reduced duration of treatment and fewer side effects, enhancing patient compliance and comfort. Additionally, the development of pan-genotypic regimens has simplified treatment protocols by effectively treating all genotypes of the Hepatitis C virus.
The Future of Hepatitis C Treatment: New Drugs and Therapeutic Approaches
Looking forward, the future of Hepatitis C treatment is promising, with several innovative drugs and therapeutic approaches in the pipeline. Researchers are focusing on even more effective and shorter-duration therapies that could further simplify treatment regimens. There is also a significant push towards developing vaccine-based strategies and immune therapies that aim to prevent the virus rather than merely managing its symptoms.
Clinical Trials and Research: How They Contribute to Better Outcomes
Clinical trials play a pivotal role in the advancement of Hepatitis C treatments. These trials test new drugs and therapies under rigorous conditions to ensure safety and efficacy before they become widely available. By participating in clinical trials, patients contribute to valuable research that can lead to breakthroughs in treatment options and potentially, a cure. Ongoing research not only helps in refining existing treatments but also assists in the discovery of novel therapeutic targets and drug formulations.
The continuous improvement in the treatment of Hepatitis C through these advancements represents a beacon of hope for millions affected worldwide, bringing us closer to a world where Hepatitis C can be a thing of the past.
Living with Hepatitis C: A Guide to Managing Your Health
Lifestyle Adjustments During Treatment
When diagnosed with Hepatitis C, making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly impact the effectiveness of your treatment and overall quality of life. Here are some practical steps to consider:
- Dietary Changes: Embrace a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limiting the intake of fatty, sugary, and processed foods can help manage your liver health. Staying hydrated is also crucial.
- Limit Alcohol and Avoid Drugs: Alcohol can exacerbate liver damage, so it’s recommended to avoid it entirely during treatment. Similarly, recreational drugs can interfere with medications and liver health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate exercise, such as walking or swimming, can improve overall health and aid in managing symptoms and side effects of treatment.
- Mental Health: Treatment can be stressful. Consider practices like meditation, yoga, or other relaxation techniques to help manage stress and emotional well-being.
- Medication Adherence: Follow your treatment regimen strictly as prescribed to maximize the chance of a cure. Keep regular appointments with your healthcare provider and discuss any side effects.
Support Systems and Resources for Patients
Building a strong support system is essential for individuals living with Hepatitis C. Here are several resources and forms of support:
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and valuable information from people who understand your experience firsthand.
- Counseling Services: Professional counselors or therapists skilled in dealing with chronic illnesses can offer strategies to cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of Hepatitis C.
- Educational Resources: Utilize resources from reputable organizations such as the American Liver Foundation or the Hepatitis C Association for up-to-date information and advice.
- Family and Friends: Educate your close circle about Hepatitis C to help them understand your condition and how they can support you.
Long-term Health Management and Follow-Up Care
Managing Hepatitis C is a long-term commitment, even after the initial treatment phase. Regular follow-up care is critical:
- Regular Monitoring: Even after successful treatment, regular check-ups and liver function tests are necessary to monitor liver health and ensure the virus has not returned.
- Vaccinations: Protect your liver from other strains of hepatitis, such as Hepatitis A and B, through vaccinations.
- Ongoing Education: Stay informed about new research and treatments that can further improve your quality of life.
By making informed lifestyle adjustments, utilizing available support resources, and adhering to a comprehensive follow-up care plan, individuals living with Hepatitis C can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Managing the disease proactively is key to long-term health and well-being.
FAQs about Hepatitis C Treatment
1. What is the first step in treating Hepatitis C?
The first step in treating Hepatitis C is to undergo a thorough diagnosis, which includes a series of blood tests to confirm the presence of the HCV virus and assess the liver’s condition. Your healthcare provider will then recommend the most appropriate treatment plan based on the genotype of the virus and your overall health.
2. Are there different types of Hepatitis C treatments?
Yes, there are several types of treatments available for Hepatitis C, primarily involving antiviral medications known as direct-acting antivirals (DAAs). These medications are highly effective and can cure the disease in most people within 8 to 12 weeks.
3. How effective are current Hepatitis C treatments?
Modern Hepatitis C treatments have success rates exceeding 90%. These treatments, which are much simpler and more effective than older therapies, typically result in a complete cure of the infection, as evidenced by the absence of the virus in the blood three months after the treatment ends.
4. What are the side effects of Hepatitis C medications?
The side effects of current Hepatitis C treatments are generally mild and manageable. Common side effects include headache, fatigue, and nausea. These symptoms are significantly less severe than those associated with older Hepatitis C treatments.
5. Can Hepatitis C be treated without medication?
No, Hepatitis C typically requires medication to be effectively treated. Untreated Hepatitis C can lead to significant health issues, including liver damage, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a successful cure.
6. Is Hepatitis C treatment available for everyone?
Hepatitis C treatment is available for nearly everyone, although access can vary depending on geographic location and healthcare coverage. It is important to consult healthcare providers for specific treatment options available in your area.
7. How long does Hepatitis C treatment last?
The duration of Hepatitis C treatment can vary depending on the specific medication used and the individual’s response to treatment. Typically, treatment lasts between 8 to 24 weeks.
8. What happens if Hepatitis C treatment fails?
In rare cases where Hepatitis C treatment fails, doctors may suggest a different combination of medications or a longer treatment duration. Ongoing research and development are continuously improving the options available for treatment-resistant Hepatitis C.
9. Can Hepatitis C return after treatment?
After successful treatment, Hepatitis C does not usually return. However, being cured of Hepatitis C does not prevent future infections. It’s important to take preventive measures to avoid re-infection.
10. Where can I find more information about Hepatitis C treatment?
For more information about Hepatitis C treatment, you should consult a healthcare provider or visit reputable health websites like those of the World Health Organization (WHO) or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the importance of recognizing, diagnosing, and treating Hepatitis C is crucial for public health. This viral infection, if left unchecked, can lead to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Early detection through proper diagnosis plays a pivotal role in managing the disease effectively and preventing its progression.
For individuals who may be at risk, including those with a history of intravenous drug use, received blood transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, or were born between 1945 and 1965, seeking Hepatitis C screening is essential. Modern treatments have high success rates, and getting screened early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
We strongly encourage everyone, especially those in high-risk groups, to consult their healthcare provider about Hepatitis C screening. It’s a proactive step that can lead to a healthier future and prevent serious health complications. Remember, your health is in your hands, and taking early action is key to combating Hepatitis C effectively.
References
For those seeking to expand their knowledge on the treatment of Hepatitis C, or looking for further validation of the information discussed, the following sources are highly reputable and can provide deeper insight:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC offers comprehensive guidelines and the latest research on Hepatitis C treatment options. Explore their resources at CDC Hepatitis C Information.
- World Health Organization (WHO) – WHO provides global statistics, treatment protocols, and policy advice on Hepatitis C. Their detailed reports are available at WHO Hepatitis C Overview.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its patient-friendly material, the Mayo Clinic has extensive information on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of Hepatitis C. Visit their site at Mayo Clinic Hepatitis C Resource.
- PubMed Central – A service of the US National Institutes of Health, PubMed Central offers access to thousands of peer-reviewed articles on Hepatitis C treatment. Access their library at PubMed Central.
- The Hepatitis C Trust – This patient-led organization provides support and up-to-date information on treatment options. Find more at The Hepatitis C Trust Treatment Page.
These resources are essential for anyone looking to understand more about the treatment of Hepatitis C and ensure they are getting the most accurate and current information available.