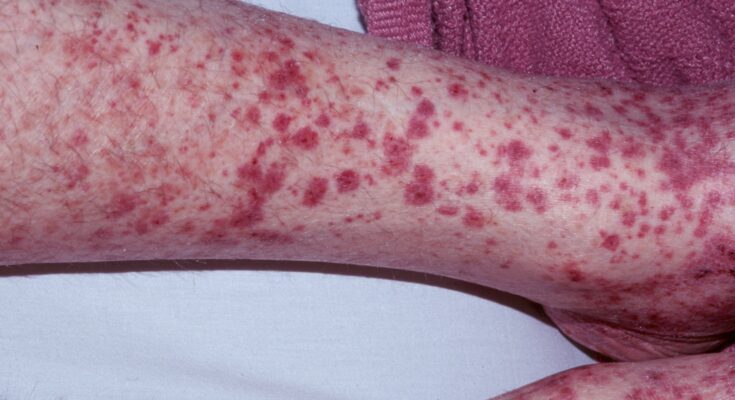
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Treatment: Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), also known as IgA vasculitis, is a form of small vessel vasculitis that primarily affects children, though it can occasionally occur in adults.
This condition is characterized by a distinctive rash, typically on the lower limbs, abdominal pain, and joint inflammation.
Understanding the comprehensive scope of HSP, including its diagnosis and treatment options, is crucial for managing the symptoms effectively and preventing complications.
What is Henoch-Schonlein Purpura?
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP), also known as IgA vasculitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of small blood vessels (vasculitis). This condition can lead to blood vessels bleeding into the skin, joints, intestines, and kidneys. It is most identifiable by its hallmark symptom: a purplish rash typically seen on the lower legs and buttocks.
Immune-Mediated Nature of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
The disease is immune-mediated, which means it results from an abnormal response of the body’s immune system. In the case of HSP, the immune system mistakenly targets the body’s own small blood vessels with antibodies, particularly Immunoglobulin A (IgA). This immune reaction causes the blood vessels to become inflamed and sometimes leak, leading to the characteristic symptoms.
Typical Age Groups Affected and Gender Prevalence
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura predominantly affects children, with the highest incidence in those aged between 2 and 6 years. However, it can occur in adults, though less commonly. While both boys and girls can develop HSP, studies have shown a slightly higher prevalence in boys. This gender difference is particularly noted in childhood cases, whereas adult cases tend to be more evenly distributed between the genders.
However, understanding HSP is crucial for early recognition and management, especially since it impacts vital organs and can influence the quality of life of those affected.
Symptoms of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and management of the condition. Here’s a detailed look at the common symptoms, their role in clinical diagnosis, and their impact on quality of life.
List of Common Symptoms
- Skin Rash: The most recognizable symptom of HSP is a purplish or reddish rash, typically appearing on the lower legs and buttocks. This rash is often raised and can be painful or itchy.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Many individuals experience swelling and pain in the joints, particularly in the knees and ankles. This arthritis or arthralgia does not usually lead to permanent damage but can significantly impair mobility.
- Abdominal Pain: Abdominal discomfort, ranging from mild to severe, is a common symptom. It can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and, in some cases, blood in the stool due to inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Kidney Involvement: Renal issues such as protein or blood in the urine can occur, which may or may not be symptomatic initially. Over time, this can lead to more severe kidney problems if not monitored and treated.
How Symptoms Lead to a Clinical Diagnosis
Diagnosis of HSP is largely based on the presence of the characteristic rash in conjunction with the above symptoms. Health professionals typically look for a combination of skin, joint, gastrointestinal, and renal symptoms to make a diagnosis. Blood tests to check kidney function and urine tests for protein and blood are also common diagnostic tools. In some cases, a biopsy of affected tissue, especially skin or kidney, may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of IgA vasculitis.
Impact of Symptoms on Quality of Life
The symptoms of HSP can significantly affect the quality of life, particularly during active phases of the disease. Joint pain and swelling can limit physical activity and participation in sports for children, which are crucial parts of social interaction and personal development. Abdominal pain and gastrointestinal symptoms can affect nutrition, growth, and overall comfort. Additionally, the visible nature of the rash can lead to psychological distress and self-esteem issues, particularly in older children and adults.
However, understanding these symptoms not only aids in timely and accurate diagnosis but also helps in managing the condition effectively to minimize its impact on daily life. It is essential for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical advice for appropriate intervention and support.
Diagnosing Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP)
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment. This section outlines the key diagnostic criteria, common tests and procedures, and the vital role of medical history and physical examination in diagnosing HSP, along with the challenges often faced by healthcare providers.
Key Diagnostic Criteria for HSP
The diagnosis of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura typically involves a combination of clinical findings and medical history. The primary diagnostic criteria include:
- Palpable Purpura: Non-thrombocytopenic purpura (small blood vessels bleeding into the skin) is the hallmark of HSP. These are typically raised bruises that are most common on the legs and buttocks.
- Abdominal Pain: Often acute and can include symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Arthritis or Arthralgia: Joint pain and swelling, usually affecting the knees and ankles.
- Renal Involvement: Kidney involvement can vary from mild to severe, potentially leading to nephritis.
Common Tests and Procedures
To confirm a diagnosis of HSP, several tests may be conducted, including:
- Blood Tests: To check for elevated levels of IgA antibodies, kidney function, and overall inflammation markers.
- Urine Analysis: To detect protein and red blood cells in the urine which signal kidney involvement.
- Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin may be taken to look for IgA deposition, confirming HSP.
- Ultrasound: For abdominal pain, an ultrasound might be performed to check for any complications in the abdomen.
Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination are crucial in diagnosing Henoch-Schonlein Purpura. This process includes:
- Past Medical History: Checking for recent infections or illnesses that can trigger HSP.
- Family History: Although not typically hereditary, understanding the genetic predispositions to autoimmune responses is beneficial.
- Physical Signs: Careful inspection of the skin, joints, and abdominal area to identify characteristic symptoms of HSP.
Challenges in Diagnosing HSP and Overcoming Them
Diagnosing HSP can be challenging due to its similarity to other conditions such as infections, other types of vasculitis, and rheumatologic disorders. To overcome these challenges:
- Comprehensive Assessment: A detailed and systematic assessment is crucial to differentiate HSP from similar conditions.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Collaboration with rheumatologists, nephrologists, and dermatologists can provide a more accurate diagnosis.
- Follow-Up: Regular monitoring of symptoms and organ function helps in managing the condition effectively and adjusting treatment plans as necessary.
Early diagnosis and proper management of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura are essential to prevent complications, especially those involving the kidneys. Awareness and understanding of the disease’s presentation and progression are key to effective treatment and the wellbeing of the patient.
Treatment Options for Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP)
Understanding the treatment options available can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Here’s a detailed guide on how to approach HSP treatment effectively.
Objectives of Treatment for Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
The primary goals in treating HSP are:
- Managing Symptoms: This includes alleviating pain, reducing swelling, and addressing any skin rashes.
- Preventing Complications: Treatment aims to prevent serious complications such as kidney damage, severe gastrointestinal manifestations, and prolonged joint pain.
Medications Commonly Used in the Treatment of HSP
Medication plays a crucial role in the management of HSP. The choice of drugs depends on the severity of the symptoms and the organs involved. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Corticosteroids: These are often used to reduce inflammation and control the immune response. Prednisone is a typical example that may help reduce the duration and intensity of symptoms.
- Immunosuppressants: In cases where steroids are ineffective or for severe symptoms, drugs like azathioprine or cyclophosphamide may be used to suppress the immune system.
Non-Medication Therapies for Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
In addition to medications, other treatments can support symptom management:
- Dietary Changes: Adjusting the diet can help manage symptoms, particularly gastrointestinal issues. A diet low in sodium and potassium may be recommended if kidney involvement is suspected.
- Physical Therapy: For patients experiencing joint pain and stiffness, physical therapy can be beneficial in maintaining mobility and reducing discomfort.
Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Every case of HSP is unique, and treatment should be tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and health status. Personalized treatment plans are developed based on:
- The severity of the symptoms
- Age of the patient
- Presence of underlying health issues
- Response to initial treatment
A personalized approach ensures that the treatment is as effective as possible, with adjustments made as the condition progresses or improves.
Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor their health and adjust treatments as necessary to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Advanced Treatment Strategies for Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
With advances in research and treatment methodologies, managing this condition has seen significant progress. This article delves into the recent advancements in pharmacological treatments, the role of biologics in severe cases, and the promising horizon of emerging therapies and clinical trials for HSP.
Recent Advancements in Pharmacological Treatments
Recent years have seen a shift in the pharmacological management of HSP, primarily aimed at alleviating symptoms and preventing complications such as kidney damage. Traditionally, corticosteroids have been the cornerstone of HSP treatment, helping reduce inflammation and pain. However, newer drugs are being explored to minimize long-term steroid use and its side effects.
One notable advancement is the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) which offer pain relief and anti-inflammatory benefits without the steroidal side effects. Additionally, immunosuppressants like azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil are gaining traction for their effectiveness in managing persistent or severe cases, particularly when kidneys are involved.
Role of Biologics in Managing Severe Cases of HSP
Biologics have revolutionized treatment options for several autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, and their role in treating severe HSP is increasingly being recognized. These protein-based drugs target specific parts of the immune system that drive inflammation, offering a more targeted approach and potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional therapies.
Drugs such as rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, have shown promise in cases where conventional treatments fail. Rituximab specifically depletes B cells, which are involved in the autoimmune response in HSP. Other biologics like TNF inhibitors are also being studied for their potential to control severe manifestations of HSP, particularly in adult patients.
Emerging Therapies and Clinical Trials
The landscape of HSP treatment is rapidly evolving with numerous emerging therapies under investigation. One exciting area of research is the development of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which have shown effectiveness in other inflammatory diseases and may offer new hope for HSP patients.
Clinical trials play a pivotal role in advancing our understanding and treatment of HSP. Ongoing trials are exploring various aspects of the disease, from the effectiveness of different drug regimens to understanding the genetic basis of the disease. These studies not only help in developing new treatments but also in refining existing protocols to improve patient outcomes.
The treatment of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura is advancing at a promising pace, with pharmacological innovations, biologics, and emerging therapies all playing a part in transforming patient care. As research continues to unveil new findings, the hope for more effective and less invasive treatments grows, offering a brighter outlook for individuals affected by this challenging condition.
Advanced Treatment Strategies for Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP)
Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP), also known as IgA vasculitis, is a condition that primarily affects the blood vessels and can lead to symptoms such as rash, joint pain, and abdominal discomfort. Over the years, treatment strategies have evolved significantly, incorporating newer pharmacological treatments, biologics for severe cases, and exploring emerging therapies through clinical trials.
Recent Advancements in Pharmacological Treatments
Traditionally, HSP treatment focuses on managing symptoms with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for joint pain and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. However, recent advancements have introduced targeted pharmacological treatments that offer more specific intervention mechanisms. For instance, advanced immunosuppressants that modulate the immune response more precisely are being utilized to prevent severe complications like kidney damage, which is a significant concern in HSP patients.
Role of Biologics in Managing Severe Cases of HSP
In severe cases of HSP, particularly where conventional therapies fail, biologics have become a cornerstone of treatment. These are genetically-engineered proteins that target specific parts of the immune system. Drugs such as Rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, have shown promise in treating patients with severe, persistent HSP by reducing the levels of IgA-containing immune complexes that contribute to inflammation and tissue damage. This targeted approach helps in managing the symptoms more effectively while minimizing overall immune suppression.
Emerging Therapies and Clinical Trials
The exploration of new therapies through clinical trials is pivotal in advancing HSP treatment. Current research is focused on new immunomodulatory agents and other novel therapeutic strategies that could offer relief without the side effects associated with traditional treatments. For example, trials involving the use of statins as an anti-inflammatory treatment are underway, hypothesizing that their use could mitigate endothelial dysfunction in HSP. Moreover, the potential application of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which have been effective in other inflammatory diseases, is being explored to determine their efficacy in HSP.
These advancements in treatment strategies for Henoch-Schönlein Purpura highlight the continuous efforts to improve patient outcomes through more effective and targeted therapies. As research progresses, these approaches promise to redefine the management of this complex condition, offering hope to those affected by HSP.
Patient Education and Support for Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
Importance of Patient Awareness and Education on Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
Educating patients about Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP) is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Understanding the symptoms, such as rash, joint pain, and abdominal discomfort, empowers patients to recognize the onset of the disease and seek timely medical intervention. Awareness also facilitates better communication between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the treatment options and expected outcomes.
Resources for Support Groups and Counseling
Dealing with HSP can be challenging, not just physically but also emotionally. Support groups play a vital role in helping patients and families cope with the disease. These groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and advice, reducing feelings of isolation. Patients can find support groups through hospitals, online health forums, and organizations dedicated to HSP. Additionally, professional counseling services may be beneficial in helping individuals manage the psychological impacts of chronic illness.
Tips for Patients and Caregivers for Managing the Disease at Home
Managing HSP at home involves several practical steps that can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications:
- Rest: Adequate rest is important, especially during flare-ups when symptoms can be more severe.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can help manage symptoms and support overall health. Special attention should be given to any dietary triggers that might exacerbate symptoms.
- Medication Management: Patients should adhere to their prescribed medication regimen and keep regular appointments with their healthcare provider to adjust treatment as necessary.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Regular monitoring of symptoms can help in early detection of flare-ups or complications, allowing for prompt treatment adjustments.
- Education on Condition: Continual learning about HSP and its developments can help patients and caregivers make informed decisions about care and lifestyle adjustments.
By focusing on these areas, patients with Henoch-Schönlein Purpura and their caregivers can improve quality of life and enhance disease management.
FAQs about Henoch-Schönlein Purpura Treatment
What is the primary treatment for Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP)?
The primary treatment for HSP generally focuses on alleviating symptoms, as the condition often resolves on its own. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
How long does it take to recover from HSP?
The duration of HSP varies, but most individuals start to see improvement within a few weeks. Complete recovery can take a month or longer, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the presence of complications like kidney involvement. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is crucial.
Can diet affect Henoch-Schönlein Purpura?
While there is no specific diet for treating HSP, maintaining a balanced and healthy diet can support overall health and recovery. Some individuals may find that certain foods exacerbate their symptoms. Keeping a food diary can help identify any triggers and discuss them with a dietitian or healthcare provider.
Are there any long-term effects of HSP?
Most people with HSP recover completely without long-term effects. However, a small percentage of patients may experience recurring symptoms or long-term kidney issues. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to manage and mitigate potential long-term effects.
When should someone with HSP see a doctor?
It is advisable to see a doctor if you suspect HSP or if the characteristic rash accompanied by joint pain, abdominal pain, or any signs of kidney problems such as blood in the urine or proteinuria. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications.
Conclusion
In summary, Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP) is a form of vasculitis that primarily affects children and can lead to symptoms such as rash, joint pain, and abdominal discomfort. With proper diagnosis and treatment, the outlook for individuals with HSP is generally favorable. Most patients recover fully, often without any serious complications, especially when the condition is managed promptly and effectively.
However, severe cases can occasionally lead to more significant health issues, such as kidney damage, necessitating ongoing medical monitoring and intervention. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest treatment protocols and for patients to receive timely care.
References
For those seeking more in-depth information or verification of the data presented in our discussion on the treatment of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura, the following sources are invaluable. Each reference is chosen for its reliability and authority in the medical field:
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – The NIH offers comprehensive resources and research papers on Henoch-Schönlein Purpura, providing readers with a thorough understanding of the condition and its treatment options. Visit NIH’s Henoch-Schönlein Purpura page.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its patient-friendly material, the Mayo Clinic provides detailed descriptions of symptoms, causes, and treatments of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura. Their guidelines can help patients manage their condition effectively. Explore Mayo Clinic’s treatment guidelines.
- Medscape – Medscape offers a detailed article on Henoch-Schönlein Purpura that includes insights into the latest treatment protocols and research developments. This resource is particularly useful for healthcare professionals and researchers. Read Medscape’s comprehensive article.
- PubMed – As a repository of medical journal articles, PubMed is a great source for finding research studies and clinical trial results related to Henoch-Schönlein Purpura. Search PubMed for related studies.
- Cleveland Clinic – The Cleveland Clinic provides another excellent resource for understanding this condition, with clear, expert-reviewed content on managing and treating Henoch-Schönlein Purpura. Visit Cleveland Clinic’s resource page.
These sources are essential for anyone looking to deepen their understanding of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura and its treatment, ensuring that readers have access to the most accurate and up-to-date information.