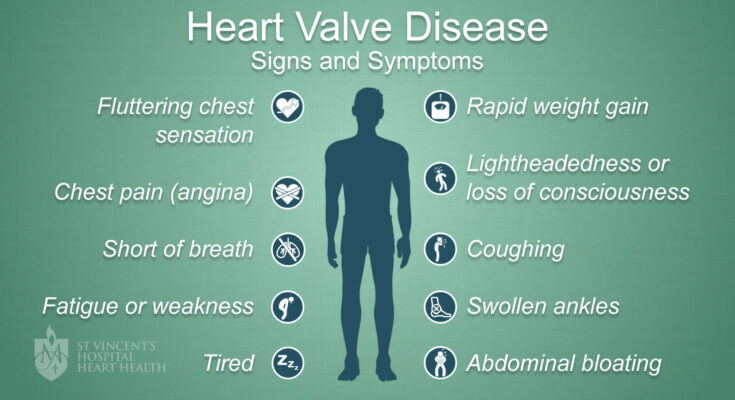
Heart Valve Disease Symptoms: Heart valve disease involves the dysfunction of one or more valves in the heart, which can significantly impact blood flow through the heart and the rest of the body.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of heart valve disease is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Understanding Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve disease is a serious condition affecting the flow of blood through the heart. This can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. A clearer understanding of the types of heart valves and their functions, along with the prevalence and impact of this disease, is essential for both patients and healthcare providers.
Types of Heart Valves and Their Functions
The human heart contains four main valves, each playing a vital role in maintaining proper blood flow:
- The Mitral Valve – located between the left atrium and left ventricle, this valve ensures that blood flows in one direction from the atrium to the ventricle.
- The Aortic Valve – situated between the left ventricle and the aorta, it controls blood flow into the aorta and prevents backflow into the ventricle.
- The Tricuspid Valve – found between the right atrium and right ventricle, it regulates blood flow between these two chambers.
- The Pulmonary Valve – positioned between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, this valve directs blood towards the lungs for oxygenation.
Each valve consists of flaps (cusps or leaflets) that open and close with each heartbeat, ensuring blood moves efficiently and in the correct direction.
Statistics on Prevalence and Impact
Heart valve disease affects a significant portion of the population, with millions experiencing varying degrees of this condition worldwide. In the United States alone, approximately 5 million individuals are diagnosed with heart valve disease annually. This condition can lead to serious health issues such as heart failure, stroke, blood clots, and death if not properly managed.
The impact of heart valve disease is substantial, as it can severely degrade quality of life. Symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and fainting can limit daily activities and require careful management and treatment. The economic burden is also notable, with healthcare systems bearing high costs for surgeries, hospitalizations, and ongoing care.
By promoting awareness and understanding of heart valve disease, patients can seek timely medical attention, potentially leading to better management strategies and improved outcomes.
Causes of Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve disease can develop due to a variety of causes that affect the functionality and health of the heart valves. Understanding these causes is crucial for prevention and management of the condition. Here are the primary causes of heart valve disease:
Congenital Valve Defects
Some individuals are born with congenital valve defects, meaning that their heart valves are not formed correctly from birth. These defects can interfere with the normal flow of blood through the heart, leading to complications and requiring medical attention or intervention at different stages of life. Such congenital issues can range from mild, requiring monitoring, to severe, necessitating surgical repair or replacement of the valve.
Age-Related Changes
As we age, our heart valves may undergo degenerative changes that affect their structure and function. Calcification or thickening of the valve tissue is common and can lead to conditions such as aortic stenosis or mitral valve regurgitation. These age-related changes are a significant cause of heart valve disease in older adults, making regular cardiovascular check-ups important as one ages.
Infectious Causes
Infections can severely damage heart valves, leading to valve disease. Rheumatic fever, which can develop after a strep throat infection, may cause rheumatic heart disease, affecting the heart valves. Similarly, infective endocarditis, an infection of the valve itself or the inner lining of the heart caused by bacteria, fungi, or other germs, can lead to severe valve damage if not promptly treated.
Other Risk Factors
Lifestyle and environmental factors also contribute to the risk of developing heart valve disease. Factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity can increase the likelihood of valve dysfunction. Additionally, certain medications or radiation therapy to the chest can exacerbate or lead to valve problems. Understanding these risks is key to both prevention and treatment of heart valve disease.
By being aware of these causes, individuals can better understand the importance of preventive measures and regular health check-ups to monitor heart health, especially as they age or if they have risk factors for heart valve disease.
Symptoms of Heart Valve Disease
Understanding the symptoms of heart valve disease is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Here, we explore the early signs, common symptoms, severe symptoms, and the differences in symptoms among the types of valve disease.
Early Signs
The early signs of heart valve disease can be subtle and often go unnoticed. However, being aware of these can lead to timely medical consultation. Early indicators include:
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired, especially after physical activities.
- Palpitations: Experiencing irregular heartbeats or a feeling that the heart is skipping beats.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing during activities that were previously manageable.
Common Symptoms
As the disease progresses, more pronounced symptoms may appear, which include:
- Dyspnea: Increased shortness of breath, particularly when lying down or during exertion.
- Edema: Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen due to fluid retention.
- Dizziness: Episodes of lightheadedness or fainting spells, especially with activity.
Severe Symptoms
In advanced stages, heart valve disease can lead to severe health complications. Severe symptoms necessitate immediate medical attention:
- Chest Pain: Occurs especially during activities or when lying flat; chest pain can be a sign of heart strain.
- Syncope: Sudden fainting episodes which may indicate a severe decrease in heart function.
- Heart Failure: Symptoms such as severe shortness of breath, persistent coughing or wheezing, and increased fatigue.
Differences in Symptoms Among Types of Valve Disease
Symptoms can vary significantly depending on the type of heart valve disease:
- Aortic Stenosis: Often characterized by severe chest pain, fainting, and pronounced fatigue.
- Mitral Regurgitation: Commonly presents with heart palpitations, fatigue, and significant shortness of breath.
- Tricuspid Valve Disease: Typically leads to notable leg swelling and abdominal fluid accumulation.
Understanding the differences in symptoms can guide more targeted and effective treatments. Each type of valve disease impacts the heart differently, and recognizing these variations can be crucial for accurate diagnosis and management.
Awareness and understanding of these symptoms are essential for individuals who may be at risk of heart valve disease. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life and outcomes for those affected by this condition.
Diagnosing Heart Valve Disease
Detecting heart valve disease early is crucial for effective management and treatment. Proper diagnosis begins with a combination of physical examinations and initial assessments, followed by specific diagnostic tests. Here’s a comprehensive look at the process:
Physical Examinations and Initial Assessments
The journey to diagnosing heart valve disease typically starts with a thorough physical examination. During this initial check-up, a healthcare provider will listen for heart murmurs—an unusual sound between heartbeats caused by turbulent blood in or near the heart. Symptoms such as shortness of breath, swelling of the feet or ankles, and fatigue are also key indicators that might prompt further investigation.
Key Diagnostic Tests
- Echocardiogram: This is the most important test for diagnosing heart valve disease. It uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart’s structure and function, allowing doctors to assess the motion of the heart valves and the flow of blood through the heart.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and helps in identifying any irregular rhythms, which can indicate the presence of heart valve issues.
- Chest X-ray: An X-ray can show the size and shape of the heart, and it can indicate whether there is enlargement of the heart due to valve disease. It can also reveal any issues in the lungs that might be related to heart problems.
- Cardiac MRI: For more detailed images of the heart’s structure and function, a cardiac MRI can be used, providing a comprehensive view that can help in intricate cases.
- Stress Tests: These tests monitor the heart’s activity during physical exertion, showing how well the heart performs when it is working hard.
Importance of Timely Diagnosis
Timely diagnosis of heart valve disease is essential. Early detection allows for a broader range of treatment options, potentially less invasive, and can significantly improve the prognosis. Delay in diagnosis can lead to worsening of the condition, complicating treatment and potentially leading to more severe health issues like heart failure or sudden cardiac death.
However, understanding and recognizing the signs and symptoms of heart valve disease, as well as undergoing regular medical check-ups, especially if you are at risk, are key to catching the disease early and managing it effectively.
Treatment Options for Heart Valve Disease
Managing this condition effectively is crucial for maintaining heart health and preventing complications. Treatment strategies can range from lifestyle adjustments and medications to surgical interventions, depending on the severity and specific type of valve disease. Here’s a closer look at these approaches:
Lifestyle Adjustments and Medication
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate exercise helps to strengthen the heart and improve circulation.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a heart-healthy diet that’s low in sodium, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage body weight and reduce strain on the heart.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation is vital as smoking can exacerbate heart valve problems and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Reducing alcohol consumption can decrease the overall workload on the heart.
- Regular Check-ups: Frequent monitoring by a healthcare provider can help manage any changes in the condition promptly.
Medication:
- Blood Pressure Medications: Drugs such as beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors can help manage blood pressure and reduce heart strain.
- Diuretics: Also known as water pills, these help remove excess fluid from the body, reducing the burden on the heart.
- Anticoagulants: These are prescribed to prevent blood clots, which is crucial in managing some types of valve disorders.
- Antibiotics: Some patients may require antibiotics before dental or surgical procedures to prevent infections that could affect damaged valves.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where medication and lifestyle changes are insufficient to manage heart valve disease, surgical options may be necessary:
- Valve Repair: This procedure involves the surgeon repairing the patient’s own valve to enable it to function adequately.
- Valve Replacement: Involves replacing the damaged valve with an artificial one. This can be done using mechanical valves or biological prostheses.
- Balloon Valvuloplasty: This minimally invasive procedure uses a balloon catheter to widen a stiff valve.
- Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR): This newer, less invasive method allows the placement of a new valve over the existing aortic valve through a catheter inserted in the leg or chest.
Ongoing Management and Follow-Up Care
Ongoing management is essential to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and make adjustments as necessary. This includes:
- Regular Monitoring: Routine check-ups and diagnostic tests, such as echocardiograms, to assess heart function and ensure that the treatment remains effective.
- Medication Adjustments: Periodic evaluation of medication efficacy and side effects to optimize dosing and combinations.
- Lifestyle Reevaluation: Continuous assessment of lifestyle and dietary habits to ensure ongoing heart health.
- Patient Education: Ensuring that patients understand their condition and the importance of compliance with treatment and follow-up schedules.
Effective management of heart valve disease requires a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual’s needs. It’s essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Living with Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve disease can significantly impact an individual’s life, necessitating various lifestyle adjustments and daily management strategies. By understanding the necessary modifications and support available, individuals can effectively manage their condition, potentially enhancing both life expectancy and quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications and Daily Management
Living with heart valve disease often requires significant changes to one’s daily routine. Emphasizing heart-healthy habits is crucial:
- Diet and Nutrition: Adopting a balanced diet low in sodium and rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage blood pressure and reduce heart strain.
- Regular Physical Activity: Depending on the severity of the condition and the advice of healthcare professionals, regular gentle to moderate exercise, such as walking or swimming, can improve cardiovascular health without overexerting the heart.
- Medication Adherence: Taking all prescribed medications on schedule is vital for controlling the symptoms of heart valve disease and preventing complications.
- Regular Check-ups: Frequent visits to a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring heart health and making timely adjustments to treatment plans.
The Impact on Life Expectancy and Quality of Life
Heart valve disease can affect life expectancy and quality of life, depending on the disease’s severity and the effectiveness of management strategies. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. However, untreated or advanced heart valve disease may lead to serious complications, including heart failure and life-threatening arrhythmias, which can diminish both lifespan and quality of life.
Support Systems and Resources
Navigating the challenges of heart valve disease is not something to do alone. A robust support system and access to reliable resources can make a substantial difference:
- Healthcare Team: Regular interactions with a team of cardiovascular specialists, primary care providers, and possibly mental health professionals can provide comprehensive care and support.
- Support Groups: Many organizations offer support groups for individuals with heart valve disease and their families, providing a platform to share experiences and coping strategies.
- Educational Resources: Reputable sources such as the American Heart Association provide valuable information that can help patients understand their condition and manage it effectively.
By integrating lifestyle modifications, adhering to medical advice, and utilizing available support systems, individuals with heart valve disease can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by their condition.
FAQs about Heart Valve Disease Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of heart valve disease?
Heart valve disease often presents with specific symptoms that may indicate the heart is not functioning properly. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, swollen feet or ankles, and chest pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Can heart valve disease cause dizziness or fainting?
Yes, heart valve disease can lead to dizziness or fainting. These symptoms occur due to inadequate blood flow to the brain, resulting from the heart’s inability to pump blood effectively. Such episodes warrant immediate medical attention.
How does heart valve disease affect daily activities?
Heart valve disease can significantly impact daily activities. Symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath may make it difficult to perform routine tasks, exercise, or engage in physical activities. Adjusting your lifestyle and treatment may help manage these symptoms.
Are the symptoms of heart valve disease constant?
The symptoms of heart valve disease can vary; they may be constant or intermittent. Some individuals might experience symptoms only during physical exertion, while others could notice them even at rest. Monitoring symptoms and their patterns is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
When should someone seek medical attention for heart valve disease symptoms?
Immediate medical attention should be sought if you experience severe chest pain, sudden dizziness, fainting, or a rapid escalation in any other symptoms. Regular check-ups are also advisable if you are diagnosed with or suspect you have heart valve disease.
Conclusion:
In summary, recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of heart valve disease is crucial for early detection and effective management. Common signs of this condition include shortness of breath, fatigue, swollen ankles or feet, and palpitations, which should not be ignored. Heart valve disease can result from age-related changes, infections, or congenital heart defects, emphasizing the need for awareness regardless of your age or health status.
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing these symptoms or who has risk factors for heart valve disease to consult with a healthcare professional. Early medical intervention can significantly improve the quality of life and outcomes for those affected by this potentially serious condition. Prioritizing your heart health and seeking timely advice from experts are your best defenses against the complications associated with heart valve disease. Remember, taking early action can lead to better health outcomes.
References
For those seeking more detailed information on heart valve disease symptoms and seeking to validate the facts provided, the following reputable sources are recommended:
- American Heart Association (AHA) – This organization provides comprehensive resources on various heart conditions, including heart valve disease. You can explore their articles, research papers, and patient resources for a deeper understanding of symptoms and treatment options. Visit their website at American Heart Association.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its detailed and medically reviewed health content, the Mayo Clinic offers a section specifically on heart valve disease. This resource includes symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment. Learn more by visiting Mayo Clinic – Heart Valve Disease.
- MedlinePlus – A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine, MedlinePlus provides trustworthy information on heart valve disease that is easy to understand. This includes an overview of the condition, symptom lists, and diagnostic approaches. Access their resources at MedlinePlus – Heart Valve Disease.
- Cleveland Clinic – A leader in cardiac care, the Cleveland Clinic offers extensive information on heart valve disease symptoms and management. Their resources are based on the latest research and clinical advances. For detailed information, visit Cleveland Clinic – Heart Valve Disease.
These sources are essential for patients, healthcare providers, and anyone interested in learning more about heart valve disease. They offer a range of materials that are both accessible and authoritative, ensuring readers receive the most accurate and up-to-date information.