Heart Valve Disease Treatment: Heart valve disease is a potentially serious condition that affects the flow of blood through the heart.
It involves either damage to or a defect in one of the four heart valves: the mitral, aortic, tricuspid, or pulmonary valves.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of heart valve disease is crucial for managing the condition effectively and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve disease involves the malfunctioning of one or more of the heart’s valves, affecting the blood flow through the heart and potentially leading to serious health issues. In this section, we’ll explore the different types of heart valve diseases, common causes and risk factors, and provide statistics on their prevalence and impact.
Types of Heart Valve Diseases
Heart valve diseases can be classified into several types, each affecting how the valves function:
- Stenosis: The valve opening becomes narrowed, restricting blood flow.
- Regurgitation: The valve does not close properly, causing blood to leak backward.
- Atresia: A valve lacks an opening, preventing proper blood flow from the onset.
- Prolapse: The valve flaps bulge or prolapse back into the upper heart chamber during a heartbeat.
Each type of valve disease can affect any of the four heart valves: the aortic, mitral, pulmonary, and tricuspid valves.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Heart valve diseases can arise from various causes and risk factors:
- Age-related changes: Degenerative changes in the heart valves can occur as a natural part of aging.
- Congenital heart defects: Being born with malformed or missing valves.
- Rheumatic fever: This condition can result from untreated strep throat or scarlet fever and can damage heart valves.
- Infections (endocarditis): Microorganisms that enter the bloodstream and attack the inner linings of the heart valves and chambers.
- Other cardiovascular diseases: Conditions like coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and heart failure can contribute to or exacerbate valve problems.
Understanding these risk factors can help in early diagnosis and treatment, potentially mitigating the effects of the disease.
Statistics on Prevalence and Impact
Heart valve disease affects a significant portion of the population, with the following statistics highlighting its prevalence and impact:
- Approximately 5 million Americans are diagnosed with heart valve disease each year.
- Heart valve diseases are more common in older adults, particularly those aged 65 and older, with the prevalence increasing as the population ages.
- Valve diseases account for around 10-20% of all cardiac surgical procedures in the United States.
- The survival rates and quality of life for patients can significantly decrease if the condition is not timely diagnosed and treated.
These statistics underscore the importance of awareness and regular check-ups, especially for those at increased risk, to manage and potentially prevent the adverse effects of heart valve diseases.
By understanding the types, causes, and impacts of heart valve diseases, individuals and healthcare providers can work together towards better heart health and outcomes.
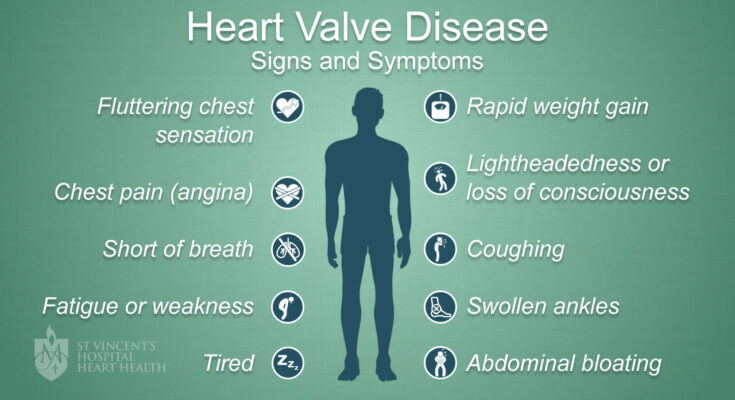
Signs and Symptoms of Heart Valve Disease
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of heart valve disease is crucial for early detection and effective management. Here’s a detailed look at the early indicators, symptoms of progressive valve disease, and how these symptoms relate to the type of valve disease.
Early Signs That Might Indicate Heart Valve Disease
The initial signs of heart valve disease are often subtle and can be easily overlooked. However, being aware of these early indicators can lead to prompt medical consultation and diagnosis. Common early signs include:
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired after performing regular activities that you previously managed without difficulty.
- Shortness of breath: Experiencing breathlessness during routine activities or while lying flat.
- Heart palpitations: Sensing irregular heartbeats, such as skipped beats or a rapid fluttering in your chest.
- Swollen ankles or feet: Fluid retention in the lower extremities can be an early sign of the heart struggling to pump blood efficiently.
Symptoms of Progressive Valve Disease
As heart valve disease progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced and debilitating. These symptoms may include:
- Chest pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, particularly during activity or when you are in a cold environment.
- Fainting or dizziness: Episodes of lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting spells could indicate that the brain is not receiving enough blood.
- Rapid weight gain: An unexplained weight increase due to fluid accumulation, indicating worsening heart function.
- Increasing shortness of breath: An escalation in breathlessness, occurring not only during physical exertion but also at rest.
How Symptoms Relate to the Type of Valve Disease
The symptoms of heart valve disease can vary depending on which valve is affected and whether the valve is stenotic (narrowed) or regurgitant (leaky):
- Mitral valve disease: Often leads to fatigue, palpitations, and shortness of breath because it affects the valve that controls the flow of blood between the left atrium and left ventricle.
- Aortic valve disease: Can cause dizziness, chest pain, and fainting, as it involves the valve managing the blood flow from the heart to the aorta, impacting how oxygen-rich blood is distributed to the body.
- Tricuspid and pulmonary valve diseases: Less common but can lead to fluid retention and swelling in the legs and abdomen, reflecting issues with blood flow from the right side of the heart to the lungs.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical advice promptly for appropriate evaluation and management.
Diagnosing Heart Valve Disease
Below, we explore the primary methods used to diagnose heart valve disease, the significance of physical examinations and patient history, and the latest advancements in diagnostic technologies.
List of Diagnostic Methods
- Echocardiogram: This is the most commonly used test for diagnosing heart valve disease. It uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart, allowing doctors to see the heart beating and the valves functioning.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and helps in identifying irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) which can be indicators of valve problems.
- Chest X-ray: This can show the size and shape of the heart. An enlarged heart might suggest valve disease.
- Cardiac MRI: This imaging technique provides highly detailed images of the heart structures and is used for assessing the severity of valve disease.
- Cardiac Catheterization: This invasive procedure involves inserting a thin tube into a blood vessel leading to the heart to provide detailed and accurate measurements of pressure in the heart and the functionality of the heart valves.
The Role of Physical Examinations and Patient History
Physical examinations and a detailed patient history are foundational in diagnosing heart valve disease. During the physical exam, doctors listen for sounds of heart murmurs which might indicate abnormal blood flow. Other signs that are closely observed include swelling in the legs or abdomen, which can suggest heart failure related to valve disease.
Patient history provides insights into symptoms, such as breathlessness, chest pain, or fainting spells, which are critical for assessing the likelihood of valve disease. A history of rheumatic fever or infections that can affect the heart, like endocarditis, is also significant information that influences diagnosis.
Latest Advances in Diagnostic Technologies
Recent advances in diagnostic technologies have greatly improved the accuracy and efficiency of heart valve disease diagnosis. Innovations include:
- Three-Dimensional Echocardiography (3D Echo): This advanced form of echocardiography provides a more detailed and accurate view of the heart’s valves and chambers, helping in better assessment and treatment planning.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE): Used when clearer images are needed, TEE involves placing an ultrasound probe down the throat into the esophagus, which lies close to the heart. This method produces highly detailed images of the heart valves.
- Cardiac CT Scan: This technique combines X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional views of the heart, offering precise details about the heart’s structure and function.
With continuous advancements in medical technology, the prospects for early detection and improved management of heart valve disease continue to enhance.
Treatment Options for Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve disease is a serious condition that can significantly impact the health and quality of life of those affected. Fortunately, advancements in medical science have provided various effective treatment options. These treatments range from medical management to cutting-edge procedures and technologies. Here’s a comprehensive look at the available treatments for heart valve disease.
Medical Management
Medical management is often the first line of treatment for heart valve disease, particularly in its early stages or when symptoms are mild. This approach typically involves medication that aims to relieve symptoms and prevent further damage. Common medications include:
- Diuretics: Help reduce fluid accumulation in the body, easing the burden on the heart.
- Beta-blockers: Lower blood pressure and decrease heart rate, reducing the heart’s workload.
- Anticoagulants: Help prevent blood clots, which are a risk with some types of valve disease.
Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise, also play a crucial role in managing the condition.
Interventional Procedures
When medication is not enough to manage the symptoms or progression of heart valve disease, interventional procedures may be necessary. These are less invasive than surgery and can offer quicker recovery times. Key procedures include:
- Balloon Valvuloplasty: A balloon is used to widen a stiff valve.
- Transcatheter Valve Replacement (TAVR): A new valve is inserted via a catheter without removing the old, damaged valve.
These procedures are particularly beneficial for patients who are at higher risk from traditional surgery.
Surgical Approaches
In cases where interventional procedures are not viable or sufficient, surgical approaches may be recommended. These surgeries are performed to repair or replace the damaged valve(s) and include:
- Valve Repair: Adjusting the original valve to help it function better.
- Valve Replacement: Removing the damaged valve and replacing it with a mechanical or biological valve.
These surgical options require hospitalization and a longer recovery period but can significantly improve survival rates and quality of life.
Emerging Treatments and Technologies
The field of heart valve disease treatment is continually evolving, with new treatments and technologies being developed. Some of the promising advancements include:
- Biological advancements: Development of more durable and biocompatible valve replacements.
- Minimally invasive techniques: Procedures that reduce recovery time and risks of complications.
- Gene therapy and molecular medicine: Potential future treatments aimed at repairing valve tissue at the molecular level.
These innovations represent the frontier of cardiac care, potentially offering more effective and less invasive treatment options in the future.
By understanding the various treatment options available for heart valve disease, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions tailored to the individual’s needs and medical condition. With ongoing research and technological advances, the outlook for managing and treating heart valve disease continues to improve.
Decision-Making in Treatment of Heart Valve Disease
When it comes to treating heart valve disease, selecting the appropriate treatment strategy is crucial and depends on multiple factors. This guide provides an overview of the decision-making process involved in the treatment of heart valve disease, emphasizing the role of patient-specific factors, comparing surgical options, and underlining the importance of personalized treatment plans.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Treatment
The choice of treatment for heart valve disease is influenced by several key factors:
- Age: Younger patients may have different options compared to older adults due to the durability needed in valve replacement materials and the ability to recover from certain types of surgeries.
- Overall Health: The general health of a patient, including the presence of other medical conditions, impacts the risk associated with different treatment approaches and can guide the choice between more or less invasive procedures.
- Type of Valve Disease: The specific valve affected and the nature of the disease—whether the valve is leaking (regurgitation) or narrowed (stenosis)—often dictate whether valve repair or replacement is advisable and which surgical method should be employed.
Minimally Invasive vs. Traditional Surgical Techniques
The choice between minimally invasive and traditional surgical techniques is a critical component of the treatment strategy for heart valve disease:
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: These procedures typically involve smaller incisions, less pain, and shorter recovery times. Techniques such as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) or robot-assisted surgery allow for the repair or replacement of valves without the need for large chest incisions.
- Traditional Surgical Techniques: Conventional surgery, such as open-heart surgery, may be necessary in complex cases or when minimally invasive approaches are not suitable. This method provides direct access to the heart, which can be crucial for certain types of valve repair or replacement.
Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Creating a personalized treatment plan is essential in managing heart valve disease effectively. Each patient’s unique health profile demands a tailored approach that considers all the aforementioned factors. Personalized plans ensure:
- Optimal Outcomes: By considering individual health needs and circumstances, healthcare providers can maximize the effectiveness of treatment and improve long-term health outcomes.
- Patient Involvement: Engaging patients in their treatment decisions increases their understanding and compliance with the treatment process, leading to better overall management of their condition.
By carefully evaluating all aspects, healthcare providers can offer the most effective and suitable treatment for each individual patient, thereby improving their quality of life and treatment success.
Living with Heart Valve Disease
Living with heart valve disease requires a comprehensive approach to lifestyle adjustments, ongoing monitoring, and accessing support resources. Here’s a breakdown of what patients can expect and how to manage their condition effectively.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Ongoing Management
When diagnosed with heart valve disease, making certain lifestyle adjustments is crucial. These changes can help manage symptoms and improve overall heart health:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet is essential. This includes eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reducing salt intake can also help manage blood pressure levels, which is important for heart valve health.
- Regular Exercise: Depending on the severity of your condition, your doctor may recommend a tailored exercise program. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can be beneficial. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
- Medication Adherence: Taking medications as prescribed can help manage the symptoms and progression of heart valve disease. Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider are necessary to adjust medications as needed.
- Avoiding Certain Activities: Some activities, particularly those that strain the heart, might need to be avoided. Your doctor can provide guidance on which activities are safe for you.
Monitoring and Long-Term Care Considerations
Long-term care for heart valve disease involves regular monitoring and check-ups:
- Routine Check-Ups: Regular visits to a cardiologist are key. These check-ups typically involve echocardiograms to monitor the heart’s condition and how well the valves are functioning.
- Symptom Tracking: Keeping a diary of any symptoms, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, or chest pain, can help your doctor make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Surgical Interventions: For some, surgery might be necessary to repair or replace a damaged valve. Discussing the risks and benefits of surgery with your healthcare provider is important.
Support and Resources for Patients
Navigating heart valve disease is not just about medical treatment; it’s also about having the right support:
- Support Groups: Many organizations offer support groups for people with heart valve disease. These groups provide a platform to share experiences and coping strategies.
- Educational Resources: Learning about your condition is vital. Many health organizations provide detailed information that can help you understand your condition and its implications.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Dealing with a chronic condition can be emotionally taxing. Counseling and therapy can be beneficial in managing mental health alongside physical health.
By making informed lifestyle adjustments, staying on top of monitoring and care, and utilizing available support resources, individuals living with heart valve disease can lead fulfilling lives. Remember, the key to managing this condition is a proactive approach to health and well-being.
Future Outlook and Research in Heart Valve Disease Treatments
Current Trends in Heart Valve Disease Research
Heart valve disease research is constantly evolving, with new methodologies and technologies driving forward our understanding and treatment capabilities. Currently, significant focus is on less invasive surgical techniques, such as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), which allows for valve replacement without traditional open-heart surgery. Additionally, advancements in medical imaging technologies are enhancing diagnostic precision, enabling earlier and more accurate detection of valve issues.
Potential Future Breakthroughs in Therapy and Management
Looking ahead, the future of heart valve disease therapy promises exciting potential breakthroughs. One area of intense research is the development of bioprosthetic heart valves that could potentially grow with the patient, reducing the need for multiple surgeries. Another promising field is regenerative medicine, which aims to repair damaged heart valves using the body’s own cells. This could revolutionize treatment, moving away from mechanical or bioprosthetic replacements towards genuine biological repair.
The Importance of Clinical Trials and Research Participation
The role of clinical trials in advancing heart valve disease treatment cannot be overstated. Clinical trials help ensure that new treatments are safe and effective before they become widely available. Participation in these trials is crucial, as it contributes to medical advancements and offers patients access to cutting-edge therapies that might not otherwise be available. Encouraging participation in clinical trials is essential for the continuous improvement of heart valve disease management and the development of innovative therapies that can save or significantly improve patients’ lives.
This ongoing research and development in heart valve disease treatments not only promises to enhance patient care but also opens up new realms of possibilities for managing this challenging condition, leading to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for patients.
FAQs about Heart Valve Disease Treatment
1. What are the common treatments for heart valve disease?
The treatment for heart valve disease primarily depends on the valve affected and the severity of the condition. Common treatments include medication to manage symptoms, surgical repair of the valve, and valve replacement via surgical or less invasive methods.
2. How do I know if I need surgery for heart valve disease?
Surgery is generally recommended if you are experiencing significant symptoms or if tests show that your heart function is affected. Decisions about surgery are personalized, considering factors like age, overall health, and the specific characteristics of your valve disease.
3. Are there risks associated with heart valve surgery?
Yes, as with any surgery, there are risks involved in heart valve surgery, including infection, bleeding, and reactions to anesthesia. However, the procedures have high success rates, and risks are minimized with advanced surgical techniques and postoperative care.
4. What is the recovery time after heart valve surgery?
Recovery varies depending on the type of surgery performed and your overall health. Generally, patients may spend a few days in the hospital and can expect a full recovery period of several weeks to a few months. Your medical team will provide a tailored recovery plan.
5. Can heart valve disease be treated without surgery?
Yes, some patients with mild symptoms or those who are not candidates for surgery can manage the condition with medication. Monitoring the condition closely with regular check-ups is crucial to adjust treatment as needed.
6. How often should I follow up with my doctor after treatment?
Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor your heart health, especially after treatment for heart valve disease. The frequency of these visits will depend on the specifics of your condition and treatment, typically ranging from every few months to annually.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing heart valve disease is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. As we have explored, recognizing the signs and symptoms early plays a vital role in effective diagnosis and treatment. Whether it’s unusual fatigue, shortness of breath, or irregular heartbeats, these indicators should not be ignored.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any symptoms associated with heart valve disease, it’s imperative to seek professional medical evaluation. Timely intervention can lead to better management of the condition and significantly improve quality of life. Remember, taking prompt action could be life-saving. Don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure your heart stays healthy.
References
For those seeking additional information or wishing to verify the details discussed in our article on heart valve disease treatment, we have compiled a list of reputable sources. These references are invaluable for patients, healthcare professionals, and anyone interested in learning more about the diagnosis, treatment, and management of heart valve disease.
- American Heart Association – Provides comprehensive resources on heart valve disease, including treatment options and patient care advice. Visit their page on heart valve disease here.
- Mayo Clinic – Offers detailed overviews of the types of heart valve diseases, symptoms, treatments, and more. Access their heart valve disease section here.
- Cleveland Clinic – Known for its expertise in heart health, they provide insights into innovative treatment options and recovery processes for heart valve disease. Learn more here.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine – Features educational articles and treatment guides on heart valve disease, including the latest research developments. Check out their resources here.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) – Offers extensive educational material on heart valve disease, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Explore their resources here.
These resources have been chosen for their authority and depth of information on heart valve disease. They provide readers with reliable data, treatment updates, and health management strategies, making them essential tools for a deeper understanding of this condition.