Heart Arrhythmia Symptoms: Heart arrhythmias, also known as cardiac dysrhythmias, represent a group of conditions that cause the heart to beat irregularly, too fast, or too slow.
Millions of individuals worldwide experience various types of arrhythmias, which can range from benign to life-threatening.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of heart arrhythmias is crucial for timely diagnosis and management.
What is Heart Arrhythmia?
Heart arrhythmia, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia, refers to any irregularity in the heart’s rhythm. It occurs when electrical impulses, which coordinate your heartbeats, don’t work properly, causing the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or erratically. When the heart doesn’t beat normally, it can affect blood flow to the body and organs, potentially leading to a variety of health issues. Understanding heart arrhythmia is crucial because it can significantly impact overall health and quality of life.
Types of Heart Arrhythmias
There are several types of heart arrhythmias, each with unique characteristics and potential implications for health. The main types include:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): This is the most common type, characterized by a rapid and irregular beating of the atrial chambers of the heart. It increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications.
- Tachycardia: Refers to a heart rate that’s too fast, generally defined as over 100 beats per minute.
- Bradycardia: Refers to a heart rate that’s too slow, typically fewer than 60 beats per minute.
- Ventricular Fibrillation (VF): An emergency situation where the ventricles twitch and are unable to contract effectively to pump blood, leading to cardiac arrest.
- Premature Contractions: Occasional early heartbeats, which are generally harmless and require no treatment unless they occur frequently and cause significant symptoms.
Statistics on Prevalence and Impact
Heart arrhythmias affect millions of people worldwide and are a major contributor to morbidity and mortality. According to recent studies:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) affects up to 6 million Americans, with expectations that this number will rise as the population ages.
- Sudden cardiac arrest, primarily caused by ventricular fibrillation, accounts for about 300,000 deaths each year in the United States alone.
- Heart arrhythmias are a leading cause of hospital admissions and are significantly associated with other cardiovascular diseases.
Awareness and early diagnosis are key to managing heart arrhythmias effectively, reducing the risk of complications, and improving outcomes for patients.
Symptoms of Heart Arrhythmia
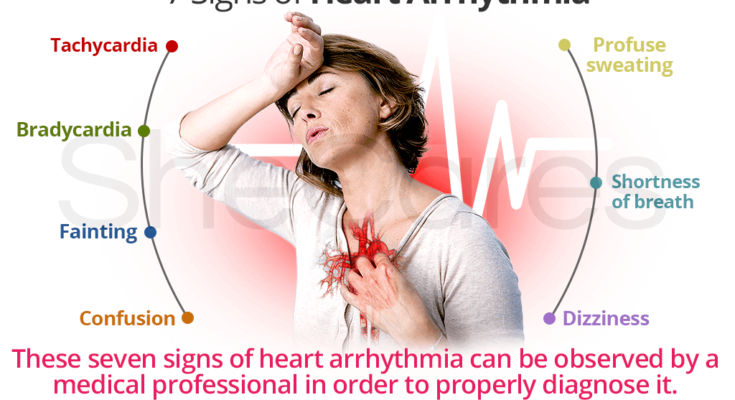
Recognizing the symptoms of heart arrhythmia is crucial for early detection and management. Here we explore the common symptoms, how they vary by type, and when it is essential to seek medical attention.
Common Symptoms of Heart Arrhythmia
The symptoms of heart arrhythmias can often be subtle or, in some cases, completely absent. However, when symptoms are present, they may include:
- Palpitations: A feeling of skipped heartbeats, fluttering, or a racing heart.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: You may feel momentarily dizzy or faint.
- Breathlessness: Experiencing shortness of breath during routine activities can be a sign of arrhythmia.
- Chest Pain: This can occur, especially if the arrhythmia causes the heart to work harder or reduces its efficiency.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired can be related to less effective heart pumping due to an irregular heartbeat.
- Syncope: Some individuals may experience fainting spells due to a drop in blood flow caused by the arrhythmia.
These symptoms can disrupt your daily life and might signal underlying heart issues that require medical evaluation.
How Symptoms Vary by Type of Arrhythmia
The symptoms of arrhythmia can vary significantly depending on the type of arrhythmia and its severity. For instance:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Often characterized by rapid and irregular heartbeats, symptoms can include palpitations, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
- Bradycardia (Slow Heartbeat): Symptoms might include severe fatigue, dizziness, and fainting due to the heart’s inability to pump enough blood.
- Tachycardia (Fast Heartbeat): Besides palpitations, symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, and in severe cases, collapse.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: This severe form of arrhythmia can lead to sudden collapse and is a medical emergency.
Understanding the specific symptoms associated with different types of arrhythmias can aid in recognizing potential heart issues early on.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is vital to seek medical attention if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, particularly if they are new, severe, or suddenly different. Some critical points to consider include:
- Emergency Situations: If you experience chest pain, fainting, or severe breathlessness, seek emergency medical care immediately.
- New or Worsening Symptoms: Schedule a visit with your healthcare provider if you notice new symptoms or if existing symptoms worsen.
- Regular Monitoring: If diagnosed with an arrhythmia, regular monitoring and follow-ups with your cardiologist are essential to manage your condition effectively.
Prompt attention to the symptoms of heart arrhythmia and professional medical evaluation are key to managing the condition successfully and maintaining a healthy life.
Causes of Heart Arrhythmia
By understanding the general causes, specific triggers, and the impact of genetic and environmental influences, individuals can better manage or mitigate their risk of developing this condition.
General Causes and Risk Factors
Heart arrhythmias can stem from several key risk factors and general causes:
- Heart Disease: Pre-existing heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, heart failure, and previous heart attacks are significant risk factors for arrhythmia.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Electrolytes such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium play a critical role in heart function. Imbalances can affect the heart’s electrical impulses, leading to arrhythmia.
- Age: Aging naturally changes heart tissue, which can increase the risk of arrhythmias.
- High Blood Pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can lead to changes in heart structure, predisposing individuals to arrhythmias.
- Thyroid Problems: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause heart rhythm disturbances.
- Diabetes: Long-standing diabetes, especially if poorly controlled, can increase the risk of arrhythmias.
Specific Triggers for Heart Arrhythmia
Certain conditions and activities can trigger an arrhythmia in people who are at risk:
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can lead to increases in adrenaline in the body, which can trigger an arrhythmia.
- Alcohol and Drug Use: Excessive alcohol consumption and the use of certain drugs like cocaine or amphetamines can disrupt heart rhythm.
- Caffeine and Nicotine: High intake of caffeine or nicotine can stimulate heart rate irregularities in some individuals.
- Certain Medications: Some over-the-counter cough and cold medications can precipitate arrhythmias, especially in people with underlying heart conditions.
- Sleep Apnea: This sleep disorder can increase the risk of arrhythmias due to intermittent oxygen deprivation during sleep.
Genetic and Environmental Influences
Genetic predispositions can significantly influence the risk of developing heart arrhythmias. People with a family history of arrhythmia or other heart conditions are at a higher risk. Genetic testing can sometimes identify specific markers associated with an increased risk of certain types of arrhythmias.
Environmental factors also play a crucial role:
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, lack of physical activity, and poor diet can increase the risk of developing heart conditions that may lead to arrhythmias.
- Exposure to Toxins: Prolonged exposure to certain environmental toxins, like lead or other heavy metals, can affect heart health.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Studies have shown that socioeconomic status can impact heart health, influencing access to healthcare and lifestyle choices.
Awareness and understanding are key components in the prevention and management of this condition, empowering individuals to take proactive steps toward maintaining heart health.
Diagnosing Heart Arrhythmia
Understanding the diagnostic procedures for heart arrhythmia is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. This article explores the common diagnostic tests and procedures used, the importance of medical history and physical examination, and the recent advances in diagnostic technology.
Common Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
The diagnosis of heart arrhythmia begins with a range of tests designed to evaluate heart rhythm and identify irregularities. The most common diagnostic tools include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This is the primary test for diagnosing arrhythmia. It records the electrical activity of the heart and helps detect abnormalities in the heart’s rhythm and structure.
- Holter Monitor: A portable device worn for 24-48 hours to record the heart’s electrical activity continuously, capturing arrhythmias that might not appear during a standard ECG.
- Event Recorder: Similar to a Holter monitor, this device is used for longer periods (up to a few weeks) and is activated by the patient when they experience symptoms of an arrhythmia.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides images of the heart’s chambers and valves, assessing the heart’s structure and function.
- Stress Test: Sometimes, arrhythmias can only be triggered or worsened by exercise. During a stress test, the heart’s activity is monitored while the patient engages in physical activity.
These tests are crucial for accurately diagnosing the type of arrhythmia and guiding the appropriate treatment plan.
Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination are foundational in diagnosing heart arrhythmia. During the consultation, doctors will inquire about symptoms such as heart palpitations, shortness of breath, or chest pain. They will also review the patient’s medical history, including any history of heart disease, medication use, and family history of cardiovascular problems. Physical examination can reveal signs like irregular pulse, heart murmurs, or signs of heart failure which are vital clues in diagnosing arrhythmia.
Recent Advances in Diagnostic Technology
The field of cardiology has seen significant technological advancements that enhance the diagnosis of heart arrhythmias. Innovations include:
- Implantable Loop Recorders: These small devices are implanted under the skin to continuously monitor heart rhythms for up to three years, providing long-term data that can be essential for diagnosing intermittent arrhythmias.
- 3D Mapping Systems: Advanced imaging technology that creates a three-dimensional model of the heart’s electrical activity, allowing for more precise identification of the areas causing arrhythmia.
- Wearable Technology: Devices like smartwatches now have capabilities to monitor heart rate and rhythm, which can detect irregularities and prompt further testing.
These advancements provide more detailed insights into heart function, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment strategies.
Diagnosing heart arrhythmia involves a combination of detailed medical history, physical examination, standard tests, and leveraging recent technological advances. With the right diagnostic approach, patients can receive timely and effective treatment to manage their condition.
Impact of Heart Arrhythmia on Daily Life
Heart arrhythmia, a condition characterized by irregular heartbeats, can significantly affect daily life and overall well-being. Understanding its impacts and how to manage them is crucial for those diagnosed with this condition.
How Arrhythmia Can Affect Lifestyle and Activities
Arrhythmia can dramatically alter an individual’s lifestyle and the ability to perform everyday activities. The unpredictability of heart palpitations, dizziness, and fatigue associated with arrhythmia can lead to a reduction in physical activity. For instance, activities that require sustained energy or are physically demanding may become challenging, leading some individuals to avoid activities like exercise, hiking, or even grocery shopping.
Moreover, arrhythmias can also influence driving, working, and participation in social events, creating a feeling of dependency or isolation. The fear of experiencing an arrhythmia episode in public can cause significant anxiety, impacting social interactions and the willingness to engage in new experiences.
Managing Heart Arrhythmia at Home
Managing heart arrhythmia effectively involves both lifestyle adjustments and medical strategies. At home, patients are often advised to monitor their heart rate regularly, either through manual pulse checks or wearable technology that tracks heart rhythm. Lifestyle changes such as reducing caffeine intake, quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet also play a critical role in managing arrhythmia symptoms.
Medical management might include medications to control heart rate or rhythm, and in some cases, procedures like catheter ablation or the installation of a pacemaker might be necessary. It’s essential for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to tailor a management plan that suits their specific needs.
Psychological Impacts and Support Systems
The psychological impact of living with heart arrhythmia can be profound. Many individuals experience anxiety and depression due to the uncertainty and limitations imposed by their condition. Fear of a cardiac event can lead to increased stress, which paradoxically can exacerbate arrhythmia symptoms.
Building a strong support system is vital. Support can come from various sources, including family, friends, support groups, and mental health professionals. Engaging with others who understand the challenges of living with heart arrhythmia can provide emotional comfort and practical advice, enhancing coping strategies.
In addition to personal support, professional counseling or therapy can help individuals manage the psychological effects of arrhythmia. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), in particular, has been shown to be effective in reducing health-related anxiety, improving patients’ quality of life, and helping them regain a sense of control over their condition.
Treatment Options for Heart Arrhythmia
Fortunately, there are various treatment options available that cater to the specific needs and conditions of each patient. Below, we explore the list of treatment methodologies, including medications, surgical options, lifestyle changes, and home remedies, to manage and treat heart arrhythmias.
List of Treatment Methodologies
Medications
Medications are often the first line of treatment for heart arrhythmia. The type of medication prescribed depends on the type of arrhythmia, the presence of other health conditions, and the overall health of the patient. Common medications include:
- Beta-blockers: These drugs slow the heart rate and reduce blood pressure.
- Calcium channel blockers: Similar to beta-blockers, these medications also slow the heart rate and decrease blood pressure, but through a different pathway.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs: These medications help restore normal heart rhythm and maintain it.
- Anticoagulants: Often referred to as blood thinners, these drugs help prevent blood clots, which are a common complication of certain types of arrhythmias.
Surgical Options
For some patients, medications alone may not be effective. In such cases, surgical interventions may be necessary:
- Catheter ablation: This procedure involves threading a thin tube through the blood vessels to the heart to correct structural problems that cause arrhythmia.
- Pacemaker: A small device implanted under the skin of the chest or abdomen to help control abnormal heart rhythms.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD): Similar to a pacemaker, this device monitors heart rhythms and delivers electric shocks when needed to restore a normal heartbeat.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, making lifestyle changes can significantly impact the management of heart arrhythmia. These include:
- Diet: Eating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can improve heart health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help maintain heart health and prevent arrhythmias.
- Stress management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can reduce stress, which is often a trigger for arrhythmia.
- Limiting stimulants: Reducing or avoiding caffeine and nicotine can decrease episodes of arrhythmia in some individuals.
It’s important for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific conditions. Managing heart arrhythmia effectively not only improves quality of life but also reduces the risk of complications such as stroke and heart failure.
Prevention and Management of Heart Arrhythmia
Managing and preventing heart arrhythmia involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medical strategies, and regular health assessments. By understanding and applying these methods, individuals can significantly reduce their risks and manage their conditions effectively.
Preventative Measures for Reducing Risk
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain heart health and prevent arrhythmias. Limiting intake of trans fats, saturated fats, and processed foods is crucial.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate physical activity for at least 150 minutes per week can strengthen the heart and improve overall cardiovascular health. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen, especially for those with existing heart conditions.
- Avoiding Stimulants: Substances like caffeine, tobacco, and alcohol can trigger arrhythmia episodes. Reducing or avoiding these stimulants can lower the risk of developing arrhythmias.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can adversely affect heart health. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and regular exercise can be effective in managing stress.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight can increase the risk of developing heart arrhythmia. Weight management through diet and exercise is a preventive measure that can also improve overall cardiovascular health.
Long-term Management Strategies
- Medication: Various medications can be prescribed to control the heart rate and rhythm. It’s essential for patients to take these medications exactly as prescribed and discuss any side effects with their doctor.
- Device Implantation: In some cases, a doctor might recommend implanting a device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). These devices help manage heart rhythm and prevent complications associated with arrhythmia.
- Catheter Ablation: This is a procedure used to treat some types of arrhythmia. It involves threading a thin tube through blood vessels to the heart to correct structural problems that cause an arrhythmia.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Continuing to maintain a healthy lifestyle is vital for long-term management, including diet, exercise, and avoiding triggers like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are critical for monitoring heart health and managing arrhythmia. These appointments allow doctors to assess the effectiveness of treatments and make necessary adjustments. Early detection of potential issues through regular monitoring can lead to better outcomes and prevent severe complications. Diagnostic tests like ECGs (electrocardiograms), stress tests, and Holter monitoring are often used to track the heart’s activity and guide treatment decisions.
By incorporating these preventive and management strategies, individuals can live healthier lives with reduced risk of heart arrhythmia complications. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatments tailored to individual health needs.
FAQ Section: Understanding Heart Arrhythmia
1. What is heart arrhythmia?
Heart arrhythmia refers to any irregularity in the heart’s rhythm. It occurs when electrical impulses, which coordinate your heartbeats, don’t work properly, causing your heart to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly. This can feel like a fluttering or racing heart and can be benign or a sign of a more serious heart condition.
2. What are the symptoms of heart arrhythmia?
Symptoms of heart arrhythmia can vary widely and may include palpitations, a feeling of the heart skipping beats, fatigue, dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting spells. Some arrhythmias may be asymptomatic and only discovered during a physical examination or through an ECG.
3. What causes heart arrhythmia?
Heart arrhythmias can be caused by various factors, including heart disease, electrolyte imbalances in the blood, changes in heart muscle, injury from a heart attack, or the healing process after heart surgery. Other risk factors may include high blood pressure, smoking, excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption, drug abuse, and stress.
4. How is heart arrhythmia diagnosed?
Heart arrhythmias are typically diagnosed using an electrocardiogram (ECG), which records the electrical activity of the heart. Other diagnostic tools might include Holter monitors, event monitors, echocardiograms, and stress tests to assess the heart’s rhythm and function over time.
5. What are the treatment options for heart arrhythmia?
Treatment for heart arrhythmia can vary depending on the type and severity of the arrhythmia. Options include medications, lifestyle changes, invasive therapies like catheter ablation, a procedure that carefully destroys tissue in the heart that may be causing irregular beats, and the use of pacemakers or defibrillators to help manage heart rhythm.
6. Can heart arrhythmia be prevented?
While not all types of heart arrhythmia can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by leading a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding excessive intake of caffeine and alcohol, not smoking, and managing stress.
7. When should I see a doctor for heart arrhythmia?
You should consult a doctor if you experience symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, or fainting. Even if the symptoms seem minor, it’s important to get checked, as some types of arrhythmia can lead to more serious health issues, including stroke and sudden cardiac arrest.
Conclusion
In summary, heart arrhythmias are irregularities in the heart’s rhythm that can manifest through a variety of symptoms, such as palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, or even fainting spells. These symptoms arise due to various causes including genetic predispositions, lifestyle factors like caffeine and alcohol consumption, and underlying medical conditions such as coronary artery disease or electrolyte imbalances. Understanding these symptoms and causes is crucial for early detection and management of heart arrhythmias.
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They can offer a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific condition. Remember, addressing heart arrhythmia promptly can significantly enhance your quality of life and prevent more serious health complications. Always prioritize your health and seek professional advice when it comes to matters of the heart.
References
For further reading and to validate the information discussed regarding the symptoms of heart arrhythmias, the following reputable sources are recommended. These links provide deeper insights and additional data that can help readers understand the complexities of heart arrhythmias and their manifestations.
- American Heart Association (AHA) – The AHA offers a comprehensive guide on the symptoms, causes, and treatments of heart arrhythmias. Visit the American Heart Association’s Heart Arrhythmia Guide.
- Mayo Clinic – Renowned for its expertise in cardiac health, the Mayo Clinic provides detailed information on various types of arrhythmias, diagnostic procedures, and management strategies. Explore Mayo Clinic’s Heart Arrhythmia Resources.
- WebMD – WebMD offers easily digestible content on heart arrhythmia symptoms, risk factors, and preventative measures, making it accessible for non-medical readers. Read more on WebMD about Heart Arrhythmias.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – For those seeking in-depth medical research and studies, the NIH provides access to a wealth of scientific papers and articles on heart arrhythmia. Access NIH resources on Heart Arrhythmia.
- Harvard Medical School – Get expert advice and updates on the latest research in heart health from one of the leading medical schools in the world. Learn from Harvard Medical School’s latest heart health research.
These sources are highly reputable in the medical field and provide reliable information that can enhance your understanding of heart arrhythmias.