Heart Arrhythmia Treatment: Heart arrhythmia, commonly known as irregular heartbeat, presents a complex challenge in both diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the nuances of this condition is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
Understanding Heart Arrhythmias
Heart arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats, are conditions where the heart beats too quickly, too slowly, or with an irregular rhythm. These disruptions can range from benign to life-threatening and often require medical attention to manage effectively.
Common Types of Arrhythmias
There are several types of heart arrhythmias, each with unique characteristics:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): This is the most common type of serious arrhythmia. It involves a rapid and irregular beating of the atrial chambers of the heart, which can lead to blood clots, stroke, and heart failure.
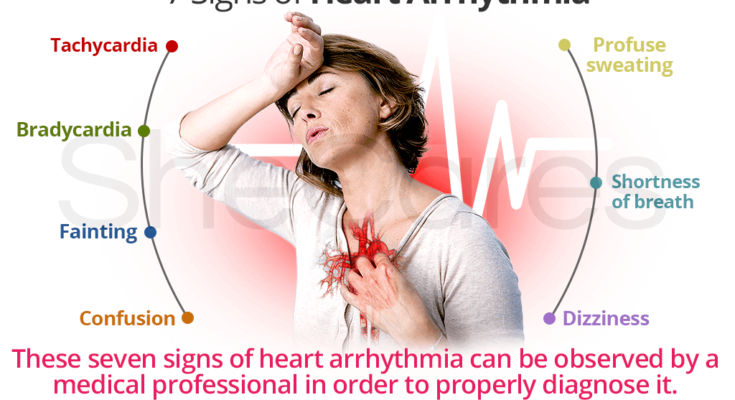
- Bradycardia: This arrhythmia is characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate, typically under 60 beats per minute. While it may be normal in athletes, it can also indicate problems with the heart’s electrical system.
- Tachycardia: Opposite to bradycardia, tachycardia refers to an unusually fast heart rate, generally over 100 beats per minute at rest. It includes several subtypes such as ventricular tachycardia and supraventricular tachycardia.
- Ventricular Fibrillation (VF): A severe form of arrhythmia, VF occurs when the heart’s lower chambers quiver ineffectively instead of pumping necessary blood to the body. It is an immediate medical emergency.
- Premature Contractions: Often perceived as a skipped heartbeat, these are extra beats that disrupt the regular heart rhythm. They can occur in the atria or the ventricles.
Causes and Risk Factors for Developing Heart Arrhythmias
Heart arrhythmias can be caused by various factors, some within control and others not. Common causes and risk factors include:
- Age: The risk of arrhythmias increases with age due to wear and tear on the heart and its electrical system.
- Heart Disease: Existing heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, heart failure, and previous heart attacks significantly increase the risk of arrhythmias.
- High Blood Pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can lead to changes in the heart that make arrhythmias more likely.
- Thyroid Problems: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause heart rhythm disturbances.
- Substance Use: Excessive use of alcohol or caffeine, smoking, and use of certain drugs like amphetamines or cocaine can trigger arrhythmias.
- Stress and Sleep Apnea: High stress levels and disorders like sleep apnea disrupt normal sleep and can affect heart rhythm.
- Genetics: Some types of arrhythmias are hereditary, making genetics a potential risk factor.
However, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing arrhythmias effectively and can help prevent more severe heart-related complications.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Heart Arrhythmias
Heart arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats, can manifest through various symptoms that may signal the need for medical attention. Understanding these symptoms and recognizing when to seek advice can be crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition.
Typical Symptoms Associated with Heart Arrhythmias
The symptoms of heart arrhythmias can vary widely, but some common ones include:
- Palpitations: These are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, or irregular heartbeat.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: You may feel faint or like you are about to pass out.
- Shortness of Breath: Experiencing difficulty breathing or catching your breath can often accompany arrhythmias.
- Chest Pain: While not always present, chest pain can occur and should always be taken seriously.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired can be a sign of an arrhythmia, as the heart may not be pumping efficiently.
Identifying these symptoms early can help in diagnosing the condition before it leads to more severe health issues.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, especially if they are new, unexpected, or seem to be getting worse. This is particularly vital if you have a history of heart disease or other risk factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or a family history of cardiac problems. Immediate medical attention should be sought if symptoms are severe or accompanied by:
- Fainting: If you experience a loss of consciousness.
- Severe Chest Pain: Indicates a possible heart attack.
- Sudden Weakness or Paralysis: Particularly if this affects one side of the body, indicating a possible stroke.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures for Heart Arrhythmia
Early detection of heart arrhythmias can be achieved through a variety of diagnostic tests and procedures. Commonly used methods include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This is the primary test for diagnosing an arrhythmia. It records the electrical activity of the heart and helps identify irregularities in the heart’s rhythm.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG device worn for a day or more to record the heart’s activity as you go about your daily routine.
- Event Monitor: Similar to a Holter monitor, this device is used for a longer period, typically a few weeks, and you activate it when you experience symptoms of an arrhythmia.
- Echocardiogram: This test uses ultrasound waves to create pictures of the heart’s chambers, valves, walls, and the blood vessels attached to the heart, providing detailed information about the heart’s structure and function.
- Stress Test: Sometimes, arrhythmias can only be triggered or worsened by exercise. During a stress test, you’ll be asked to exercise while being monitored with an ECG.
- Electrophysiology Study (EPS): This test involves guiding thin electrical wires into the heart through a vein in the groin to measure the electrical activity and to map the spread of electrical impulses through the heart.
However, understanding these tests and when they might be necessary helps you and your healthcare provider better manage potential arrhythmias. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly reduce the risks of complications, improving overall heart health.
Treatment Options for Heart Arrhythmia
Managing heart arrhythmia effectively is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart rhythm and preventing potential complications. Here, we explore various treatment options aimed at achieving specific goals, alongside both pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical approaches.
Goals of Arrhythmia Treatment
The treatment of heart arrhythmia focuses on several key objectives:
- Restoring Normal Heart Rhythm: The primary goal is to return the heart’s rhythm to normalcy.
- Controlling Heart Rate: Managing the heart rate helps to alleviate symptoms and prevent further cardiac issues.
- Preventing Blood Clots: This reduces the risk of stroke, which is elevated in some types of arrhythmias.
- Reducing Risk of Complications: Treatment aims to minimize the long-term risks associated with arrhythmia, such as heart failure and other heart-related problems.
- Improving Quality of Life: Alleviating symptoms to enhance day-to-day activities and overall wellbeing.
Medications Commonly Used
A variety of medications are used to treat arrhythmias, each serving different functions based on the specific type and severity of the arrhythmia:
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Such as amiodarone, flecainide, and propafenone, these medications help in maintaining a normal heart rhythm.
- Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): Drugs like warfarin and newer agents (e.g., dabigatran, rivaroxaban) prevent blood clot formation, crucial in preventing stroke in atrial fibrillation patients.
- Beta-blockers: Like metoprolol and atenolol, these are used to slow the heart rate and reduce the burden on the heart.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Medications such as diltiazem and verapamil help control the heart rate, particularly in patients with supraventricular tachycardia.
- Digitalis Preparations: These increase the force of the heart’s contractions and can control heart rate in conditions such as atrial fibrillation.
Non-Pharmaceutical Treatments
For some patients, medication alone isn’t sufficient to manage arrhythmia effectively. Non-pharmaceutical treatments include:
- Cardiac Ablation: A procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to destroy small areas of heart tissue that cause abnormal electrical signals.
- Pacemaker Installation: A device implanted in the chest to help control abnormal heart rhythms.
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD): Similar to a pacemaker, this device monitors heart rhythms and delivers electric shocks when necessary to restore normal rhythm.
- Lifestyle Changes: Modifying diet, increasing physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol can significantly impact heart rhythm management.
Consulting with a cardiologist is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the specific characteristics of the arrhythmia and the patient’s overall health.
Living with Heart Arrhythmia
Living with heart arrhythmia can present unique challenges, but with effective management strategies and regular medical oversight, individuals can lead full and active lives. This section explores daily life with arrhythmia, emphasizes the importance of regular check-ups, and shares patient stories to illustrate successful management and treatment.
Daily Life and Management Strategies for Individuals with Arrhythmia
Managing heart arrhythmia on a daily basis involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medication adherence, and continuous monitoring. Individuals diagnosed with arrhythmia need to be mindful of their daily activities and how they might impact their heart rhythm. Here are key strategies to help manage the condition:
- Medication Management: Adhering to prescribed medication schedules is crucial. It’s important for patients to understand their medications, including when and how to take them, and the potential side effects.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Incorporating heart-healthy habits can significantly impact the management of arrhythmia. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity tailored to one’s abilities and medical advice, avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol, and quitting smoking.
- Stress Reduction: Stress can trigger or exacerbate arrhythmias, so employing stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
- Regular Monitoring: Patients may be advised to use home monitoring devices to keep track of their heart rate. These devices can help detect irregularities early, allowing for prompt medical intervention.
Importance of Regular Check-Ups and Monitoring
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are vital for anyone living with heart arrhythmia. These appointments allow doctors to monitor the condition closely and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. During check-ups, healthcare providers might perform various tests such as EKGs (electrocardiograms), stress tests, and blood tests to assess the heart’s condition and the effectiveness of the current treatment regime.
The benefits of consistent medical monitoring include:
- Early Detection of Changes: Regular assessments can help identify changes in heart rhythm or health before they become more serious.
- Tailored Treatment Adjustments: As the condition evolves, treatments might need to be adjusted. Regular interaction with healthcare providers ensures that treatments remain effective and appropriate.
- Preventative Care: Proactive management can prevent complications associated with arrhythmia, such as stroke or heart failure.
Patient Stories and Case Studies
Real-life stories of individuals who have successfully managed their heart arrhythmia can provide both inspiration and practical advice. For instance, John, a 52-year-old teacher, was able to regain control over his life after a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation. By closely following his treatment plan, which included medication and lifestyle adjustments, and maintaining regular check-ups, John has been symptom-free for the past three years. His story emphasizes the importance of compliance and proactive health management.
Another case is Lisa, a 30-year-old athlete, who experienced sudden cardiac arrhythmia during a marathon. After her recovery, she began using a heart rate monitor to keep an eye on her condition during training. Her proactive approach has allowed her to continue her athletic pursuits with confidence, illustrating the critical role of regular monitoring in living with arrhythmia.
FAQs about Heart Arrhythmia Treatment
What is heart arrhythmia and why does it require treatment?
Heart arrhythmia refers to any irregularity in the heartbeat—whether it’s too fast, too slow, or erratic. Treatment is crucial because arrhythmias can disrupt the effective pumping of blood throughout the body, leading to various health issues including fatigue, heart failure, or stroke.
What are the common treatments for heart arrhythmia?
Treatments for heart arrhythmia vary depending on the type and severity of the condition but commonly include medications, lifestyle changes, and possibly procedures like electrical cardioversion, catheter ablation, or the implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator.
Is heart arrhythmia treatment invasive?
The invasiveness of treatment depends on the arrhythmia’s nature and severity. While many arrhythmias can be managed with non-invasive methods such as medication and lifestyle adjustments, others may require invasive procedures like catheter ablation or surgery to implant a device.
Are there any side effects of arrhythmia treatments?
Yes, like all treatments, those for heart arrhythmia can have side effects. Medications might cause nausea, dizziness, or unusual tiredness. Invasive procedures carry risks such as infections, bleeding, or in rare cases, more serious complications. Discussing these with a healthcare provider is important.
How effective are the treatments for heart arrhythmia?
The effectiveness of arrhythmia treatments can vary widely. Many people experience significant improvements with proper treatment and can manage their condition effectively, leading normal, active lives. However, some cases might require ongoing adjustments in treatment to maintain heart rhythm.
Can lifestyle changes improve heart arrhythmia?
Absolutely. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and regular physical activity can significantly improve heart health and reduce the symptoms or severity of arrhythmias.
When should I see a doctor for heart arrhythmia?
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms like chest pain, fainting, severe dizziness, or rapid heartbeat. These could indicate a serious arrhythmia that requires immediate attention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the effective diagnosis and treatment of heart arrhythmias are critical to maintaining heart health and preventing serious complications. As we’ve explored, understanding the various types of arrhythmias and the latest treatment options can greatly enhance quality of life and reduce the risks associated with these irregular heartbeats.
If you suspect you might have an arrhythmia or if you’re experiencing symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Personalized medical advice from a professional is invaluable in accurately diagnosing and effectively managing heart arrhythmias. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference, so don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance and support.
References
For further reading and to validate the information provided on Heart Arrhythmia Treatment, we recommend consulting the following reputable sources:
- American Heart Association (AHA)
The AHA provides comprehensive guides and latest research findings on the various types of heart arrhythmias and their treatments. Read more about Heart Arrhythmia on American Heart Association. - Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic offers detailed patient-focused resources, including symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for heart arrhythmia. Explore Heart Arrhythmia resources at Mayo Clinic. - National Health Service (NHS)
The NHS site includes useful information on heart arrhythmia, including lifestyle tips and treatment advice relevant to patients. Visit NHS for more on Heart Arrhythmia. - PubMed Central
A service of the US National Institutes of Health, PubMed Central offers access to numerous scholarly articles on the latest research in the treatment and management of heart arrhythmia. Search PubMed for Heart Arrhythmia studies.
These resources are recognized for their authority and reliability in the medical field, making them excellent references for anyone looking to understand more about heart arrhythmia and its treatments.