Hearing Loss Treatment: Hearing loss is a prevalent health issue that affects millions of individuals globally.
It can result from genetic causes, environmental exposure, or as part of the aging process. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing the condition effectively.
This article provides an in-depth look at the diagnosis and treatment of hearing loss, equipping readers with the necessary knowledge to address this complex health challenge.
Understanding Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a widespread condition affecting millions globally, characterized by a partial or total inability to hear sounds in one or both ears. This impairment can vary greatly in severity and can either be temporary or permanent. Understanding the different types of hearing loss, their common causes, and who is most at risk can help in early detection and management. Below, we delve into the types of hearing loss, explore the common causes and risk factors, and examine the prevalence and demographics most affected.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is generally classified into three main types:
- Conductive Hearing Loss: This type occurs when sound is not conducted efficiently through the outer ear canal to the eardrum and the tiny bones of the middle ear. It usually involves a reduction in sound level or the ability to hear faint sounds. Causes can include ear infections, fluid in the middle ear, earwax blockage, and abnormalities of the ear drum or middle ear.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL): SNHL is the most common type of permanent hearing loss. This occurs when there is damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or to the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. Major causes include aging, exposure to loud noise, genetics, and diseases.
- Mixed Hearing Loss: This is a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. There may be damage in the outer or middle ear and in the inner ear or auditory nerve.
Understanding these types is crucial for determining the most effective treatment options, which can range from medical intervention to hearing aids or cochlear implants.
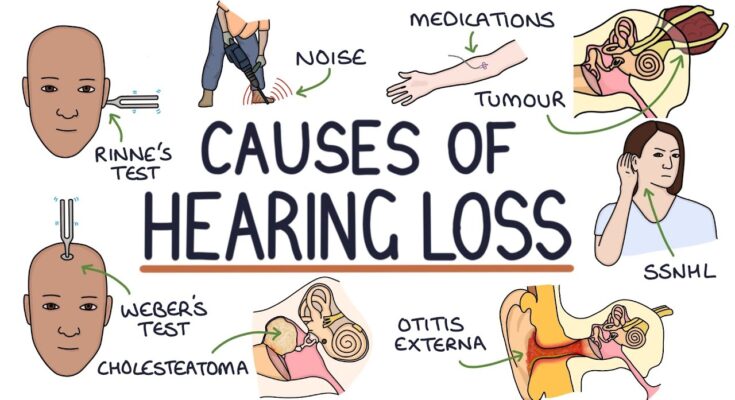
Common Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of hearing loss vary across different age groups and populations. Some of the most common causes include:
- Aging: The wear and tear from sounds over the years can damage the cells of the inner ear.
- Loud Noise: Exposure to loud noises can cause permanent damage to the inner ear cells.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as meningitis, can lead to hearing impairment.
- Injuries: Trauma to the head can impact the ear and hearing abilities.
- Medications: Some medications are known to be ototoxic, potentially damaging the inner ear.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in hearing loss, especially in congenital forms.
Risk factors also include lifestyle choices such as smoking and poor diet, which can affect hearing over time.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Impacted
Hearing loss affects people of all ages and backgrounds, but prevalence increases with age. According to the World Health Organization, over 5% of the world’s population (or 430 million individuals) requires rehabilitation to address ‘disabling’ hearing loss. Among those over 65, nearly one-third are affected by disabling hearing loss, highlighting its prevalence in the elderly population.
Children are also at risk, particularly those in environments with poor health care, where common childhood diseases like mumps, measles, and chronic ear infections can lead to hearing loss if not properly treated.
Understanding the demographics and prevalence of hearing loss is essential for public health measures and interventions designed to prevent and treat hearing impairments across different life stages.
By recognizing the types, causes, and extensive impact of hearing loss, individuals and healthcare providers can better manage and mitigate the effects of this common sensory impairment.
Symptoms and Early Signs of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can creep up gradually, making it essential to recognize the early signs and symptoms. Understanding these indicators can ensure timely intervention and treatment. Here’s what to look out for and when to consider seeking professional help.
Key Symptoms to Watch Out For
Hearing loss can manifest in several ways, varying from person to person. However, some common symptoms include:
- Difficulty Understanding Conversations: Struggling to follow discussions, especially in noisy environments or when multiple people are speaking, is a typical early sign.
- Asking for Repetitions: Frequently asking others to repeat themselves during conversations can indicate a reduction in hearing ability.
- Increased Volume Needs: Turning up the volume higher than usual on the television, radio, or other devices often suggests hearing difficulties.
- Muffled Sounds: Perceiving sounds as muffled or distant is a common symptom, making it hard to pinpoint where sounds are coming from.
- Tinnitus: Experiencing ringing, buzzing, or other persistent noises in the ears can be associated with hearing loss.
Importance of Recognizing Early Signs
Identifying the early signs of hearing loss is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevent Further Damage: Early detection can help prevent the progression of hearing loss.
- Better Treatment Outcomes: Timely and appropriate intervention can lead to more effective treatment options and potentially restore or maintain hearing levels.
- Improved Quality of Life: Addressing hearing issues early can significantly improve communication abilities, social interactions, and overall well-being.
When to Seek Professional Help
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if you or someone you know exhibits signs of hearing loss. Key moments to seek help include:
- Persistence of Symptoms: If symptoms persist or worsen over a few weeks, it’s time to see a specialist.
- Impact on Daily Life: When hearing loss begins to interfere with daily activities, professional assessment becomes necessary.
- Post-Loud Noise Exposure: After exposure to a loud event (e.g., a concert or explosion), if hearing issues occur, immediate consultation is advisable.
Recognizing the symptoms and early signs of hearing loss is the first step towards managing this common health issue effectively. Early intervention not only enhances the effectiveness of treatments but also helps maintain a higher quality of life.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss
Diagnosing this condition involves a systematic process to assess hearing acuity, determine the type and degree of loss, and identify the most effective treatment options. Here’s a detailed look at the diagnostic process, the common tests and procedures used, and the role of healthcare professionals in diagnosing hearing loss.
Diagnostic Process for Hearing Loss
The process of diagnosing hearing loss typically involves several steps, starting with a detailed medical history and progressing through specific auditory tests. The typical diagnostic process includes:
- Initial Consultation: The process begins with a consultation, where the healthcare professional gathers information about the patient’s medical history, exposure to noise, and any familial history of hearing loss.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the ears, head, and neck is conducted to check for any physical factors that might be contributing to hearing loss, such as blockages or structural abnormalities.
- Hearing Tests: Various auditory tests are performed to evaluate the extent and type of hearing loss.
Common Tests and Procedures
Several key tests are integral to accurately diagnosing hearing loss:
- Audiometry: This test involves using an audiometer to check how well a person can hear sounds at different pitches and volumes. The patient listens to short tones in a soundproof room and indicates when they can hear them.
- Tympanometry: This procedure assesses the health of the middle ear and eardrum by measuring the ear’s response to light pressure waves. It helps in identifying issues like fluid in the ear or problems with the eardrum.
- Speech Recognition Test: This test measures how well the patient can hear and understand speech at different volume levels. It helps in understanding the practical implications of hearing loss in everyday environments.
Additional tests may include acoustic reflex testing, otoacoustic emissions (OAEs), and auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing, which provide further details on the inner ear’s health and auditory pathway functionality.
Role of Healthcare Professionals in Diagnosis
Audiologists and ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialists play critical roles in the diagnostic process:
- Audiologists: These professionals specialize in the study of hearing, hearing disorders, and related auditory systems. They conduct the hearing tests, interpret the results, and recommend management strategies or hearing aids.
- ENT Specialists: Also known as otolaryngologists, these doctors specialize in conditions affecting the ear, nose, and throat. They can diagnose and treat structural issues, infections, and diseases that may cause hearing loss.
However, early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life and prevent further auditory damage. With the right approach and expert care, individuals with hearing loss can achieve better hearing management and a more comfortable daily life.
Treatment Options for Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can significantly impact the quality of life, making effective treatment options essential for those affected. Here’s an overview of the current strategies and emerging technologies aimed at managing and potentially restoring hearing.
General Approach to Treating Hearing Loss
The treatment for hearing loss depends largely on the cause and severity of the condition. Here are the most common approaches:
- Hearing Aids: These devices are the primary treatment for many types of hearing loss. They amplify sound, making it easier for the user to hear. Modern hearing aids are highly customizable and discreet.
- Cochlear Implants: For individuals who don’t benefit from hearing aids, cochlear implants may be an option. These devices bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, allowing users to hear.
- Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs): These include specialized telephones, TV listening systems, and FM systems designed to enhance sound in various environments.
- Medication and Surgery: In cases where hearing loss is due to infections or abnormal bone growths, medications or surgical interventions can be effective.
- Therapy: Speech and hearing therapy can help individuals cope with hearing loss and improve communication skills.
Emerging Technologies and Future Prospects
The future of hearing loss treatment is promising, with several innovative technologies on the horizon:
- Gene Therapy: Research is ongoing into how gene therapy can be used to correct the genetic mutations that cause hearing loss or to promote the regeneration of hair cells in the inner ear.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Scientists are exploring the potential of stem cells to regenerate inner ear sensory cells, which could lead to breakthroughs in restoring hearing.
- Advanced Cochlear Implants: New designs and technology are making cochlear implants more effective and less invasive. Future implants may interface more directly with neural pathways to enhance sound quality.
- Regenerative Medicine: Efforts in regenerative medicine aim to restore normal function in damaged ears by regenerating hair cells and other structures within the ear.
- Personalized Medicine: As understanding of the genetic basis of hearing loss improves, treatments can be increasingly tailored to the individual’s specific condition, potentially improving outcomes.
As research progresses, these advanced technologies promise to revolutionize the treatment of hearing loss, offering hope that one day, restoring full hearing could be a reality. Meanwhile, ongoing advancements in hearing aids and implants continue to improve the quality of life for many.
Rehabilitation and Management of Hearing Loss
Here, we delve into the importance of auditory rehabilitation, detail communication strategies and tools, and highlight lifestyle adjustments and support systems essential for individuals experiencing hearing loss.
Importance of Auditory Rehabilitation
Auditory rehabilitation is vital for individuals with hearing loss as it aims to restore and maximize their ability to communicate effectively. This process involves various therapies and techniques designed to improve hearing function and enhance speech comprehension. Auditory rehabilitation not only supports better communication but also helps individuals regain confidence and maintain their social connections, contributing to overall mental and emotional well-being.
Communication Strategies and Tools
To manage hearing loss effectively, various communication strategies and tools can be utilized:
- Hearing Aids: These devices amplify sounds, making it easier for the user to hear in different environments. They can be customized to fit the specific hearing loss needs of the individual.
- Cochlear Implants: For those with severe hearing loss, cochlear implants can be a viable option. These electronic devices bypass damaged portions of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, helping to provide a sense of sound.
- Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs): ALDs like amplified phones, FM systems, and personal amplifiers can assist in specific listening environments, such as classrooms or meetings.
- Speechreading: Learning to use visual cues such as lip movements, facial expressions, and gestures can enhance understanding, especially in quiet environments.
- Clear Speech Techniques: Encouraging speakers to talk slowly, enunciate clearly, and use simple sentences can improve communication efficiency.
- Communication Apps: Various mobile applications are available to transcribe speech in real-time, offering another layer of support for understanding conversations.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Support Systems
Adapting to life with hearing loss involves making several lifestyle adjustments and leveraging support systems:
- Educating Close Contacts: Teaching family, friends, and colleagues about your hearing loss can help them adjust their communication habits to better support you.
- Noise Management: Minimizing background noise can significantly improve hearing capabilities in social situations. For instance, choosing seating away from loud speakers or noise sources in restaurants can help.
- Joining Support Groups: Support groups for those with hearing loss provide a platform to share experiences, tips, and emotional support. These groups can be invaluable in coping with the challenges of hearing loss.
- Professional Counseling: Psychological counseling might be necessary for some individuals to adjust to the emotional impacts of hearing loss. Counselors specialized in hearing loss can provide strategies and support for dealing with communication barriers and social isolation.
- Regular Check-ups: Ongoing assessments with hearing health professionals ensure that any changes in hearing levels are monitored and that treatments are adjusted accordingly.
Adopting effective communication tools, making necessary lifestyle adjustments, and relying on a robust support system are all essential steps in the rehabilitation and management of hearing loss.
Prevention and Awareness of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can significantly impact quality of life, but many cases are preventable with the right knowledge and strategies. Here’s how you can protect your hearing health through prevention, awareness, and the support of dedicated organizations.
Tips for Preventing Hearing Loss
- Protect Your Ears: Exposure to loud noises is a common cause of hearing damage. Use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in noisy environments like concerts, factories, or when using power tools.
- Turn Down the Volume: Listening to music or watching TV at high volumes, especially through headphones, can damage your hearing over time. Follow the 60/60 rule: listen at no more than 60% volume for no longer than 60 minutes at a time.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular hearing tests, especially if you are frequently exposed to loud noises. Early detection of hearing loss can lead to better outcomes.
- Keep Your Ears Dry: Excess moisture can lead to infections that might harm hearing. Gently towel dry your ears after swimming or bathing and consider custom-fit swimmer’s earplugs.
- Avoid Ototoxic Chemicals: Some medications and chemicals have harmful effects on hearing. Always discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider and follow directions for use carefully.
The Role of Public Awareness and Education
Education plays a crucial role in hearing loss prevention. Increased public awareness can lead to earlier detection and treatment. Health campaigns and school programs should focus on:
- The dangers of loud noise exposure.
- The importance of protecting hearing in recreational activities.
- How to recognize the early signs of hearing loss.
Such initiatives can shift public behavior towards better hearing health practices and reduce the incidence of preventable hearing loss.
Resources and Support Organizations
Numerous organizations worldwide are dedicated to helping individuals prevent and cope with hearing loss. These include:
- National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD): Provides research and educational materials on hearing loss.
- Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA): Offers support and resources for people affected by hearing loss, including local chapters and events.
- World Health Organization (WHO): Shares global research and practical guidelines for preventing hearing loss at a public health level.
Leveraging these resources can provide valuable support and information for those looking to educate themselves or others about hearing health.
By embracing these tips, supporting educational efforts, and utilizing available resources, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of hearing loss while enhancing their overall well-being.
FAQs about Hearing Loss Treatment
What are the common treatments for hearing loss?
The treatment for hearing loss depends on its cause and severity. Common approaches include hearing aids, cochlear implants, and surgery. For some, medications and managing underlying conditions can also improve hearing.
Can hearing loss be cured?
Hearing loss is generally irreversible, especially if it’s sensorineural (related to nerve damage). However, treatments like cochlear implants and hearing aids can significantly improve hearing abilities and quality of life.
Are there any natural remedies for hearing loss?
While no natural remedies can cure hearing loss, certain lifestyle changes and supplements are thought to support ear health. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
How do I know if I need a hearing aid?
If you’re experiencing difficulties in hearing conversations, especially in noisy environments, or find yourself frequently asking others to repeat themselves, it might be time to consult an audiologist who can assess your hearing and recommend appropriate aids.
Is hearing loss treatment covered by insurance?
Coverage for hearing loss treatment varies by insurance provider and plan. Some insurance plans cover part of the cost of hearing aids and diagnostic evaluations, while others might not. Always check with your insurance provider for specific coverage details.
Can children be treated for hearing loss?
Yes, children can and should be treated for hearing loss as early as possible. Early intervention, such as fitting hearing aids or cochlear implants and speech therapy, is crucial for normal speech and language development.
What advances are there in hearing loss treatment?
Recent advances in hearing loss treatment include improvements in hearing aid technology, such as wireless connectivity and rechargeable batteries, and advances in cochlear implant technology. Research into gene therapy and regenerative medicine also holds promise for future treatments.
Conclusion
Understanding the significance of promptly diagnosing and treating hearing loss is crucial for maintaining our quality of life. Early intervention not only helps in preserving hearing but also in preventing associated risks such as cognitive decline, social isolation, and emotional distress.
If you or someone you know is experiencing signs of hearing loss, it is vital to seek professional help immediately. Numerous effective treatments and supportive technologies are available today that can dramatically improve hearing and overall well-being.
Taking action early can lead to a better, more engaged life. Don’t hesitate to reach out for help and explore the options that can reintegrate sounds back into your life. Remember, addressing hearing loss is not just about hearing better—it’s about living better.
References
For further information and to validate the treatments discussed regarding hearing loss, you can explore the following reputable sources. These links provide additional insights and comprehensive data to help understand the nuances and effectiveness of various hearing loss treatments.
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Hearing Loss Treatment Guidelines
The WHO provides global guidelines and detailed reports on hearing loss prevention, management, and treatment strategies. - Mayo Clinic – Hearing Loss Treatments
Mayo Clinic offers expert medical advice and treatment options for hearing loss, including the latest in surgical and non-surgical treatments. - American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) – Treatment of Hearing Loss
ASHA is a trusted resource for information on the treatment of hearing impairment, including therapeutic approaches and hearing aids. - Hearing Loss Association of America – Treatment and Management of Hearing Loss
This association provides resources and support for individuals with hearing loss, focusing on treatment options and coping strategies. - National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) – Hearing Loss Treatment Research
The NIDCD offers up-to-date research findings on hearing loss treatments, emphasizing innovative therapies and technologies.
These sources are excellent starting points for anyone seeking to deepen their understanding of hearing loss treatments or explore advanced therapeutic techniques.