Head and Neck Cancers Treatment: Head and neck cancers are a diverse group of diseases that arise in the head or neck region, including the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, nasal cavity, and salivary glands.
These cancers are significant not only because of their prevalence but also due to the complexity of their treatment and diagnosis.
Understanding Head and Neck Cancers
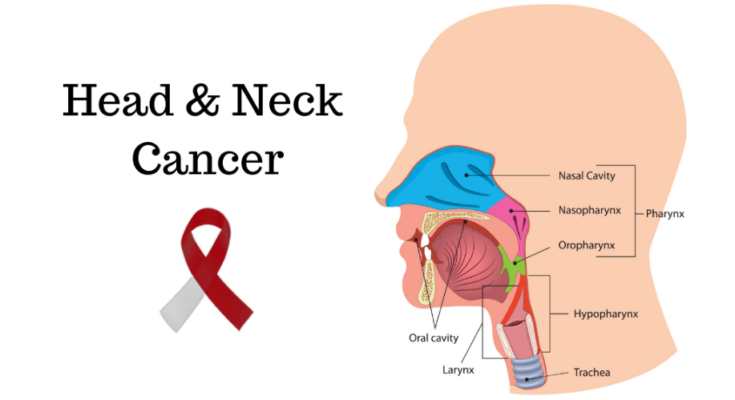
Head and neck cancers primarily originate in the squamous cells that line the moist surfaces inside the head and neck areas, such as the mouth, nose, and throat. Understanding the types, risk factors, and symptoms of these cancers is essential for early detection and effective treatment.
Types of Head and Neck Cancers
Head and neck cancers encompass a variety of malignancies found in several distinct areas. The most common types include:
- Oral Cavity Cancer: Affects the lips, the inside lining of the cheeks and lips, teeth gums, the front two-thirds of the tongue, the floor and roof of the mouth.
- Oropharyngeal Cancer: Occurs in the oropharynx, which includes the back third of the tongue, the back of the throat, the tonsils, and the soft palate.
- Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer: Develops in the passages behind the nose and the hollow spaces in the bones surrounding the nose.
- Laryngeal Cancer: Starts in the larynx or voice box.
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Located in the nasopharynx, the area of the upper throat behind the nose.
- Salivary Gland Cancer: Begins in the salivary glands, which are located under the jaw and in other areas of the face.
Each type of head and neck cancer has specific characteristics and should be diagnosed and treated based on its location and stage.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing head and neck cancers, including:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes and using chewing tobacco are the most significant risk factors for head and neck cancers.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol use is a potent risk factor, especially when combined with tobacco.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Infections with certain types of HPV, particularly HPV16, are linked to oropharyngeal cancers.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged sun exposure is a known cause of cancer in the lip area.
- Age and Gender: These cancers are more common in people over the age of 40 and are more prevalent in men than in women.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet deficient in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of these cancers.
Understanding these risk factors can lead to proactive health choices and regular screening, which are vital for early detection.
Symptoms to Watch for Early Detection
Early detection of head and neck cancers can significantly improve the outcome. Key symptoms to watch for include:
- Persistent Sore Throat: A sore throat that does not go away could signal throat cancer.
- Change in Voice: Hoarseness or other voice changes that persist could indicate laryngeal cancer.
- Swelling or Lumps: Any lumps on the neck, throat, or mouth that do not go away should be evaluated.
- Pain in the Mouth: Pain or numbness in any area of the mouth or lips.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without trying can be a symptom of cancer.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Persistent difficulty swallowing can indicate a problem in the throat or esophagus.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider promptly for a thorough evaluation.
Diagnostic Approaches for Head and Neck Cancers
Detecting head and neck cancers early is crucial for effective treatment and improved patient outcomes. The diagnostic process for these cancers involves a series of steps and tests to accurately identify and assess the extent of the cancer. Below, we explore the primary diagnostic approaches used in the evaluation of head and neck cancers.
Initial Evaluation: Physical Exams and Patient History
The first step in diagnosing head and neck cancer typically involves a thorough physical examination and a detailed review of the patient’s medical history. During the physical exam, doctors look for abnormal signs such as lumps, swelling, or other physical changes in the head and neck area. The medical history review helps to identify any risk factors or symptoms that the patient may have experienced, such as difficulty swallowing, changes in voice, or unexplained weight loss.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests play a vital role in the diagnosis of head and neck cancers, providing detailed images of the structures inside the head and neck. These tests help to determine the location and size of the cancer, and whether it has spread to other areas.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scans: CT scans create detailed cross-sectional images that can help detect the presence and spread of tumors. They are particularly useful for examining changes in bone structures and detecting lymph node involvement.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Scans: MRI scans produce highly detailed images through magnetic fields and radio waves, making them excellent for viewing soft tissues. They are especially valuable for assessing the extent of cancer and checking if it has invaded muscles or surrounding tissues.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography) Scans: Often combined with CT scans (PET/CT), these scans can detect cancerous cells based on their activity level, helping to identify cancer when it is active and determining if the treatment has been effective.
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy is a definitive method for diagnosing head and neck cancers. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is removed from the suspected area and examined under a microscope for cancer cells.
- Types of Biopsies: There are several types of biopsy procedures used, including fine needle aspiration biopsy, which involves using a thin needle to remove tissue or fluid samples, and excisional or incisional biopsies, where part or all of a suspicious area is surgically removed.
- Significance of Biopsy: The biopsy not only confirms the presence of cancer but also helps in determining the type of cancer, which is crucial for planning the most effective treatment strategy.
By combining the results from the physical exams, imaging tests, and biopsies, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose head and neck cancers and tailor treatment plans that best suit the individual needs of the patient.
Treatment Options for Head and Neck Cancers
Effective management of these cancers involves a range of modalities tailored to the individual’s specific condition and needs. Below, we explore the main treatment options available, highlight emerging therapies, and discuss the critical role of multidisciplinary care in planning and executing treatment.
List of Treatment Modalities
1. Surgery: Surgical intervention remains a cornerstone in the treatment of head and neck cancers, particularly for tumors that are localized and accessible. Techniques vary from minimally invasive procedures to more extensive surgeries depending on the tumor’s size, location, and spread.
2. Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. For head and neck cancers, radiation therapy can be external beam radiation or more targeted modalities like intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), which minimizes damage to surrounding tissues.
3. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells and is often used in conjunction with other treatments. For advanced stages of head and neck cancers, chemotherapy can help reduce symptoms and control tumor growth.
4. Targeted Therapy: This modality focuses on specific molecules and signaling pathways that are crucial for cancer cell growth and survival. Targeted therapy tends to have fewer side effects than chemotherapy as it aims to preserve healthy cells.
5. Immunotherapy: A newer form of treatment that helps the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. Drugs like checkpoint inhibitors have shown promise in treating certain types of head and neck cancers that have specific genetic markers.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
Research into head and neck cancer treatments is ongoing, with several promising therapies on the horizon:
1. Gene Therapy: Scientists are exploring ways to correct or replace faulty genes responsible for cancer or to introduce genes that might kill cancer cells directly.
2. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): This involves using light-sensitive medication and a light source to destroy cancerous cells, with the potential for treating superficial or early-stage cancers more precisely.
3. Advanced Personalized Medicine: As we understand more about the genetic basis of cancers, treatments are increasingly being tailored to the genetic profile of an individual’s tumor, improving the efficacy and reducing the side effects of therapy.
The Role of Multidisciplinary Care in Treatment Planning
The complexity of head and neck cancers often necessitates a multidisciplinary approach to treatment planning. This involves a team of specialists, including oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, pathologists, nurses, and support staff, who work together to create a cohesive and comprehensive treatment plan. This team approach ensures that all aspects of a patient’s care are addressed, from diagnosis through to treatment and post-treatment rehabilitation. Multidisciplinary teams also facilitate more personalized care plans that can adapt to the nuances of each patient’s condition, improving outcomes and enhancing the quality of life during and after treatment.
By integrating these varied treatment options and leveraging the expertise of diverse healthcare professionals, patients with head and neck cancers can receive the most advanced care possible, tailored to their unique health needs.
Challenges in Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers
Treating head and neck cancers presents a variety of challenges, largely influenced by the location and size of the tumor, as well as the need to manage side effects and complications associated with both the disease and its treatment. Addressing these challenges effectively is crucial for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Impact of Tumor Location and Size on Treatment Choices
The anatomical complexity of the head and neck area means that the location and size of a tumor can significantly impact treatment options. Tumors located in critical areas like the throat, larynx, or near the base of the skull require highly specialized approaches to preserve essential functions such as speech and swallowing. Larger tumors, or those that have spread to vital structures, often necessitate more aggressive treatments, which may include extensive surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The primary goal is to eliminate cancer while minimizing damage to the surrounding tissues, a balance that is critical yet challenging to achieve.
Strategies for Managing Side Effects and Complications
The treatment of head and neck cancers often leads to side effects that can significantly impact a patient’s life. These may include pain, difficulty in swallowing, speech issues, and cosmetic concerns, among others. Managing these side effects requires a multidisciplinary approach:
- Pain Management: Effective pain control is essential and can be managed through medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
- Nutritional Support: Many patients experience difficulty swallowing and may require dietary modifications or feeding tubes to maintain adequate nutrition.
- Speech and Swallowing Therapy: Early intervention with speech and swallowing therapy can help maintain these functions and improve quality of life.
- Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgery: For patients facing significant disfigurement, reconstructive surgeries may be necessary to restore appearance and function.
Furthermore, addressing the psychological impact of cancer diagnosis and treatment is crucial. Psychological support and counseling should be integral parts of the treatment plan, helping patients and their families cope with the emotional burden of cancer.
Role of Rehabilitation in Recovery from Head and Neck Cancers
Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in the recovery process for patients diagnosed with head and neck cancers. These cancers, often challenging due to their critical location affecting vital functions like speech and swallowing, necessitate a comprehensive approach to treatment and recovery. Rehabilitation services such as speech therapy and dietary adjustments are essential for restoring function and improving quality of life.
Importance of Rehabilitation Services
Speech Therapy: After treatment for head and neck cancers, patients may face difficulties with speech and swallowing due to the location of the tumor and the nature of its treatment. Speech therapy is crucial as it helps patients regain their ability to speak clearly and swallow safely. This therapy is tailored to meet individual needs, depending on the specific areas affected by the cancer and its treatment. Engaging with a speech therapist early in the recovery process can significantly enhance the patient’s communication abilities and dietary intake.
Dietary Changes: Nutritional support is another cornerstone of rehabilitation for head and neck cancer patients. Treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can affect one’s ability to eat and digest food normally, leading to challenges like malnutrition and significant weight loss. Dietitians play a critical role in assessing the patient’s nutritional needs and developing a personalized eating plan that accommodates their specific requirements. This plan may include modified diets or supplemental nutrition to ensure that patients maintain adequate nutrition levels, which is vital for recovery and overall health.
Long-Term Care and Monitoring for Recurrence
Continuous follow-up care is essential for patients recovering from head and neck cancers. Regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to monitor for any signs of recurrence, manage ongoing complications, and adjust rehabilitation plans as needed. These appointments are crucial for early detection of any new issues, which is key to improving long-term survival rates. The monitoring also includes regular imaging tests, physical examinations, and, in some cases, additional biopsies to ensure the cancer has not returned.
Support Systems and Resources for Patients and Families
Recovering from head and neck cancer is not only a physical challenge but also an emotional journey. Support systems and resources play a vital role in helping patients and their families navigate the complexities of cancer recovery. Many hospitals and clinics offer support groups where patients can connect with others facing similar challenges. These groups provide emotional support, share practical advice, and offer encouragement throughout the recovery process.
Additionally, various organizations and resources are available to assist with the broader aspects of living with cancer, including financial guidance, psychological counseling, and patient education. These resources ensure that patients and their families have access to the necessary tools to manage the impact of cancer effectively.
However, rehabilitation is a critical component of the recovery process for patients with head and neck cancers, involving specialized services like speech therapy and dietary management. Along with long-term care and robust support systems, these services empower patients to regain their health and improve their quality of life post-treatment.
Innovations and Future Directions in Head and Neck Cancer Treatments
The landscape of head and neck cancer treatment is rapidly evolving, with significant advancements in research and clinical trials paving the way for more effective therapies. This section delves into the recent research developments, explores the potential future of treatment modalities, and examines the critical role of personalized medicine in enhancing treatment outcomes for patients.
Recent Research Developments and Clinical Trials
Recent years have seen a surge in innovative research and groundbreaking clinical trials aimed at improving the prognosis for head and neck cancer patients. Targeted therapy, which uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells without harming normal cells, has emerged as a particularly promising area of study. For instance, trials involving immunotherapy have shown that activating the immune system can be a potent strategy in fighting cancer. Additionally, advancements in molecular biology have led to the development of therapies that are tailored to the genetic profiles of individual tumors, potentially increasing the precision and effectiveness of treatment.
The Future of Head and Neck Cancer Treatments
Looking ahead, the future of head and neck cancer treatments appears promising and is likely to be characterized by more personalized approaches. Researchers are constantly exploring the potential of novel therapies such as gene editing techniques and are harnessing the power of artificial intelligence to improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. Furthermore, there is an ongoing effort to develop less invasive surgical techniques that not only effectively remove tumors but also preserve patients’ quality of life by minimizing side effects associated with traditional treatments.
The Role of Personalized Medicine in Enhancing Treatment Efficacy
Personalized medicine is set to transform the treatment landscape for head and neck cancer significantly. By understanding the unique genetic makeup of each patient’s cancer, clinicians can tailor treatments to individual needs, enhancing efficacy and reducing the likelihood of adverse reactions. This approach not only helps in selecting the appropriate therapeutic strategies but also in determining the optimal dosages for individual patients. Personalized medicine’s integration into clinical practice promises to optimize treatment outcomes and represents the next frontier in the battle against head and neck cancer.
These innovations and future directions underscore a move towards more targeted, efficient, and patient-centered care in the field of head and neck cancer treatment. With ongoing research and the integration of new technologies and personalized approaches, the future holds the potential for transformative changes that will significantly improve patient outcomes.
FAQs about Head and Neck Cancers Treatment
What are the most common treatments for head and neck cancers?
The most common treatments for head and neck cancers include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the type, location, and stage of the cancer. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are also increasingly used as treatment options.
Can head and neck cancers be cured?
Many head and neck cancers can be cured, especially if they are diagnosed early. The likelihood of a cure depends on several factors including the type of cancer, its stage at diagnosis, and the overall health of the patient. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving survival rates.
What are the side effects of treatment for head and neck cancers?
Treatment for head and neck cancers can cause a variety of side effects, which vary depending on the type of treatment. Common side effects include pain, swelling, difficulty swallowing, speech problems, and changes in appearance. Long-term side effects may include dry mouth, thyroid changes, and changes in taste.
How long is the treatment for head and neck cancer?
The length of treatment for head and neck cancer varies based on the treatment plan. Surgery may involve a single procedure, while radiation therapy and chemotherapy might require several weeks to several months of treatment. The specific duration depends on the cancer’s response to treatment and the patient’s overall health.
Is follow-up necessary after treatment?
Yes, follow-up care is crucial after treatment for head and neck cancer. Regular check-ups help monitor recovery, manage side effects, and detect any signs of cancer recurrence. The frequency and type of follow-up vary, but typically include physical exams, imaging tests, and, if needed, additional treatments.
What lifestyle changes are recommended after treatment?
After treatment for head and neck cancer, doctors often recommend lifestyle changes to help recovery and improve quality of life. These may include quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol, eating a balanced diet, and regular physical activity. Supportive care services such as speech therapy, nutritional counseling, and psychological support may also be beneficial.
Conclusion
Understanding and recognizing symptoms early is crucial for managing any health condition effectively. A timely diagnosis can significantly improve the outcome by enabling appropriate and early interventions. It’s essential for both patients and healthcare providers to stay informed and vigilant about the initial signs of health issues.
We encourage patients to actively participate in their health journey and discuss their symptoms openly with their healthcare providers. Meanwhile, healthcare professionals should remain open to a range of treatment options, tailoring their approach to suit individual patient needs and circumstances. Exploring various treatment possibilities can lead to more effective management and better patient outcomes.
Empowerment through knowledge and proactive healthcare can make a significant difference in the lives of patients. Always seek professional advice at the first sign of a problem and consider all available treatment options to ensure the best possible care.
References
For those interested in delving deeper into the treatment of head and neck cancers, a variety of reputable sources offer detailed information and further validation of the treatments discussed. Below are several recommended resources:
- National Cancer Institute (NCI) – The NCI provides comprehensive information on the types of head and neck cancer, treatment options, and ongoing research into new therapies. Access their detailed guide here.
- American Cancer Society (ACS) – ACS offers a thorough overview of what patients can expect during head and neck cancer treatment, including side effects and recovery. Find their resources here.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its patient-focused approach, the Mayo Clinic provides insights into diagnosis, treatment plans, and supportive care for head and neck cancers. Visit their page here.
- PubMed Central – A service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health, PubMed Central offers access to thousands of free, full-text scholarly articles on head and neck cancer treatments. Search their database here.
- Cancer Research UK – This site offers information about the latest research in cancer treatment, including specific information on head and neck cancers. Learn more here.
By exploring these references, readers can enhance their understanding of head and neck cancer treatments and stay informed about the latest advancements in medical research.