Growth Plate Fractures Symptoms: Growth plate fractures are critical injuries that affect the developing bones of children and adolescents.
These fractures occur in the growth plate, which is the area of developing tissue near the ends of long bones in children and teenagers. This area is also known as the epiphyseal plate or physis.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of growth plate fractures is essential for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
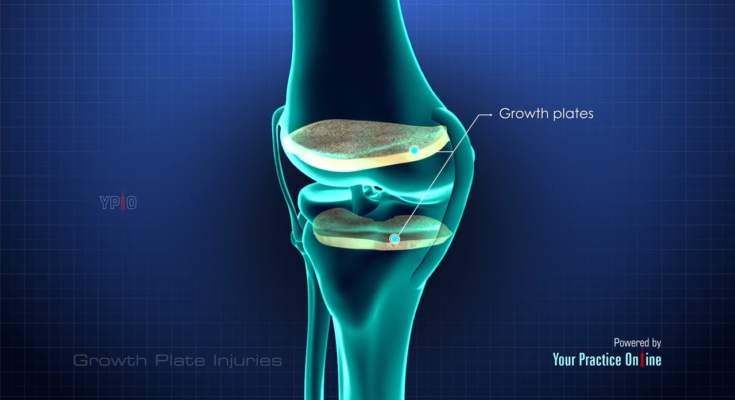
Understanding Growth Plates
Growth plates, also known as epiphyseal plates, are crucial areas of developing tissue at the ends of long bones in children and adolescents. These plates are found in various bones, including the femur, tibia, and humerus, and are essential for bone growth. As a child matures, these plates gradually harden into solid bone in a process called ossification, which is typically completed by the end of adolescence.
The Role of Growth Plates in Child Development
Growth plates are the engine of bone growth, enabling bones to lengthen from infancy through adolescence. Each growth plate consists of cartilage, a rubbery, flexible material that provides the framework for new bone cells to develop. As these cells multiply and mature, they contribute to the increasing length of the bone, ultimately determining an individual’s height and limb proportions.
Why Growth Plates Are Susceptible to Fractures
Growth plates are particularly vulnerable to fractures for several reasons. Firstly, because they are softer than the ossified bone, they are less able to withstand impact and stress. Children and adolescents are often engaged in physical activities and sports that increase the risk of injuries to these areas. Secondly, the flexibility of the cartilage in growth plates, while essential for growth, also makes them more susceptible to damage compared to the tougher, more resilient mature bone.
Fractures to growth plates can have serious implications. If not properly managed, they can result in stunted growth or the bone growing in a crooked manner. Therefore, recognizing and treating injuries to growth plates promptly and effectively is crucial for maintaining healthy development in children.
By understanding the importance and vulnerability of growth plates, parents and caregivers can better support safe physical activities for children, helping to prevent injuries and ensure healthy growth and development.
Common Causes of Growth Plate Fractures
Understanding the common causes of these injuries can help in prevention and proper treatment. Below, we explore the primary factors that contribute to growth plate fractures and discuss how these causes specifically affect the growth plates.
Trauma from Falls or Accidents
The most frequent cause of growth plate fractures is trauma resulting from falls or accidents. Whether it occurs during sports, playground activities, or a simple misstep, the sudden impact can cause the delicate cartilage in the growth plate to crack or break. High-impact sports like football, basketball, or soccer are particularly associated with such injuries.
Repetitive Stress
Repetitive stress or overuse injuries are another significant cause of growth plate fractures. Activities that involve repetitive motions, such as gymnastics, running, or baseball pitching, can place continuous stress on the growth plates, leading to fractures over time. This type of fracture often develops slowly and can be more difficult to diagnose initially.
Rapid Growth Spurts
During periods of rapid growth, children’s bones and muscles are particularly vulnerable. The growth plates are more susceptible to injury because they are the last portion of the bones to harden and fully develop. During these growth spurts, even normal activities and lower-impact sports can result in injuries to the growth plates.
Poor Nutrition
Nutrition plays a critical role in the health of growing bones. A diet deficient in calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients essential for bone health can weaken the growth plates, making them more prone to fractures. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in these nutrients is crucial for the prevention of growth plate injuries.
Genetic Factors
In some cases, genetic factors may predispose children to growth plate fractures. Conditions that affect bone density and development, such as osteogenesis imperfecta or other bone dysplasias, can increase the risk of fractures in the growth plates. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital for managing these conditions effectively.
Impact on Growth Plates
Growth plates are the areas of growing tissue near the ends of children’s long bones. They are made up of cartilage, which is less dense and more vulnerable to injury compared to mature bone. When a growth plate is fractured, it can interfere with the bone’s normal growth and development. In severe cases, such fractures can result in shortened limbs or other permanent deformities if not properly treated. Prompt medical attention and appropriate care are essential to ensure proper healing and minimize long-term effects.
However, understanding these causes and their impact on growth plates is critical for protecting children’s health and ensuring proper bone development. Parents, coaches, and caregivers should be aware of these risks and take preventive measures to safeguard young athletes and active children.
Symptoms of Growth Plate Fractures
Recognizing the symptoms of these fractures early can lead to prompt treatment, preventing long-term damage to the growth plate. Here’s a detailed list of common symptoms and advice on how to differentiate these from other injuries.
Common Symptoms of Growth Plate Fractures
- Pain and Tenderness: The most immediate symptom of a growth plate fracture is pain at the site of the injury, which is often severe and worsens with movement.
- Swelling and Redness: Swelling is typically localized around the affected area. The skin near the growth plate may also appear red and feel warm to the touch.
- Difficulty Moving the Affected Limb: Children with growth plate fractures may find it painful to move the affected limb. In severe cases, the child might refuse to use the limb altogether due to discomfort.
- Visible Deformity: In some cases, the affected limb may look deformed. This could be a sign that the bone has been displaced.
- Inability to Put Weight on the Affected Limb: Especially with fractures in the leg or foot, the child might be unable to bear weight or walk normally.
Differentiating Growth Plate Fractures from Other Injuries
Distinguishing growth plate fractures from other types of injuries involves observing specific symptoms and understanding their implications:
- Severity and Location of Pain: Growth plate fractures tend to cause intense localized pain directly over the growth plate area, unlike sprains or strains where the discomfort may be more spread out.
- Response to Movement: While soft tissue injuries like sprains may improve slightly with gentle movement or over time, the pain from a growth plate fracture usually intensifies with movement and does not ease up.
- Physical Deformity: Unlike bruises or mild sprains, a visible deformity often accompanies growth plate fractures, indicating a more serious injury.
- Age of the Child: Growth plate fractures predominantly occur in children and teenagers. If a child experiences severe pain following an injury, a growth plate fracture should be considered, especially if located near the ends of long bones.
To conclusively diagnose a growth plate fracture, a medical professional will typically recommend imaging tests, such as an X-ray. It’s crucial for parents to seek medical advice if a growth plate fracture is suspected, as improper healing can affect the bone’s growth and development. Early detection and appropriate treatment are key to a full recovery.
Diagnosing Growth Plate Fractures
Accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial to ensure proper treatment and to prevent potential long-term issues such as stunted growth or misaligned limbs. Below are the steps typically followed to diagnose these fractures effectively.
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing a growth plate fracture involves a thorough physical examination. During this examination, a healthcare provider will assess the injured area for signs of swelling, tenderness, and deformity. The physician may also check the range of motion and compare the injured limb to the uninjured one. This initial assessment helps to determine the severity of the injury and whether further tests are needed.
Medical Imaging
Following a physical exam, medical imaging is often required to confirm the presence of a growth plate fracture and to evaluate its type and extent. The most common imaging techniques include:
- X-rays: These are typically the first imaging technique used as they can clearly show most fractures of the bones.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI may be used if the X-ray results are inconclusive or if there’s a need to assess the soft tissues around the growth plate.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Although less common for growth plate injuries, a CT scan may be utilized to provide a more detailed view when complex fractures are suspected.
These imaging tools are pivotal in not only diagnosing the fracture but also in planning out the appropriate treatment approach.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis of growth plate fractures is vital for several reasons. Misdiagnosed or untreated fractures can lead to complications such as:
- Stunted or uneven growth: The growth plate is responsible for bone growth. A fracture in this area can disrupt normal growth patterns.
- Joint problems: Improperly healed fractures can result in joint misalignment, leading to long-term mobility issues or arthritis.
Early and precise identification of these fractures allows for interventions that can correctly align and stabilize the bones, thereby minimizing the risk of future complications.
However, diagnosing growth plate fractures requires a systematic approach starting with a detailed physical examination followed by appropriate medical imaging. Ensuring an accurate diagnosis is crucial to avoid long-term health issues and to support the child’s growth and development effectively.
Treatment Options for Growth Plate Fractures
Proper treatment is crucial to ensure normal growth and function. Here, we explore the various treatment options available and discuss the importance of adhering to medical advice during the recovery process.
General Treatment Methods for Growth Plate Fractures
- Casting or Splinting: The most common treatment for growth plate fractures involves immobilizing the affected limb with a cast or splint. This method helps keep the bones in a fixed position, allowing the growth plate to heal correctly.
- Surgery: In cases where the fracture is severe or displaced, surgical intervention may be required to realign the bones properly. Surgery typically involves the use of pins, screws, or plates to stabilize the bone during healing.
- Physical Therapy: After immobilization, physical therapy is often recommended to restore strength and flexibility to the affected area. Physical therapists design exercises that safely encourage movement and support recovery.
- Rest and Activity Modification: Limiting activities that put stress on the injured area is crucial. Doctors often advise avoiding sports and heavy physical activities until the growth plate has fully healed.
- Pain Management: Managing pain is essential for a comfortable recovery. Doctors may prescribe pain relievers or recommend over-the-counter medications to help alleviate discomfort during the healing process.
Importance of Following Medical Advice for Recovery
Following medical advice after a growth plate fracture is essential for several reasons:
- Prevent Complications: Proper adherence to treatment plans helps prevent complications such as misaligned bones or disrupted growth.
- Ensure Proper Healing: Following the recommended treatment regimen ensures that the growth plate heals correctly, thereby promoting normal bone development.
- Avoid Long-Term Damage: Incorrect healing can lead to long-term issues like chronic pain or arthritis. Adhering to medical advice helps minimize these risks.
- Faster Return to Activities: Patients who follow their doctor’s recommendations typically experience quicker recovery times, allowing them to return to their daily activities and sports sooner.
However, addressing growth plate fractures with appropriate treatment and following medical guidance diligently are pivotal to a child’s recovery and future bone health. Parents and caregivers should ensure that children adhere to their treatment plans and attend all follow-up appointments to achieve the best possible outcome.
Prevention Tips for Growth Plate Fractures
Growth plate fractures can have lasting effects on a child’s development, making prevention crucial. Here are some key strategies to help protect young athletes and active children from these injuries:
1. Use Proper Safety Equipment for Sports
Ensuring that children wear the right safety gear is fundamental in preventing growth plate fractures. This includes helmets, knee pads, elbow pads, and wrist guards, which are especially important in contact sports and activities like skateboarding or cycling. Equipments should be well-fitted and specific to the sport to provide the best protection.
2. Practice Safe Play
Encouraging safe play practices is another essential step in minimizing the risk of injuries to growth plates. This means teaching children the rules of the game and enforcing them. It also includes supervising younger children to make sure that they are using sports equipment and playgrounds appropriately. Safe play also involves using age-appropriate and size-appropriate sports gear and facilities.
3. Emphasize Proper Training and Conditioning
Proper training and conditioning go a long way in preventing all kinds of sports injuries, including growth plate fractures. Children should be taught correct techniques and postures from the start. Regular, age-appropriate fitness routines that include exercises to strengthen muscles, increase flexibility, and improve balance can help protect their growth plates. Furthermore, it’s important that children warm up and cool down properly before and after activities to keep their joints and muscles supple.
By adhering to these preventative measures, parents and coaches can significantly reduce the risk of growth plate fractures in children. Investing time in educating young athletes about the importance of safety, proper training, and appropriate equipment can lead to a healthier, more active childhood with a reduced risk of injury.
FAQs about Growth Plate Fracture Symptoms
1. What are growth plate fractures?
Growth plate fractures refer to injuries that affect the area of developing tissues at the end of a child’s long bones. These fractures can interfere with the normal growth and development of the bone.
2. What are the common symptoms of growth plate fractures?
The most noticeable symptoms of growth plate fractures include pain at the site of the fracture, swelling near the end of the affected bone, tenderness to the touch, and difficulty moving the injured area. In some cases, there may also be a visible deformity if the bone is displaced.
3. How can I tell if my child has a growth plate fracture?
If your child exhibits persistent pain, swelling, or difficulty in using a limb following an injury, it’s essential to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can perform physical examinations and imaging tests, such as X-rays, to diagnose a growth plate fracture.
4. Are there specific activities that increase the risk of growth plate fractures?
Yes, children who participate in sports or physical activities are at a higher risk of sustaining growth plate fractures due to increased chances of falls and impacts. Sports that involve contact, jumping, or rapid changes in direction contribute significantly to this risk.
5. Can growth plate fractures be treated without surgery?
Many growth plate fractures can be treated non-surgically with methods such as immobilization using casts or splints. However, the treatment depends on the severity and location of the fracture. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure proper healing and bone growth.
6. What is the long-term outlook for a child with a growth plate fracture?
With appropriate treatment, most children recover fully from growth plate fractures without long-term complications. However, if the growth plate is severely damaged, it could lead to problems with bone growth and require further medical intervention.
7. When should I take my child to see a doctor for a growth plate fracture?
You should consult a doctor immediately if your child shows signs of a fracture, such as severe pain, swelling, or difficulty in moving after an injury. Prompt medical evaluation is vital to prevent complications and ensure proper management of the fracture.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the symptoms and recognizing the causes of growth plate fractures is essential. These injuries can have significant implications on a child’s development and future bone health. Common signs include pain, swelling, and the inability to move the affected area, which should never be ignored.
We strongly encourage parents and guardians to seek prompt medical attention if a growth plate fracture is suspected. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to ensure proper healing and to prevent potential long-term complications. Remember, taking immediate action can make a significant difference in your child’s recovery and overall well-being. Prioritizing health and timely care is paramount in managing these injuries effectively.
References
For further reading and validation of the information provided on symptoms of growth plate fractures, the following reputable sources are recommended. These resources offer detailed insights and additional data that can be useful for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of this medical condition:
- Mayo Clinic – A comprehensive guide to the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for growth plate fractures. Access their detailed article here.
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) – Provides an in-depth overview of growth plate fractures, including how these injuries can affect children’s developing bones. Read more on the AAOS website here.
- KidsHealth from Nemours – Offers easy-to-understand information aimed at parents and guardians about the symptoms and treatments of growth plate fractures in children. The article is available here.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine – A valuable resource for information on the potential long-term effects of growth plate injuries and how they are managed. Visit their page here.
- MedlinePlus – A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine that provides robust information on various health topics, including growth plate fractures. They feature a resource page that can be found here.
Each of these resources has been selected for their authority and reliability in the field of orthopedics and pediatric medicine. They provide a solid foundation for understanding the complexities associated with growth plate fractures.