Growth Plate Fractures Treatment: Growth plate fractures are critical injuries that affect children and adolescents whose bones are still developing.
These fractures occur in the growth plate, which is the area of developing tissues at the end of the long bones. This region is crucial as it determines the future length and shape of the mature bone.
Understanding the mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of growth plate fractures is essential for optimal recovery and prevention of potential long-term complications.
Understanding Growth Plate Fractures
Growth plate fractures are a significant concern in pediatric orthopedics, primarily affecting children and adolescents whose bones are still developing. This article will explore what growth plates are, their critical role in child development, the common causes of growth plate fractures, and the symptoms parents and caregivers should watch for.
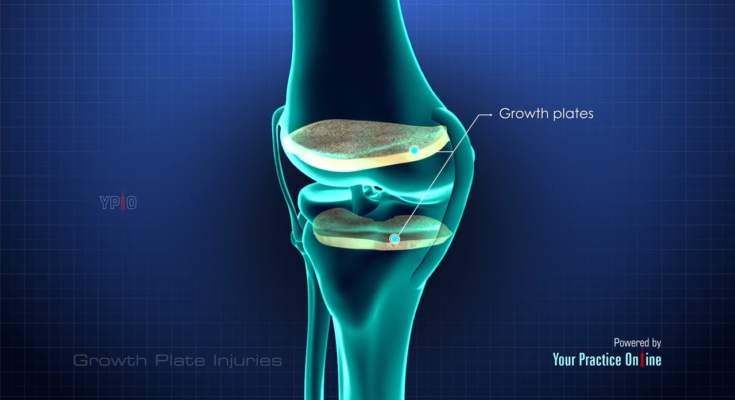
What are Growth Plates?
Growth plates, also known as epiphyseal plates, are areas of cartilage located near the ends of long bones in children and adolescents. These plates are found in many bones, such as the femur, tibia, and forearm bones. They are crucial for bone growth and determine the future length and shape of the mature bone. As a child grows, these plates gradually harden and transform into solid bone, a process that completes by the end of adolescence.
Causes of Growth Plate Fractures
Growth plate fractures can occur from several causes, each linked to the vulnerability of these developing tissues. Key causes include:
- Physical Trauma: Common in sports accidents, falls, or serious impacts during play or athletic activities.
- Overuse: Repetitive stress from sports like gymnastics or baseball can lead to stress fractures in the growth plates.
- Auto Accidents: High-force impacts during auto accidents can cause severe growth plate injuries.
- Falls: A fall from a height, like from playground equipment, can cause direct harm to these sensitive areas.
Common Symptoms of Growth Plate Fractures
Recognizing the symptoms of a growth plate fracture early can lead to better outcomes and prevent long-term damage. Here are the most common symptoms to look out for:
- Pain and Tenderness: The affected area will be painful, especially during movement or when pressure is applied.
- Swelling and Redness: The area around the injured growth plate may swell and appear red.
- Difficulty Moving the Affected Limb: If the fracture is near a joint, the child might have trouble moving that limb normally.
- Visible Deformity: In severe cases, the limb may look crooked or unusually shaped.
Parents and caregivers who observe these symptoms should seek medical advice promptly to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention is crucial to manage growth plate fractures effectively and to support the child’s ongoing growth and development.
Diagnosing Growth Plate Fractures
Accurately diagnosing these fractures is crucial for ensuring appropriate treatment and preventing potential long-term issues in bone growth. Here, we delve into the diagnostic process, highlighting the critical steps and challenges involved.
Steps in the Diagnostic Process
1. Medical History Evaluation: The first step in diagnosing a growth plate fracture involves a thorough review of the child’s medical history. Doctors will ask about the circumstances of the injury, any previous injuries, and the presence of symptoms such as pain, swelling, or difficulty in using the affected limb.
2. Physical Examination Highlights: During the physical examination, medical professionals will look for signs of growth plate fractures. This includes checking for tenderness at the site of the growth plate, assessing the range of motion, and evaluating any apparent deformities or swelling.
3. Imaging Tests: Imaging plays a pivotal role in diagnosing growth plate fractures.
- X-rays: These are typically the first imaging tests used. X-rays can show if there are any disruptions or shifts at the growth plate.
- MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is utilized when the X-ray results are inconclusive or to assess the extent of soft tissue involvement. MRI is particularly useful in identifying growth plate fractures that do not appear on X-rays.
Challenges in Diagnosing Growth Plate Fractures
Diagnosing growth plate fractures can be challenging. These fractures may not always be visible on X-rays, especially if they are non-displaced (the bone fragments remain aligned). Additionally, since growth plates have not yet hardened into solid bone, they can be difficult to differentiate from normal growth patterns on standard X-rays. This makes MRI and sometimes CT scans essential tools when the diagnosis is unclear.
Importance of Early and Accurate Diagnosis
The importance of early and accurate diagnosis of growth plate fractures cannot be overstated. Incorrect or delayed diagnosis can lead to improper healing, which might result in permanent deformities or discrepancies in limb length. Early detection and appropriate management ensure that children can recover fully and continue to grow normally.
However, diagnosing growth plate fractures requires a combination of detailed medical history, careful physical examination, and precise imaging techniques. Recognizing the challenges in identifying these injuries is key to managing them effectively and preventing potential long-term complications in a young patient’s growth and development.
Treatment Options for Growth Plate Fractures
This guide outlines effective treatment strategies, focusing on principles such as immobilization and rest, non-surgical and surgical interventions, and post-treatment care.
General Treatment Principles
The initial approach to treating growth plate fractures typically involves general principles aimed at stabilizing the fracture and promoting healing:
- Immobilization: Using casts, splints, or braces to keep the affected limb stable and prevent further injury.
- Rest: Limiting activities that put stress on the injured area to reduce pain and facilitate healing.
- Ice and Elevation: Applying ice packs to reduce swelling and elevating the affected limb to decrease inflammation.
These steps are critical in preventing further damage and ensuring the best possible healing environment for the growth plate.
Non-surgical Treatments
In many cases, growth plate fractures can be effectively managed without surgery:
- Casting: Most common non-surgical treatment that involves placing the injured limb in a cast to ensure proper alignment and stability as the fracture heals.
- Physical Therapy: After sufficient healing has occurred, physical therapy may be recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Activity Modifications: Adjusting the child’s activities and avoiding high-impact sports until the fracture has completely healed.
Non-surgical treatments are preferred whenever possible, as they involve less risk and typically result in excellent outcomes.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery might be necessary if the fracture is severe, particularly if the pieces of bone are misaligned (displaced fracture):
- Reduction Surgery: This procedure involves the surgeon manually aligning the displaced bones before immobilizing them with a cast.
- Internal Fixation: In cases where alignment cannot be maintained with casting alone, surgical pins, screws, or plates may be used to hold the bones in place.
- Follow-up Surgeries: Occasionally, additional surgeries are required to remove hardware or address complications or delays in healing.
Surgical treatment aims to ensure that bones are properly aligned for normal growth and development.
Post-treatment Care and Monitoring
After initial treatment, whether surgical or non-surgical, ongoing care and monitoring are essential to ensure optimal recovery:
- Regular Follow-ups: Visiting a healthcare provider for periodic check-ups to monitor the healing progress.
- Monitoring for Complications: Keeping an eye on potential issues such as delayed healing, infection, or abnormal bone growth.
- Gradual Return to Activities: Slowly reintroducing physical activities, guided by a healthcare professional, to avoid re-injury.
Effective post-treatment care is crucial for a full recovery and to minimize the risk of long-term effects on the growth plate.
By adhering to these treatment guidelines, growth plate fractures can be managed successfully, allowing children and adolescents to return to their daily activities without lasting damage.
Complications and Management of Growth Plate Fractures
Here, we delve into the potential complications and explore the management strategies essential for promoting optimal recovery and minimizing long-term impact.
Potential Complications of Growth Plate Fractures
- Growth Disturbances: The most significant complication of a growth plate fracture is the potential disturbance in the bone’s growth. Depending on the severity and location of the fracture, it can lead to shortened or uneven limb lengths.
- Angular Deformities: If the growth plate heals improperly, it can cause the bone to grow at an angle, resulting in deformities that might require surgical intervention to correct.
- Joint Problems: Fractures that extend into the joints can lead to arthritis early in life due to the joint surface becoming uneven.
- Functional Impairment: Severe growth plate fractures can impact the function of the affected limb, affecting mobility and daily activities.
Understanding these complications underscores the importance of effective management strategies to ensure a child’s healthy growth and development post-injury.
Long-term Management Strategies
- Timely and Accurate Diagnosis: Early and accurate assessment using X-rays, MRI, or CT scans is crucial for determining the severity of the fracture and planning the treatment accordingly.
- Appropriate Treatment Options: Treatment may range from non-invasive methods like casting and rest to surgical interventions, depending on the fracture’s complexity. Ensuring the treatment is suitable for the type of fracture is key to effective healing.
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: After the initial treatment, ongoing rehabilitation through physical therapy is vital to restore full function and strength to the affected area.
- Monitoring Growth and Development: Regular check-ups are necessary to monitor the affected limb’s growth and catch any deviations early enough to manage them effectively.
Role of Follow-Up Visits and Ongoing Care
- Regular Monitoring: Follow-up visits allow healthcare providers to monitor the healing process, ensuring that the bone is healing correctly and the growth plate is functioning well.
- Adjusting Treatment as Needed: Ongoing care might involve adjusting treatment plans based on how well the fracture is healing. This can include modifying physical therapy routines or, in some cases, additional surgical interventions.
- Educating the Family: Keeping the family informed about the care process and what signs to watch for regarding potential complications is crucial. Education also involves teaching families how to support their child’s recovery at home.
- Psychological Support: Offering support to deal with the emotional impact of a long-term recovery process can be beneficial, especially for young patients who may struggle with temporary limitations.
By understanding the complications, adhering to long-term management strategies, and emphasizing the importance of follow-up visits, healthcare providers can significantly influence the outcomes for young patients with these injuries.
Preventing Growth Plate Fractures
Proper awareness and preventive strategies are essential in reducing the risk of these injuries. Here, we explore effective measures to prevent growth plate fractures and the importance of educating both parents and coaches on the risk factors and early signs.
Preventive Measures
- Appropriate Equipment: Ensure that children use sports equipment that is appropriate for their age, size, and skill level. This includes protective gear such as helmets, wrist guards, and proper footwear, which can significantly decrease the risk of injury.
- Proper Training and Techniques: Children should be trained in proper techniques and form, especially in sports that involve jumping and physical contact. This training should be age-appropriate and gradually increase in intensity to avoid overloading their developing bones.
- Adequate Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Encouraging a routine of pre- and post-activity warm-ups and cool-downs can help prevent injuries. Stretching and light activities that increase heart rate gradually prepare the body for more strenuous exercise and reduce stress on growth plates.
- Balanced Nutrition: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone strength and development. Ensuring that children have a balanced diet that includes dairy products, leafy greens, and suitable supplements as recommended can contribute to stronger bones and a lower risk of fractures.
- Regular Rest: Adequate rest is crucial, especially during periods of rapid growth. Overuse injuries can occur when children are too active without enough recovery time, so ensuring regular rest days and adequate sleep is key.
Educating Parents and Coaches on Risk Factors and Early Signs
Education plays a pivotal role in preventing growth plate fractures. Parents and coaches should be made aware of the risk factors and signs of potential injuries:
- Recognizing Overuse: Teach parents and coaches to recognize the signs of overuse, such as persistent pain in a specific area, which often worsens with activity.
- Understanding the Impact of Physical Stress: Both parents and coaches should understand that excessive physical stress can lead to growth plate fractures, particularly in sports that require repetitive movements.
- Early Detection: Early detection of growth plate fractures can prevent more severe injury. Signs of a possible fracture include visible swelling, difficulty moving the affected limb, and acute pain during activity.
- Seeking Timely Medical Advice: It’s crucial that any concerns about potential growth plate injuries are addressed by a healthcare professional promptly to avoid long-term complications.
However, awareness and proper care can help maintain the health and well-being of growing children, ensuring they can safely enjoy the benefits of sports and physical activities.
FAQs on Growth Plate Fracture Treatment
What is a growth plate fracture?
A growth plate fracture refers to a break in the growth plate, which is the area of growing tissue near the ends of a child’s long bones. These fractures can occur in children and adolescents, impacting bone growth if not properly treated.
How are growth plate fractures diagnosed?
Growth plate fractures are diagnosed through physical examinations and imaging tests. Doctors often use X-rays to confirm the presence of a fracture. In some cases, MRI or CT scans might be required to assess the severity of the injury and to ensure accurate treatment planning.
What are the treatment options for growth plate fractures?
Treatment for growth plate fractures varies depending on the type and severity of the fracture. Common treatments include:
- Casting or splinting: To immobilize the affected area and allow it to heal properly.
- Surgery: In cases where the fracture is severe or displaced, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign and stabilize the bones.
- Physical therapy: After immobilization, physical therapy may be recommended to restore movement and strengthen the surrounding muscles.
How long does it take for a growth plate fracture to heal?
The healing time for a growth plate fracture depends on the severity of the fracture and the child’s age. Typically, it can take several weeks to months. Younger children often heal faster than older adolescents.
Can growth plate fractures lead to future problems?
If a growth plate fracture is not adequately treated, it can lead to issues such as stunted growth or the affected limb becoming shorter or crooked. Timely and appropriate treatment minimizes the risk of long-term complications.
Are there any activities to avoid during recovery?
During recovery, it’s crucial to avoid activities that put stress on the injured limb. High-impact activities such as jumping, running, or any contact sports should be avoided until the doctor confirms that the bone has sufficiently healed.
What should I do if I suspect my child has a growth plate fracture?
If you suspect that your child has sustained a growth plate fracture, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. Avoid applying pressure or trying to realign the limb yourself.
How can growth plate fractures be prevented?
While accidents happen, ensuring that children use appropriate safety equipment during sports and play can reduce the risk of fractures. Educating children on safe practices and supervising high-risk activities can also help prevent injuries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the significance of promptly recognizing and treating growth plate fractures is essential for ensuring the proper development and long-term health of children and adolescents. These fractures, if left untreated or mismanaged, can lead to serious complications, including improper bone growth and potential long-term mobility issues. Therefore, it’s crucial to seek expert medical advice immediately if a growth plate injury is suspected.
Parents, coaches, and caregivers are encouraged to act swiftly when an injury occurs, consulting healthcare professionals to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. By prioritizing the health of the growth plates, we can help maintain the overall well-being and physical development of young individuals.
Remember, the timely and effective treatment of growth plate fractures not only aids in a quicker recovery but also minimizes the risk of future complications. Always err on the side of caution and consult a medical professional to ensure the best care for our youth’s growing bodies.
References
For those seeking more information or wishing to verify the details provided regarding the treatment of growth plate fractures, we recommend consulting the following reputable sources. These resources offer comprehensive insights and are recognized for their credibility in the field of orthopedics and pediatric medicine.
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) – This site provides a detailed overview of growth plate fractures, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Read more about growth plate fractures at AAOS.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its patient-centered approach, the Mayo Clinic offers extensive information on the causes, treatments, and prevention of growth plate fractures. Visit Mayo Clinic’s resource on growth plate fractures.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine – A leader in medical research, Johns Hopkins provides valuable insights into pediatric fractures and their implications on child development. Explore Johns Hopkins Medicine for more on pediatric fractures.
- Medscape – Medscape offers a detailed article with professional insights into the diagnosis and management of growth plate fractures, which is particularly useful for healthcare providers. Learn more from Medscape on growth plate fractures.
- PubMed Central – An invaluable resource for those interested in academic and clinical studies, PubMed Central hosts multiple research articles on growth plate injuries and their treatments. Search for studies on growth plate fractures at PubMed Central.
These resources will provide comprehensive information and are excellent starting points for understanding the complexity and treatment of growth plate fractures in a pediatric population.