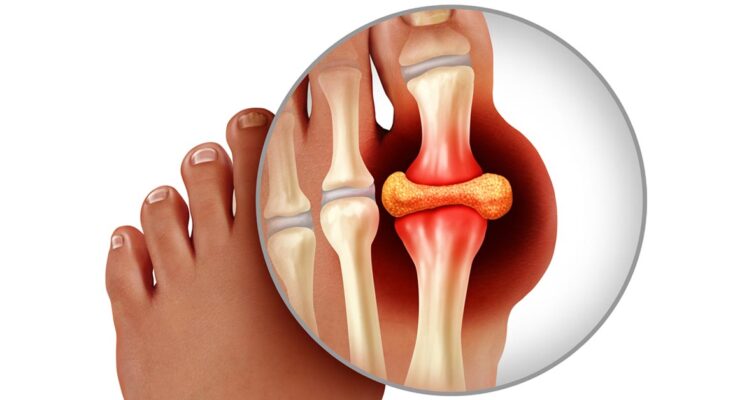
Gout Treatment: Gout is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, and redness in the joints.
It is caused by the deposition of urate crystals, typically resulting from elevated levels of uric acid in the blood.
Commonly affecting the base of the big toe, gout can influence other joints as well, including the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists.
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, often affecting the base of the big toe. It occurs when urate crystals accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation and intense pain. These crystals can form when there is a high level of uric acid in the blood, which might be due to dietary choices, certain health disorders, or family history.
Causes of Gout
Gout is primarily caused by hyperuricemia, where there is too much uric acid in the body. The following factors contribute to increased levels of uric acid, leading to gout:
- Dietary Choices: Consumption of foods rich in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood, increases the risk of developing gout. Beverages sweetened with fructose and alcoholic drinks, especially beer, can also elevate uric acid levels.
- Health Conditions: Certain diseases and conditions can increase susceptibility to gout, including high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome.
- Medications: Some medications may increase the level of uric acid, such as diuretics (used to treat hypertension), the anti-rejection drugs prescribed for transplant patients, and low-dose aspirin.
- Genetics: Family history of gout increases the likelihood of the condition manifesting.
Risk Factors for Developing Gout
Understanding the risk factors associated with gout can help in prevention and management. These include:
- Gender and Age: Gout is more common in men than women and typically affects men between the ages of 30 and 50. Women become more susceptible to gout after menopause.
- Lifestyle Factors: Excessive alcohol intake, particularly beer, and a diet high in purine-rich foods (e.g., red meats, certain seafood) significantly increase the risk of gout attacks.
- Obesity: Higher body weight is associated with increased uric acid production and decreased elimination of uric acid.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, heart and kidney diseases also raise the risk.
- Medication Use: Use of certain medications like diuretics and drugs that contain salicylate can contribute to elevated uric acid levels.
By managing these risk factors through lifestyle changes and medication, it is possible to reduce the frequency of gout attacks and improve quality of life for those affected.
Symptoms of Gout
Understanding the common symptoms of gout and how it differs from other joint-related issues is crucial for timely diagnosis and management.
Common Symptoms Associated with Gout
The symptoms of gout are distinct and typically occur suddenly, often waking people during the night with the sensation that their affected joint is on fire. The key symptoms include:
- Intense Joint Pain: Gout usually affects the large joint of your big toe, but it can occur in any joint. Other commonly affected areas include the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers. The pain is most severe within the first four to twelve hours after it begins.
- Lingering Discomfort: After the most severe pain subsides, some joint discomfort may last from a few days to a few weeks. Subsequent attacks are likely to last longer and affect more joints.
- Inflammation and Redness: The affected joint or joints become swollen, tender, warm, and red.
- Limited Range of Motion: As gout progresses, you may not be able to move your joints normally.
Differentiating Gout from Other Joint-Related Issues
Gout can be mistaken for other joint conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, or septic arthritis due to overlapping symptoms. However, gout has unique characteristics that help differentiate it:
- Sudden Onset of Pain: Unlike other forms of arthritis that develop slowly, gout typically manifests as sudden, intense bouts of pain.
- Affected Areas: Gout often targets the joint at the base of the big toe, which is less common in other arthritis types.
- Uric Acid Crystals: Gout is caused by an accumulation of urate crystals in the joint, resulting from high levels of uric acid in the blood. This is a specific cause not associated with other forms of arthritis.
- Response to Diet: Gout can be triggered by dietary factors like red meat, alcohol, and seafood, which is less typical for other joint disorders.
If you suspect you have gout, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider who can perform tests, such as joint fluid analysis or blood tests, to confirm the diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment strategies.
Diagnosis of Gout
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here’s a closer look at the initial assessment, the diagnostic tests involved, and why early diagnosis is vital.
Initial Assessment and Medical History Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing gout involves a detailed evaluation of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination. Healthcare providers will ask about the frequency, duration, and severity of joint pain episodes. They will also inquire about lifestyle factors such as diet, alcohol consumption, and family history of gout or kidney disease. This information helps to distinguish gout from other types of arthritis and conditions with similar symptoms.
List of Diagnostic Tests for Gout
To confirm a diagnosis of gout, several tests are typically performed:
- Joint Fluid Analysis (Arthrocentesis): The most definitive test for gout involves extracting fluid from the affected joint and examining it under a microscope for the presence of urate crystals.
- Blood Tests: While not definitive, blood tests can measure the levels of uric acid in the blood; however, some people may have high uric acid levels without having gout.
- Ultrasound: This imaging test can detect urate crystals in joints or soft tissue, even when there is no active inflammation.
- X-rays: These can help rule out other joint or bone-related issues but cannot detect gout in its early stages.
- Dual-energy CT Scan: This specialized imaging test can detect the presence of urate crystals in joints, even when there is no visible inflammation, making it useful in complex cases.
Importance of Early Diagnosis in Gout Management
Early diagnosis of gout is essential for several reasons. Timely treatment can help manage the pain and inflammation associated with acute attacks and prevent future flare-ups. Early intervention also reduces the risk of complications, such as the development of tophi (hard, urate crystal deposits under the skin) or chronic joint damage.
Moreover, managing gout effectively from the onset can improve the quality of life and prevent the disease’s progression, which is crucial since gout can be linked with other serious health issues, including kidney disease and cardiovascular problems.
However, understanding the importance of an accurate and early diagnosis can empower patients to seek prompt medical advice and adhere to treatment plans, thereby improving outcomes in gout management.
Treatment Options for Gout
Gout, a form of arthritis characterized by severe pain, redness, and tenderness in joints, primarily demands a strategic treatment plan aimed at managing acute symptoms and preventing future attacks. Understanding the treatment options available can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively and maintain a higher quality of life.
Introduction to Treatment Goals
The primary goals of treating gout include managing the intense pain during flare-ups and minimizing the risk of future attacks. Successful management also aims at reducing uric acid levels, which are often the underlying cause of gout, to prevent the formation of urate crystals in the joints. By achieving these objectives, patients can reduce the frequency and severity of gout episodes and minimize potential complications, such as joint damage or kidney stones.
Medications Used in Gout Treatment
A variety of medications are available that target different aspects of gout management:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These are often the first line of defense in treating gout pain and inflammation. Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen reduce inflammation and pain, whereas higher strength NSAIDs may be prescribed for more severe symptoms.
- Colchicine: This medication is particularly effective at reducing gout pain and is often used when patients cannot tolerate NSAIDs. It works by decreasing the build-up of uric acid crystals, thus mitigating inflammation and discomfort.
- Corticosteroids: For patients who cannot take NSAIDs or Colchicine, corticosteroids can be an alternative. They can be taken orally or injected directly into the inflamed joint to quickly reduce swelling and pain.
Latest Advancements in Medications and Therapies
The field of gout treatment has seen significant advancements with the development of new medications and therapeutic approaches:
- Uric Acid-Lowering Drugs: New drugs, such as febuxostat and allopurinol, focus on reducing the production of uric acid or increasing its excretion. These medications are helpful for chronic management and in preventing the complications associated with high uric acid levels.
- Biologic Agents: Recent breakthroughs include the use of biologic agents that target specific inflammatory pathways involved in gout. For example, drugs like pegloticase offer options for patients who have not responded to traditional therapies, by helping to rapidly decrease high levels of uric acid.
- Diet and Lifestyle Modifications: Alongside medications, dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing and preventing gout. Reducing consumption of foods high in purines, such as red meat and seafood, and eliminating alcohol can significantly lower the risk of flare-ups.
By staying informed about the latest treatment options and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with gout can effectively manage their symptoms and reduce the frequency of attacks. Advances in medication and ongoing research promise even more effective treatments in the future, offering hope to those suffering from this painful condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies of Gout
Managing gout effectively involves more than just medication; it also requires specific lifestyle adjustments and home remedies. These changes can help reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks. Here’s what you need to know about dietary recommendations, hydration, and the role of weight management and exercise.
Dietary Recommendations and Foods to Avoid
Diet plays a crucial role in managing gout, as certain foods can trigger flare-ups by raising uric acid levels in the blood. Here are some dietary tips:
- Limit Purine-Rich Foods: High-purine foods can increase uric acid. Avoid or reduce intake of red meat, organ meats like liver, and certain seafood such as anchovies and sardines.
- Cut Down on Sugary Foods and Beverages: Sugary foods and drinks, especially those containing high-fructose corn syrup, can also elevate uric acid levels.
- Reduce Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, can trigger gout attacks. Limiting alcohol intake can significantly reduce the risk.
- Incorporate Low-Purine Foods: Focus on eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins like chicken or turkey. These foods are lower in purines and are healthier choices for individuals with gout.
Importance of Hydration and Specific Beneficial Practices
Staying well-hydrated is essential for gout sufferers because it helps the body flush out uric acid, thereby reducing the risk of painful crystal formations in joints:
- Drink Plenty of Water: Aim for 8-10 glasses of water a day. This helps to dilute uric acid in the urine and promotes its excretion.
- Consider Adding Lemon to Water: Some studies suggest that lemon water can help neutralize uric acid in the bloodstream, making it a beneficial practice for gout patients.
Impact of Weight Management and Exercise on Gout Symptoms
Managing your weight and maintaining a regular exercise routine can have a significant impact on the management of gout:
- Weight Management: Being overweight increases the risk of developing gout, and losing weight can reduce uric acid levels and gout attacks. Aim for gradual weight loss through a balanced diet rather than extreme calorie restriction, which can temporarily increase uric acid levels.
- Regular Exercise: Exercise helps reduce uric acid levels and maintain a healthy weight. However, it’s important to choose low-impact activities that do not strain the joints, such as swimming, biking, or yoga.
By implementing these lifestyle and dietary changes, individuals with gout can often see a noticeable improvement in their symptoms and overall health. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are also important to monitor the condition and adjust any treatments as needed.
Alternative Treatments and Supplements for Gout
In addition to traditional medical treatments, many individuals turn to alternative treatments and supplements to help manage their symptoms. Here, we explore the effectiveness of natural remedies, supplements, and complementary therapies for gout relief.
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Gout
Cherry Extract
Cherry extract is one of the most popular natural supplements for gout. Studies have shown that cherries help reduce the levels of uric acid in the blood, which is the main cause of gout attacks. Cherries also possess anti-inflammatory properties that may help lessen inflammation associated with gout flare-ups. Consuming cherry extract or fresh cherries regularly can be a beneficial addition to gout management strategies.
Celery Seed Extract
Celery seed extract is another supplement favored by those seeking natural gout relief. It is believed to have several beneficial properties, including diuretic effects that can help eliminate uric acid from the body. Additionally, celery seed has anti-inflammatory agents that might reduce the swelling and pain of gout attacks. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting celery seed extract, especially for those on diuretics or other medications.
Complementary Therapies for Gout
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to balance energy flow. For gout sufferers, acupuncture may help alleviate pain and improve joint function by reducing inflammation and promoting circulation. Although more research is needed to fully understand its benefits for gout, many patients report significant relief from their symptoms following acupuncture treatment.
Reflexology
Reflexology involves applying pressure to specific points on the feet, hands, or ears, which correspond to different body organs and systems. While there is limited scientific research specifically on reflexology for gout, it is thought to help by enhancing relaxation, reducing stress, and improving circulation. These effects can indirectly contribute to reducing gout flare-ups and pain.
While conventional medical treatments should not be overlooked, incorporating alternative treatments and supplements like cherry and celery seed extracts, as well as therapies such as acupuncture and reflexology, can provide additional relief from gout symptoms. As with any treatment, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure these options are safe and appropriate for your specific health needs. By considering a holistic approach to gout management, individuals may find more comprehensive relief and potentially reduce the frequency and intensity of their symptoms.
Long-Term Management of Gout: Effective Strategies and Essential Practices
Managing gout effectively over the long term is crucial to prevent complications and reduce the frequency of painful flare-ups. By incorporating strategic preventive measures, regular medical consultations, and thorough patient education, individuals with gout can lead healthier and more comfortable lives. This guide outlines the key components of long-term gout management.
Preventing Gout Complications and Reducing Flare-Up Frequency
Preventive strategies play a pivotal role in managing gout long-term. Key to these strategies is the modification of diet and lifestyle factors that trigger gout attacks. Reducing the intake of purine-rich foods, such as red meats and certain types of seafood, and minimizing alcohol consumption, especially beer, are foundational steps. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can significantly lower the risk of recurrent gout attacks. Regular exercise not only helps in weight management but also improves overall metabolic health, further reducing gout flare-ups.
The Role of Regular Medical Check-Ups and Ongoing Treatment Adjustments
Regular medical check-ups are essential for effective gout management. These visits allow healthcare providers to monitor the effectiveness of prescribed treatments and make necessary adjustments. Blood tests to measure uric acid levels are a common aspect of these check-ups. Based on these results, medications such as allopurinol or febuxostat may be adjusted to maintain uric acid at a healthy level, preventing the formation of urate crystals in the joints.
Moreover, during these appointments, doctors can assess the need for anti-inflammatory treatments to manage pain during acute gout attacks. This proactive approach ensures that treatment remains tailored to individual needs and responses, which is crucial for long-term disease management.
Importance of Patient Education on Gout Management
Educating patients about gout and its management is fundamental to successful long-term outcomes. Comprehensive patient education includes understanding the causes of gout, factors that trigger flare-ups, and the importance of adherence to prescribed treatment regimens. Equipping patients with this knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about their health and to recognize early signs of flare-ups, enabling prompt action to mitigate symptoms.
Furthermore, patient education should also cover the effective use of medications, including their potential side effects and the importance of regular medication intake even when symptoms are not present. This understanding helps prevent the common pitfalls of discontinuing medication prematurely, which can lead to severe complications.
Long-term management of gout involves a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, regular medical oversight, and comprehensive patient education. By adhering to these strategies, individuals with gout can manage their condition effectively, reducing both the frequency of flare-ups and the risk of complications. Ultimately, a proactive and informed approach to gout management fosters better health outcomes and an improved quality of life.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is gout and how is it diagnosed?
Gout is a type of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, often the joint at the base of the big toe. Diagnosis typically involves a review of medical history, a physical examination, and tests such as blood tests to measure uric acid levels and joint fluid tests where fluid is drawn from the affected joint to look for urate crystals.
What are the common treatments for gout?
Gout treatment focuses on relieving pain during attacks and reducing uric acid levels to prevent future episodes. Common medications include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids for managing acute attacks. To reduce uric acid levels, medications like allopurinol and febuxostat may be prescribed.
Can diet affect gout symptoms?
Yes, diet plays a significant role in managing gout symptoms. Foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and some seafood, should be avoided as they can increase uric acid levels. Alcohol, especially beer and liquors, and sugary beverages should also be limited. Emphasizing low-purine foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, can help manage symptoms.
Is exercise recommended for someone with gout?
Exercise is beneficial for overall health and can help maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for managing gout. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking are generally safe and beneficial for individuals with gout. It’s important to avoid high-impact activities during acute gout attacks as they can exacerbate pain and inflammation.
How long do gout attacks last, and can they be prevented?
Gout attacks typically last from a few days to a couple of weeks and can be prevented with medication and lifestyle changes. Regularly taking prescribed medications, managing diet, maintaining a healthy body weight, and staying hydrated are essential steps in preventing recurrent gout attacks.
Can gout lead to other health issues?
If left untreated, gout can lead to more severe health issues, including chronic arthritis, kidney stones, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. It is important to manage uric acid levels effectively to prevent these complications.
When should I see a doctor for gout?
You should see a doctor if you experience sudden, intense pain in any joint, recurrent joint pain, or signs of an infection such as fever and joint swelling. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing gout effectively and preventing complications.
Conclusion
In summary, gout is a manageable condition with a variety of effective treatments available. From lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and increased physical activity to medical treatments like anti-inflammatory drugs and uric acid-lowering medications, patients have several options to control and alleviate their symptoms. It’s important to remember that while these treatments can significantly improve quality of life, they are most effective when tailored to individual needs and conditions by a healthcare professional.
If you are experiencing symptoms of gout or have concerns about your treatment plan, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider. They can offer personalized advice and adjustments to your treatment strategy, ensuring you receive the most appropriate care. Don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice to manage your gout effectively and maintain your health.
By staying informed and proactive in your healthcare decisions, you can effectively manage gout and lead a healthier, more comfortable life.
References
For those interested in further exploring the treatment options and research related to gout, we recommend consulting the following reputable sources. These references provide in-depth information and validation of the treatments discussed, aiding in a better understanding of managing this condition.
- Mayo Clinic – Gout Treatment and Drugs: The Mayo Clinic offers a comprehensive overview of gout treatments, including medications and lifestyle changes that can help manage the disease. Explore their guide at Mayo Clinic Gout Treatment.
- Arthritis Foundation – Managing a Gout Attack: This resource provides practical tips on managing acute gout attacks and long-term treatment to prevent future flare-ups. Read more at Arthritis Foundation Gout Management.
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) – Gout: NIAMS offers detailed information on the causes, symptoms, and treatments of gout, supported by the latest research. Visit their site at NIAMS Gout Information.
- American College of Rheumatology – Gout: This professional organization provides guidelines and educational materials on the best practices for the treatment of gout. Learn more by accessing American College of Rheumatology Guidelines.
Each of these sources is recognized for its authority and reliability in the field of healthcare, making them excellent starting points for anyone looking to understand more about gout and its management.