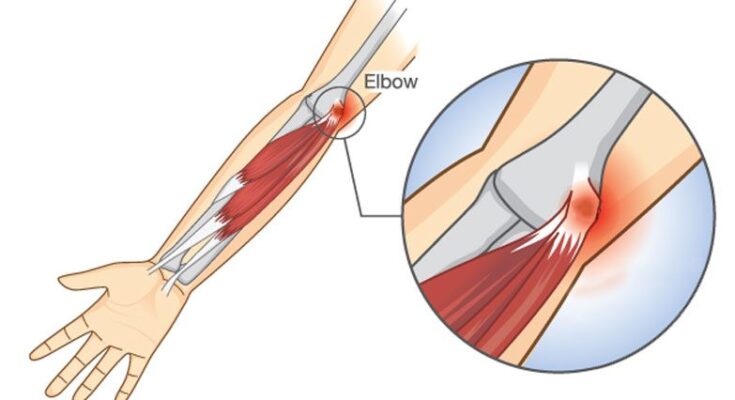
Golfer’s Elbow Treatment: Golfer’s elbow, medically known as medial epicondylitis, is a condition that affects the muscles and tendons of the forearm that attach to the medial epicondyle—the inner aspect of the elbow.
It is characterized by pain and tenderness on the inside of the elbow, which can significantly affect one’s ability to grip or carry objects.
Contrary to what the name might suggest, this condition is not limited to golfers and can affect anyone who engages in activities that require repetitive wrist and forearm movements.
Understanding Golfer’s Elbow
Golfer’s elbow, medically known as medial epicondylitis, is a condition that results from overuse or strain on the muscles and tendons of the forearm, leading to pain and tenderness on the inside of the elbow. Unlike its counterpart, tennis elbow, which affects the outside of the elbow, golfer’s elbow is characterized by discomfort on the inner side. The condition stems from activities that require repetitive wrist and finger motions, not just limited to golf, making it a common ailment among various sports enthusiasts and manual laborers.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of golfer’s elbow is repetitive or excessive stress, particularly forceful wrist and finger motions. Here are some common causes and risk factors:
- Sports Activities: While it’s named after golf, other sports such as baseball, bowling, and racket sports can also lead to golfer’s elbow due to similar repetitive movements.
- Occupational Hazards: Jobs that involve repetitive motions, like construction, plumbing, or painting, can increase the risk of developing golfer’s elbow.
- Age and Frequency: Individuals aged between 40 and 60 are more susceptible. Frequent and intense activity can exacerbate the strain on the muscles and tendons.
- Improper Technique: Using the wrong technique in sports or at work can put unnecessary pressure on the elbow, leading to the condition.
Symptoms to Recognize Golfer’s Elbow
Recognizing the symptoms of golfer’s elbow early can aid in effective management and prevention of further injury. Key symptoms include:
- Pain and Tenderness: Pain on the inner side of the elbow, which might extend along the inner forearm.
- Stiffness: The elbow may feel stiff, and making a fist might be painful.
- Weakness: Weakness in the hands and wrists is common, making it difficult to perform routine tasks like opening a jar or holding a coffee cup.
- Numbness or Tingling: Some may experience tingling sensations that extend into the fingers, usually affecting the ring and little fingers.
However, understanding these aspects of golfer’s elbow is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. If you suspect you have golfer’s elbow, consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Diagnosing Golfer’s Elbow
Proper diagnosis is key to managing and treating this condition effectively. Below, we outline when to seek medical advice, which health professionals to consult, and the diagnostic tests and procedures that may be employed.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent pain on the inside of the elbow that does not improve with basic home care, such as rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers. Other signs that warrant professional medical advice include:
- Pain that worsens or does not improve after several days of home treatment
- Severe elbow pain, swelling, or redness
- Pain that radiates from the elbow towards the wrist
- Difficulty in moving the elbow or performing daily activities
- Signs of an infection, such as fever or a feeling of warmth around the elbow
Health Professionals Who Can Diagnose Golfer’s Elbow
Several types of health professionals can diagnose Golfer’s Elbow, depending on the severity of the symptoms:
- Primary Care Physicians: Often the first point of contact, they can provide initial diagnosis and treatment.
- Orthopedic Specialists: Doctors specialized in bone, muscle, and joint issues, ideal for severe cases.
- Sports Medicine Physicians: Experts in sports injuries who offer specialized care for sports-related musculoskeletal issues.
- Physical Therapists: They can diagnose and help manage the condition through therapeutic exercises and other rehabilitation techniques.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
To confirm a diagnosis of Golfer’s Elbow, healthcare providers may use several methods:
- Physical Exams: The doctor may apply pressure to the affected area or ask you to move your elbow, wrist, and fingers in various ways to check for pain and stiffness.
- Imaging Tests: Although not always necessary, tests like X-rays can rule out other causes of elbow pain, such as fractures or arthritis. In some cases, more detailed imaging, such as MRI or ultrasound, might be recommended to assess the soft tissue in the elbow.
- Medical History: A thorough discussion of your symptoms, activities, and any prior injuries that may contribute to the condition.
If you suspect you have this condition, seeking timely medical advice is the first step towards recovery. With the right combination of professional care and self-management strategies, most individuals can return to their normal activities without lasting discomfort.
Treatment Options for Golfer’s Elbow
Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available, ranging from home remedies to surgical interventions for more severe cases. Here’s a closer look at the treatment options for golfer’s elbow.
Home Remedies and Self-Care Strategies
For many, the treatment of golfer’s elbow begins with simple home remedies and self-care strategies. These are particularly effective in early stages or mild cases:
- Rest and Ice: Giving your arm proper rest is crucial; avoid activities that exacerbate the pain. Applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression and Elevation: Using an elbow strap to reduce strain on the injured tendons can be beneficial. Elevating the arm can also help reduce swelling.
- Exercises and Stretching: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can improve flexibility and reduce tension in the muscles. It’s important to do these under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid further injury.
- Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or aspirin can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any medication.
Medical Treatments
If symptoms persist despite the application of home remedies, consulting a healthcare provider for medical treatment is advised:
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to gradually stretch and strengthen the muscles around the elbow. Therapy may also include techniques like ultrasound, massage, or muscle-stimulating techniques to improve muscle healing.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For more severe or persistent pain, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation. However, the effects are usually temporary and repeated use can weaken tendons over time.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections: This newer treatment involves injecting a concentration of a patient’s own platelets to accelerate the healing of injured tendons. Research on the effectiveness of PRP for golfer’s elbow is ongoing.
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
In cases where nonsurgical treatments fail to relieve symptoms after 6 to 12 months, surgery may be considered:
- Open Surgery: The most common approach for treating severe golfer’s elbow involves making an incision over the elbow to remove the damaged muscle and reattach healthy muscle back to bone.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: In some cases, the procedure can be performed using an arthroscope, a type of endoscope inserted into the joint through a small incision. This method is less invasive and can reduce recovery time.
It’s essential to discuss all available treatment options with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate approach based on the severity of your condition. Effective management and treatment of golfer’s elbow are crucial to ensure a full return to daily activities without persistent pain.
Recovery and Management of Golfer’s Elbow
Expected Recovery Times
Recovering from Golfer’s Elbow can vary significantly from one individual to another, depending on the severity of the condition and the treatment approach used. Typically, recovery time can range from several weeks to a few months. For mild cases, individuals may experience significant improvement within 3 to 6 weeks. However, more severe cases may require a few months of consistent treatment and rest to fully heal. It is crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance and not rush the recovery process, as premature return to activity can exacerbate the condition.
Tips for Managing Symptoms During Recovery
Managing symptoms effectively can accelerate your recovery from Golfer’s Elbow. Here are some practical tips to help you manage symptoms and aid in the healing process:
- Rest: Give your arm adequate rest and avoid activities that strain the elbow or cause pain.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs to the elbow for 15-20 minutes every few hours to reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Compression: Use an elbow strap or brace to reduce strain on the injured tendon and alleviate pain.
- Elevate: Keep your arm elevated when possible to help reduce swelling.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be used to manage pain and inflammation, following your doctor’s recommendations.
- Physical Therapy: Engage in physical therapy exercises tailored to strengthen the forearm muscles and improve flexibility without overstraining the tendon.
Strategies to Prevent Golfer’s Elbow Recurrence
Preventing the recurrence of Golfer’s Elbow involves adopting strategies that strengthen and protect your elbow. Here are effective strategies to minimize the risk:
- Strengthening Exercises: Regularly perform exercises that strengthen the forearm muscles.
- Proper Technique: Ensure proper technique in sports and activities, particularly in golf and tennis, to avoid unnecessary strain on the elbow.
- Equipment Check: Use equipment that suits your strength and body size. For instance, using a golf club or tennis racket that is too heavy can increase the risk of injury.
- Warm-Up: Always warm up before engaging in physical activity to prepare the muscles and tendons for the stress of exercise.
- Stretching: Incorporate stretching exercises into your routine to improve the flexibility of the forearm muscles.
- Gradual Increase in Activity: Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your activities to avoid sudden stress on the elbow.
By understanding and implementing these recovery and management strategies, you can effectively heal from Golfer’s Elbow and reduce the risk of its recurrence. Remember, consistent adherence to these guidelines is key to a successful recovery.
Alternative Treatments and Therapies for Golfer’s Elbow
Complementary Therapies
When managing the discomfort and symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow, many individuals turn to complementary therapies to enhance traditional medical treatments. Popular options include:
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting fine needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to stimulate nerves and muscles, potentially providing relief from pain and improving muscle function.
- Massage Therapy: Regular massage can help alleviate tension in the muscles and tendons affected by Golfer’s Elbow. It improves circulation, which aids in faster recovery and provides relief from pain and stiffness.
These therapies are generally considered safe and can be used alongside conventional medical treatments to manage symptoms more effectively.
Recent Advancements in the Treatment of Golfer’s Elbow
The field of sports medicine is continuously evolving, bringing forward new and innovative treatments for conditions like Golfer’s Elbow. Recent advancements include:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections: This treatment involves injecting a concentration of a patient’s own platelets directly into the affected tissue. The growth factors in the platelets promote natural healing and have shown promising results in reducing pain and improving joint function.
- Ultrasound Therapy: High-frequency sound waves are used to stimulate the deep tissues within the elbow. This method can help reduce inflammation, promote healing, and decrease pain.
These emerging treatments offer hope for those who do not respond well to traditional approaches, providing more options for effective management of the condition.
Discussion on the Effectiveness of Alternative Treatments
While alternative treatments for Golfer’s Elbow are gaining popularity, it is essential to discuss their effectiveness. Studies have shown mixed results, and the success of such treatments can vary significantly from person to person. For instance, acupuncture has been praised for its ability to reduce pain and inflammation in some, but not all, patients. Similarly, while massage therapy is widely used for muscle relaxation and pain management, its long-term benefits in treating Golfer’s Elbow specifically require more research.
Patients considering alternative treatments should consult with healthcare professionals to ensure these therapies are appropriate for their specific condition. Additionally, combining these therapies with conventional treatments, such as physical therapy and medication, often yields the best results.
By staying informed about the latest developments and understanding the potential of various treatments, individuals suffering from Golfer’s Elbow can make educated decisions about their health care and potentially improve their quality of life.
FAQs about Golfer’s Elbow Treatment
What is golfer’s elbow?
Golfer’s elbow, medically known as medial epicondylitis, is a condition that results from overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons near the elbow joint. It typically causes pain and tenderness on the inside of the elbow and forearm.
What are the main treatments for golfer’s elbow?
The primary treatments for golfer’s elbow include rest, ice application, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and, in severe cases, corticosteroid injections. It’s crucial to avoid activities that trigger pain, and gently stretch and strengthen the forearm muscles.
Can exercises help in recovering from golfer’s elbow?
Yes, specific exercises can aid in recovery. Stretching and strengthening exercises tailored to the forearm can improve flexibility and reduce stress on the elbow. However, it’s essential to perform these under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure they’re done correctly and safely.
How long does it take to recover from golfer’s elbow?
Recovery time can vary depending on the severity of the condition and adherence to treatment protocols. Typically, mild cases might improve within a few weeks, while more severe cases could take several months. Consistent management and following medical advice are key to recovery.
Is surgery necessary for golfer’s elbow?
Surgery is rarely required for golfer’s elbow. It is usually considered only after all other treatments have failed and the pain persists for 6 to 12 months. Surgical options can relieve pain and restore function but are typically the last resort.
Can golfer’s elbow recur?
Yes, golfer’s elbow can recur, especially if the underlying causes, such as repetitive motion activities, are not adequately addressed. Prevention strategies include using proper technique in sports and activities, strengthening exercises, and taking regular breaks.
When should I see a doctor for golfer’s elbow?
You should consult a doctor if you experience persistent elbow pain, significant swelling, or if the pain interferes with your daily activities. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from worsening.
Conclusion
In summary, treating Golfer’s Elbow involves a combination of rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and sometimes more advanced options like injections or surgery. While these treatments can significantly aid in recovery, it’s crucial to remember that every individual’s situation is unique.
For those suffering from this condition, we highly encourage consulting with a healthcare professional who can provide a personalized treatment plan. A tailored approach ensures that you receive the most appropriate care for your specific needs, enhancing your chances of a swift and effective recovery.
Remember, taking early action and seeking professional advice are key steps towards returning to your active lifestyle without the hindrance of pain.
References
For more detailed information and to validate the treatments discussed in this article, you can consult the following reputable sources:
- Mayo Clinic – Comprehensive overview of symptoms, causes, and treatments for Golfer’s Elbow. Access the guide here: Golfer’s Elbow – Mayo Clinic.
- WebMD – Provides insights into non-surgical treatments and preventative measures for Golfer’s Elbow. Read more at: Golfer’s Elbow Treatment – WebMD.
- Healthline – Explore an article on physical therapy exercises specifically designed for Golfer’s Elbow rehabilitation. Visit: Physical Therapy for Golfer’s Elbow – Healthline.
- PubMed Central – Research studies on the effectiveness of various treatments for Golfer’s Elbow, ideal for in-depth scientific understanding. Check out the studies: Treatment Research – PubMed Central.
Each of these resources offers valuable insights and evidence-based information to help you understand and manage Golfer’s Elbow effectively.