Glomerulonephritis Treatment: Glomerulonephritis, often referred to as glomerular nephritis, is an inflammatory condition of the glomeruli, the tiny structures in the kidneys responsible for blood filtration.
This critical renal disorder can lead to severe kidney dysfunction and, if not managed properly, to chronic kidney disease or kidney failure.
Understanding the diagnosis and comprehensive treatment options is essential for managing glomerulonephritis effectively.
What is Glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis, also known as glomerular nephritis, is a serious medical condition affecting the kidneys’ glomeruli. The glomeruli are tiny structures within the kidneys that perform the critical function of filtering blood to produce urine. When these structures become inflamed, the kidneys’ ability to filter waste, excess water, and electrolytes from the blood is compromised. This inflammation can result from a variety of causes, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and other systemic conditions. It may occur suddenly, referred to as acute glomerulonephritis, or develop slowly over time, known as chronic glomerulonephritis.
Types of Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis can be classified into several types based on its cause and the nature of the immune response involved:
- Acute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis: Typically follows a streptococcal infection of the throat or skin.
- IgA Nephropathy: Characterized by the deposition of the IgA antibody in the glomerulus.
- Membranous Nephropathy: Involves thickening of the glomerular basement membrane.
- Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis: A severe form that can lead to rapid loss of kidney function within days to weeks.
- Chronic Glomerulonephritis: Develops slowly and can lead to long-term kidney damage without significant symptoms initially.
Statistics on Prevalence and Impact
Glomerulonephritis is a leading cause of kidney disease worldwide. It is estimated to affect millions of individuals globally, significantly contributing to cases of acute and chronic kidney failure. In terms of impact, the condition not only affects individuals’ health by leading to potential kidney failure but also imposes a considerable economic burden due to long-term treatment costs and loss of productivity. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are critical in preventing severe outcomes associated with glomerulonephritis.
Causes and Risk Factors of Glomerulonephritis
Understanding the common causes and risk factors associated with this condition is crucial for both prevention and management.
Common Causes of Glomerulonephritis
- Infections: Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis can develop after infections of the throat or skin by certain strains of streptococcus bacteria.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like lupus and Goodpasture’s syndrome can prompt the body’s immune system to attack its own kidney tissues.
- Vascular diseases: Diseases such as vasculitis cause inflammation of the blood vessels, which can affect the kidneys.
- Other medical conditions: Chronic diseases, including diabetes and high blood pressure, can lead to glomerulonephritis as a secondary complication.
Risk Factors That Increase the Likelihood of Developing Glomerulonephritis
Several risk factors can increase a person’s chances of developing glomerulonephritis:
- Family history: Genetics play a significant role, with certain types of glomerulonephritis running in families.
- Age and gender: Some forms are more prevalent in younger individuals, particularly males.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups may be at higher risk depending on the genetic predisposition.
- Existing health conditions: Individuals with autoimmune diseases or recurrent infections are more susceptible.
- Environmental exposure: Exposure to certain chemicals or drugs can trigger glomerulonephritis.
The Role of Genetics and Environmental Factors
Genetics significantly influence the susceptibility to glomerulonephritis, with some types directly linked to genetic mutations. For instance, Alport syndrome, a genetic form of the disease, affects collagen in the kidneys. On the environmental side, factors like drug use, exposure to solvents, and certain infections can precipitate or exacerbate the condition. Understanding both genetic predispositions and environmental triggers can help in early diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies.
By identifying and mitigating these risk factors, individuals can better manage or even prevent the onset of glomerulonephritis, thus safeguarding kidney health. Awareness and regular medical check-ups are key components in the early detection and management of this condition.
Symptoms of Glomerulonephritis
Recognizing the symptoms of glomerulonephritis is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Below, we explore the common symptoms of this condition, differences between its acute and chronic forms, and guidance on when to seek medical advice.
Common Symptoms of Glomerulonephritis
Individuals with glomerulonephritis may experience a range of symptoms, which can vary in severity. The most common symptoms include:
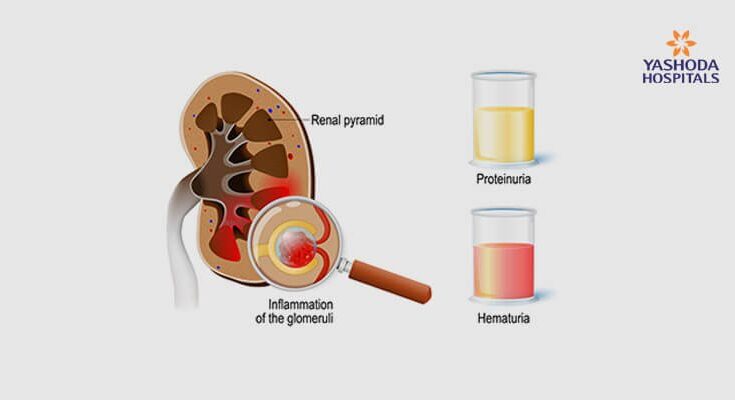
- Blood in Urine (Hematuria): This can appear as pink or cola-colored urine, indicating the presence of red blood cells.
- Protein in Urine (Proteinuria): This may cause the urine to be foamy, a result of excess protein leaking into the urine.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Often difficult to detect without a blood pressure monitor, persistent high blood pressure is a common sign.
- Swelling (Edema): Swelling often occurs in the face, hands, feet, or abdomen due to the kidneys’ inability to remove excess fluid from the body.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Decreased kidney function can lead to a build-up of toxins in the blood, resulting in feelings of fatigue or general weakness.
Acute vs. Chronic Glomerulonephritis
While the symptoms of both acute and chronic glomerulonephritis can overlap, there are distinct differences primarily in how quickly symptoms appear and progress.
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Symptoms develop suddenly and can be severe. This form is often triggered by infections or other underlying health issues and may resolve with appropriate treatment.
- Chronic Glomerulonephritis: Progresses more slowly and can be subtler in its onset. It may develop over several years without noticeable symptoms until significant kidney damage has occurred.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent or unusual swelling in any part of the body.
- Changes in urine color or consistency, especially if urine appears foamy or has visible blood.
- Sudden rise in blood pressure or persistent high readings.
- Unexplained fatigue or a general feeling of being unwell.
If you are at risk or suspect you might have symptoms of this condition, seeking prompt medical evaluation is essential. This not only helps in managing symptoms but also in addressing the underlying cause of the disease to improve long-term health outcomes.
Diagnosing Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis, a critical condition affecting the kidneys’ filtering units, requires precise diagnosis to ensure effective treatment. Here’s an overview of the key diagnostic procedures and the vital role of accurate diagnosis and imaging.
List of Diagnostic Procedures
To accurately diagnose glomerulonephritis, healthcare providers rely on a combination of clinical evaluation and specific tests:
- Urinalysis – Checks for protein, blood, and other substances in the urine.
- Blood Tests – Measures levels of creatinine and urea to assess kidney function.
- Kidney Biopsy – Involves taking a small sample of kidney tissue to examine under a microscope for signs of inflammation or scarring.
- Imaging Tests – Includes ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI to visualize the structure and size of the kidneys, helping to identify abnormalities.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis in Planning Treatment
An accurate diagnosis of glomerulonephritis is crucial for several reasons:
- Targeted Treatment: It helps in tailoring specific treatments that can address the underlying cause of the kidney inflammation.
- Preventing Progression: Early and precise diagnosis can prevent the progression of the disease, reducing the risk of kidney failure.
- Monitoring Response: It enables healthcare providers to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment regimen and make necessary adjustments.
Role of Imaging in Diagnosing Glomerulonephritis
Imaging plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis and management of glomerulonephritis. Techniques like ultrasound, CT, and MRI are non-invasive and provide valuable information about the kidneys’ condition:
- Detecting Anomalies: Helps in identifying structural abnormalities that might not be detected through physical examination.
- Guiding Biopsies: Imaging is often used to guide kidney biopsies to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Evaluating Chronic Damage: Regular imaging can monitor changes in kidney size and structure, offering insights into the progression of the disease.
By integrating these diagnostic tools, medical professionals can develop an effective treatment plan, monitor the disease accurately, and significantly improve patient outcomes in cases of glomerulonephritis.
Glomerulonephritis Treatment Options
Managing this disease typically involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and dietary modifications.
General Approach to Treatment
The treatment strategy for glomerulonephritis is tailored to the specific cause of the inflammation and the severity of the symptoms. The primary goal is to reduce kidney inflammation and prevent further damage. Treatment often begins with tests to determine the underlying cause, which can include infections, autoimmune diseases, or systemic conditions. Once the cause is identified, a targeted treatment plan is developed.
Medications Used in the Management
A variety of medications are employed to control the symptoms and progression of glomerulonephritis:
- Corticosteroids: These drugs, such as prednisone, are commonly used to reduce inflammation in the kidneys. They can be very effective in treating certain forms of glomerulonephritis, especially those caused by autoimmune disorders.
- Immunosuppressants: For cases where the immune system attacks the kidneys, drugs like cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, or azathioprine might be used. These medications help suppress the immune response and prevent further damage to the kidneys.
- Blood Pressure Medications: Medications such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs are often prescribed not only to manage high blood pressure but also to reduce proteinuria, which can exacerbate kidney disease.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Supportive Care
In addition to medication, making certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and improve overall kidney health:
- Activity and Rest: Balancing activity with adequate rest is crucial. While regular, moderate exercise can help maintain good health, periods of rest are also important to prevent fatigue.
- Fluid Management: Depending on the kidney’s ability to balance fluid levels, doctors may recommend adjusting fluid intake to either increase or decrease hydration.
Role of Diet and Nutrition in Managing Glomerulonephritis
Diet plays a critical role in managing kidney health. The specific dietary recommendations can vary based on the individual’s kidney function and health needs, but common advice includes:
- Protein Intake: Managing protein consumption is crucial since too much protein can put additional strain on the kidneys. The ideal amount varies, so it’s important to work with a healthcare provider to determine what’s right for you.
- Salt Reduction: Reducing salt intake can help control blood pressure, which is essential for protecting the kidneys from further damage.
- Potassium and Phosphorus Control: Depending on the stage of kidney disease, it might also be necessary to monitor and adjust the intake of potassium and phosphorus.
Regular consultations with a dietitian who specializes in kidney disease can provide personalized guidance, ensuring that the diet supports kidney health without compromising nutritional needs.
By combining the right medications, making appropriate lifestyle changes, and adhering to a kidney-friendly diet, people with glomerulonephritis can often manage their symptoms effectively and slow the progression of the disease.
Advanced Glomerulonephritis Treatment Techniques
Understanding and accessing advanced treatment techniques are crucial for managing this condition effectively. This section discusses the latest treatments, ongoing research, and potential future therapies for glomerulonephritis.
Cutting-edge Treatments and Research Findings
Recent advancements in the treatment of glomerulonephritis have focused on more precise and targeted therapies. One such advancement is the use of monoclonal antibodies that specifically target immune cells responsible for inflammation in the kidneys. For example, Rituximab, originally used for treating blood cancers, has shown promise in treating certain types of glomerulonephritis by reducing the activity of B cells that may contribute to kidney inflammation.
Another innovative approach is the use of complement inhibitors. These drugs work by blocking the complement system (a part of the immune system) that can exacerbate kidney inflammation. Eculizumab, a complement inhibitor, has been tested in clinical trials and offers hope for patients with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis who do not respond well to conventional therapies.
Potential Future Therapies in Development
Research into glomerulonephritis is continually evolving, with many potential therapies in the pipeline. One area of interest is the development of new immunomodulatory drugs that offer fewer side effects and improved efficacy compared to current treatments. Researchers are also exploring the potential of regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy, which could help repair damaged kidney tissues and restore function.
Gene therapy is another exciting frontier. By targeting specific genetic mutations that contribute to glomerulonephritis, this approach could offer a customized treatment strategy that addresses the root cause of the disease in each individual patient.
Importance of Clinical Trials in Advancing Treatment Options
Clinical trials play a pivotal role in the development of new treatments for glomerulonephritis. They help determine the safety and effectiveness of new therapies and can uncover novel ways to use existing treatments more effectively. Participating in clinical trials also provides patients with access to cutting-edge therapies that are not yet widely available.
Moreover, clinical trials contribute to our understanding of glomerulonephritis at a molecular level, which can lead to more effective, personalized treatment strategies. It is through these trials that researchers can gather evidence necessary to gain regulatory approval, ensuring that safe and effective new treatments become available to patients who need them.
As research continues to advance, the hope for more effective and targeted treatments for glomerulonephritis becomes increasingly tangible. Patients and healthcare providers are encouraged to stay informed about the latest treatment options and clinical trials to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Living with Glomerulonephritis
Living with glomerulonephritis, a form of kidney disease that involves inflammation of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, can be challenging. However, with proper management, individuals can maintain a good quality of life. Here’s how to manage symptoms effectively, understand the importance of regular monitoring, and find valuable support resources.
Managing Symptoms and Maintaining Quality of Life
Proper management of glomerulonephritis focuses on controlling the symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease. This includes:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a kidney-friendly diet that limits certain proteins, sodium, and potassium can help reduce kidney strain. It’s essential to consult a dietitian who specializes in kidney disease to tailor a plan that suits your needs.
- Fluid Intake Management: Depending on your condition, your doctor might recommend adjusting your fluid intake to help manage swelling and blood pressure.
- Medication Adherence: Taking prescribed medications as directed can control symptoms like high blood pressure and swelling. These medications might include blood pressure drugs, diuretics, and immunosuppressants.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, smoking cessation, and minimizing stress are crucial. These steps not only help manage symptoms but also improve overall health.
Importance of Regular Follow-Up and Monitoring
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is critical in managing glomerulonephritis. These check-ups typically involve:
- Blood and Urine Tests: Monitoring kidney function and detecting any changes early on.
- Blood Pressure Checks: Essential for preventing complications related to hypertension.
- Review of Treatment Efficacy: Adjusting medications and dietary recommendations as needed based on your progress.
Staying vigilant about follow-ups ensures that any necessary adjustments in your treatment plan are made promptly, enhancing the effectiveness of the management strategy.
Support Resources and Patient Education
Navigating glomerulonephritis is easier with the right support and education. Here are some resources:
- Patient Support Groups: Connecting with others who face similar challenges can provide emotional support and practical advice on coping with the disease.
- Educational Materials: Many kidney health organizations offer materials that help patients understand their condition and manage it effectively.
- Professional Counseling: Talking to a counselor or therapist can help manage the emotional and psychological impacts of living with a chronic illness.
By utilizing these strategies, individuals living with glomerulonephritis can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by the condition. Regular medical care, adequate support, and appropriate lifestyle changes play pivotal roles in managing the disease effectively.
FAQs about Glomerulonephritis Treatment
What are the common treatments for glomerulonephritis?
Treatment for glomerulonephritis depends on the type and severity of the condition. Common approaches include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, immunosuppressive drugs to control the immune system’s response, and medications to manage symptoms such as high blood pressure and swelling. In severe cases, plasmapheresis, which removes antibodies from the blood, may be recommended.
Is diet important in managing glomerulonephritis?
Yes, dietary changes can play a crucial role in managing glomerulonephritis. Limiting protein intake may help reduce kidney strain, while reducing salt intake can control blood pressure and swelling. A dietitian specializing in kidney health can provide personalized guidance based on your specific condition.
How long does treatment for glomerulonephritis typically last?
The duration of treatment can vary widely depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the disease. Some patients may experience improvement within weeks, while others might need long-term therapy. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment as necessary.
Can glomerulonephritis be cured?
In some cases, glomerulonephritis can resolve completely with treatment, especially if diagnosed early and managed effectively. However, chronic forms of the disease may not be curable and require ongoing management to prevent progression to kidney failure.
What are the risks of not treating glomerulonephritis?
Untreated glomerulonephritis can lead to serious complications, including chronic kidney disease, acute kidney failure, or permanent kidney damage. Timely and effective treatment is critical to minimize the risk of these severe outcomes.
Are there any new treatments on the horizon for glomerulonephritis?
Ongoing research is exploring various new treatments, including targeted biological therapies that can more precisely control the immune response without extensive side effects. Clinical trials are also underway to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of these emerging therapies.
Conclusion
In summary, the early diagnosis and effective treatment of glomerulonephritis are critical to managing this complex kidney disorder successfully. Timely medical intervention can significantly slow disease progression, improve outcomes, and enhance quality of life for those affected. It’s essential for patients to recognize the symptoms early and seek medical advice promptly.
We strongly encourage patients to maintain open communication with their healthcare providers. Working closely with your medical team allows for personalized treatment plans that address your specific health needs. Remember, your active participation in your health care journey is vital for managing glomerulonephritis effectively. Stay informed, stay proactive, and take control of your health for a better, healthier future.
References
For further reading on the treatment of glomerulonephritis and to validate the information provided, consider exploring the following reputable sources. These resources offer comprehensive insights into current treatment strategies and research updates in the field of nephrology.
- National Kidney Foundation (NKF) – Provides a detailed overview of glomerulonephritis, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Access their resources at National Kidney Foundation.
- Mayo Clinic – Offers extensive information on the types of glomerulonephritis and the latest treatment methods. Read more on their official site at Mayo Clinic.
- PubMed Central – A valuable resource for accessing peer-reviewed scientific papers on glomerulonephritis treatment research. Visit PubMed Central to find relevant studies.
- American Society of Nephrology (ASN) – Features guidelines and research articles on glomerulonephritis. Explore their content at American Society of Nephrology.
- Kidney International – A journal known for publishing high-quality research articles on kidney diseases, including glomerulonephritis. Access their articles at Kidney International.
Each of these sources is recognized for their authority and reliability in the field of nephrology and provides essential information for both medical professionals and patients managing glomerulonephritis.